Deck 32: The Immune System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/80
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 32: The Immune System
1
During a major infection a fever often develops.What best explains the origin of this change in body temperature?
A) The infectious pathogens produce chemicals that stimulate the brain to elevate the temperature,creating an environment more suitable to bacterial growth.
B) The immune system stimulates the brain to elevate the temperature,an action that both limits bacterial growth and increases the rate of phagocytosis.
C) The infectious pathogens damage tissues throughout the body,creating a negative thermoregulatory feedback cycle.
D) The subsequent low energy levels that result from the metabolic demands of fever impair the nervous system and disable the homeostatic system that controls body temperature.
A) The infectious pathogens produce chemicals that stimulate the brain to elevate the temperature,creating an environment more suitable to bacterial growth.
B) The immune system stimulates the brain to elevate the temperature,an action that both limits bacterial growth and increases the rate of phagocytosis.
C) The infectious pathogens damage tissues throughout the body,creating a negative thermoregulatory feedback cycle.
D) The subsequent low energy levels that result from the metabolic demands of fever impair the nervous system and disable the homeostatic system that controls body temperature.
B
2
Mammals use several strategies to prevent inhaled pathogens from entering the body through the lungs;in this instance the
A) lung secretions create an acidic and inhospitable environment for pathogens.
B) mucus secreted into the bronchioles traps pathogens and is eventually removed by the action of the cilia lining the airway.
C) multiple layers of dead epithelial cells within the lungs that create a virtually impenetrable barrier to pathogen movement.
D) macrophages in the lungs produce the immobilizing toxins that paralyze pathogens before they can infect the body.
A) lung secretions create an acidic and inhospitable environment for pathogens.
B) mucus secreted into the bronchioles traps pathogens and is eventually removed by the action of the cilia lining the airway.
C) multiple layers of dead epithelial cells within the lungs that create a virtually impenetrable barrier to pathogen movement.
D) macrophages in the lungs produce the immobilizing toxins that paralyze pathogens before they can infect the body.
B
3
Which of the following immune cells is likely to be the first to encounter the pathogen during a bacterial infection?
A) a macrophage
B) a neutrophil
C) a T helper cell
D) a cytotoxic T cell
A) a macrophage
B) a neutrophil
C) a T helper cell
D) a cytotoxic T cell
B
4
The blood of vertebrates contains a large number of cells that participate in both the innate and adaptive immune responses.To what group of blood components do these cells belong?
A) the red blood cells
B) the white blood cells
C) the endothelial cells
D) the blood platelets
A) the red blood cells
B) the white blood cells
C) the endothelial cells
D) the blood platelets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
White blood cells (WBCs)have the unusual ability of being able to migrate through capillary walls into the surrounding tissues;why is this ability important?
A) WBCs coordinate the assembly of complement molecules into functional units outside the circulatory system to minimize the potential for clot formation.
B) WBCs become the antibodies that target the multicellular parasites that are too large to fit within the vascular system.
C) The majority of infections begin in locations other than the circulatory system.
D) WBCs leave the circulatory system to collect and return the red blood cells that are lost from the capillary during the inflammatory process.
A) WBCs coordinate the assembly of complement molecules into functional units outside the circulatory system to minimize the potential for clot formation.
B) WBCs become the antibodies that target the multicellular parasites that are too large to fit within the vascular system.
C) The majority of infections begin in locations other than the circulatory system.
D) WBCs leave the circulatory system to collect and return the red blood cells that are lost from the capillary during the inflammatory process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A ________ can be a very challenging injury for the immune system to respond to because ________.
A) bruise;blood vessels lose so much blood into the surrounding tissues
B) puncture;the first line of defense is immediately bypassed and depending on the depth of the puncture much of the second line may also be ineffective
C) blistering sunburn;the acidity of skin is compromised
D) laceration;the salt and acid on the skin's surface can enter through the wound
A) bruise;blood vessels lose so much blood into the surrounding tissues
B) puncture;the first line of defense is immediately bypassed and depending on the depth of the puncture much of the second line may also be ineffective
C) blistering sunburn;the acidity of skin is compromised
D) laceration;the salt and acid on the skin's surface can enter through the wound

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The image below depicts
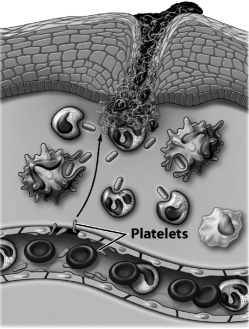
A) adaptive immunity: antibodies are being made.
B) passive immunity: neutrophils are being destroyed.
C) innate immunity: memory cells are being made.
D) inflammatory response: blood vessels are porous and leaking fluid.

A) adaptive immunity: antibodies are being made.
B) passive immunity: neutrophils are being destroyed.
C) innate immunity: memory cells are being made.
D) inflammatory response: blood vessels are porous and leaking fluid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Prostaglandins are lipid-based signaling molecules produced during an infection;they have a variety of effects that include
A) shutting down the capillaries near a wound.
B) stimulating the production and release of histamines.
C) attaching to the surface of pathogenic cells as secondary antigens to attract lymphocytes.
D) producing the fever,pain,and drowsiness that often accompanies an infection.
A) shutting down the capillaries near a wound.
B) stimulating the production and release of histamines.
C) attaching to the surface of pathogenic cells as secondary antigens to attract lymphocytes.
D) producing the fever,pain,and drowsiness that often accompanies an infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The pathology of a virus is very different from that of a bacterium or fungal cell,and unique innate strategies exist for combating each.During a viral infection,infected cells may
A) release interferon,which reduces the probability that the virus will enter neighboring,uninfected cells.
B) self-destruct before the reproductive cycle of the virus has been completed.
C) release interferon,which mutates the DNA of the virus and prevents viral replication.
D) release histamine,which exaggerates the inflammatory response and prevents viral migration within the body.
A) release interferon,which reduces the probability that the virus will enter neighboring,uninfected cells.
B) self-destruct before the reproductive cycle of the virus has been completed.
C) release interferon,which mutates the DNA of the virus and prevents viral replication.
D) release histamine,which exaggerates the inflammatory response and prevents viral migration within the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
On occasion the immune response in inappropriate;for example,an allergy occurs when the immune system
A) initiates a response to a substance that is not actually pathogenic.
B) misinterprets normal body cells for pathogenic ones and mounts an immune response against those tissues.
C) ignores a pathogen,like a parasitic worm,and permits it to reside and reproduce within the body.
D) suffers a genetic defect that disables or accentuates certain elements,resulting in either too little or too much response.
A) initiates a response to a substance that is not actually pathogenic.
B) misinterprets normal body cells for pathogenic ones and mounts an immune response against those tissues.
C) ignores a pathogen,like a parasitic worm,and permits it to reside and reproduce within the body.
D) suffers a genetic defect that disables or accentuates certain elements,resulting in either too little or too much response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Different genetic versions of a particular pathogen are known as different
A) species.
B) strains.
C) antibodies.
D) disease hosts.
A) species.
B) strains.
C) antibodies.
D) disease hosts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Histamine
A) makes the capillaries near a wound more porous.
B) is converted to prostaglandin near a wound.
C) vasoconstricts the arterioles near a wound.
D) is one of the classes of antibody.
A) makes the capillaries near a wound more porous.
B) is converted to prostaglandin near a wound.
C) vasoconstricts the arterioles near a wound.
D) is one of the classes of antibody.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Complement proteins
A) kill pathogenic cells directly or mark them for subsequent phagocytosis.
B) are the precursor molecules that eventually become antibodies.
C) provide a protective covering on healthy cells that redirects any macrophage that may be inappropriately targeting it.
D) attach directly to the antigens on the surface of a pathogen.
A) kill pathogenic cells directly or mark them for subsequent phagocytosis.
B) are the precursor molecules that eventually become antibodies.
C) provide a protective covering on healthy cells that redirects any macrophage that may be inappropriately targeting it.
D) attach directly to the antigens on the surface of a pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following areas of the human body is NOT the location of a major concentration of white blood cells?
A) the tonsils
B) the appendix
C) the kidneys
D) the spleen
A) the tonsils
B) the appendix
C) the kidneys
D) the spleen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The body responds to tissue damage by mounting an immediate and coordinated sequence of events called the ________ response.
A) specific immune
B) prostaglandin
C) inflammatory
D) histamine
A) specific immune
B) prostaglandin
C) inflammatory
D) histamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
All of the following have been associated with disease,but ________ is a vector that introduces the actual pathogen rather than being a pathogen itself and does NOT cause any illness directly.
A) a bacterium
B) the flea
C) a protist
D) a virus
A) a bacterium
B) the flea
C) a protist
D) a virus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The site of an injury like a scratch or a splinter initially becomes red and painful.In some instances a yellowish thickened fluid may be present at the injury site.Commonly called pus,this fluid is
A) blood plasma and the dead neutrophils,macrophages,and bacteria that have accumulated at the wound.
B) the surviving bacteria that have been successful in avoiding the innate immune response.
C) dead body cells collaterally killed by the activation of the complement system.
D) the coagulated cytoplasm and hemoglobin produced by the blood cells injured during the infection.
A) blood plasma and the dead neutrophils,macrophages,and bacteria that have accumulated at the wound.
B) the surviving bacteria that have been successful in avoiding the innate immune response.
C) dead body cells collaterally killed by the activation of the complement system.
D) the coagulated cytoplasm and hemoglobin produced by the blood cells injured during the infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
One of the most common examples of innate immunity component is the
A) production of antibodies from T cells.
B) production of antibodies from B cells.
C) production of memory cells following a vaccination.
D) acidic environment that develops in the stomach.
A) production of antibodies from T cells.
B) production of antibodies from B cells.
C) production of memory cells following a vaccination.
D) acidic environment that develops in the stomach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Macrophages may be unable to digest the pathogens they phagocytize.If so,the pathogen can still be prevented from affecting healthy tissues by
A) transferring the pathogen to an NK cell.
B) releasing the pathogen after having added additional antigen to its surface.
C) producing internal antibodies that mark the pathogen for destruction by complement.
D) encapsulation within the macrophage cytoplasm.
A) transferring the pathogen to an NK cell.
B) releasing the pathogen after having added additional antigen to its surface.
C) producing internal antibodies that mark the pathogen for destruction by complement.
D) encapsulation within the macrophage cytoplasm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following would explain why organ donors and organ recipients are genetically matched before an organ transplant is performed?
A) The DNA of a person determines the specific antibody a person makes.In the case of an organ transplant,doctors want to ensure the antibody made within the new organ will not react with the antibody made by the recipient.
B) The self-identification markers on the surface of cells are genetically determined.If the surfaces of the donor's cells and the recipient's cells are not similar,the recipient's immune system will probably reject the new organ.
C) Different genetic sequences may cause the donor and the recipient to produce different strains of interferon,which would result in an autoimmune disease.
D) After entering a cell,an antibody molecule will move into its nucleus and will bind to any DNA segment lacking the self-identification sequence.This can cause organ rejection.
A) The DNA of a person determines the specific antibody a person makes.In the case of an organ transplant,doctors want to ensure the antibody made within the new organ will not react with the antibody made by the recipient.
B) The self-identification markers on the surface of cells are genetically determined.If the surfaces of the donor's cells and the recipient's cells are not similar,the recipient's immune system will probably reject the new organ.
C) Different genetic sequences may cause the donor and the recipient to produce different strains of interferon,which would result in an autoimmune disease.
D) After entering a cell,an antibody molecule will move into its nucleus and will bind to any DNA segment lacking the self-identification sequence.This can cause organ rejection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Cytotoxic T cells
A) directly kill viruses.
B) kill cells that are infected by viruses.
C) cause B cells to proliferate when they are bound to their antigen.
D) bind to B cells and then to infected cells.
A) directly kill viruses.
B) kill cells that are infected by viruses.
C) cause B cells to proliferate when they are bound to their antigen.
D) bind to B cells and then to infected cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Folklore has produced this advice: "Starve a cold,feed a fever." Based on your knowledge of immune action,how would you evaluate the suggestion of eating less?
A) It is appropriate because the reduced food intake will allow the body to generate its cellular energy from stored foods that the pathogen is unable to utilize.
B) It is appropriate because eating less denies the energy needed to support the infection.
C) It is inappropriate because foods that are nutritious for humans are generally toxic to human pathogens.
D) It is inappropriate because the body needs nutrients and energy to support the cloning of adaptive immune cells and the extensive synthesis of antibodies.
A) It is appropriate because the reduced food intake will allow the body to generate its cellular energy from stored foods that the pathogen is unable to utilize.
B) It is appropriate because eating less denies the energy needed to support the infection.
C) It is inappropriate because foods that are nutritious for humans are generally toxic to human pathogens.
D) It is inappropriate because the body needs nutrients and energy to support the cloning of adaptive immune cells and the extensive synthesis of antibodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
After their activation following an encounter with antigen,B cells undergo cloning and become either effector or memory cells.Effector cells
A) produce the specific complement molecules that ultimately bind to antibody.
B) produce and secrete free soluble antibodies into the blood and lymphatic circulations.
C) produce and release soluble antigens.
D) seek out and destroy infected T cells.
A) produce the specific complement molecules that ultimately bind to antibody.
B) produce and secrete free soluble antibodies into the blood and lymphatic circulations.
C) produce and release soluble antigens.
D) seek out and destroy infected T cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following both prevents blood loss and the invasion of pathogens in vertebrates?
A) the formation of blood clots
B) phagocytosis
C) humoral immunity
D) cell-mediated immunity
A) the formation of blood clots
B) phagocytosis
C) humoral immunity
D) cell-mediated immunity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Proteins and carbohydrates on the surface of the cells of disease organisms help the vertebrate immune system recognize the specific invader;these molecules are knows as
A) platelets.
B) antigens.
C) lymphocytes.
D) antibodies.
A) platelets.
B) antigens.
C) lymphocytes.
D) antibodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Examine the figure below.
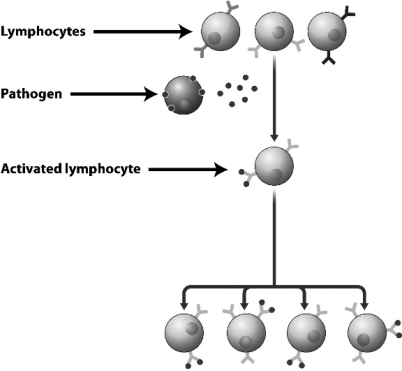
Why is only one of the lymphocytes in this diagram activated by the pathogen?
A) Antigens move through the immune system by diffusion,so the lymphocyte closest to the site of infection binds the antigen first.Once a lymphocyte is activated,it produces chemicals that prevent the activation of other lymphocytes.
B) Lymphocytes are only activated if all of their receptors are bound by antigens.In this case,there were only enough antigens to fully activate one cell.
C) The immune system contains many different lymphocytes,each displaying a different antigen-binding protein.In this case,the antigen only matched the binding protein on the cell that was activated.
D) Lymphocytes can only be activated by chemicals produced by the innate immune system.Only one of the cells in this diagram has been exposed to these chemicals.

Why is only one of the lymphocytes in this diagram activated by the pathogen?
A) Antigens move through the immune system by diffusion,so the lymphocyte closest to the site of infection binds the antigen first.Once a lymphocyte is activated,it produces chemicals that prevent the activation of other lymphocytes.
B) Lymphocytes are only activated if all of their receptors are bound by antigens.In this case,there were only enough antigens to fully activate one cell.
C) The immune system contains many different lymphocytes,each displaying a different antigen-binding protein.In this case,the antigen only matched the binding protein on the cell that was activated.
D) Lymphocytes can only be activated by chemicals produced by the innate immune system.Only one of the cells in this diagram has been exposed to these chemicals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Examine the figure below.
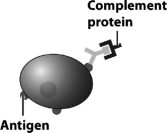
Which events have occurred previously to create the situation depicted with the bacterium shown in this figure?
A) The bacterium has successfully overcome the first two barriers of the host's immune response: its barriers and the adaptive response.
B) The presence of an antibody molecule indicates that the antigen has been contacted by a B cell,the B cell underwent cloning,and one of the cloned effector cells has begun antibody production.
C) A cytotoxic T cell recognized the bacterium's antigen and transferred the toxic complement protein directly onto its surface.
D) The bacterium has phagocytized a lymphocyte and is using the captured complement protein to mask itself from other immune cells.

Which events have occurred previously to create the situation depicted with the bacterium shown in this figure?
A) The bacterium has successfully overcome the first two barriers of the host's immune response: its barriers and the adaptive response.
B) The presence of an antibody molecule indicates that the antigen has been contacted by a B cell,the B cell underwent cloning,and one of the cloned effector cells has begun antibody production.
C) A cytotoxic T cell recognized the bacterium's antigen and transferred the toxic complement protein directly onto its surface.
D) The bacterium has phagocytized a lymphocyte and is using the captured complement protein to mask itself from other immune cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Helper T cells perform all of the following EXCEPT
A) stimulate the proliferation of cytotoxic T cells when bound to their specific antigen.
B) stimulate the proliferation of B cells when bound to their specific antigen.
C) proliferate rapidly when bound to their specific antigen.
D) identify,contact,and destroy invasive organisms.
A) stimulate the proliferation of cytotoxic T cells when bound to their specific antigen.
B) stimulate the proliferation of B cells when bound to their specific antigen.
C) proliferate rapidly when bound to their specific antigen.
D) identify,contact,and destroy invasive organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following statements correctly describes the immune response when the infectious pathogen is a virus?
A) The antigen molecules on the viral DNA allow the immune system to prevent the infection.
B) Lymphocytes are not involved in the immune response.
C) The lack of nucleic acid in a virus complicates the immune response.
D) Lymphocytes initially respond to infected cells rather than to the virus itself.
A) The antigen molecules on the viral DNA allow the immune system to prevent the infection.
B) Lymphocytes are not involved in the immune response.
C) The lack of nucleic acid in a virus complicates the immune response.
D) Lymphocytes initially respond to infected cells rather than to the virus itself.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Active artificial immunity results from injecting
A) a harmless form of a pathogen.
B) live pathogens.
C) live B cells from another person.
D) antibodies.
A) a harmless form of a pathogen.
B) live pathogens.
C) live B cells from another person.
D) antibodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Several types of immunity are recognized;which type of immunity is produced through successful vaccination?
A) active artificial immunity
B) active natural immunity
C) passive artificial immunity
D) passive natural immunity
A) active artificial immunity
B) active natural immunity
C) passive artificial immunity
D) passive natural immunity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following statements about an adaptive response to an invasive single-celled pathogen or virus is FALSE?
A) The host immune system must be able to recognize the difference between its own cells and those of the pathogen.
B) A successful response requires the production of antibodies.
C) The presence of antibodies stimulates the production and release of soluble antigen.
D) Phagocytes will engulf and digest some of the pathogen.
A) The host immune system must be able to recognize the difference between its own cells and those of the pathogen.
B) A successful response requires the production of antibodies.
C) The presence of antibodies stimulates the production and release of soluble antigen.
D) Phagocytes will engulf and digest some of the pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Lymphocytes are relatively abundant,accounting for approximately 20 percent of all white blood cells;what is their origin?
A) They are produced by the conversion of other white blood cells,like macrophages,during an infectious event.
B) They originate in the thymus.
C) They are generated in lymph nodes by mitotic division of the cells lining the lymphatic pathway.
D) Like all blood cells,they are produced by the division of stem cells in the bone marrow.
A) They are produced by the conversion of other white blood cells,like macrophages,during an infectious event.
B) They originate in the thymus.
C) They are generated in lymph nodes by mitotic division of the cells lining the lymphatic pathway.
D) Like all blood cells,they are produced by the division of stem cells in the bone marrow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The term clonal in clonal selection refers to the fact that
A) a lymphocyte can be easily converted into a stem cell line for laboratory research.
B) a single activated B cell produces many identical copies of the antibody,which react to the antigen that activated the B cell.
C) an activated B cell can convert itself quickly into helper and cytotoxic T cells that are specific for the same antigen.
D) once activated,a specific lymphocyte divides mitotically,producing identical copies of itself.
A) a lymphocyte can be easily converted into a stem cell line for laboratory research.
B) a single activated B cell produces many identical copies of the antibody,which react to the antigen that activated the B cell.
C) an activated B cell can convert itself quickly into helper and cytotoxic T cells that are specific for the same antigen.
D) once activated,a specific lymphocyte divides mitotically,producing identical copies of itself.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Because the receptors on each T cell and B cell lineage are unique,the receptor is able to bind to only one specific type of
A) antibody.
B) neutrophil.
C) antigen.
D) prostaglandin.
A) antibody.
B) neutrophil.
C) antigen.
D) prostaglandin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Memory cells
A) include B and T cells that remain in the body for long periods of time after the first exposure to a pathogen.
B) are macrophages that store copies of antibodies for decades.
C) make copies of T cells that remain active long after the primary response has ended.
D) become T cells during a secondary response to a pathogen.
A) include B and T cells that remain in the body for long periods of time after the first exposure to a pathogen.
B) are macrophages that store copies of antibodies for decades.
C) make copies of T cells that remain active long after the primary response has ended.
D) become T cells during a secondary response to a pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Examine the figure below.
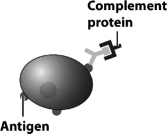
Which of the following could happen to the bacterium depicted in this figure?
A) The bacterium could use the complement protein to mimic the host's self-antigens and avoid detection.
B) The complement protein could attract a cytotoxic B cell that would phagocytize the bacterium.
C) The complement proteins could attract other complement proteins that would form a complex that forms a hole in the bacterium's plasma membrane.
D) The complement protein could attract a cytotoxic T cell that would inject toxins into the bacterium.

Which of the following could happen to the bacterium depicted in this figure?
A) The bacterium could use the complement protein to mimic the host's self-antigens and avoid detection.
B) The complement protein could attract a cytotoxic B cell that would phagocytize the bacterium.
C) The complement proteins could attract other complement proteins that would form a complex that forms a hole in the bacterium's plasma membrane.
D) The complement protein could attract a cytotoxic T cell that would inject toxins into the bacterium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The antibodies released by activated B cells specifically target
A) activated cytotoxic T cells,initiating the cloning process.
B) the antigen(s)that initially activated the B cell by binding to its receptors.
C) any cell lacking the host's self antigen surface markers.
D) APCs,stimulating them to display captured antigen and thereby recruit additional lymphocytes.
A) activated cytotoxic T cells,initiating the cloning process.
B) the antigen(s)that initially activated the B cell by binding to its receptors.
C) any cell lacking the host's self antigen surface markers.
D) APCs,stimulating them to display captured antigen and thereby recruit additional lymphocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An autoimmune disease could occur if
A) B cells fail to recognize and interact with helper T cells.
B) a helper T cell was unable to match its receptor to the antigen of an infectious agent.
C) B cells and T cells were unable to recognize the self-antigens displayed by host cells.
D) the antibodies produced in an earlier infection were reactivated in the bloodstream.
A) B cells fail to recognize and interact with helper T cells.
B) a helper T cell was unable to match its receptor to the antigen of an infectious agent.
C) B cells and T cells were unable to recognize the self-antigens displayed by host cells.
D) the antibodies produced in an earlier infection were reactivated in the bloodstream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
At the site of a wound or cut,platelets combine with proteins in our blood to form
A) macrophages.
B) antibodies.
C) prostaglandins.
D) clots.
A) macrophages.
B) antibodies.
C) prostaglandins.
D) clots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
________ proteins attach to antibodies bound to antigens on the surfaces of invading cells.This helps macrophages bind to these cells in preparation for phagocytosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A lymphocyte is activated when one of its surface receptors binds to a protein found on the surface of a pathogen.These proteins perform essential tasks for the pathogen,but because they can also evoke an immune response they are termed ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Phagocytosis is one of the primary strategies of the innate immune response,which is hardly surprising considering that approximately 70 percent of the circulating white blood cells are the phagocytic ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following statements about vaccinations given to humans is true?
A) The vaccination acts as the first exposure to a virus,allowing the much more effective second exposure response to occur when the virus actually infects the body.
B) A vaccination primes the body so that it will no longer respond to an invasion by a virus.
C) There is a chance of a person's getting the disease from a vaccination,because vaccination involves the injection of the entire living disease organism.
D) Vaccinations prime the virus so that the virus will not kill as many body cells as it would in a nonvaccinated person.
A) The vaccination acts as the first exposure to a virus,allowing the much more effective second exposure response to occur when the virus actually infects the body.
B) A vaccination primes the body so that it will no longer respond to an invasion by a virus.
C) There is a chance of a person's getting the disease from a vaccination,because vaccination involves the injection of the entire living disease organism.
D) Vaccinations prime the virus so that the virus will not kill as many body cells as it would in a nonvaccinated person.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The diagnosis of cancer represents a failure of the body's cancer ________ system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A variety of strategies have been utilized for the preparation of vaccines,but regardless of the method used to prepare it,one feature shared in common by all vaccines is that each contains one or more ________ from the targeted pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following is an autoimmune disease?
A) cystic fibrosis: the immune system attacks the epithelial cells that form the lung's inner surface
B) sickle-cell anemia: the immune system attacks the components in the bone marrow that give rise to red blood cells
C) type 1 diabetes: the immune system attacks the pancreatic cells that produce insulin
D) Tay-Sachs disease: the immune system attacks the cells associated with energy storage within the nervous system.
A) cystic fibrosis: the immune system attacks the epithelial cells that form the lung's inner surface
B) sickle-cell anemia: the immune system attacks the components in the bone marrow that give rise to red blood cells
C) type 1 diabetes: the immune system attacks the pancreatic cells that produce insulin
D) Tay-Sachs disease: the immune system attacks the cells associated with energy storage within the nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The immune system can recognize almost all foreign cells because they lack the genetically determined pattern of ________ and ________ found on the plasma membrane of its own cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Each of the five types of white blood cells or leukocytes makes a contribution to the immune response,but the white blood cell that coordinates adaptive immunity,the most critical immune response,is the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following statements about infection by HIV,the virus that causes AIDS,is FALSE?
A) Most AIDS victims go through a period of up to 15 years between infection and the onset of AIDS symptoms.
B) In the early part of the infection,cytotoxic T lymphocytes destroy helper T lymphocytes infected by the virus.
C) The antigens on the protein coat of the HIV remain the same through time.
D) The victim's immune system eventually collapses,and normally harmless infections cause death.
A) Most AIDS victims go through a period of up to 15 years between infection and the onset of AIDS symptoms.
B) In the early part of the infection,cytotoxic T lymphocytes destroy helper T lymphocytes infected by the virus.
C) The antigens on the protein coat of the HIV remain the same through time.
D) The victim's immune system eventually collapses,and normally harmless infections cause death.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
When pathogens overcome the barrier defenses and enter the body they are quickly met by macrophages and neutrophils,two types of cells that constitute a large fraction of the nonspecific or ________ response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A disease-causing agent is called a(n)________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The ability to resist specific pathogens using a coordinated combination of specialized cells and molecules is the primary function of the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The immune system is considered to consist of two subdivisions,a nonspecific component consisting primarily of barriers and phagocytes known as the innate response and a highly specific component consisting primarily of antibody and cell-mediated strategies known as the ________ response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Cells infected with virus almost never survive,but they may aid neighboring cells by releasing ________,a protein that attaches to the membrane of a healthy cell and inhibits viral entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
At discrete points along the lymphatic ducts the walls are modified to house huge numbers of white blood cells that trap bacteria,viruses,and foreign proteins.These structures are termed ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following statements about the human immune response is true?
A) Host cells are never destroyed by macrophages,even if they are damaged.
B) Neutrophils mount a specific response to particular species of invading organisms.
C) The immune response is more effective during the second exposure to an invader.
D) Lymphocytes are one of the components of blood clots.
A) Host cells are never destroyed by macrophages,even if they are damaged.
B) Neutrophils mount a specific response to particular species of invading organisms.
C) The immune response is more effective during the second exposure to an invader.
D) Lymphocytes are one of the components of blood clots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Several types of immunity are recognized.Which experience would produce an artificial passive immunity to the virus that causes hepatitis A?
A) contracting and surviving hepatitis A
B) placental transfer in utero or when a newborn nurses,provided the mother has an immunity to hepatitis A
C) receiving an injection of preformed antibodies (immunoglobulins)recovered from an individual undergoing an active immune response for hepatitis A
D) receiving a successful vaccination for hepatitis A
A) contracting and surviving hepatitis A
B) placental transfer in utero or when a newborn nurses,provided the mother has an immunity to hepatitis A
C) receiving an injection of preformed antibodies (immunoglobulins)recovered from an individual undergoing an active immune response for hepatitis A
D) receiving a successful vaccination for hepatitis A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If HIV is allowed to enter the epithelium of the vaginal walls,what is the first level of the immune system it would have to defeat to cause an infection?
A) the innate immune system
B) humoral immunity
C) cell-mediated immunity
D) the autoimmune system
A) the innate immune system
B) humoral immunity
C) cell-mediated immunity
D) the autoimmune system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
One aspect of inflammation is swelling;it develops when capillary permeability changes and ________ moves from the vascular system into the interstitial spaces around the cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
To verify the successfulness of a vaccination procedure,researchers could either challenge the individual with an exposure to the pathogen or demonstrate the presence of ________ in the bloodstream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Salt in the sweat is a component of adaptive immunity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Virally infected cells release interferon in order to protect neighboring cells from infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Macrophages are smaller than neutrophils but have a similar function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Lymphocytes surround and digest any damaged host cells and any cell marked with antibody and/or complement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A fever is the product of an out-of-control immune response to a parasite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
After the initial exposure to a pathogen,subsequent infections with the same pathogen are unlikely because the initial response produced a small population of fast-acting lymphocytes known as ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The human immune system has a more effective response to an invader during a second exposure than during the first exposure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In the illustration below of the lymphatic system,the arrow is pointing to a kidney.
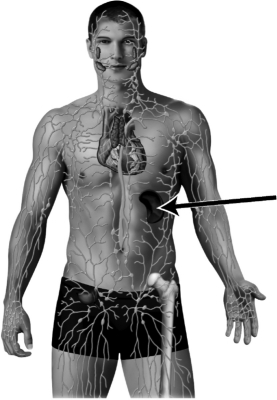


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The first exposure to a particular antigen initiates a(n)________ immune response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Vaccinations are required prior to traveling to many foreign locations;the goal of vaccination is to create populations of memory cells,so that any future exposure to the pathogen produces a secondary rather than primary response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Despite its suitability as an infection site,the surface of the eye is rarely infected because tears release lysozyme,an antibacterial enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
HIV attacks B lymphocytes;this lowers the effectiveness of the antibody-mediated response but leaves cell-mediated immunity entirely intact.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Because the first line of defense has failed and the infection is gaining ground,the adaptive immune response tends to develop more rapidly than the innate immune response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Some individuals may share one or more self-antigen components with one another;if so,they are much better candidates for tissue transplants (donor-recipient)than those with no similarities at all.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The immune system can detect cancerous cells because they display different cell surface proteins and carbohydrates than normal self cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In the case of AIDS,death is more likely to result from other infections that the immune system CANNOT control than from HIV itself.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Macrophages,cells derived from a type of white blood cell that leaves the circulation to reside in the tissues,destroy invading pathogens by phagocytosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Individuals with HIV often experience infections that most individuals are easily able to resist;their vulnerability to infection arises because HIV targets the ________,a cell that plays an essential role in the activation of both antibody- and cellular-mediated immunity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The graph below depicts the change in antibody concentration following an initial and a later pathogen exposure.
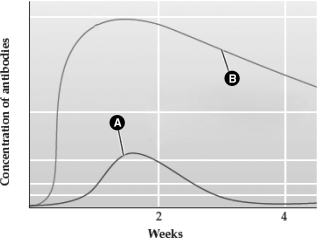
The line labeled with the letter ________ represents the response after the initial exposure.

The line labeled with the letter ________ represents the response after the initial exposure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



