Deck 18: Electrochemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/115
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Electrochemistry
1
Balance the following redox reaction if it occurs in basic solution.What are the coefficients in front of Cr(OH)4⁻ and ClO⁻ in the balanced reaction?
Cr(OH)4⁻(aq)+ ClO⁻(aq)→ CrO42-(aq)+ Cl⁻(aq)
A)Cr(OH)4⁻ = 2,ClO⁻ = 3
B)Cr(OH)4⁻ = 1,ClO⁻ = 1
C)Cr(OH)4⁻ = 1,ClO⁻ = 2
D)Cr(OH)4⁻ = 2,ClO⁻ = 6
E)Cr(OH)4⁻ = 6,ClO⁻ = 5
Cr(OH)4⁻(aq)+ ClO⁻(aq)→ CrO42-(aq)+ Cl⁻(aq)
A)Cr(OH)4⁻ = 2,ClO⁻ = 3
B)Cr(OH)4⁻ = 1,ClO⁻ = 1
C)Cr(OH)4⁻ = 1,ClO⁻ = 2
D)Cr(OH)4⁻ = 2,ClO⁻ = 6
E)Cr(OH)4⁻ = 6,ClO⁻ = 5
Cr(OH)4⁻ = 2,ClO⁻ = 3
2
What is the reducing agent in the redox reaction represented by the following cell notation?
Ni(s)∣ Ni2+(aq)∣∣ Ag+(aq)∣ Ag(s)
A)Ni(s)
B)Ni2+(aq)
C)Ag+(aq)
D)Ag(s)
E)Pt
Ni(s)∣ Ni2+(aq)∣∣ Ag+(aq)∣ Ag(s)
A)Ni(s)
B)Ni2+(aq)
C)Ag+(aq)
D)Ag(s)
E)Pt
Ni(s)
3
Balance the following redox reaction if it occurs in basic solution.What are the coefficients in front of Al and F2 in the balanced reaction?
Al(s)+ F2(g)→ Al3+(aq)+ F-(aq)
A)Al = 2,F2 = 3
B)Al = 2,F2 = 6
C)Al = 1,F2 = 1
D)Al = 2,F2 = 1
E)Al = 3,F2 = 2
Al(s)+ F2(g)→ Al3+(aq)+ F-(aq)
A)Al = 2,F2 = 3
B)Al = 2,F2 = 6
C)Al = 1,F2 = 1
D)Al = 2,F2 = 1
E)Al = 3,F2 = 2
Al = 2,F2 = 3
4
Balance the following redox reaction if it occurs in basic solution.What are the coefficients in front of ClO2 and H2O in the balanced reaction?
H2O2(l)+ ClO2(aq)→ ClO2⁻(aq)+ O2(g)
A)ClO2 = 1,H2O = 1
B)ClO2 = 1,H2O = 2
C)ClO2 = 4,H2O = 3
D)ClO2 = 4,H2O = 2
E)ClO2 = 2,H2O = 2
H2O2(l)+ ClO2(aq)→ ClO2⁻(aq)+ O2(g)
A)ClO2 = 1,H2O = 1
B)ClO2 = 1,H2O = 2
C)ClO2 = 4,H2O = 3
D)ClO2 = 4,H2O = 2
E)ClO2 = 2,H2O = 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What element is being reduced in the following redox reaction?
MnO4⁻(aq)+ H2C2O4(aq)→ Mn2+(aq)+ CO2(g)
A)C
B)O
C)Mn
D)H
MnO4⁻(aq)+ H2C2O4(aq)→ Mn2+(aq)+ CO2(g)
A)C
B)O
C)Mn
D)H

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What element is being oxidized in the following redox reaction?
Zn2+(aq)+ NH4+(aq)→ Zn(s)+ NO3⁻(aq)
A)Zn
B)N
C)H
D)O
Zn2+(aq)+ NH4+(aq)→ Zn(s)+ NO3⁻(aq)
A)Zn
B)N
C)H
D)O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Determine the cell notation for the redox reaction given below.
3 Cl2(g)+ 2 Fe(s)→ 6 Cl⁻(aq)+ 2 Fe3+(aq)
A)Cl2(g)∣ Cl⁻(aq)∣ Pt ∣∣ Fe(s)∣ Fe3+(aq)
B)Cl⁻(aq)∣ Cl2(g)∣ Pt ∣∣ Fe3+(aq) ∣ Fe(s)
C)Fe3+(aq)∣ Fe(s)∣∣ Cl⁻(aq)∣ Cl2(g)∣ Pt
D)Fe(s)∣ Cl2(g)∣∣ Fe3+(aq)∣ Cl⁻(aq)∣ Pt
E)Fe(s)∣ Fe3+(aq)∣∣ Cl2(g)∣ Cl⁻(aq)∣ Pt
3 Cl2(g)+ 2 Fe(s)→ 6 Cl⁻(aq)+ 2 Fe3+(aq)
A)Cl2(g)∣ Cl⁻(aq)∣ Pt ∣∣ Fe(s)∣ Fe3+(aq)
B)Cl⁻(aq)∣ Cl2(g)∣ Pt ∣∣ Fe3+(aq) ∣ Fe(s)
C)Fe3+(aq)∣ Fe(s)∣∣ Cl⁻(aq)∣ Cl2(g)∣ Pt
D)Fe(s)∣ Cl2(g)∣∣ Fe3+(aq)∣ Cl⁻(aq)∣ Pt
E)Fe(s)∣ Fe3+(aq)∣∣ Cl2(g)∣ Cl⁻(aq)∣ Pt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Balance the following redox reaction if it occurs in acidic solution.What are the coefficients in front of H⁺ and Fe3+ in the balanced reaction?
Fe2+(aq)+ MnO4⁻(aq)→ Fe3+(aq)+ Mn2+(aq)
A)H+ = 2,Fe3+ = 3
B)H+ = 8,Fe3+ = 5
C)H+ = 3,Fe3+ = 2
D)H+ = 5,Fe3+ = 1
E)H+ = 8,Fe3+ = 1
Fe2+(aq)+ MnO4⁻(aq)→ Fe3+(aq)+ Mn2+(aq)
A)H+ = 2,Fe3+ = 3
B)H+ = 8,Fe3+ = 5
C)H+ = 3,Fe3+ = 2
D)H+ = 5,Fe3+ = 1
E)H+ = 8,Fe3+ = 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Balance the following redox reaction if it occurs in acidic solution.What are the coefficients in front of Zn and H+ in the balanced reaction?
Zn2+(aq)+ NH4+(aq)→ Zn(s)+ NO3⁻(aq)
A)Zn = 1,H+ = 8
B)Zn = 1,H+ = 4
C)Zn = 4,H+ = 10
D)Zn = 2,H+ = 4
E)Zn = 3,H+ = 5
Zn2+(aq)+ NH4+(aq)→ Zn(s)+ NO3⁻(aq)
A)Zn = 1,H+ = 8
B)Zn = 1,H+ = 4
C)Zn = 4,H+ = 10
D)Zn = 2,H+ = 4
E)Zn = 3,H+ = 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Determine the redox reaction represented by the following cell notation.
Mg(s)∣ Mg2+(aq)∣∣ Cu2+(aq)∣ Cu(s)
A)Cu(s)+ Mg2+(aq)→ Mg(s)+ Cu2+(aq)
B)Mg(s)+ Cu2+(aq)→ Cu(s)+ Mg2+(aq)
C)2 Mg(s)+ Cu2+(aq)→ Cu(s)+ 2 Mg2+(aq)
D)2 Cu(s)+ Mg2+(aq)→ Mg(s)+ 2 Cu2+(aq)
E)3 Mg(s)+ 2 Cu2+(aq)→ 2 Cu(s)+ 3 Mg2+(aq)
Mg(s)∣ Mg2+(aq)∣∣ Cu2+(aq)∣ Cu(s)
A)Cu(s)+ Mg2+(aq)→ Mg(s)+ Cu2+(aq)
B)Mg(s)+ Cu2+(aq)→ Cu(s)+ Mg2+(aq)
C)2 Mg(s)+ Cu2+(aq)→ Cu(s)+ 2 Mg2+(aq)
D)2 Cu(s)+ Mg2+(aq)→ Mg(s)+ 2 Cu2+(aq)
E)3 Mg(s)+ 2 Cu2+(aq)→ 2 Cu(s)+ 3 Mg2+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Balance the following redox reaction if it occurs in basic solution.What are the coefficients in front of Br2 and OH⁻ in the balanced reaction?
Br2(l)→ BrO3⁻(aq)+ Br⁻(aq)
A)Br2 = 1,OH⁻ = 2
B)Br2 = 2,OH⁻ = 5
C)Br2 = 3,OH⁻ = 3
D)Br2 = 3,OH⁻ = 6
E)Br2 = 1,OH⁻ = 6
Br2(l)→ BrO3⁻(aq)+ Br⁻(aq)
A)Br2 = 1,OH⁻ = 2
B)Br2 = 2,OH⁻ = 5
C)Br2 = 3,OH⁻ = 3
D)Br2 = 3,OH⁻ = 6
E)Br2 = 1,OH⁻ = 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Identify oxidation.
A)increase in oxidation number
B)loss of electrons
C)gain of electrons
D)decrease in oxidation number
E)both A and B
A)increase in oxidation number
B)loss of electrons
C)gain of electrons
D)decrease in oxidation number
E)both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What element is being oxidized in the following redox reaction?
Cr(OH)4⁻(aq)+ ClO⁻(aq)→ CrO42-(aq)+ Cl⁻(aq)
A)Cr
B)O
C)H
D)Cl
Cr(OH)4⁻(aq)+ ClO⁻(aq)→ CrO42-(aq)+ Cl⁻(aq)
A)Cr
B)O
C)H
D)Cl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Balance the following redox reaction if it occurs in acidic solution.What are the coefficients in front of H2C2O4 and H2O in the balanced reaction?
MnO4⁻(aq)+ H2C2O4(aq)→ Mn2+(aq)+ CO2(g)
A)H2C2O4 = 5,H2O = 8
B)H2C2O4 = 1,H2O = 1
C)H2C2O4 = 5,H2O = 1
D)H2C2O4 = 1,H2O = 4
E)H2C2O4 = 3,H2O = 2
MnO4⁻(aq)+ H2C2O4(aq)→ Mn2+(aq)+ CO2(g)
A)H2C2O4 = 5,H2O = 8
B)H2C2O4 = 1,H2O = 1
C)H2C2O4 = 5,H2O = 1
D)H2C2O4 = 1,H2O = 4
E)H2C2O4 = 3,H2O = 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Balance the following redox reaction if it occurs in acidic solution.What are the coefficients in front of Cd and Ag+ in the balanced reaction?
Cd(s)+ Ag+(aq)→ Ag(s)+ Cd2+(aq)
A)Cd = 1,Ag+ = 2
B)Cd = 1,Ag+ = 1
C)Cd = 2,Ag+ = 1
D)Cd = 2,Ag+ = 2
E)Cd = 3,Ag+ = 1
Cd(s)+ Ag+(aq)→ Ag(s)+ Cd2+(aq)
A)Cd = 1,Ag+ = 2
B)Cd = 1,Ag+ = 1
C)Cd = 2,Ag+ = 1
D)Cd = 2,Ag+ = 2
E)Cd = 3,Ag+ = 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Determine the cell notation for the redox reaction given below.
Sn(s)+ 2 Ag⁺(aq)→ Sn2+(aq)+ 2 Ag(s)
A)Ag+(aq)∣ Ag(s)∣∣ Sn(s)∣ Sn2+(aq)
B)Ag(s)∣ Ag+(aq)∣∣ Sn2+(aq)∣ Sn(s)
C)Sn(s)∣ Sn2+(aq)∣∣ Ag+(aq)∣ Ag(s)
D)Sn2+(aq)∣ Sn(s)∣∣ Ag(s)∣ Ag+(aq)
E)Sn(s)∣ Ag(s)∣∣ Sn2+(aq)∣ Ag+(aq)
Sn(s)+ 2 Ag⁺(aq)→ Sn2+(aq)+ 2 Ag(s)
A)Ag+(aq)∣ Ag(s)∣∣ Sn(s)∣ Sn2+(aq)
B)Ag(s)∣ Ag+(aq)∣∣ Sn2+(aq)∣ Sn(s)
C)Sn(s)∣ Sn2+(aq)∣∣ Ag+(aq)∣ Ag(s)
D)Sn2+(aq)∣ Sn(s)∣∣ Ag(s)∣ Ag+(aq)
E)Sn(s)∣ Ag(s)∣∣ Sn2+(aq)∣ Ag+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What element is being reduced in the following redox reaction?
H2O2(l)+ ClO2(aq)→ ClO2⁻(aq)+ O2(g)
A)H
B)O
C)Cl
D)N
E)C
H2O2(l)+ ClO2(aq)→ ClO2⁻(aq)+ O2(g)
A)H
B)O
C)Cl
D)N
E)C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the oxidizing agent in the redox reaction represented by the following cell notation?
Fe(s)∣ Fe3+(aq) Cl2(g)∣ Cl⁻(aq)∣ Pt
Cl2(g)∣ Cl⁻(aq)∣ Pt
A)Fe(s)
B)Fe3+(aq)
C)Cl2(g)
D)Cl⁻(aq)
E)Pt
Fe(s)∣ Fe3+(aq)
 Cl2(g)∣ Cl⁻(aq)∣ Pt
Cl2(g)∣ Cl⁻(aq)∣ PtA)Fe(s)
B)Fe3+(aq)
C)Cl2(g)
D)Cl⁻(aq)
E)Pt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Determine the cell notation for the redox reaction given below.
Pb(s)+ 2 H⁺(aq)→ Pb2+(aq)+ H2(g)
A)H+(aq)∣ H2(g)∣ Pt ∣∣ Pb(s)∣ Pb2+(aq)
B)H2(g)∣ H+(aq)∣ Pt ∣∣ Pb2+(aq)∣ Pb(s)
C)Pb2+(aq)∣ Pb(s)∣∣ H2(g)∣ H+(aq)∣ Pt
D)Pb(s)∣ Pb2+(aq)∣∣ H+(aq)∣ H2(g)∣ Pt
E)Pb(s)∣ H2(g)∣∣ Pb2+(aq)∣ H+(aq)∣ Pt
Pb(s)+ 2 H⁺(aq)→ Pb2+(aq)+ H2(g)
A)H+(aq)∣ H2(g)∣ Pt ∣∣ Pb(s)∣ Pb2+(aq)
B)H2(g)∣ H+(aq)∣ Pt ∣∣ Pb2+(aq)∣ Pb(s)
C)Pb2+(aq)∣ Pb(s)∣∣ H2(g)∣ H+(aq)∣ Pt
D)Pb(s)∣ Pb2+(aq)∣∣ H+(aq)∣ H2(g)∣ Pt
E)Pb(s)∣ H2(g)∣∣ Pb2+(aq)∣ H+(aq)∣ Pt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Identify the location of oxidation in an electrochemical cell.
A)the anode
B)the cathode
C)the electrode
D)the salt bridge
E)the socket
A)the anode
B)the cathode
C)the electrode
D)the salt bridge
E)the socket

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Use the standard half-cell potentials listed below to calculate the standard cell potential for the following reaction occurring in an electrochemical cell at 25°C.(The equation is balanced. )
Sn(s)+ 2 Ag⁺(aq)→ Sn2+(aq)+ 2 Ag(s)
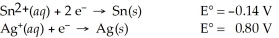
A)1.74 V
B)0.94 V
C)1.08 V
D)-1.08 V
E)-1.74 V
Sn(s)+ 2 Ag⁺(aq)→ Sn2+(aq)+ 2 Ag(s)
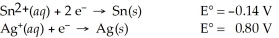
A)1.74 V
B)0.94 V
C)1.08 V
D)-1.08 V
E)-1.74 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is undergoing oxidation in the redox reaction represented by the following cell notation?
Pb(s)∣ Pb2+(aq)∣∣ H+(aq)∣ H2(g)∣ Pt
A)H2(g)
B)H+(aq)
C)Pb2+(aq)
D)Pb(s)
E)Pt
Pb(s)∣ Pb2+(aq)∣∣ H+(aq)∣ H2(g)∣ Pt
A)H2(g)
B)H+(aq)
C)Pb2+(aq)
D)Pb(s)
E)Pt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is undergoing reduction in the redox reaction represented by the following cell notation?
Fe(s)∣ Fe3+(aq)∣∣ Cl2(g)∣ Cl⁻(aq)∣ Pt
A)Fe(s)
B)Fe3+(aq)
C)Cl2(g)
D)Cl⁻(aq)
E)Pt
Fe(s)∣ Fe3+(aq)∣∣ Cl2(g)∣ Cl⁻(aq)∣ Pt
A)Fe(s)
B)Fe3+(aq)
C)Cl2(g)
D)Cl⁻(aq)
E)Pt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Determine which of the following pairs of reactants will result in a spontaneous reaction at 25°C. 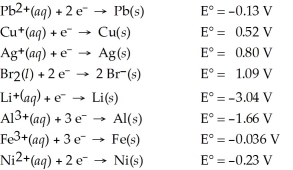
A)Pb2+(aq)+ Cu(s)
B)Ag+(aq)+ Br⁻(aq)
C)Li+(aq)+ Al(s)
D)Fe3+(aq)+ Ni(s)
E)None of the above pairs will react.
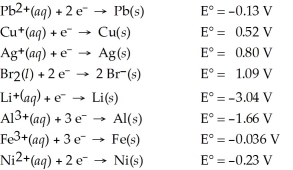
A)Pb2+(aq)+ Cu(s)
B)Ag+(aq)+ Br⁻(aq)
C)Li+(aq)+ Al(s)
D)Fe3+(aq)+ Ni(s)
E)None of the above pairs will react.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is the weakest reducing agent? 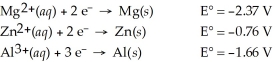
A)Al(s)
B)Zn(s)
C)Mg(s)
D)Al3+(aq)
E)Mg2+(aq)
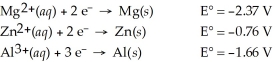
A)Al(s)
B)Zn(s)
C)Mg(s)
D)Al3+(aq)
E)Mg2+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is the weakest oxidizing agent? 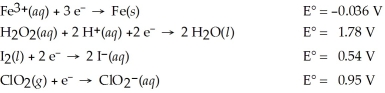
A)H2O2(aq)
B)Fe3+(aq)
C)ClO2(g)
D)I2(s)
E)Fe(s)
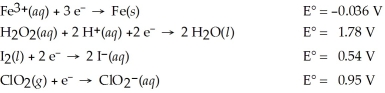
A)H2O2(aq)
B)Fe3+(aq)
C)ClO2(g)
D)I2(s)
E)Fe(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Use the standard half-cell potentials listed below to calculate the standard cell potential for the following reaction occurring in an electrochemical cell at 25°C.(The equation is balanced. )
3 Cl2(g)+ 2 Fe(s)→ 6 Cl⁻(aq)+ 2 Fe3+(aq)
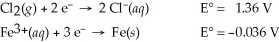
A)4.16 V
B)-1.40 V
C)-1.32 V
D)1.32 V
E)1.40 V
3 Cl2(g)+ 2 Fe(s)→ 6 Cl⁻(aq)+ 2 Fe3+(aq)
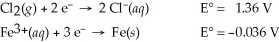
A)4.16 V
B)-1.40 V
C)-1.32 V
D)1.32 V
E)1.40 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Use the standard half-cell potentials listed below to calculate the standard cell potential for the following reaction occurring in an electrochemical cell at 25 °C.(The equation is balanced. )
2 K(s)+ I2(s)→ 2 K⁺(aq)+ 2 I⁻(aq)
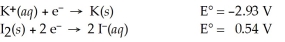
A)6.40 V
B)1.85 V
C)-5.32 V
D)3.47 V
E)5.32 V
2 K(s)+ I2(s)→ 2 K⁺(aq)+ 2 I⁻(aq)
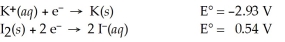
A)6.40 V
B)1.85 V
C)-5.32 V
D)3.47 V
E)5.32 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Use the standard half-cell potentials listed below to calculate the standard cell potential for the following reaction occurring in an electrochemical cell at 25°C.(The equation is balanced. )
Mg(s)+ Cu2+(aq)→ Cu(s)+ Mg2+(aq)

A)2.04 V
B)-2.04 V
C)2.72 V
D)-1.36 V
E)1.36 V
Mg(s)+ Cu2+(aq)→ Cu(s)+ Mg2+(aq)

A)2.04 V
B)-2.04 V
C)2.72 V
D)-1.36 V
E)1.36 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What statement is not true about standard electrode potentials?
A)E°cell is positive for spontaneous reactions.
B)Electrons will flow from more negative electrode to more positive electrode.
C)The electrode potential of the standard hydrogen electrode is exactly zero.
D)E°cell is the difference in voltage between the anode and the cathode.
E)The electrode in any half-cell with a greater tendency to undergo reduction is positively charged relative to the standard hydrogen electrode and therefore has a positive E°.
A)E°cell is positive for spontaneous reactions.
B)Electrons will flow from more negative electrode to more positive electrode.
C)The electrode potential of the standard hydrogen electrode is exactly zero.
D)E°cell is the difference in voltage between the anode and the cathode.
E)The electrode in any half-cell with a greater tendency to undergo reduction is positively charged relative to the standard hydrogen electrode and therefore has a positive E°.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is the strongest oxidizing agent? 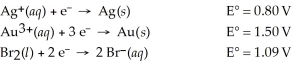
A)Br2(l)
B)Au3+(aq)
C)Ag(s)
D)Br⁻(aq)
E)Au(s)
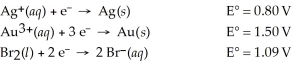
A)Br2(l)
B)Au3+(aq)
C)Ag(s)
D)Br⁻(aq)
E)Au(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Use the standard half-cell potentials listed below to calculate the standard cell potential for the following reaction occurring in an electrochemical cell at 25°C.(The equation is balanced. )
Pb(s)+ Br2(l)→ Pb2+(aq)+ 2 Br⁻(aq)
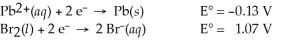
A)1.20 V
B)0.94 V
C)-0.94 V
D)-1.20 V
E)-0.60 V
Pb(s)+ Br2(l)→ Pb2+(aq)+ 2 Br⁻(aq)
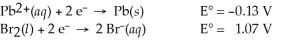
A)1.20 V
B)0.94 V
C)-0.94 V
D)-1.20 V
E)-0.60 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Determine which of the following pairs of reactants will result in a spontaneous reaction at 25°C. 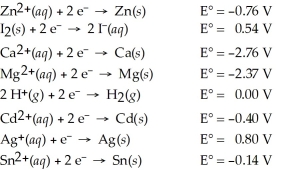
A)I-(aq)+ Zn2+(aq)
B)Ca(s)+ Mg2+(aq)
C)H2(g)+ Cd2+(aq)
D)Ag(s)+ Sn2+(aq)
E)All of the above pairs will react.
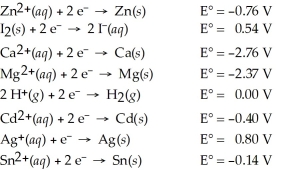
A)I-(aq)+ Zn2+(aq)
B)Ca(s)+ Mg2+(aq)
C)H2(g)+ Cd2+(aq)
D)Ag(s)+ Sn2+(aq)
E)All of the above pairs will react.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is the strongest reducing agent? 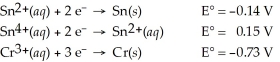
A)Sn2+(aq)
B)Cr3+(aq)
C)Sn4+(aq)
D)Cr(s)
E)Sn(s)
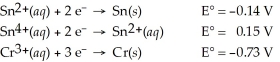
A)Sn2+(aq)
B)Cr3+(aq)
C)Sn4+(aq)
D)Cr(s)
E)Sn(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the oxidizing agent in the redox reaction represented by the following cell notation?
Sn(s)∣ Sn2+(aq)∣∣ Ag+(aq)∣ Ag(s)
A)Sn(s)
B)Ag+(aq)
C)Sn2+(aq)
D)Ag(s)
E)Pt
Sn(s)∣ Sn2+(aq)∣∣ Ag+(aq)∣ Ag(s)
A)Sn(s)
B)Ag+(aq)
C)Sn2+(aq)
D)Ag(s)
E)Pt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is the strongest oxidizing agent? 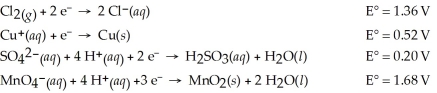
A)MnO2(s)
B)Cl⁻(aq)
C)Cu⁺(aq)
D)SO42-(aq)
E)MnO4⁻(aq)
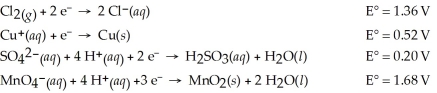
A)MnO2(s)
B)Cl⁻(aq)
C)Cu⁺(aq)
D)SO42-(aq)
E)MnO4⁻(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is the strongest reducing agent? 
A)Al(s)
B)Zn(s)
C)Mg(s)
D)Al3+(aq)
E)Mg2+(aq)

A)Al(s)
B)Zn(s)
C)Mg(s)
D)Al3+(aq)
E)Mg2+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is the strongest reducing agent? 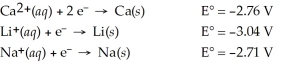
A)Na(s)
B)Li+(aq)
C)Ca(s)
D)Ca2+(aq)
E)Li(s)
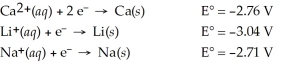
A)Na(s)
B)Li+(aq)
C)Ca(s)
D)Ca2+(aq)
E)Li(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Determine which of the following pairs of reactants will result in a spontaneous reaction at 25°C. 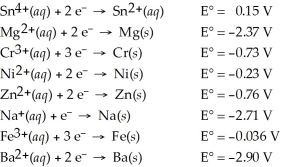
A)Sn4+(aq)+ Mg(s)
B)Cr3+(aq)+ Ni(s)
C)Zn(s)+ Na+(aq)
D)Fe(s)+ Ba2+(aq)
E)None of the above pairs will react.
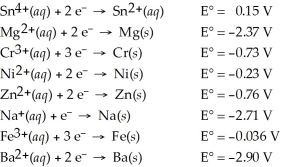
A)Sn4+(aq)+ Mg(s)
B)Cr3+(aq)+ Ni(s)
C)Zn(s)+ Na+(aq)
D)Fe(s)+ Ba2+(aq)
E)None of the above pairs will react.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is the strongest oxidizing agent? 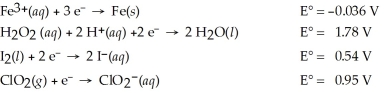
A)H2O2(aq)
B)Fe3+(aq)
C)ClO2(g)
D)I2(s)
E)Fe(s)
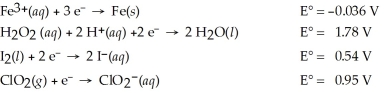
A)H2O2(aq)
B)Fe3+(aq)
C)ClO2(g)
D)I2(s)
E)Fe(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Calculate the cell potential for the following reaction that takes place in an electrochemical cell at 25°C.
Sn(s)∣ Sn2+(aq,0.022 M) Ag+(aq,2.7 M)∣ Ag(s)
Ag+(aq,2.7 M)∣ Ag(s)
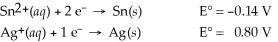
A)1.01 V
B)-0.83 V
C)1.31 V
D)0.01 V
E)-0.66 V
Sn(s)∣ Sn2+(aq,0.022 M)
 Ag+(aq,2.7 M)∣ Ag(s)
Ag+(aq,2.7 M)∣ Ag(s)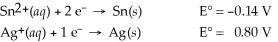
A)1.01 V
B)-0.83 V
C)1.31 V
D)0.01 V
E)-0.66 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Give the criteria for a nonspontaneous reaction.
A)ΔG° < 0,E°cell > 0,K > 1
B)ΔG° > 0,E°cell > 0,K > 1
C)ΔG° > 0,E°cell < 0,K > 1
D)ΔG° < 0,E°cell > 0,K < 1
E)ΔG° > 0,E°cell < 0,K < 1
A)ΔG° < 0,E°cell > 0,K > 1
B)ΔG° > 0,E°cell > 0,K > 1
C)ΔG° > 0,E°cell < 0,K > 1
D)ΔG° < 0,E°cell > 0,K < 1
E)ΔG° > 0,E°cell < 0,K < 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Calculate the cell potential for the following reaction that takes place in an electrochemical cell at 25°C.
Sn(s)∣ Sn2+(aq,1.8 M)∣∣ Ag+(aq,0.055 M)∣ Ag(s)
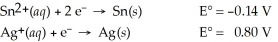
A)-0.94 V
B)-0.85 V
C)+1.02 V
D)+0.98 V
E)+0.86 V
Sn(s)∣ Sn2+(aq,1.8 M)∣∣ Ag+(aq,0.055 M)∣ Ag(s)
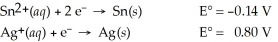
A)-0.94 V
B)-0.85 V
C)+1.02 V
D)+0.98 V
E)+0.86 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
How many electrons are transferred in the following reaction? (The reaction is unbalanced. )
Mg(s)+ Al3+(aq)→ Al(s)+ Mg2+(aq)
A)6
B)2
C)3
D)1
E)4
Mg(s)+ Al3+(aq)→ Al(s)+ Mg2+(aq)
A)6
B)2
C)3
D)1
E)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Calculate the cell potential for the following reaction that takes place in an electrochemical cell at 25°C.
Fe(s)∣ Fe3+(aq,0.0011 M)∣∣ Fe3+(aq,2.33 M)∣ Fe(s)
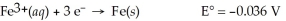
A)0.066 V
B)-0.036 V
C)0.00 V
D)-0.099 V
E)0.20 V
Fe(s)∣ Fe3+(aq,0.0011 M)∣∣ Fe3+(aq,2.33 M)∣ Fe(s)
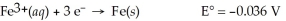
A)0.066 V
B)-0.036 V
C)0.00 V
D)-0.099 V
E)0.20 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following reactions would be the most spontaneous at 298 K?
A)A + 2 B → C;E°cell = 0.98 V
B)A + B → 2 C;E°cell = -0.030 V
C)A + B → 3 C;E°cell = 0.15 V
D)A + B → C;E°cell = 1.22 V
E)More information is needed to determine.
A)A + 2 B → C;E°cell = 0.98 V
B)A + B → 2 C;E°cell = -0.030 V
C)A + B → 3 C;E°cell = 0.15 V
D)A + B → C;E°cell = 1.22 V
E)More information is needed to determine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Give the criteria for a spontaneous reaction.
A)ΔG° < 0,E°cell > 0,K > 1
B)ΔG° > 0,E°cell > 0,K > 1
C)ΔG° > 0,E°cell < 0,K > 1
D)ΔG° < 0,E°cell > 0,K < 1
E)ΔG° > 0,E°cell < 0,K < 1
A)ΔG° < 0,E°cell > 0,K > 1
B)ΔG° > 0,E°cell > 0,K > 1
C)ΔG° > 0,E°cell < 0,K > 1
D)ΔG° < 0,E°cell > 0,K < 1
E)ΔG° > 0,E°cell < 0,K < 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Use the tabulated half-cell potentials below to calculate ΔG° for the following redox reaction.
2 Al(s)+ 3 Mg2+(aq)→ 2 Al3+(aq)+ 3 Mg(s)

A)4.1 × 102 kJ
B)1.4 × 102 kJ
C)-2.3 × 102 kJ
D)-7.8 × 102 kJ
E)6.8 × 102 kJ
2 Al(s)+ 3 Mg2+(aq)→ 2 Al3+(aq)+ 3 Mg(s)

A)4.1 × 102 kJ
B)1.4 × 102 kJ
C)-2.3 × 102 kJ
D)-7.8 × 102 kJ
E)6.8 × 102 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Use the tabulated half-cell potentials below to calculate the equilibrium constant (K)for the following balanced redox reaction at 25°C.
Pb2+(aq)+ Cu(s)→ Pb(s)+ Cu2+(aq)
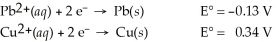
A)7.9 × 10-8
B)8.9 × 107
C)7.9 × 1015
D)1.3 × 10-16
E)1.1 × 10-8
Pb2+(aq)+ Cu(s)→ Pb(s)+ Cu2+(aq)
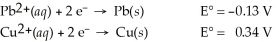
A)7.9 × 10-8
B)8.9 × 107
C)7.9 × 1015
D)1.3 × 10-16
E)1.1 × 10-8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following metals will dissolve in HCl? 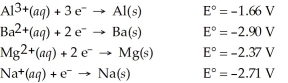
A)Ba
B)Na
C)Mg
D)Al
E)All of the above
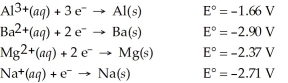
A)Ba
B)Na
C)Mg
D)Al
E)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the tabulated half-cell potentials below to calculate ΔG° for the following balanced redox reaction.
3 I2(s)+ 2 Fe(s)→ 2 Fe3+(aq)+ 6 I⁻(aq)
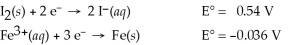
A)-1.1 × 102 kJ
B)4.9 × 101 kJ
C)-9.7 × 101 kJ
D)2.3 × 102 kJ
E)-3.3 × 102 kJ
3 I2(s)+ 2 Fe(s)→ 2 Fe3+(aq)+ 6 I⁻(aq)
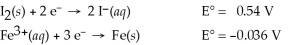
A)-1.1 × 102 kJ
B)4.9 × 101 kJ
C)-9.7 × 101 kJ
D)2.3 × 102 kJ
E)-3.3 × 102 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Use the tabulated half-cell potentials below to calculate ΔG° for the following balanced redox reaction.
Pb2+(aq)+ Cu(s)→ Pb(s)+ Cu2+(aq)
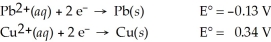
A)-41 kJ
B)-0.47 kJ
C)46 kJ
D)91 kJ
E)-21 kJ
Pb2+(aq)+ Cu(s)→ Pb(s)+ Cu2+(aq)
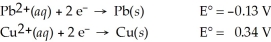
A)-41 kJ
B)-0.47 kJ
C)46 kJ
D)91 kJ
E)-21 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Use the tabulated half-cell potentials below to calculate the equilibrium constant (K)for the following balanced redox reaction at 25°C.
2 Al(s)+ 3 Mg2+(aq)→ 2 Al3+(aq)+ 3 Mg(s)
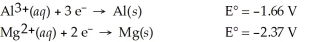
A)1.1 × 1072
B)8.9 × 10-73
C)1.1 × 10-72
D)1.0 × 1024
E)4.6 × 1031
2 Al(s)+ 3 Mg2+(aq)→ 2 Al3+(aq)+ 3 Mg(s)
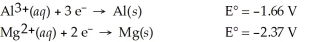
A)1.1 × 1072
B)8.9 × 10-73
C)1.1 × 10-72
D)1.0 × 1024
E)4.6 × 1031

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
How many electrons are transferred in the following reaction? (The reaction is unbalanced. )
I2(s)+ Fe(aq)→ Fe3+(s)+ I⁻(aq)
A)1
B)2
C)6
D)3
E)4
I2(s)+ Fe(aq)→ Fe3+(s)+ I⁻(aq)
A)1
B)2
C)6
D)3
E)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Calculate the cell potential for the following reaction that takes place in an electrochemical cell at 25°C.
Mg(s)∣ Mg2+(aq,2.74 M)∣∣ Cu2+(aq,0.0033 M)∣ Cu(s)
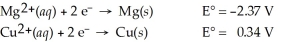
A)-2.80 V
B)2.62 V
C)2.71 V
D)2.12 V
E)-1.94 V
Mg(s)∣ Mg2+(aq,2.74 M)∣∣ Cu2+(aq,0.0033 M)∣ Cu(s)
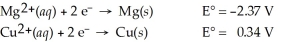
A)-2.80 V
B)2.62 V
C)2.71 V
D)2.12 V
E)-1.94 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Use the tabulated half-cell potentials below to calculate the equilibrium constant (K)for the following balanced redox reaction at 25°C.
3 I2(s)+ 2 Fe(s)→ 2 Fe3+(aq)+ 6 I⁻(aq)
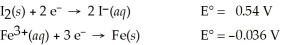
A)3.5 × 10-59
B)1.1 × 1017
C)2.4 × 1058
D)8.9 × 10-18
E)1.7 × 1029
3 I2(s)+ 2 Fe(s)→ 2 Fe3+(aq)+ 6 I⁻(aq)
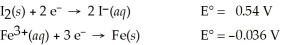
A)3.5 × 10-59
B)1.1 × 1017
C)2.4 × 1058
D)8.9 × 10-18
E)1.7 × 1029

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following metals will dissolve in nitric acid but not hydrochloric? 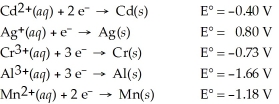
A)Cd
B)Cr
C)Mn
D)Ag
E)Al
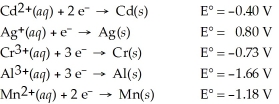
A)Cd
B)Cr
C)Mn
D)Ag
E)Al

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How many electrons are transferred in the following reaction? (The reaction is unbalanced. )
Fe2+(aq)+ K(s)→ Fe(s)+ K+(aq)
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)6
Fe2+(aq)+ K(s)→ Fe(s)+ K+(aq)
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following reactions would have the smallest value of K at 298 K?
A)A + B → C;E°cell = +1.22 V
B)A + 2 B → C;E°cell = 0.98 V
C)A + B → 2 C;E°cell = -0.030 V
D)A + B → 3 C;E°cell = 0.15 V
E)More information is needed to determine.
A)A + B → C;E°cell = +1.22 V
B)A + 2 B → C;E°cell = 0.98 V
C)A + B → 2 C;E°cell = -0.030 V
D)A + B → 3 C;E°cell = 0.15 V
E)More information is needed to determine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following metals will dissolve in nitric acid but not hydrochloric? 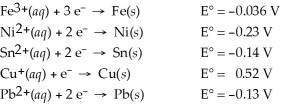
A)Fe
B)Pb
C)Cu
D)Sn
E)Ni
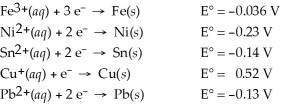
A)Fe
B)Pb
C)Cu
D)Sn
E)Ni

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Explain the use of a salt bridge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match the following.
Q > K
A)Ecell = E°cell
B)Ecell = 0
C)E°cell < 0
D)Ecell < 0
E)E°cell > 0
F)Ecell > 0
Q > K
A)Ecell = E°cell
B)Ecell = 0
C)E°cell < 0
D)Ecell < 0
E)E°cell > 0
F)Ecell > 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
For the galvanic cell reaction,expressed below using shorthand notation,what half-reaction occurs at the cathode?
Zn(s)∣ Zn2+(aq)∣∣ Ni2+(aq)∣ Ni(s)
A)Zn(s)→ Zn2+(aq)+ 2 e-
B)Zn2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Zn(s)
C)Ni(s)→ Ni2+(aq)+ 2 e-
D)Ni2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Ni(s)
Zn(s)∣ Zn2+(aq)∣∣ Ni2+(aq)∣ Ni(s)
A)Zn(s)→ Zn2+(aq)+ 2 e-
B)Zn2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Zn(s)
C)Ni(s)→ Ni2+(aq)+ 2 e-
D)Ni2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Ni(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is the shorthand notation that represents the following galvanic cell reaction?
Pb(s)+ Cu(NO3)2(aq)→ Pb(NO3)2(aq)+ Cu(s)
A)Pb(s)∣ Pb2+(aq)∣∣ Cu2+(aq)∣ Cu(s)
B)Cu(s)∣ Cu2+(aq)∣∣ Pb2+(aq)∣ Pb(s)
C)Pb(s)∣ NO3-(aq)∣∣ NO3-(aq)∣ Cu(s)
D)Cu(s)∣ Cu(NO3)2(aq)∣∣ Pb(NO3)2(aq)∣ Pb(s)
Pb(s)+ Cu(NO3)2(aq)→ Pb(NO3)2(aq)+ Cu(s)
A)Pb(s)∣ Pb2+(aq)∣∣ Cu2+(aq)∣ Cu(s)
B)Cu(s)∣ Cu2+(aq)∣∣ Pb2+(aq)∣ Pb(s)
C)Pb(s)∣ NO3-(aq)∣∣ NO3-(aq)∣ Cu(s)
D)Cu(s)∣ Cu(NO3)2(aq)∣∣ Pb(NO3)2(aq)∣ Pb(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What mass of aluminum can be plated onto an object in 755 minutes at 5.80 A of current?
A)73.5 g
B)24.5 g
C)220.g
D)147 g
E)8.17 g
A)73.5 g
B)24.5 g
C)220.g
D)147 g
E)8.17 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Calculate the cell potential for the following reaction that takes place in an electrochemical cell at 25°C.
Al(s)∣ Al3+(aq,0.115 M)∣∣ Al3+(aq,3.89 M)∣ Al(s)
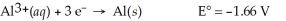
A)1.66 V
B)0.060 V
C)0.00 V
D)0.090 V
E)0.030 V
Al(s)∣ Al3+(aq,0.115 M)∣∣ Al3+(aq,3.89 M)∣ Al(s)
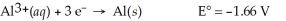
A)1.66 V
B)0.060 V
C)0.00 V
D)0.090 V
E)0.030 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Explain the significance of the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)in the tabulation of standard reduction potentials of other species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What is the reduction half-reaction for the following overall galvanic cell reaction?
Zn2+(aq)+ 2 Ag(s)→ Zn(s)+ 2 Ag+(aq)
A)Ag(s)+ e- → Ag+(aq)
B)Ag+(aq)+ e- → Ag(s)
C)Zn2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Zn(s)
D)Zn2+(aq)+ e- → Zn(s)
Zn2+(aq)+ 2 Ag(s)→ Zn(s)+ 2 Ag+(aq)
A)Ag(s)+ e- → Ag+(aq)
B)Ag+(aq)+ e- → Ag(s)
C)Zn2+(aq)+ 2 e- → Zn(s)
D)Zn2+(aq)+ e- → Zn(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Match the following.
Q = 1
A)Ecell = E°cell
B)Ecell = 0
C)E°cell < 0
D)Ecell < 0
E)E°cell > 0
F)Ecell > 0
Q = 1
A)Ecell = E°cell
B)Ecell = 0
C)E°cell < 0
D)Ecell < 0
E)E°cell > 0
F)Ecell > 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Match the following.
Q < K
A)Ecell = E°cell
B)Ecell = 0
C)E°cell < 0
D)Ecell < 0
E)E°cell > 0
F)Ecell > 0
Q < K
A)Ecell = E°cell
B)Ecell = 0
C)E°cell < 0
D)Ecell < 0
E)E°cell > 0
F)Ecell > 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Match the following.
ΔG° > 0
A)Ecell = E°cell
B)Ecell = 0
C)E°cell < 0
D)Ecell < 0
E)E°cell > 0
F)Ecell > 0
ΔG° > 0
A)Ecell = E°cell
B)Ecell = 0
C)E°cell < 0
D)Ecell < 0
E)E°cell > 0
F)Ecell > 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Why,if we multiply a reaction by 2,don't we multiply its E°red by 2?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Give the type of battery that most cars contain.
A)lead-acid battery
B)dry-cell battery
C)alkaline battery
D)nickel-cadmium battery
E)nickel-metal hydride battery
A)lead-acid battery
B)dry-cell battery
C)alkaline battery
D)nickel-cadmium battery
E)nickel-metal hydride battery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What is the difference between a voltaic cell and an electrolytic cell?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Match the following.
ΔG° < 0
A)Ecell = E°cell
B)Ecell = 0
C)E°cell < 0
D)Ecell < 0
E)E°cell > 0
F)Ecell > 0
ΔG° < 0
A)Ecell = E°cell
B)Ecell = 0
C)E°cell < 0
D)Ecell < 0
E)E°cell > 0
F)Ecell > 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Nickel can be plated from aqueous solution according to the following half reaction.How long would it take (in minutes)to plate 29.6 g of nickel at 4.7 A?
Ni2+(aq)+ 2 e⁻ → Ni(s)
A)1.7 × 102 minutes
B)5.9 × 102 minutes
C)3.5 × 102 minutes
D)4.8 × 102 minutes
E)6.2 × 102 minutes
Ni2+(aq)+ 2 e⁻ → Ni(s)
A)1.7 × 102 minutes
B)5.9 × 102 minutes
C)3.5 × 102 minutes
D)4.8 × 102 minutes
E)6.2 × 102 minutes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Match the following.
Q = K
A)Ecell = E°cell
B)Ecell = 0
C)E°cell < 0
D)Ecell < 0
E)E°cell > 0
F)Ecell > 0
Q = K
A)Ecell = E°cell
B)Ecell = 0
C)E°cell < 0
D)Ecell < 0
E)E°cell > 0
F)Ecell > 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Calculate the cell potential for the following reaction that takes place in an electrochemical cell at 25°C.
Cu(s)∣ Cu2+(aq,0.0032 M)∣∣ Cu2+(aq,4.48 M)∣ Cu(s)
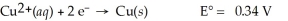
A)0.00 V
B)0.093 V
C)0.34 V
D)0.186 V
E)0.052 V
Cu(s)∣ Cu2+(aq,0.0032 M)∣∣ Cu2+(aq,4.48 M)∣ Cu(s)
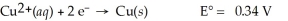
A)0.00 V
B)0.093 V
C)0.34 V
D)0.186 V
E)0.052 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What mass of silver can be plated onto an object in 33.5 minutes at 8.70 A of current?
Ag⁺(aq)+ e⁻ → Ag(s)
A)19.6 g
B)0.326 g
C)9.78 g
D)3.07 g
E)0.102 g
Ag⁺(aq)+ e⁻ → Ag(s)
A)19.6 g
B)0.326 g
C)9.78 g
D)3.07 g
E)0.102 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Why are iron nails coated with zinc?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



