Deck 21: Univariate Statistical Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Univariate Statistical Analysis
1
Statistical power is how much ability exists to find a significant effect using a specific statistical tool.
True
2
A larger sample reduces the chance of a Type II error and increases statistical power.
True
3
In practical terms,researchers state only the substantive (i.e. ,alternative)hypothesis implying what is expected to be observed in the sample.
True
4
A Type I error occurs when you fail to reject the null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The two major groupings of statistical procedures are parametric statistics and nonparametric statistics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A Type II error occurs when you reject the null hypothesis when,in fact,it is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Parametric statistics are based on the assumption that the data in the study are drawn from a population with a normal (bell-shaped)distribution and/or normal sampling distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Monovariate statistical analysis tests hypotheses involving only one variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Nonparametric statistical tests are frequently referred to as "distribution free."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A rule of thumb is that statistical power should be 0.95.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The term p-value stands for power-value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The exact point where the hypothesis changes from not being support to being supported depends on how much risk the researcher is willing to accept and on the variability of the measure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The researcher's hypothesis is generally stated in the form of a null hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
You have not made a mistake if the null hypothesis is false,and you decide to reject the null hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In hypothesis testing,the values of t that lie on the boundary of the region of rejection are called the critical values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The scale of measurement used by the researcher determines the allowable statistical techniques in the research study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A significance level is a critical probability associated with a statistical hypothesis test that indicates how likely it is that an inference supporting a difference between an observed value and some statistical expectation is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Nominal scales typically use parametric statistical tests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The researcher using sampling runs the risk of committing two types of errors: primary errors and secondary errors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In hypothesis testing,the symbol typically used to specify the significance level of the test is b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A hypothesis test of a proportion is conceptually similar to hypothesis testing when the mean is the characteristic of interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The two types of errors researcher run the risk of committing when sampling are:
A)primary and secondary errors
B)Type I and Type II errors
C)critical and noncritical errors
D)Type A and Type B errors
A)primary and secondary errors
B)Type I and Type II errors
C)critical and noncritical errors
D)Type A and Type B errors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Alan is testing a hypothesis and is examining the data to determine whether or not the observed relationship between background music in a store and sales are significantly related.Which of the following will he use to determine the significance level of the results?
A)c
B)e
C)y-value
D)p-value
A)c
B)e
C)y-value
D)p-value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The values that lie exactly on the boundary of the region of rejection for hypothesis-testing are called the:
A)degrees of freedom
B)critical values
C)significance level
D)confidence interval
A)degrees of freedom
B)critical values
C)significance level
D)confidence interval

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The logic behind the chi-square test is to compare the observed frequencies with the expected frequencies in the data set.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In statistical testing,the significance level is commonly denoted by the symbol:
A)b
B)a
C)Zobs
D)c
A)b
B)a
C)Zobs
D)c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which type of statistical analysis test hypotheses involves only one variable?
A)primary statistical analysis
B)bivariate statistical analysis
C)univariate statistical analysis
D)monovariate statistical analysis
A)primary statistical analysis
B)bivariate statistical analysis
C)univariate statistical analysis
D)monovariate statistical analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which type of error occurs when the researcher concludes a relationship exists when in fact one does not exist?
A)Type I
B)Type II
C)Type A
D)Type B
A)Type I
B)Type II
C)Type A
D)Type B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Failing to identify a hypothesized difference using a sample result when one really does exist in the population is which type of error?
A)primary
B)secondary
C)Type I
D)Type II
A)primary
B)secondary
C)Type I
D)Type II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The mathematical equation for statistical power is:
A)power = 1 - b
B)power = b - 1
C)power = a - b
D)power = b - a
A)power = 1 - b
B)power = b - 1
C)power = a - b
D)power = b - a

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A univariate p-test is appropriate for testing hypotheses involving some observed mean against some specified value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following becomes key indicator of whether or not a hypothesis can be supported?
A)critical value
B)significance level
C)chi-square
D)degrees of freedom
A)critical value
B)significance level
C)chi-square
D)degrees of freedom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The t-test is strictly appropriate for tests involving small sample sizes with unknown standard deviations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Degrees of freedom are determined by the number of distinct calculations that are possible given a set of information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When a researcher sets an acceptable significance level a priori (a),he or she is determining how much tolerance he or she has for which type of error?
A)Type I
B)Type II
C)Type A
D)Type B
A)Type I
B)Type II
C)Type A
D)Type B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The error caused by rejecting the null hypothesis when it is,in fact,true is called a:
A)Type II error
B)confidence level error
C)confidence interval error
D)Type I error
A)Type II error
B)confidence level error
C)confidence interval error
D)Type I error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the population mean is expected to be 85 and the sample mean is 80,the sample standard deviation is 20,and the sample consists of 100 consumers,the observed value of the Z-statistic is approximately:
A)2.50
B)-10.00
C)-2.50
D)-0.25
A)2.50
B)-10.00
C)-2.50
D)-0.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is a measure of how much ability exists to find a significant effect using a specific statistical tool?
A)significance level
B)statistical power
C)statistical norm
D)alpha
A)significance level
B)statistical power
C)statistical norm
D)alpha

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The opposite of the null hypothesis is called the ____ hypothesis.
A)pure
B)alpha
C)alternative
D)secondary
A)pure
B)alpha
C)alternative
D)secondary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When the probability of a Type II error is ____,the probability of a Type I error is ____.
A)reduced,increased
B)reduced;reduced
C)increased;increased
D)none of the above
A)reduced,increased
B)reduced;reduced
C)increased;increased
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A statement which expresses the opposite of the null hypothesis is called the ____________________ hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Another name for an observed or computed significance level is ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
For which statistical test does the formula given below apply?
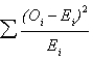
A)Z-test
B)F-test
C)Chi-square test
D)W-square
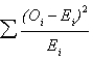
A)Z-test
B)F-test
C)Chi-square test
D)W-square

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Researchers conventionally rely on a rule of thumb that statistical power should be:
A)0.25
B)0.50
C)0.80
D)1.5
A)0.25
B)0.50
C)0.80
D)1.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Laura has a frequency table with the number of stores in three different categories: stand-alone,shopping center,and mall locations.Which statistical test is appropriate for testing hypothesizes she might have regarding these frequencies?
A)b test
B)X² test
C)a test
D)g test
A)b test
B)X² test
C)a test
D)g test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
For a one-group t-test,the degrees of freedom are:
A)n + 1
B)n(n - 1)
C)n - 1
D)n(n + 1)
A)n + 1
B)n(n - 1)
C)n - 1
D)n(n + 1)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When the data are in ____ form,and the sample size is ____,the researcher should use parametric statistical procedures.
A)nominal;large
B)ordinal;large
C)interval;large
D)nominal;small
A)nominal;large
B)ordinal;large
C)interval;large
D)nominal;small

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When a researcher wishes to analyze data that is nominal,which type of statistics is appropriate?
A)Type I
B)Type II
C)parametric
D)nonparametric
A)Type I
B)Type II
C)parametric
D)nonparametric

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The critical probability associated with a statistical hypothesis test that indicates how likely it is that an inference supporting a difference between an observed value and some statistical expectation is true is called ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Selection of the appropriate statistical test to use in a research study depends on:
A)the type of research question asked
B)the number of variables
C)the measurement scale used
D)all of the above
A)the type of research question asked
B)the number of variables
C)the measurement scale used
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Suppose that a group of 100 consumers are asked to rate how much they liked the taste of a new soft drink on a 5-point scale (where 5 = good taste and 1 = poor taste)and the mean rating was 4.2 with a standard deviation of 1.48.Suppose,further,that the standard error of the mean for this study was 0.15.If you wanted to find the 95 percent confidence interval (two-tailed test),and if the Z-value at the 0.05 level of significance is 1.96,the confidence interval lies between:
A)3.91 and 4.49
B)4.17 and 4.23
C)3.98 and 4.42
D)4.00 and 5.00
A)3.91 and 4.49
B)4.17 and 4.23
C)3.98 and 4.42
D)4.00 and 5.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The t-distribution has a mean of ____ and a standard deviation of ____.
A)one;zero
B)zero;one
C)one;two
D)two;one
A)one;zero
B)zero;one
C)one;two
D)two;one

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Suppose that past research studies have found that 70 percent of a particular target market segment were aware of the Nike "swoosh" brand mark.If 65 percent of this target market in a sample of 60 people are aware of this brand mark,and if the standard error of the proportion is 0.06,the observed Z-test value is approximately:
A)-13.19
B)-0.83
C)0.83
D)13.19
A)-13.19
B)-0.83
C)0.83
D)13.19

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The number of observations minus the number of constraints or assumptions needed to calculate a statistical term is called:
A)statistical power
B)t-level
C)degrees of freedom
D)significance level
A)statistical power
B)t-level
C)degrees of freedom
D)significance level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following represents how well some computed table or matrix of values matches some population or predetermined table or matrix of the same size?
A)statistical power
B)Z-value
C)t-value
D)goodness-of-fit (GOF)
A)statistical power
B)Z-value
C)t-value
D)goodness-of-fit (GOF)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Analyses that test hypotheses and models involving multiple (three or more)variables or sets of variables are referred to as ____________________ statistical analyses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The type of statistical analysis that deals with a hypothesis about a single variable (e.g.market share)is called ____________________ statistical analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which type of statistics involves numbers with known,continuous distributions?
A)Type I
B)Type II
C)parametric
D)nonparametric
A)Type I
B)Type II
C)parametric
D)nonparametric

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When sample size (n)is larger than ____,the t-distribution and Z-distribution are almost identical.
A)10
B)20
C)25
D)30
A)10
B)20
C)25
D)30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In a brand awareness study of 80 consumers,52 of them were able to identify "Fusion" as a type of Ford automobile.The chi-square value for a test of this brand awareness was approximately:
A)2.30
B)7.20
C)0.60
D)3.60
A)2.30
B)7.20
C)0.60
D)3.60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The appropriate test to use when testing hypotheses involving an observed mean against some specified value is the univariate ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When the researcher does not know how the data are distributed,the researcher should use ____________________ methods of statistics in analyzing the data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The error caused by rejecting the null hypothesis when,in fact,it is true is called a(n)____________________ error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Describe the chi-square test for goodness-of-fit and explain when it is the appropriate test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Explain the appropriate statistical analysis for the following hypothesis:
H₁: The average household income in zip code 71227 is greater than $50,000.
H₁: The average household income in zip code 71227 is greater than $50,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Compare and contrast parametric statistics and nonparametric statistics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The error caused by failing to reject the null hypothesis when,in fact,the alternative hypothesis is true is called a(n)____________________ error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A general term representing how well some computed table or matrix of values matches some population or predetermined table or matrix of the same size is ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When the data are interval or ratio scaled and the sample size is large,____________________ statistical procedures are appropriate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The symmetrical,bell-shaped distribution that has a mean of zero and a standard deviation of one is called the ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
____________________ is a measure of how much ability exists to find a significant effect using a specific statistical tool and is equal to 1 -b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In hypothesis testing,the number of observations minus the number of constraints needed to calculate a statistical term is called the ____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Compare and contrast Type I errors and Type II errors and explain which one is of more concern to researchers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
List the factors to consider when choosing the appropriate statistical technique.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In hypothesis testing,the values that lie exactly on the boundary of the region of rejection are referred to as the ____________________ values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



