Deck 22: A: Industry Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/33
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: A: Industry Supply
1
Suppose that the garden gnome industry was in long-run equilibrium given the circumstances described in Problem 1. Suppose, as in Problem 2, that it was discovered to everyone's surprise on January 1, 1993, after it was too late to change orders for gnome molds, that the cost of the plaster and labor needed to make a gnome had changed to $8. If the demand curve does not change, what will happen to the equilibrium price of gnomes?
A) Rises by $1.
B) Falls by $1.
C) Stays constant.
D) Rises by $8.
E) Falls by $4.
A) Rises by $1.
B) Falls by $1.
C) Stays constant.
D) Rises by $8.
E) Falls by $4.
C
2
In Problem 1, if the cost of plaster and labor were $5 per gnome and everything else is as in the problem (gnome molds cost $1,000, interest rate is 10%), what is the lowest price of gnomes at which there would be a positive supply in the long run?
A) $5.50
B) $7.20
C) $5
D) $10
E) $6
A) $5.50
B) $7.20
C) $5
D) $10
E) $6
B
3
Suppose that the cost of capturing a cockatoo and transporting him to the United States is about $40 per bird. Cockatoos are drugged and smuggled in suitcases to the United States. Half of the smuggled cockatoos die in transit. Each smuggled cockatoo has a 10% probability of being discovered, in which case the smuggler is fined. If the fine imposed for each smuggled cockatoo is increased to $1,100, then the equilibrium price of cockatoos in the United States will be
A) $150.
B) $95.
C) $73.
D) $333.33.
E) $244.44.
A) $150.
B) $95.
C) $73.
D) $333.33.
E) $244.44.
D
4
Suppose that the cost of capturing a cockatoo and transporting him to the United States is about $40 per bird. Cockatoos are drugged and smuggled in suitcases to the United States. Half of the smuggled cockatoos die in transit. Each smuggled cockatoo has a 10% probability of being discovered, in which case the smuggler is fined. If the fine imposed for each smuggled cockatoo is increased to $700, then the equilibrium price of cockatoos in the United States will be
A) $61.
B) $244.44.
C) $75.
D) $110.
E) $155.56.
A) $61.
B) $244.44.
C) $75.
D) $110.
E) $155.56.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suppose that the cost of capturing a cockatoo and transporting him to the United States is about $40 per bird. Cockatoos are drugged and smuggled in suitcases to the United States. Half of the smuggled cockatoos die in transit. Each smuggled cockatoo has a 10% probability of being discovered, in which case the smuggler is fined. If the fine imposed for each smuggled cockatoo is increased to $1,000, then the equilibrium price of cockatoos in the United States will be
A) $311.11.
B) $140.
C) $90.
D) $70.
E) $222.22.
A) $311.11.
B) $140.
C) $90.
D) $70.
E) $222.22.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In Problem 1, if the cost of plaster and labor were $13 per gnome and everything else is as in the problem (gnome molds cost $1,000, interest rate is 10%), what is the lowest price of gnomes at which there would be a positive supply in the long run?
A) $14.30
B) $26
C) $15.20
D) $13
E) $15.60
A) $14.30
B) $26
C) $15.20
D) $13
E) $15.60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Suppose that the garden gnome industry was in long-run equilibrium given the circumstances described in Problem 1. Suppose, as in Problem 2, that it was discovered to everyone's surprise on January 1, 1993, after it was too late to change orders for gnome molds, that the cost of the plaster and labor needed to make a gnome had changed to $6. If the demand curve does not change, what will happen to the equilibrium price of gnomes?
A) Falls by $1.
B) Rises by $6.
C) Stays constant.
D) Rises by $1.
E) Falls by $3.
A) Falls by $1.
B) Rises by $6.
C) Stays constant.
D) Rises by $1.
E) Falls by $3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In Problem 1, if the cost of plaster and labor were $11 per gnome and everything else is as in the problem (gnome molds cost $1,000, interest rate is 10%), what is the lowest price of gnomes at which there would be a positive supply in the long run?
A) $11
B) $22
C) $13.20
D) $12.10
E) $13.20
A) $11
B) $22
C) $13.20
D) $12.10
E) $13.20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In Problem 1, if the cost of plaster and labor were $10 per gnome and everything else is as in the problem (gnome molds cost $1,000, interest rate is 10%), what is the lowest price of gnomes at which there would be a positive supply in the long run?
A) $10
B) $11
C) $20
D) $12.20
E) $12
A) $10
B) $11
C) $20
D) $12.20
E) $12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Suppose that the garden gnome industry was in long-run equilibrium as described in Problem 1. On January 1, 1993, the cost of plaster and labor remained at $7 per gnome, gnome molds still cost $1,000, and the interest rate remained at 10%, but the government introduced a tax of $4 on every garden gnome sold. Then the equilibrium price of garden gnomes in 1993 would be
A) $13.
B) $4.
C) $9.20.
D) $11.
E) $15.
A) $13.
B) $4.
C) $9.20.
D) $11.
E) $15.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose that the garden gnome industry was in long-run equilibrium given the circumstances described in Problem 1. Suppose, as in Problem 2, that it was discovered to everyone's surprise on January 1, 1993, after it was too late to change orders for gnome molds, that the cost of the plaster and labor needed to make a gnome had changed to $9. If the demand curve does not change, what will happen to the equilibrium price of gnomes?
A) Stays constant.
B) Rises by $2.
C) Falls by $2.
D) Rises by $9.
E) Falls by $4.50.
A) Stays constant.
B) Rises by $2.
C) Falls by $2.
D) Rises by $9.
E) Falls by $4.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Suppose that the cost of capturing a cockatoo and transporting him to the United States is about $40 per bird. Cockatoos are drugged and smuggled in suitcases to the United States. Half of the smuggled cockatoos die in transit. Each smuggled cockatoo has a 10% probability of being discovered, in which case the smuggler is fined. If the fine imposed for each smuggled cockatoo is increased to $900, then the equilibrium price of cockatoos in the United States will be
A) $130.
B) $85.
C) $288.89.
D) $67.
E) $200.
A) $130.
B) $85.
C) $288.89.
D) $67.
E) $200.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Suppose that the garden gnome industry was in long-run equilibrium as described in Problem 1. On January 1, 1993, the cost of plaster and labor remained at $7 per gnome, gnome molds still cost $1,000, and the interest rate remained at 10%, but the government introduced a tax of $4 on every garden gnome sold. Then the equilibrium price of garden gnomes in 1993 would be
A) $11.
B) $9.20.
C) $13.
D) $4.
E) $15.
A) $11.
B) $9.20.
C) $13.
D) $4.
E) $15.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose that the garden gnome industry was in long-run equilibrium given the circumstances described in Problem 1. Suppose, as in Problem 2, that it was discovered to everyone's surprise on January 1, 1993, after it was too late to change orders for gnome molds, that the cost of the plaster and labor needed to make a gnome had changed to $6. If the demand curve does not change, what will happen to the equilibrium price of gnomes?
A) Stays constant.
B) Falls by $1.
C) Rises by $6.
D) Rises by $1.
E) Falls by $3.
A) Stays constant.
B) Falls by $1.
C) Rises by $6.
D) Rises by $1.
E) Falls by $3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Suppose that the garden gnome industry was in long-run equilibrium given the circumstances described in Problem 1. Suppose, as in Problem 2, that it was discovered to everyone's surprise on January 1, 1993, after it was too late to change orders for gnome molds, that the cost of the plaster and labor needed to make a gnome had changed to $6. If the demand curve does not change, what will happen to the equilibrium price of gnomes?
A) Rises by $6.
B) Rises by $1.
C) Stays constant.
D) Falls by $1.
E) Falls by $3.
A) Rises by $6.
B) Rises by $1.
C) Stays constant.
D) Falls by $1.
E) Falls by $3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose that the garden gnome industry was in long-run equilibrium as described in Problem 1. On January 1, 1993, the cost of plaster and labor remained at $7 per gnome, gnome molds still cost $1,000, and the interest rate remained at 10%, but the government introduced a tax of $7 on every garden gnome sold. Then the equilibrium price of garden gnomes in 1993 would be
A) $16.
B) $9.20.
C) $7.
D) $14.
E) $21.
A) $16.
B) $9.20.
C) $7.
D) $14.
E) $21.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In Problem 1, if the cost of plaster and labor were $5 per gnome and everything else is as in the problem (gnome molds cost $1,000, interest rate is 10%), what is the lowest price of gnomes at which there would be a positive supply in the long run?
A) $5
B) $10
C) $7.20
D) $5.50
E) $6
A) $5
B) $10
C) $7.20
D) $5.50
E) $6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Suppose that the garden gnome industry was in long-run equilibrium as described in Problem 1. On January 1, 1993, the cost of plaster and labor remained at $7 per gnome, gnome molds still cost $1,000, and the interest rate remained at 10%, but the government introduced a tax of $9 on every garden gnome sold. Then the equilibrium price of garden gnomes in 1993 would be
A) $16.
B) $9.
C) $18.
D) $9.20.
E) $25.
A) $16.
B) $9.
C) $18.
D) $9.20.
E) $25.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Suppose that the garden gnome industry was in long-run equilibrium as described in Problem 1. On January 1, 1993, the cost of plaster and labor remained at $7 per gnome, gnome molds still cost $1,000, and the interest rate remained at 10%, but the government introduced a tax of $8 on every garden gnome sold. Then the equilibrium price of garden gnomes in 1993 would be
A) $17.
B) $8.
C) $9.20.
D) $15.
E) $23.
A) $17.
B) $8.
C) $9.20.
D) $15.
E) $23.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose that the cost of capturing a cockatoo and transporting him to the United States is about $40 per bird. Cockatoos are drugged and smuggled in suitcases to the United States. Half of the smuggled cockatoos die in transit. Each smuggled cockatoo has a 10% probability of being discovered, in which case the smuggler is fined. If the fine imposed for each smuggled cockatoo is increased to $1,000, then the equilibrium price of cockatoos in the United States will be
A) $140.
B) $90.
C) $70.
D) $311.11.
E) $222.22.
A) $140.
B) $90.
C) $70.
D) $311.11.
E) $222.22.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In Problem 4, suppose that each firm has the cost function c(y) = y2 + 9 for y > 0 and c(0) = 0. With industry demand given by D(p) = 51 - p, the equilibrium price and equilibrium number of firms in the industry (in that order) will be
A) $8 and 11.
B) $3 and 18.
C) $3 and 48.
D) $6 and 15.
E) $6 and 45.
A) $8 and 11.
B) $3 and 18.
C) $3 and 48.
D) $6 and 15.
E) $6 and 45.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In Problem 13, in the absence of government interference, there is a constant marginal cost of $5 per ounce for growing marijuana and delivering it to buyers. If the probability that any shipment of marijuana seized is .30 and the fine if a shipper caught is $50 per ounce, then the equilibrium price of marijuana per ounce is
A) $28.57.
B) $20.
C) $55.
D) $3.50.
E) $6.50.
A) $28.57.
B) $20.
C) $55.
D) $3.50.
E) $6.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In Problem 8, the supply curve of any firm is Si(p) = 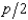 . If a firm produces 2 units of output, what are its total variable costs?
. If a firm produces 2 units of output, what are its total variable costs?
A) $8
B) $6
C) $2
D) $4
E) There is not enough information given to determine total variable costs.
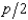 . If a firm produces 2 units of output, what are its total variable costs?
. If a firm produces 2 units of output, what are its total variable costs?A) $8
B) $6
C) $2
D) $4
E) There is not enough information given to determine total variable costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In Problem 13, in the absence of government interference, there is a constant marginal cost of $5 per ounce for growing marijuana and delivering it to buyers. If the probability that any shipment of marijuana seized is .50 and the fine if a shipper caught is $40 per ounce, then the equilibrium price of marijuana per ounce is
A) $50.
B) $2.50.
C) $25.
D) $45.
E) $7.50.
A) $50.
B) $2.50.
C) $25.
D) $45.
E) $7.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In Problem 13, in the absence of government interference, there is a constant marginal cost of $5 per ounce for growing marijuana and delivering it to buyers. If the probability that any shipment of marijuana seized is .50 and the fine if a shipper caught is $40 per ounce, then the equilibrium price of marijuana per ounce is
A) $50.
B) $45.
C) $2.50.
D) $25.
E) $7.50.
A) $50.
B) $45.
C) $2.50.
D) $25.
E) $7.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In Problem 13, in the absence of government interference, there is a constant marginal cost of $5 per ounce for growing marijuana and delivering it to buyers. If the probability that any shipment of marijuana seized is .10 and the fine if a shipper caught is $20 per ounce, then the equilibrium price of marijuana per ounce is
A) $25.
B) $4.50.
C) $7.78.
D) $7.
E) $5.50.
A) $25.
B) $4.50.
C) $7.78.
D) $7.
E) $5.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In Problem 8, if market demand is equal to D(p) = 20 - 3p, the equilibrium price and number of firms operating in the market are (in that order)
A) $3.08 and 7
B) $3.00 and 6
C) $3.00 and 8
D) $3.14 and 3
E) $3.33 and 5
A) $3.08 and 7
B) $3.00 and 6
C) $3.00 and 8
D) $3.14 and 3
E) $3.33 and 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In Problem 8, the supply curve of any firm is Si(p) = 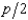 . If a firm produces 5 units of output, what are its total variable costs?
. If a firm produces 5 units of output, what are its total variable costs?
A) $37.50
B) $25
C) $50
D) $23
E) There is not enough information given to determine total variable costs.
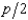 . If a firm produces 5 units of output, what are its total variable costs?
. If a firm produces 5 units of output, what are its total variable costs?A) $37.50
B) $25
C) $50
D) $23
E) There is not enough information given to determine total variable costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In Problem 8, the supply curve of any firm is Si(p) = 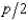 . If a firm produces 6 units of output, what are its total variable costs?
. If a firm produces 6 units of output, what are its total variable costs?
A) $72
B) $34
C) $54
D) $36
E) There is not enough information given to determine total variable costs.
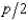 . If a firm produces 6 units of output, what are its total variable costs?
. If a firm produces 6 units of output, what are its total variable costs?A) $72
B) $34
C) $54
D) $36
E) There is not enough information given to determine total variable costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In Problem 8, the supply curve of any firm is Si(p) = 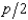 . If a firm produces 4 units of output, what are its total variable costs?
. If a firm produces 4 units of output, what are its total variable costs?
A) $16
B) $14
C) $24
D) $32
E) There is not enough information given to determine total variable costs.
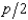 . If a firm produces 4 units of output, what are its total variable costs?
. If a firm produces 4 units of output, what are its total variable costs?A) $16
B) $14
C) $24
D) $32
E) There is not enough information given to determine total variable costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In Problem 13, in the absence of government interference, there is a constant marginal cost of $5 per ounce for growing marijuana and delivering it to buyers. If the probability that any shipment of marijuana seized is .20 and the fine if a shipper caught is $45 per ounce, then the equilibrium price of marijuana per ounce is
A) $50.
B) $17.50.
C) $4.
D) $14.
E) $6.
A) $50.
B) $17.50.
C) $4.
D) $14.
E) $6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In Problem 9, if the demand curve for pollicles is negatively sloped and the government imposes a tax t on every unit of output sold by the industry, in the long run
A) fewer pollicles will be sold.
B) more pollicles will be sold.
C) each firm in the industry produces more pollicles.
D) each firm in the industry produces fewer pollicles.
E) the same number of pollicles will be sold.
A) fewer pollicles will be sold.
B) more pollicles will be sold.
C) each firm in the industry produces more pollicles.
D) each firm in the industry produces fewer pollicles.
E) the same number of pollicles will be sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In Problem 8, the supply curve of any firm is Si(p) = 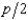 . If a firm produces 3 units of output, what are its total variable costs?
. If a firm produces 3 units of output, what are its total variable costs?
A) $9
B) $13.50
C) $7
D) $18
E) There is not enough information given to determine total variable costs.
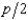 . If a firm produces 3 units of output, what are its total variable costs?
. If a firm produces 3 units of output, what are its total variable costs?A) $9
B) $13.50
C) $7
D) $18
E) There is not enough information given to determine total variable costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



