Deck 29: Alterations of Cardiovascular Function
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/71
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 29: Alterations of Cardiovascular Function
1
What are the vasoconstricting factors regulated by endothelium?
A) Thromboxane A and endothelin
B) Norepinephrine and acetylcholine
C) Bradykinin and leukotriene
D) Serotonin and prostacyclin
A) Thromboxane A and endothelin
B) Norepinephrine and acetylcholine
C) Bradykinin and leukotriene
D) Serotonin and prostacyclin
Thromboxane A and endothelin
2
Even though air is lighter than blood,it can form an embolism and cause the occlusion of a blood vessel.
True
3
Decreasing low-density lipoproteins (LDL)can cause regression of atherosclerotic lesions and improve endothelial function.
True
4
Which inflammatory cytokines are released when endothelial cells are injured?
A) Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)
B) Beta-interferon (ß-IFN),interleukin 6 (Il-6),and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF).
C) Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-),gamma interferon (-IFN),and interleukin 1 (Il-1).
D) Interferon alpha (IFN-
A) Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)
B) Beta-interferon (ß-IFN),interleukin 6 (Il-6),and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF).
C) Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-),gamma interferon (-IFN),and interleukin 1 (Il-1).
D) Interferon alpha (IFN-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Many cases of mitral valve prolapse are completely asymptomatic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Atrial and brain natriuretic peptides are increased in congestive heart failure and may have some protective effect in decreasing preload.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Acute rheumatic fever can develop only as a sequel to pharyngeal infection by group A 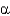
-streptococcus.
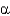
-streptococcus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the effect of oxidized low-density lipoproteins (LDL)in atherosclerosis?
A) It causes smooth muscle proliferation.
B) It causes regression of atherosclerotic plaques.
C) It increases levels of inflammatory cytokines.
D) It directs macrophages to the site within the endothelium.
A) It causes smooth muscle proliferation.
B) It causes regression of atherosclerotic plaques.
C) It increases levels of inflammatory cytokines.
D) It directs macrophages to the site within the endothelium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Raynaud disease is characterized by vasospasms of large peripheral arteries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Chronic venous insufficiency can progress to varicose veins and valvular incompetence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Although cholesterol can be easily obtained via dietary intake,most body cells are also capable of synthesizing cholesterol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Many people with diabetes mellitus type 2,who were treated with drugs that increased insulin sensitivity,experienced a decline in their blood pressure without taking antihypertensive drugs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Angina pectoris is chest pain caused by myocardial ischemia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When fluid collects gradually in a pericardial effusion,the pericardium stretches to accommodate large quantities of fluid without compressing the heart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In high output failure,the heart increases its output,but the body's metabolic needs are still not met.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Once fatty streaks accumulate,they form foam cells that cause immunologic changes that damage the endothelium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Chorea or St.Vitus dance is the most definitive sign of rheumatic fever.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An increase in left ventricular end-diastolic volume in diastolic heart failure may lead to pulmonary edema.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the primary mechanism of atherogenesis?
A) The release of the inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-),interferon gamma (IFN-),and interleukin 1 (Il-1)
B) The release of the growth factor granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)
C) The release of toxic oxygen radicals that oxidize low-density lipoproteins (LDL)
D) The release of the inflammatory cytokines interferon beta (IFN-ß),interleukin 6 (Il-6),and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)
A) The release of the inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-),interferon gamma (IFN-),and interleukin 1 (Il-1)
B) The release of the growth factor granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)
C) The release of toxic oxygen radicals that oxidize low-density lipoproteins (LDL)
D) The release of the inflammatory cytokines interferon beta (IFN-ß),interleukin 6 (Il-6),and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Coronary artery disease can diminish the myocardial blood supply until deprivation impairs myocardial metabolism enough to cause _____,a local state in which the cells are temporarily deprived of blood supply.
A) infarction
B) ischemia
C) necrosis
D) inflammation
A) infarction
B) ischemia
C) necrosis
D) inflammation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Of the following risk factors for coronary artery disease,which is responsible for a twofold to threefold increase in risk?
A) Diabetes mellitus
B) Hypertension
C) Obesity
D) High alcohol consumption
A) Diabetes mellitus
B) Hypertension
C) Obesity
D) High alcohol consumption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What are the differences in arterial walls versus vs.walls that promote clot formation?
A) There is inflammation of the endothelium of the artery and roughing of the endothelium of the vein.
B) There is vasoconstriction of the endothelium of the artery and hypertrophy of the endothelium of the vein.
C) There is excessive clot formation of the endothelium of the artery and lipid accumulation of the endothelium of the vein.
D) There is roughening of the endothelium of the artery and inflammation of the endothelium of the vein.
A) There is inflammation of the endothelium of the artery and roughing of the endothelium of the vein.
B) There is vasoconstriction of the endothelium of the artery and hypertrophy of the endothelium of the vein.
C) There is excessive clot formation of the endothelium of the artery and lipid accumulation of the endothelium of the vein.
D) There is roughening of the endothelium of the artery and inflammation of the endothelium of the vein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
How does nicotine increase atherosclerosis?
A) By the release of histamine
B) By decreasing nitric oxide
C) By the release of angiotensin II
D) By the release of epinephrine and norepinephrine
A) By the release of histamine
B) By decreasing nitric oxide
C) By the release of angiotensin II
D) By the release of epinephrine and norepinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What factor is responsible for the hypertrophy of the myocardium associated with hypertension?
A) Increased norepinephrine
B) Adducin
C) Angiotensin II
D) Insulin resistance
A) Increased norepinephrine
B) Adducin
C) Angiotensin II
D) Insulin resistance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which source of emboli introduces antigens,cells,and protein aggregates that trigger an immune response within the bloodstream?
A) Amniotic fluid
B) Fat
C) Bacteria
D) Air
A) Amniotic fluid
B) Fat
C) Bacteria
D) Air

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Cardiac cells can withstand ischemic conditions and still return to a viable state for _____ minutes.
A) 10
B) 15
C) 20
D) 25
A) 10
B) 15
C) 20
D) 25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the usual source of pulmonary emboli?
A) Deep vein thrombosis
B) Endocarditis
C) Valvular disease
D) Left heart failure
A) Deep vein thrombosis
B) Endocarditis
C) Valvular disease
D) Left heart failure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which value may be protective for the development of atherosclerosis?
A) High values of very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDL)
B) High values of low-density lipoproteins (LDL)
C) High values of high-density lipoproteins (HDL)
D) High values of triglycerides (TG)
A) High values of very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDL)
B) High values of low-density lipoproteins (LDL)
C) High values of high-density lipoproteins (HDL)
D) High values of triglycerides (TG)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which is a description of thromboangiitis obliterans (Buerger disease)?
A) An inflammatory disorder of small- and medium-sized arteries in the feet and sometimes in the hands
B) A vasospastic disorder of the small arteries and arterioles of the fingers,and less commonly the toes
C) An autoimmune disorder of the large arteries and veins of the upper and lower extremities
D) A neoplastic disorder of the lining of the arteries and veins of the upper extremities
A) An inflammatory disorder of small- and medium-sized arteries in the feet and sometimes in the hands
B) A vasospastic disorder of the small arteries and arterioles of the fingers,and less commonly the toes
C) An autoimmune disorder of the large arteries and veins of the upper and lower extremities
D) A neoplastic disorder of the lining of the arteries and veins of the upper extremities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Superior vena cava syndrome is a progressive _____ of the superior vena cava that leads to venous distention of the upper extremities and head.
A) inflammation
B) occlusion
C) distention
D) sclerosis
A) inflammation
B) occlusion
C) distention
D) sclerosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What pathologic change occurs in kidneys of people with hypertension that leads to dysfunction of the glomeruli?
A) Compression of the renal tubules
B) Ischemia of the tubule
C) Increased pressure from within the tubule
D) Obstruction of the renal tubule
A) Compression of the renal tubules
B) Ischemia of the tubule
C) Increased pressure from within the tubule
D) Obstruction of the renal tubule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
_____ are manufactured by the liver and primarily contains cholesterol and protein.
A) Very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDL)
B) Low-density lipoproteins (LDL)
C) High-density lipoproteins (HDL)
D) Triglycerides (TG)
A) Very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDL)
B) Low-density lipoproteins (LDL)
C) High-density lipoproteins (HDL)
D) Triglycerides (TG)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Cerebral aneurysms frequently occur in the:
A) vertebral arteries.
B) basilar artery.
C) circle of Willis.
D) carotid arteries.
A) vertebral arteries.
B) basilar artery.
C) circle of Willis.
D) carotid arteries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which is a description of Raynaud phenomenon and disease?
A) An inflammatory disorder of small- and medium-sized arteries in the feet and sometimes in the hands.
B) A neoplastic disorder of the lining of the arteries and veins of the upper extremities.
C) A vasospastic disorder of the small arteries and arterioles of the fingers,and less commonly the toes.
D) An autoimmune disorder of the large arteries and veins of the upper and lower extremities.
A) An inflammatory disorder of small- and medium-sized arteries in the feet and sometimes in the hands.
B) A neoplastic disorder of the lining of the arteries and veins of the upper extremities.
C) A vasospastic disorder of the small arteries and arterioles of the fingers,and less commonly the toes.
D) An autoimmune disorder of the large arteries and veins of the upper and lower extremities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which lab test is an indirect measure of atherosclerotic plaque?
A) Homocysteine
B) Low-density lipoproteins (LDL)
C) Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
D) C reactive protein (CPR)
A) Homocysteine
B) Low-density lipoproteins (LDL)
C) Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
D) C reactive protein (CPR)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
How does atherosclerosis cause aneurysms?
A) A reduction in oxygen causes ischemia of the intimA.
B) An increase in endothelin increases nitric oxide.
C) Plaque formation erodes the vessel wall.
D) The vessel is obstructed by plaques and thrombus formation.
A) A reduction in oxygen causes ischemia of the intimA.
B) An increase in endothelin increases nitric oxide.
C) Plaque formation erodes the vessel wall.
D) The vessel is obstructed by plaques and thrombus formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What alteration occurs in injured endothelial cells that contributes to atherosclerosis?
A) They release toxic oxygen radicals that oxidize low-density lipoproteins (LDL).
B) They are unable to make the normal amount of vasodilating cytokines.
C) They produce an increased amount of antithrombic cytokines.
D) They develop a hypersensitivity to homocystine and lipids.
A) They release toxic oxygen radicals that oxidize low-density lipoproteins (LDL).
B) They are unable to make the normal amount of vasodilating cytokines.
C) They produce an increased amount of antithrombic cytokines.
D) They develop a hypersensitivity to homocystine and lipids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What changes in veins occur to create varicose veins?
A) An increase in osmotic pressure
B) Damage to the valves with veins
C) Damage to the venous endothelium
D) An increase in hydrostatic pressure
A) An increase in osmotic pressure
B) Damage to the valves with veins
C) Damage to the venous endothelium
D) An increase in hydrostatic pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following risk factors is associated with a twofold increase in the risk for coronary artery disease death and up to a sixfold risk for stroke?
A) Diabetes mellitus
B) Hypertension
C) Obesity
D) High alcohol consumption
A) Diabetes mellitus
B) Hypertension
C) Obesity
D) High alcohol consumption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is the significance of pulsus paradoxus that occurs in a pericardial effusion?
A) It reflects impairment of the diastolic filling pressures of the right ventricle and reduction of blood volume in both ventricles.
B) It reflects impairment of the blood ejected from the right atria and reduction of blood volume in the right ventricle.
C) It reflects impairment of the blood ejected from the left atria and reduction of blood volume in the left ventricle.
D) It reflects impairment of the diastolic filling pressures of the left ventricle and reduction of blood volume in all four heart chambers.
A) It reflects impairment of the diastolic filling pressures of the right ventricle and reduction of blood volume in both ventricles.
B) It reflects impairment of the blood ejected from the right atria and reduction of blood volume in the right ventricle.
C) It reflects impairment of the blood ejected from the left atria and reduction of blood volume in the left ventricle.
D) It reflects impairment of the diastolic filling pressures of the left ventricle and reduction of blood volume in all four heart chambers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When scar tissue replaces the myocardium after a myocardial infarction (MI),the forming scar tissue is very mushy and vulnerable to injury at about day _____ after MI.
A) 5 to 9
B) 10 to 14
C) 15 to 20
D) 20 to 30
A) 5 to 9
B) 10 to 14
C) 15 to 20
D) 20 to 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A patient is diagnosed with pulmonary disease and elevated pulmonary vascular resistance.Which of the following heart failures may result from this condition?
A) Right heart failure
B) Left heart failure
C) Low-output failure
D) High-output failure
A) Right heart failure
B) Left heart failure
C) Low-output failure
D) High-output failure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
How does angiotensin II increase the workload of the heart after a myocardial infarction?
A) By increasing the peripheral vascular resistance
B) By causing dysrhythmias as a result of hyperkalemia
C) By reducing the contractility of the myocardium
D) By stimulating the sympathetic nervous system
A) By increasing the peripheral vascular resistance
B) By causing dysrhythmias as a result of hyperkalemia
C) By reducing the contractility of the myocardium
D) By stimulating the sympathetic nervous system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
For which disorder are the risk factors genitourinary instrumentation,dental procedure,hemodialysis,and intravenous drug use?
A) Rheumatic fever
B) Infective endocarditis
C) Mitral regurgitation
D) Aortic regurgitation
A) Rheumatic fever
B) Infective endocarditis
C) Mitral regurgitation
D) Aortic regurgitation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Ventricular remodeling is a result of:
A) left ventricular hypertrophy.
B) right ventricular failure.
C) myocardial ischemia.
D) contractile dysfunction.
A) left ventricular hypertrophy.
B) right ventricular failure.
C) myocardial ischemia.
D) contractile dysfunction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The hallmark of _____ cardiomyopathy is a disproportionate thickening of the interventricular septum.
A) dystrophic
B) hypertrophic
C) septal
D) dilated
A) dystrophic
B) hypertrophic
C) septal
D) dilated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What are clinical manifestations of aortic stenosis?
A) Jugular vein distension
B) Bounding pulses
C) Peripheral edema
D) Dyspnea on exertion
A) Jugular vein distension
B) Bounding pulses
C) Peripheral edema
D) Dyspnea on exertion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A patient complains of sudden onset of severe chest pain that radiates to the back and worsens with respiratory movement and when lying down.What is causing these clinical manifestations?
A) Myocardial infarction
B) Pericardial effusion
C) Restrictive pericarditis
D) Acute pericarditis
A) Myocardial infarction
B) Pericardial effusion
C) Restrictive pericarditis
D) Acute pericarditis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An individual is demonstrating elevated levels of troponin,creatine kinase (CK),and lactic dehydrogenase (LDH).These elevated levels indicate:
A) myocardial ischemiA.
B) hypertension.
C) myocardial infarction.
D) coronary artery disease.
A) myocardial ischemiA.
B) hypertension.
C) myocardial infarction.
D) coronary artery disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Infective endocarditis is most often caused by:
A) a virus.
B) a fungus.
C) a bacteria.
D) rickettsiae.
A) a virus.
B) a fungus.
C) a bacteria.
D) rickettsiae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
_____ cardiomyopathy is characterized by ventricular dilation and grossly impaired systolic function,leading to dilated heart failure.
A) Dilated
B) Hypertrophic
C) Septal
D) Dystrophic
A) Dilated
B) Hypertrophic
C) Septal
D) Dystrophic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is the expected electrocardiogram pattern for a patient when a thrombus in a coronary artery lodges permanently in the vessel and the infarction extends through the myocardium from the endocardium to the epicardium?
A) Prolonged Q-T interval
B) ST elevation (STEMI)
C) ST depression (STDMI)
D) Non-ST elevation (non-STEMI)
A) Prolonged Q-T interval
B) ST elevation (STEMI)
C) ST depression (STDMI)
D) Non-ST elevation (non-STEMI)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which valvular disorder is thought to have an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern,to be associated with connective tissue disease that tends to be most prevalent in young women?
A) Mitral valve prolapse
B) Tricuspid stenosis
C) Tricuspid valve prolapse
D) Aortic insufficiency
A) Mitral valve prolapse
B) Tricuspid stenosis
C) Tricuspid valve prolapse
D) Aortic insufficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
_____ cardiomyopathy is usually caused by an infiltrative disease of the myocardium,such as amyloidosis,hemochromatosis,or glycogen storage disease.
A) Infiltrative
B) Restrictive
C) Septal
D) Hypertrophic
A) Infiltrative
B) Restrictive
C) Septal
D) Hypertrophic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Aortic and mitral regurgitation and mitral stenosis are all caused by which of the following?
A) Congenital malformation
B) Cardiac failure
C) Rheumatic fever
D) Coronary artery disease
A) Congenital malformation
B) Cardiac failure
C) Rheumatic fever
D) Coronary artery disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which disorder causes a transitory truncal rash that is nonpruritic and pink with erythematous macules that may fade in the center,making them appear as a ringworm?
A) Fat emboli
B) Rheumatic fever
C) Bacterial endocarditis
D) Myocarditis of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
A) Fat emboli
B) Rheumatic fever
C) Bacterial endocarditis
D) Myocarditis of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
_____ angina occurs because of vasospasms of one or more coronary arteries and often during sleep.
A) Unstable
B) Stable
C) Silent
D) Prinzmetal
A) Unstable
B) Stable
C) Silent
D) Prinzmetal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Biventricular dilation is the result of _____ cardiomyopathy.
A) hypertrophic
B) restrictive
C) congestive
D) inflammatory
A) hypertrophic
B) restrictive
C) congestive
D) inflammatory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the most common cardiac disorder associated with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)resulting from myocarditis and infective endocarditis?
A) Inflammatory cardiomyopathy
B) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
C) Dilated cardiomyopathy
D) Restrictive cardiomyopathy
A) Inflammatory cardiomyopathy
B) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
C) Dilated cardiomyopathy
D) Restrictive cardiomyopathy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match the descriptions with the corresponding terms.
Usually caused by infiltrative disease,such as amyloidosis
A)Restrictive cardiomyopathy
B)Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
C)Dilated cardiomyopathy
Usually caused by infiltrative disease,such as amyloidosis
A)Restrictive cardiomyopathy
B)Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
C)Dilated cardiomyopathy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match the descriptions with the corresponding terms.
Usually caused by ischemic or valvular heart disease
A)Restrictive cardiomyopathy
B)Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
C)Dilated cardiomyopathy
Usually caused by ischemic or valvular heart disease
A)Restrictive cardiomyopathy
B)Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
C)Dilated cardiomyopathy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Match the descriptions with the corresponding terms.
Results in muscular subaortic stenosis
A)Restrictive cardiomyopathy
B)Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
C)Dilated cardiomyopathy
Results in muscular subaortic stenosis
A)Restrictive cardiomyopathy
B)Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
C)Dilated cardiomyopathy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
MATCHING
Match the descriptions with the corresponding terms.
Aortic stenosis
A)Impairs flow from left atrium to left ventricle
B)Impairs flow from the left ventricle
C)Backflow into left atrium
D)Backflow into right atrium
E)Backflow into left ventricle
Match the descriptions with the corresponding terms.
Aortic stenosis
A)Impairs flow from left atrium to left ventricle
B)Impairs flow from the left ventricle
C)Backflow into left atrium
D)Backflow into right atrium
E)Backflow into left ventricle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
MATCHING
Match the descriptions with the corresponding terms.
Tricuspid regurgitation
A)Impairs flow from left atrium to left ventricle
B)Impairs flow from the left ventricle
C)Backflow into left atrium
D)Backflow into right atrium
E)Backflow into left ventricle
Match the descriptions with the corresponding terms.
Tricuspid regurgitation
A)Impairs flow from left atrium to left ventricle
B)Impairs flow from the left ventricle
C)Backflow into left atrium
D)Backflow into right atrium
E)Backflow into left ventricle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Match the descriptions with the corresponding terms.
Seen in alcoholics
A)Restrictive cardiomyopathy
B)Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
C)Dilated cardiomyopathy
Seen in alcoholics
A)Restrictive cardiomyopathy
B)Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
C)Dilated cardiomyopathy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Match the descriptions with the corresponding terms.
May be an autosomal dominant disorder
A)Restrictive cardiomyopathy
B)Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
C)Dilated cardiomyopathy
May be an autosomal dominant disorder
A)Restrictive cardiomyopathy
B)Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
C)Dilated cardiomyopathy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
MATCHING
Match the descriptions with the corresponding terms.
Aortic regurgitation
A)Impairs flow from left atrium to left ventricle
B)Impairs flow from the left ventricle
C)Backflow into left atrium
D)Backflow into right atrium
E)Backflow into left ventricle
Match the descriptions with the corresponding terms.
Aortic regurgitation
A)Impairs flow from left atrium to left ventricle
B)Impairs flow from the left ventricle
C)Backflow into left atrium
D)Backflow into right atrium
E)Backflow into left ventricle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
MATCHING
Match the descriptions with the corresponding terms.
Mitral stenosis
A)Impairs flow from left atrium to left ventricle
B)Impairs flow from the left ventricle
C)Backflow into left atrium
D)Backflow into right atrium
E)Backflow into left ventricle
Match the descriptions with the corresponding terms.
Mitral stenosis
A)Impairs flow from left atrium to left ventricle
B)Impairs flow from the left ventricle
C)Backflow into left atrium
D)Backflow into right atrium
E)Backflow into left ventricle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In systolic heart failure,what effect does angiotensin II have on stroke volume?
A) Increases preload and decreases afterload
B) Increases preload and increases afterload
C) Decreases preload and increases afterload
D) Decreases preload and decreases afterload
A) Increases preload and decreases afterload
B) Increases preload and increases afterload
C) Decreases preload and increases afterload
D) Decreases preload and decreases afterload

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
MATCHING
Match the descriptions with the corresponding terms.
Mitral regurgitation
A)Impairs flow from left atrium to left ventricle
B)Impairs flow from the left ventricle
C)Backflow into left atrium
D)Backflow into right atrium
E)Backflow into left ventricle
Match the descriptions with the corresponding terms.
Mitral regurgitation
A)Impairs flow from left atrium to left ventricle
B)Impairs flow from the left ventricle
C)Backflow into left atrium
D)Backflow into right atrium
E)Backflow into left ventricle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



