Deck 9: Imperfect Competition and Monopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/80
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Imperfect Competition and Monopoly
1
In the situation of imperfect competition, the relation between market price P and marginal revenue MR for each supplying firm is that:
A)P is less than MR at all or most output levels.
B)P is greater than MR at all or most output levels.
C)P is the same as MR at all output levels.
D)P is either less than MR at particular output levels or the same as MR.
E)none of the above, since P is not related to MR.
A)P is less than MR at all or most output levels.
B)P is greater than MR at all or most output levels.
C)P is the same as MR at all output levels.
D)P is either less than MR at particular output levels or the same as MR.
E)none of the above, since P is not related to MR.
P is greater than MR at all or most output levels.
2
Imperfect competition prevails in an industry when what condition exists:
A)individual sellers cannot affect price.
B)individual sellers can affect price.
C)price is set by the consumer.
D)price is set by the government.
E)none of the above are correct.
A)individual sellers cannot affect price.
B)individual sellers can affect price.
C)price is set by the consumer.
D)price is set by the government.
E)none of the above are correct.
individual sellers can affect price.
3
Which of the following eliminates the possibility of perfect competition in a market?
A)The industry faces a downward sloping demand curve.
B)Individual firms face downward sloping demand curves.
C)Firms face decreasing returns to scale.
D)Firms display constant returns to scale.
E)The market lacks product differentiation.
A)The industry faces a downward sloping demand curve.
B)Individual firms face downward sloping demand curves.
C)Firms face decreasing returns to scale.
D)Firms display constant returns to scale.
E)The market lacks product differentiation.
Individual firms face downward sloping demand curves.
4
A monopoly exists when:
A)a single seller has complete control over the industry.
B)a single seller has no control over the industry.
C)many sellers are in control of the industry.
D)no one controls the industry.
E)none of the above.
A)a single seller has complete control over the industry.
B)a single seller has no control over the industry.
C)many sellers are in control of the industry.
D)no one controls the industry.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Use the following to answer questions :
Table 9-1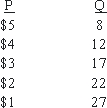
Consider the demand curve given in Table 9-1.If the imperfectly competitive firm is able to produce at any output level, then the price and quantity which maximize total revenue are:
A)P = 5; q = 8
B)P = 4; q = 12.
C)P = 3; q = 17.
D)P = 2; q = 22.
E)P = 1; q = 27.
Table 9-1
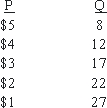
Consider the demand curve given in Table 9-1.If the imperfectly competitive firm is able to produce at any output level, then the price and quantity which maximize total revenue are:
A)P = 5; q = 8
B)P = 4; q = 12.
C)P = 3; q = 17.
D)P = 2; q = 22.
E)P = 1; q = 27.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A natural monopoly is:
A)a market in which the industry's output can be efficiently produced only by a single firm.
B)a market in which the industry's output is produced by a single firm.
C)a market where many sellers can produce the output.
D)not a real option.
E)none of the above.
A)a market in which the industry's output can be efficiently produced only by a single firm.
B)a market in which the industry's output is produced by a single firm.
C)a market where many sellers can produce the output.
D)not a real option.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If a firm finds out that its marginal revenue is greater than its marginal cost, it should:
A)increase production and sales.
B)decrease production and sales.
C)encourage the entry of other firms into the market.
D)keep raising its selling price till marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
E)change nothing because profits are maximized.
A)increase production and sales.
B)decrease production and sales.
C)encourage the entry of other firms into the market.
D)keep raising its selling price till marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
E)change nothing because profits are maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements concerning the monopolist with the cost and demand curves shown in the figure below is true? 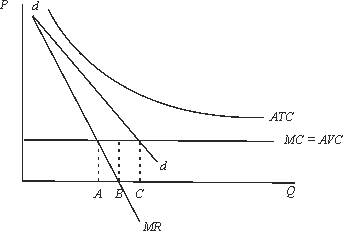
A)At output B, the firm is minimizing losses in the short run; in the long run it should shut down.
B)At output C, P = MC, and the firm is maximizing profits.
C)At output A, the firm is maximizing profits; however, in the long run the firm should go out of business.
D)At output B, the firm should shut down in the short run.
E)None of the above are true.

A)At output B, the firm is minimizing losses in the short run; in the long run it should shut down.
B)At output C, P = MC, and the firm is maximizing profits.
C)At output A, the firm is maximizing profits; however, in the long run the firm should go out of business.
D)At output B, the firm should shut down in the short run.
E)None of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If you are the only mechanic in town which of the following is true about your demand curve?
A)You don't have one, it is all about supply.
B)it will be a downward sloping curve.
C)it will be a straight line.
D)it will be an upward sloping curve.
E)None of the above.
A)You don't have one, it is all about supply.
B)it will be a downward sloping curve.
C)it will be a straight line.
D)it will be an upward sloping curve.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A monopoly finds that, at its present level of output and sales, marginal revenue equals $5 and marginal cost is $4.10.Which of the following will maximize profits?
A)Leave price and output unchanged.
B)Increase price and leave output unchanged.
C)Increase price and decrease output.
D)Decrease price and increase output.
E)Decrease price and leave output unchanged.
A)Leave price and output unchanged.
B)Increase price and leave output unchanged.
C)Increase price and decrease output.
D)Decrease price and increase output.
E)Decrease price and leave output unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Use the following to answer questions :
Table 9-1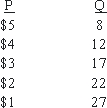
Suppose an imperfect competitor faces the demand curve defined in Table 9-1, and its MC is constant at $2.00.If the firm is able to produce at any output level, then it maximizes profits at:
A)P = 5; q = 8
B)P = 4; q = 12.
C)P = 3; q = 17.
D)P = 2; q = 22.
E)none of the above if fixed costs are less than $1.00.
Table 9-1
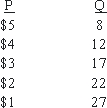
Suppose an imperfect competitor faces the demand curve defined in Table 9-1, and its MC is constant at $2.00.If the firm is able to produce at any output level, then it maximizes profits at:
A)P = 5; q = 8
B)P = 4; q = 12.
C)P = 3; q = 17.
D)P = 2; q = 22.
E)none of the above if fixed costs are less than $1.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
To maximize profits or minimize losses (if the firm produces), a firm must be sure it is producing at an output where:
A)total revenue is greater than average cost.
B)total revenue is equal to average cost.
C)marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost.
D)marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
E)none of the above is correct.
A)total revenue is greater than average cost.
B)total revenue is equal to average cost.
C)marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost.
D)marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
E)none of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a monopoly is attempting to maximize profits, which of the following, if any, should it attempt to do?
A)Maximize revenues.
B)Maximize profit per unit.
C)Select that output at which average total cost is at a minimum.
D)Select that output at which average fixed cost is at a minimum.
E)None of the above.
A)Maximize revenues.
B)Maximize profit per unit.
C)Select that output at which average total cost is at a minimum.
D)Select that output at which average fixed cost is at a minimum.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Perfect competition differs from imperfect competition in that:
A)it does not maximize profits at the point where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B)perfect competition's industry demand curve never slopes down.
C)perfect competition lacks any externalities.
D)perfectly competitive firms cannot affect prices.
E)none of the above accurately describe a difference.
A)it does not maximize profits at the point where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B)perfect competition's industry demand curve never slopes down.
C)perfect competition lacks any externalities.
D)perfectly competitive firms cannot affect prices.
E)none of the above accurately describe a difference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If a firm's demand curve is horizontal, then the firm's marginal revenue is:
A)less than the price of the product.
B)equal to the price of the product.
C)greater than the price of the product.
D)greater than, equal to, or less than the price of the product, depending on the particular circumstances.
E)not determinable from the above information.
A)less than the price of the product.
B)equal to the price of the product.
C)greater than the price of the product.
D)greater than, equal to, or less than the price of the product, depending on the particular circumstances.
E)not determinable from the above information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Two possible reasons for the existence of an imperfectly competitive market are:
A)product differentiation and free trade.
B)constant returns to scale and a lack of market regulation.
C)increasing returns to scale and barriers to free entry.
D)a lack of market segmentation and "U" shaped marginal cost curves.
E)none of the above.
A)product differentiation and free trade.
B)constant returns to scale and a lack of market regulation.
C)increasing returns to scale and barriers to free entry.
D)a lack of market segmentation and "U" shaped marginal cost curves.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Imperfect competition does not mean "no competition.Many firms have rivals but are still in an imperfect competition industry.A rival wants to do which of the following:
A)increase profits.
B)increase market share.
C)advertise to shift out their demand curve.
D)all of the above.
E)none of the above.
A)increase profits.
B)increase market share.
C)advertise to shift out their demand curve.
D)all of the above.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An oligopoly exists when:
A)a few sellers have complete control over the industry.
B)a few sellers have no control over the industry.
C)many sellers are in control of the industry.
D)no one controls the industry.
E)none of the above.
A)a few sellers have complete control over the industry.
B)a few sellers have no control over the industry.
C)many sellers are in control of the industry.
D)no one controls the industry.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the firm described in the previous question has no fixed costs, its profits are:
A)$48.
B)$54.
C)$24.
D)$4.
E)-$12
A)$48.
B)$54.
C)$24.
D)$4.
E)-$12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A perfect competitor's output in the short run is the quantity that:
A)sets MC equal to MR = P.
B)sets AVC = P.
C)minimizes ATC.
D)sets ATC = P.
E)none of the above are correct.
A)sets MC equal to MR = P.
B)sets AVC = P.
C)minimizes ATC.
D)sets ATC = P.
E)none of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Use the following to answer questions :
Figure 9-1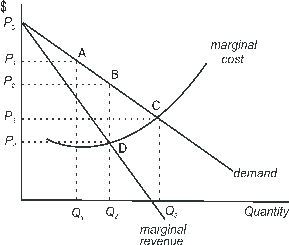
Which of the following points in Figure 9-1 can be used to identify a profit maximizing monopolist's production and the price it charges?
A)Ql, Pl
B)Q2, P2
C)Q3, P3
D)Q2, P4
E)Q2, P3
Figure 9-1

Which of the following points in Figure 9-1 can be used to identify a profit maximizing monopolist's production and the price it charges?
A)Ql, Pl
B)Q2, P2
C)Q3, P3
D)Q2, P4
E)Q2, P3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If a monopoly is attempting to maximize profits, which of the following should it attempt to do?
A)Maximize revenues.
B)Maximize profit per unit.
C)Select that output at which average total cost is at a minimum.
D)Set price equal to total cost.
E)None of the above.
A)Maximize revenues.
B)Maximize profit per unit.
C)Select that output at which average total cost is at a minimum.
D)Set price equal to total cost.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If the price of a monopoly firm is located on the inelastic portion of its demand curve, to maximize profits it should necessarily:
A)increase output and decrease price.
B)decrease output and increase price.
C)increase output and increase price.
D)not change output or price.
E)do none of the above.
A)increase output and decrease price.
B)decrease output and increase price.
C)increase output and increase price.
D)not change output or price.
E)do none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Use the following to answer questions :
Figure 9-1
The difference in consumer surplus between a monopoly market and a perfectly competitive one illustrated by Figure 9-1 is represented by area:
A)P5P1A.
B)P2P3CB.
C)P3P4DC.
D)Q1ABQ2.
E)None of the above.
Figure 9-1

The difference in consumer surplus between a monopoly market and a perfectly competitive one illustrated by Figure 9-1 is represented by area:
A)P5P1A.
B)P2P3CB.
C)P3P4DC.
D)Q1ABQ2.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Falling marginal revenue facing an individual firm is incompatible with:
A)growth of the firm.
B)perfect competition.
C)oligopoly.
D)barriers to entry.
E)none of the above.
A)growth of the firm.
B)perfect competition.
C)oligopoly.
D)barriers to entry.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A firm is maximizing its profits when:
A)average costs are at a minimum.
B)total revenue is at a maximum.
C)marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost by the maximum amount.
D)its profit per unit sold is at a maximum.
E)none of the above are necessarily maximum-profit points.
A)average costs are at a minimum.
B)total revenue is at a maximum.
C)marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost by the maximum amount.
D)its profit per unit sold is at a maximum.
E)none of the above are necessarily maximum-profit points.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the short run, under imperfect competition, a firm that wishes to maximize profits or minimize losses should produce that output which:
A)equates marginal cost with marginal revenue.
B)equates marginal cost with price.
C)corresponds to the lowest point on the average variable cost curve.
D)corresponds to the lowest point on the average total cost curve.
E)equates average cost with price.
A)equates marginal cost with marginal revenue.
B)equates marginal cost with price.
C)corresponds to the lowest point on the average variable cost curve.
D)corresponds to the lowest point on the average total cost curve.
E)equates average cost with price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The marginal cost schedule facing an imperfect competitor is constant at $12.The demand curve is given in Table 9-3.The profit maximizing output for this firm is: Table 9-3 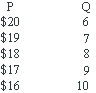
A)6 units
B)7 units
C)8 units
D)9 units
E)10 units

A)6 units
B)7 units
C)8 units
D)9 units
E)10 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following describe the relationship between price elasticity of demand and marginal revenue?
A)marginal revenue is positive when demand is elastic.
B)marginal revenue is zero when demand is unit elastic.
C)marginal revenue is negative when demand is inelastic.
D)all of the above.
E)A and C only.
A)marginal revenue is positive when demand is elastic.
B)marginal revenue is zero when demand is unit elastic.
C)marginal revenue is negative when demand is inelastic.
D)all of the above.
E)A and C only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In perfect competition, how is the market price related to marginal revenue for each supplying firm?
A)P is the same as MR at all output levels.
B)P is less than MR at all (or most)output levels.
C)P is greater than MR at all (or most)output levels.
D)P is either greater than MR or less than MR at particular output levels, but never the same as MR.
E)None of the above.
A)P is the same as MR at all output levels.
B)P is less than MR at all (or most)output levels.
C)P is greater than MR at all (or most)output levels.
D)P is either greater than MR or less than MR at particular output levels, but never the same as MR.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Imperfect competition can result in all of the following except:
A)less quantity than perfect competition.
B)a higher price than perfect competition.
C)more economic efficiency (i.e.less deadweight loss)than under perfect competition.
D)all of the above.
E)none of the above.
A)less quantity than perfect competition.
B)a higher price than perfect competition.
C)more economic efficiency (i.e.less deadweight loss)than under perfect competition.
D)all of the above.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Use the following to answer questions :
Table 9-2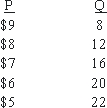
The demand curve facing an imperfect competitor is given in Table 9-2.If the firm is able to produce at any output level, then the price and quantity which maximize total revenue are:
A)P = 9; q = 8.
B)P = 8; q = 12.
C)P = 7; q = 16.
D)P = 6; q = 20.
E)P = 5; q = 22.
Table 9-2

The demand curve facing an imperfect competitor is given in Table 9-2.If the firm is able to produce at any output level, then the price and quantity which maximize total revenue are:
A)P = 9; q = 8.
B)P = 8; q = 12.
C)P = 7; q = 16.
D)P = 6; q = 20.
E)P = 5; q = 22.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following are barriers to entry into a market:
A)legal restrictions.
B)high cost of entry.
C)advertising cost.
D)product differentiation.
E)all of the above.
A)legal restrictions.
B)high cost of entry.
C)advertising cost.
D)product differentiation.
E)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A rational firm will only seek to maximize total revenue if:
A)it faces a totally inelastic demand curve.
B)its marginal cost curve falls and then rises.
C)its average costs are falling.
D)it is a perfect monopoly.
E)its variable costs are zero.
A)it faces a totally inelastic demand curve.
B)its marginal cost curve falls and then rises.
C)its average costs are falling.
D)it is a perfect monopoly.
E)its variable costs are zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Network industries most often generate:
A)perfectly competitive markets.
B)negative externalities.
C)product differentiation.
D)natural monopolies.
E)none of the above.
A)perfectly competitive markets.
B)negative externalities.
C)product differentiation.
D)natural monopolies.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Use the following to answer questions :
Figure 9-1
Which of the following points in Figure 9-1 can be used to identify production and price in a perfectly competitive industry?
A)Q1,P1.
B)Q2,P2.
C)Q3,P3.
D)Q2,P4.
E)Q2,P3.
Figure 9-1

Which of the following points in Figure 9-1 can be used to identify production and price in a perfectly competitive industry?
A)Q1,P1.
B)Q2,P2.
C)Q3,P3.
D)Q2,P4.
E)Q2,P3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following can take on a negative value?
A)Marginal Revenue
B)Total Revenue
C)Quantity demanded.
D)Quantity supplied.
E)All of the above.
A)Marginal Revenue
B)Total Revenue
C)Quantity demanded.
D)Quantity supplied.
E)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If a firm finds that its marginal revenue exceeds its marginal cost, then the maximum profit rules require the firm to:
A)increase its output in perfect, but not necessarily in imperfect competition.
B)increase its output in imperfect, but not necessarily in perfect competition.
C)increase its output in both perfect and imperfect competition.
D)decrease its output in both perfect and imperfect competition.
E)do none of the above.
A)increase its output in perfect, but not necessarily in imperfect competition.
B)increase its output in imperfect, but not necessarily in perfect competition.
C)increase its output in both perfect and imperfect competition.
D)decrease its output in both perfect and imperfect competition.
E)do none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
MR becomes negative when:
A)the demand price becomes negative.
B)the demand elasticity drops from elastic to inelastic.
C)total revenue becomes negative.
D)the loss on previous units is at its maximum.
E)both b and c.
A)the demand price becomes negative.
B)the demand elasticity drops from elastic to inelastic.
C)total revenue becomes negative.
D)the loss on previous units is at its maximum.
E)both b and c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Use the following to answer questions :
Table 9-2
The demand curve facing an imperfect competitor is given in Table 9-2.MC is constant at $3.50.If the firm is able to produce at any output level, then it maximizes profits at:
A)P = 9; q = 8.
B)P = 8; q = 12.
C)P = 7; q = 16.
D)P = 6; q = 20.
E)P = 5; q = 22.
Table 9-2

The demand curve facing an imperfect competitor is given in Table 9-2.MC is constant at $3.50.If the firm is able to produce at any output level, then it maximizes profits at:
A)P = 9; q = 8.
B)P = 8; q = 12.
C)P = 7; q = 16.
D)P = 6; q = 20.
E)P = 5; q = 22.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A natural monopoly features which of the following up to and including quantities that might be demanded at the lowest prices?
A)A declining average cost curve.
B)An increasing marginal cost curve.
C)A U shaped average cost curve.
D)An increasing average cost curve.
E)Both A and B.
A)A declining average cost curve.
B)An increasing marginal cost curve.
C)A U shaped average cost curve.
D)An increasing average cost curve.
E)Both A and B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If a profit-maximizing firm, with an increasing average cost curve, finds that it is producing a level of output at which marginal costs are $100, while marginal revenue is $5, what action should it take?
A)Raise output.
B)Lower prices.
C)Declare bankruptcy.
D)Decrease output.
E)None of the above.
A)Raise output.
B)Lower prices.
C)Declare bankruptcy.
D)Decrease output.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following are major sources of imperfect competition?
A)Government tariffs.
B)Patent laws.
C)Copyright laws.
D)Economies of scale.
E)All of the above.
A)Government tariffs.
B)Patent laws.
C)Copyright laws.
D)Economies of scale.
E)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Oligopoly means exactly two sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Imperfect competition means that there is only one or two sellers in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If marginal revenue becomes negative, this must mean that the firm's total revenue is declining with additional output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Wheat farming in the U.S.can be best described as an oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Steel is an oligopolistic industry in the U.S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The marginal principle means:
A)people will maximize their income or profits or satisfactions by counting only marginal benefits of a decision.
B)people will maximize their income or profits or satisfactions by counting the total benefits of a decision.
C)people will maximize their income or profits or satisfactions by counting none of the benefits of a decision.
D)people will maximize their income or profits or satisfactions by counting the negative aspects of a decision.
E)none of the above.
A)people will maximize their income or profits or satisfactions by counting only marginal benefits of a decision.
B)people will maximize their income or profits or satisfactions by counting the total benefits of a decision.
C)people will maximize their income or profits or satisfactions by counting none of the benefits of a decision.
D)people will maximize their income or profits or satisfactions by counting the negative aspects of a decision.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If marginal revenue is 0:
A)total revenue is increasing.
B)total revenue is maximized.
C)the demand curve is unit elastic.
D)B and C only.
E)A and C only.
A)total revenue is increasing.
B)total revenue is maximized.
C)the demand curve is unit elastic.
D)B and C only.
E)A and C only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The output level that maximizes a firm's profits also maximizes the marginal profit on the last unit produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A monopolist and a perfect competitor can both sell 10 units of a good they produce for $5 a piece.Which of the following is not true?
A)The perfect competitor can sell unit 11 for $5.
B)The perfect competitor's MR curve is a straight line at $5.
C)The monopolist can sell unit 11 for $5.
D)The monopolist has a decreasing marginal revenue curve.
E)None of the above.
A)The perfect competitor can sell unit 11 for $5.
B)The perfect competitor's MR curve is a straight line at $5.
C)The monopolist can sell unit 11 for $5.
D)The monopolist has a decreasing marginal revenue curve.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following describe the concept of "loss aversion"?
A)people will resist taking a loss on an item even though it is not costly to hold on to an asset.
B)people will resist taking a loss on an item even though it is costly to hold on to an asset.
C)people will accept taking a loss on an item when it is costly to hold on to an asset.
D)people will accept taking a loss on an item even though it is not costly to hold on to an asset.
E)none of the above.
A)people will resist taking a loss on an item even though it is not costly to hold on to an asset.
B)people will resist taking a loss on an item even though it is costly to hold on to an asset.
C)people will accept taking a loss on an item when it is costly to hold on to an asset.
D)people will accept taking a loss on an item even though it is not costly to hold on to an asset.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Under conditions of perfect competition, marginal revenue and price are equal for the individual firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following might be an industry characterized by a model of an unregulated monopoly?
A)Public utilities.
B)Local telephone carriers.
C)Farming/agriculture.
D)Gasoline distribution (for automobiles).
E)None of the above.
A)Public utilities.
B)Local telephone carriers.
C)Farming/agriculture.
D)Gasoline distribution (for automobiles).
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Since Microsoft is a monopoly, it can change the price of its operating system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A perfect competitor is distinguished by having no control over price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A profit-maximizing imperfect competitor is at equilibrium when marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Oligopolists differ from monopolists in that they:
A)equate marginal revenue with average cost.
B)equate marginal cost with a price read from a demand curve.
C)face a competitor selling a similar product.
D)maximize total revenue.
E)all of the above.
A)equate marginal revenue with average cost.
B)equate marginal cost with a price read from a demand curve.
C)face a competitor selling a similar product.
D)maximize total revenue.
E)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
At a profit maximizing point:
A)profits are always positive.
B)marginal revenue is 0.
C)marginal cost is 0.
D)total revenue is maximized.
E)none of the above.
A)profits are always positive.
B)marginal revenue is 0.
C)marginal cost is 0.
D)total revenue is maximized.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Personal computers are considered differentiated products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If a firm has zero marginal costs, then its maximum-profit output is where marginal revenue is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Microsoft's Windows product generated monopoly power by exploiting network externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Regardless of demand, monopoly profits are always positive in the absence of government regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If marginal cost is constant, then the profit maximizing monopoly output is indeterminant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The automobile industry in the United States can best be described as an oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Monopolists tend to charge a higher price than the market will bear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Monopolistic competition is categorized as an industry with few sellers and no competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The market demand curve and the demand curve facing the firm are the same in all imperfectly competitive markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
An individual perfect competitor faces a horizontal demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Product differentiation is not an example of a barrier to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The output level that maximizes a firm's profits also minimizes marginal costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A firm should decrease its output if marginal cost is greater than marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The monopolist sets MR = P above MC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Profits are maximized when the rate of change of total revenue equals the rate of change of total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The slope of the total profit curve is always equal to marginal revenue minus marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If all firms in an industry sell identical products, then it would never pay to advertise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Unlike the curve for a monopolist, the total revenue curve for a single perfect competitor would be a straight line rising to the right from the origin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Intense rivalry between Chrysler, Ford and GM means perfect competition in the U.S.auto industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Rivalry can exist in an imperfect competition industry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



