Deck 21: Asymmetric Information
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Asymmetric Information
1
Informed parties try to overcome problems of adverse selection through _________; uninformed parties try to overcome problems of adverse selection through _______.
A) social insurance; market unraveling
B) market unraveling; signaling
C) signaling; screening
D) screening; social insurance
A) social insurance; market unraveling
B) market unraveling; signaling
C) signaling; screening
D) screening; social insurance
signaling; screening
2
In many cases,signaling offers a partial solution to problems that arise from:
A) adverse selection.
B) moral hazard.
C) separating equilibria.
D) market unraveling.
A) adverse selection.
B) moral hazard.
C) separating equilibria.
D) market unraveling.
adverse selection.
3
The problem of adverse selection was first studied by economist ________ who showed how it can undermine the possibilities for trade in the market for _______.
A) Joseph Stiglitz; used cars
B) Joseph Stiglitz; college education
C) George Akerloff; used cars
D) George Akerloff; college education
A) Joseph Stiglitz; used cars
B) Joseph Stiglitz; college education
C) George Akerloff; used cars
D) George Akerloff; college education
George Akerloff; used cars
4
Suppose all workers in a certain labor market are of either high quality or low quality.Potential employers value a high-quality worker at $15,000 per month and a low-quality worker at $7,500 per month.The monthly supply of high-quality workers is QsH = 0.04(W - 1,500)and the supply of low-quality workers is QsL = 0.08(W - 1,500),where W is the monthly wage.If workers' abilities are not observable to employers,what is the equilibrium wage?
A) $5,000
B) $7,500
C) $10,000
D) $12,500
A) $5,000
B) $7,500
C) $10,000
D) $12,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suppose all workers in a certain labor market are of either high quality or low quality.Potential employers value a high-quality worker at $15,000 per month and a low-quality worker at $7,500 per month.The monthly supply of high-quality workers is QsH = 0.04(W - 1,500)and the supply of low-quality workers is QsL = 0.08(W - 1,500),where W is the monthly wage.If workers' abilities are observable to employers,what are the equilibrium wages?
A) WH = $15,000; WL = $7,500
B) WH = $7,500; WL = $7,500
C) WH = $12,500; WL = $12,500
D) WH = $5,250; WL = $4,500
A) WH = $15,000; WL = $7,500
B) WH = $7,500; WL = $7,500
C) WH = $12,500; WL = $12,500
D) WH = $5,250; WL = $4,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If a person takes a costly action simply to influence others' beliefs then this person is engaged in what economists call:
A) market unraveling.
B) adverse selection.
C) moral hazard.
D) signaling.
A) market unraveling.
B) adverse selection.
C) moral hazard.
D) signaling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Suppose all workers in a certain labor market are of either high quality or low quality.Potential employers value a high-quality worker at $15,000 per month and a low-quality worker at $7,500 per month.The monthly supply of high-quality workers is QsH = 0.04(W - 1,500)and the supply of low-quality workers is QsL = 0.08(W - 1,500),where W is the monthly wage.If workers' abilities are not observable to employers,what is the deadweight loss due to asymmetric information?
A) $750,000
B) $1,500,000
C) $1,125,000
D) $500,000
A) $750,000
B) $1,500,000
C) $1,125,000
D) $500,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Mandated minimum quality standards can be a way to:
A) reduce information asymmetry.
B) promote information asymmetry.
C) provide a public good.
D) screen.
A) reduce information asymmetry.
B) promote information asymmetry.
C) provide a public good.
D) screen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When analyzing cases of signaling,economists tend to focus their attention primarily on:
A) general equilibria.
B) pooling equilibria.
C) separating equilibria.
D) asymmetric equilibria.
A) general equilibria.
B) pooling equilibria.
C) separating equilibria.
D) asymmetric equilibria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When informed parties prefer trading circumstances that are disadvantageous to uninformed trading partners,economists say that ________ has occurred.
A) information disequilibrium
B) moral hazard
C) signaling
D) adverse selection
A) information disequilibrium
B) moral hazard
C) signaling
D) adverse selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Adverse selection occurs when an informed individual is ________ willing to trade in situations that make trading ________ to an uninformed trading partner.
A) more; more advantageous
B) more; less advantageous
C) less; more advantageous
D) less; less advantageous
A) more; more advantageous
B) more; less advantageous
C) less; more advantageous
D) less; less advantageous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Private organizations,such as Consumer Reports,are able to earn a profit by serving as quality certifiers because:
A) some well-informed buyers are willing to provide good information.
B) some well-informed sellers want to send signals to buyers.
C) some poorly informed buyers are willing to pay for better information.
D) some poorly informed sellers are willing to pay to reduce the quality of buyers' information.
A) some well-informed buyers are willing to provide good information.
B) some well-informed sellers want to send signals to buyers.
C) some poorly informed buyers are willing to pay for better information.
D) some poorly informed sellers are willing to pay to reduce the quality of buyers' information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Suppose all workers in a certain labor market are of either high quality or low quality.Potential employers value a high-quality worker at $15,000 per month and a low-quality worker at $7,500 per month.The monthly supply of high-quality workers is QsH = 0.04(W - 1,500)and the supply of low-quality workers is QsL = 0.08(W - 1,500),where W is the monthly wage.If workers' abilities are not observable to employers,how many workers of each type do employers hire?
A) QH = 540; QL = 480
B) QH = 510; QL = 510
C) QH = 680; QL = 340
D) QH = 340; QL = 680
A) QH = 540; QL = 480
B) QH = 510; QL = 510
C) QH = 680; QL = 340
D) QH = 340; QL = 680

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose all workers in a certain labor market are of either high quality or low quality.Potential employers value a high-quality worker at $15,000 per month and a low-quality worker at $7,500 per month.The monthly supply of high-quality workers is QsH = 0.04(W - 1,500)and the supply of low-quality workers is QsL = 0.08(W - 1,500),where W is the monthly wage.If workers' abilities are observable to employers,how many workers of each type do employers hire?
A) QH = 440; QL = 440
B) QH = 540; QL = 480
C) QH = 440; QL = 880
D) QH = 270; QL = 240
A) QH = 440; QL = 440
B) QH = 540; QL = 480
C) QH = 440; QL = 880
D) QH = 270; QL = 240

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The requirement by some life insurance companies that applicants must undergo medical examinations is an attempt on the part of the life insurance company to mitigate the problem of adverse selection by:
A) collecting information.
B) sharing information.
C) sending hard-to-interpret signals.
D) providing social insurance.
A) collecting information.
B) sharing information.
C) sending hard-to-interpret signals.
D) providing social insurance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Adverse selection can cause attractive trading partners to be driven from a market by unattractive trading partners,whose presence alters prices at which attractive trading partners could trade.This unfortunate result is known as:
A) market unraveling.
B) signal confusion.
C) moral hazard.
D) conspicuous consumption.
A) market unraveling.
B) signal confusion.
C) moral hazard.
D) conspicuous consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The individual mandate in the Affordable Care Act is a means of preventing:
A) asymmetric information.
B) adverse selection.
C) market unraveling.
D) social insurance.
A) asymmetric information.
B) adverse selection.
C) market unraveling.
D) social insurance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When one party to a transaction has more information about the characteristics of the good or service to be trade than does the other party,economists say that information is:
A) uneven.
B) asymmetric.
C) imperfect.
D) disequilibriated.
A) uneven.
B) asymmetric.
C) imperfect.
D) disequilibriated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
People with different information choose different alternatives in ________ equilibria; they choose the same alternatives,despite having different information,in ________ equilibria.
A) asymmetric; pooling
B) separating; pooling
C) asymmetric; coordinating
D) separating; coordinating
A) asymmetric; pooling
B) separating; pooling
C) asymmetric; coordinating
D) separating; coordinating

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Adverse selection can drive good used cars from the market because:
A) sellers have no way of convincing buyers that they have good information.
B) sellers are unable to distinguish good used cars from bad used cars.
C) buyers reduce their willingness to pay for used cars because they are wary of bad cars.
D) buyers decide to purchase only bad cars.
A) sellers have no way of convincing buyers that they have good information.
B) sellers are unable to distinguish good used cars from bad used cars.
C) buyers reduce their willingness to pay for used cars because they are wary of bad cars.
D) buyers decide to purchase only bad cars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The slope of the indifference curves in Figure 21.1 reveals the assumption that: 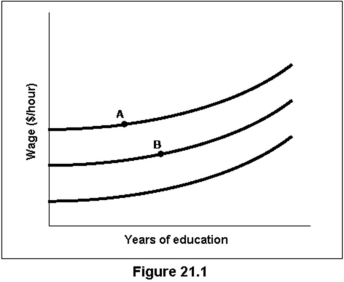
A) wages and education are both bads.
B) workers do not consider the impact on wages when deciding to pursue an education.
C) the costs of time and effort to get an education outweigh the pleasure of learning.
D) getting an education provides only benefits and no costs.

A) wages and education are both bads.
B) workers do not consider the impact on wages when deciding to pursue an education.
C) the costs of time and effort to get an education outweigh the pleasure of learning.
D) getting an education provides only benefits and no costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When employers use screening to distinguish high-ability workers from sufficiently numerous low-ability workers,the burden of asymmetric information falls on _________ because they ________ than when employers are well-informed.
A) low-ability workers; perform more tasks
B) low-ability workers; are paid less per task
C) high-ability workers; perform more tasks
D) high-ability workers; are paid less per task
A) low-ability workers; perform more tasks
B) low-ability workers; are paid less per task
C) high-ability workers; perform more tasks
D) high-ability workers; are paid less per task

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If Vincent van Gogh cut off his ear at the request of a love interest seeking proof of his love,this would be an example of:
A) signaling.
B) screening.
C) market unraveling.
D) emotional maturity.
A) signaling.
B) screening.
C) market unraveling.
D) emotional maturity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The indifference curves in Figure 21.1 slope upward because: 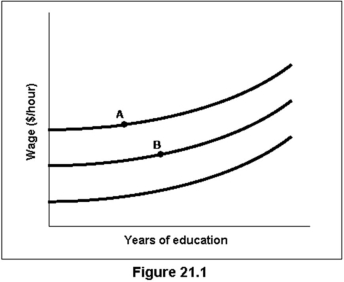
A) a higher wage is necessary in order to compensate someone for getting more years of education.
B) as people achieve higher levels of education, they generally receive higher wages.
C) all indifference curves slope upward.
D) education is an inferior good.

A) a higher wage is necessary in order to compensate someone for getting more years of education.
B) as people achieve higher levels of education, they generally receive higher wages.
C) all indifference curves slope upward.
D) education is an inferior good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Suppose in the market for labor years of education is used as a signal of ability,and that there is a separating equilibrium such that high-ability workers receive EH years of education and low-ability workers receive EL years.Each of the following must be true about EL and EH EXCEPT:
A) EH cannot be so low that it is easy for low-ability workers to masquerade as high-ability workers.
B) EH cannot be so high that high-ability workers choose to masquerade as low-ability workers.
C) EH and EL cannot be equal.
D) EH may be higher or lower than EL.
A) EH cannot be so low that it is easy for low-ability workers to masquerade as high-ability workers.
B) EH cannot be so high that high-ability workers choose to masquerade as low-ability workers.
C) EH and EL cannot be equal.
D) EH may be higher or lower than EL.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If Vincent van Gogh cut off his ear to demonstrate his love for someone,this would be an example of:
A) signaling.
B) screening.
C) social insurance.
D) perfect mental health.
A) signaling.
B) screening.
C) social insurance.
D) perfect mental health.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Screening is a process that is employed by:
A) a party at an informational advantage.
B) a party at an informational disadvantage.
C) both parties in cases of information asymmetry.
D) both parties in cases of equal and perfect information.
A) a party at an informational advantage.
B) a party at an informational disadvantage.
C) both parties in cases of information asymmetry.
D) both parties in cases of equal and perfect information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The value of a worker's marginal product is $40 per hour for high-ability workers and $5 per hour for low-ability workers.The preferences of high-ability workers correspond to the utility function UH(E,W)= W - 5E,and the preferences of low-ability workers correspond to the utility function UL(E,W)= W - 8E.By law,everyone is required to attend at least ten years of school.Three-fourths of the population has low ability,and one-fourth has high ability.What can be said about the educational attainment of each type of worker in a separating equilibrium?
A) EL = 10; 10 < EH < 14.375
B) EL = 10; EH < 17
C) EL = 10; EH > 14.375
D) EL = 10; 14.375 < EH < 17
A) EL = 10; 10 < EH < 14.375
B) EL = 10; EH < 17
C) EL = 10; EH > 14.375
D) EL = 10; 14.375 < EH < 17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In competitive markets,cross-subsidization is:
A) certain to emerge.
B) impossible.
C) one of many possible equilibrium outcomes.
D) a profit-maximizing strategy.
A) certain to emerge.
B) impossible.
C) one of many possible equilibrium outcomes.
D) a profit-maximizing strategy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The value of a worker's marginal product is $50 per hour for high-ability workers and $15 per hour for low-ability workers.The preferences of high-ability workers correspond to the utility function UH(E,W)= W - 4E,and the preferences of low-ability workers correspond to the utility function UL(E,W)= W - 10E.By law,everyone is required to attend at least ten years of school.Three-fifths of the population has low ability,and two-fifths has high ability.Would it be Pareto efficient for the government to ban schooling beyond 10 years rather than allow a separating equilibrium?
A) Yes, because both UL and UH would rise.
B) Yes, because although UH would fall, UL would rise.
C) No, because although UL would rise, UH would fall.
D) No, because both UL and UH would fall.
A) Yes, because both UL and UH would rise.
B) Yes, because although UH would fall, UL would rise.
C) No, because although UL would rise, UH would fall.
D) No, because both UL and UH would fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Government intervention is frequently justified in insurance markets due to the presence of market failures caused by:
A) adverse selection and competitive screening.
B) competitive screening and competitive signaling.
C) over-signaling and under-screening.
D) advantageous selection and market unraveling.
A) adverse selection and competitive screening.
B) competitive screening and competitive signaling.
C) over-signaling and under-screening.
D) advantageous selection and market unraveling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The value of a worker's marginal product is $50 per hour for high-ability workers and $15 per hour for low-ability workers.The preferences of high-ability workers correspond to the utility function UH(E,W)= W - 4E,and the preferences of low-ability workers correspond to the utility function UL(E,W)= W - 10E.By law,everyone is required to attend at least ten years of school.Three-fifths of the population has low ability,and two-fifths has high ability.What is the most efficient separating equilibrium?
A) EL = 13.5; EH = 13.5
B) EL = 10; EH = 13.5
C) EL = 13.5; EH = 16.125
D) EL = 10; EH = 10
A) EL = 13.5; EH = 13.5
B) EL = 10; EH = 13.5
C) EL = 13.5; EH = 16.125
D) EL = 10; EH = 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Figure 21.1 shows a set of: 
A) signals.
B) demand curves for education.
C) isoprofit lines.
D) indifference curves.

A) signals.
B) demand curves for education.
C) isoprofit lines.
D) indifference curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In Figure 21.1: 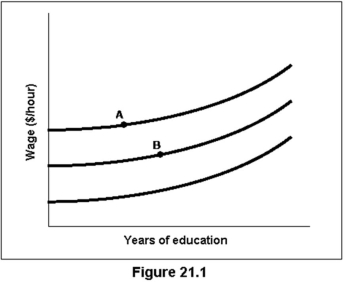
A)points A and B represent the same level of well-being.
B)point A represents greater well-being than does point B.
C)point B represents greater well-being than does point A.
D)it is impossible to rank the well-being represented by points A and B without more information.

A)points A and B represent the same level of well-being.
B)point A represents greater well-being than does point B.
C)point B represents greater well-being than does point A.
D)it is impossible to rank the well-being represented by points A and B without more information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In an insurance market,________ occurs when one type of policy generates losses,while another type of policy generates profits,and all policies collectively break even.
A) cross-subsidization
B) pooling
C) a separating equilibrium
D) screening
A) cross-subsidization
B) pooling
C) a separating equilibrium
D) screening

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Screening mechanisms are designed to ________ the problems of informational asymmetry.
A) reveal
B) help to alleviate
C) completely solve
D) exacerbate
A) reveal
B) help to alleviate
C) completely solve
D) exacerbate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The value of a worker's marginal product is $40 per hour for high-ability workers and $5 per hour for low-ability workers.The preferences of high-ability workers correspond to the utility function UH(E,W)= W - 5E,and the preferences of low-ability workers correspond to the utility function UL(E,W)= W - 8E.By law,everyone is required to attend at least ten years of school.Three-fourths of the population has low ability,and one-fourth has high ability.What is the most efficient separating equilibrium?
A) EL = 10; EH = 14.375
B) EL = 10; EH = 17
C) EL = 10; EH = 10
D) EL = 14.375; EH = 14.375
A) EL = 10; EH = 14.375
B) EL = 10; EH = 17
C) EL = 10; EH = 10
D) EL = 14.375; EH = 14.375

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The value of a worker's marginal product is $50 per hour for high-ability workers and $15 per hour for low-ability workers.The preferences of high-ability workers correspond to the utility function UH(E,W)= W - 4E,and the preferences of low-ability workers correspond to the utility function UL(E,W)= W - 10E.By law,everyone is required to attend at least ten years of school.Three-fifths of the population has low ability,and two-fifths has high ability.What can be said about the educational attainment of each type of worker in a separating equilibrium?
A) EL = 10; 13.5 < EH < 18.75
B) EL = 10; EH = 16.125
C) EL = 10; EH = 10
D) EL = 13.5; EH < 18.75
A) EL = 10; 13.5 < EH < 18.75
B) EL = 10; EH = 16.125
C) EL = 10; EH = 10
D) EL = 13.5; EH < 18.75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The value of a worker's marginal product is $40 per hour for high-ability workers and $5 per hour for low-ability workers.The preferences of high-ability workers correspond to the utility function UH(E,W)= W - 5E,and the preferences of low-ability workers correspond to the utility function UL(E,W)= W - 8E.By law,everyone is required to attend at least ten years of school.Three-fourths of the population has low ability,and one-fourth has high ability.Would it be Pareto efficient for the government to ban schooling beyond 10 years rather than allow a separating equilibrium?
A) Yes, because both UL and UH would rise.
B) Yes, because although UH would fall, UL would rise.
C) No, because although UL would rise, UH would fall.
D) No, because both UL and UH would fall.
A) Yes, because both UL and UH would rise.
B) Yes, because although UH would fall, UL would rise.
C) No, because although UL would rise, UH would fall.
D) No, because both UL and UH would fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If in the model for educational attainment among workers a pooling equilibrium emerges then workers' choices about education send:
A) no signals.
B) weak signals.
C) strong signals.
D) contradictory signals.
A) no signals.
B) weak signals.
C) strong signals.
D) contradictory signals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following explains why a compensation contract designed to combat employee moral hazard that features strong incentives might be worse than having no incentive scheme at all?
A) Generally, an employee's effort and ability are the only two determinants of the employee's performance.
B) Employers are generally pretty skilled at measuring the aspects of job performance in which they are the most interested.
C) Workers may choose to concentrate only on the most measurable aspects of job performance at the expense at those aspects that are less easily measured.
D) Compensation contracts with strong incentives are never efficient in the presence of moral hazard.
A) Generally, an employee's effort and ability are the only two determinants of the employee's performance.
B) Employers are generally pretty skilled at measuring the aspects of job performance in which they are the most interested.
C) Workers may choose to concentrate only on the most measurable aspects of job performance at the expense at those aspects that are less easily measured.
D) Compensation contracts with strong incentives are never efficient in the presence of moral hazard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If homes owned by real estate agents stay on the market longer and sell for higher prices than homes owned by people who hire real estate agents,this may be evidence of:
A) signaling.
B) screening.
C) moral hazard.
D) adverse selection.
A) signaling.
B) screening.
C) moral hazard.
D) adverse selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Figure 21.2 shows the benefit functions for low-ability workers and high-ability workers (A and B),along with one indifference curve for each worker type (C and D).The employer cannot observe worker type directly but has created two positions,E and F,as a screening mechanism.Which of the following is true? 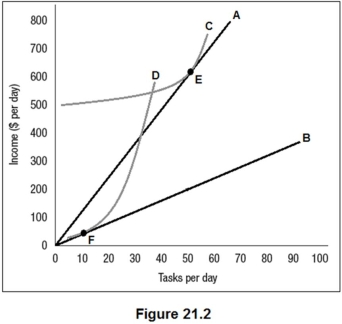
A)High- and low-ability workers will choose position E.
B)High-ability workers will choose position E and low ability workers will choose position F.
C)High- and low-ability workers will choose position F.
D)High-ability workers will choose position F and low ability workers will choose position E.

A)High- and low-ability workers will choose position E.
B)High-ability workers will choose position E and low ability workers will choose position F.
C)High- and low-ability workers will choose position F.
D)High-ability workers will choose position F and low ability workers will choose position E.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Figure 21.2 shows the benefit functions for low-ability workers and high-ability workers (A and B),along with one indifference curve for each worker type (C and D).The employer cannot observe worker type directly but has created two positions,E and F,as a screening mechanism.Which of the following is true? 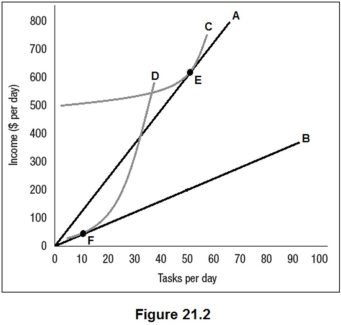
A) Curve A is an indifference curve for a low-ability worker, and curve B is an indifference curve for a high-ability worker.
B) Curve A is the benefit curve for high-ability workers, and curve B is an indifference curve for a high ability worker.
C) Curve A is an indifference curve for a high-ability worker, and curve C is the benefit curve for high-ability workers.
D) Curve A is the benefit curve for high-ability workers, and curve C is an indifference curve for a high ability worker.

A) Curve A is an indifference curve for a low-ability worker, and curve B is an indifference curve for a high-ability worker.
B) Curve A is the benefit curve for high-ability workers, and curve B is an indifference curve for a high ability worker.
C) Curve A is an indifference curve for a high-ability worker, and curve C is the benefit curve for high-ability workers.
D) Curve A is the benefit curve for high-ability workers, and curve C is an indifference curve for a high ability worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Moral hazard is ________ in employment settings because _______.
A) common; employee effort is easy to observe
B) common; employee effort is difficult to observe
C) uncommon; employee effort is easy to observe
D) uncommon; employee effort is difficult to observe
A) common; employee effort is easy to observe
B) common; employee effort is difficult to observe
C) uncommon; employee effort is easy to observe
D) uncommon; employee effort is difficult to observe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Figure 21.2 shows the benefit functions for low-ability workers and high-ability workers (A and B),along with one indifference curve for each worker type (C and D).The employer cannot observe worker type directly but has created two positions,E and F,as a screening mechanism.The equilibrium shown here is: 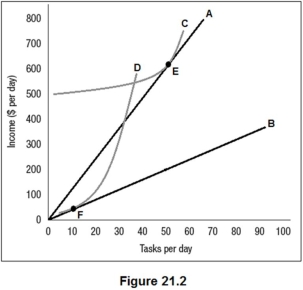
A) a separating equilibrium.
B) a pooling equilibrium.
C) a market unraveling equilibrium.
D) an example of adverse selection.

A) a separating equilibrium.
B) a pooling equilibrium.
C) a market unraveling equilibrium.
D) an example of adverse selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Moral hazard occurs if one party to a transaction takes actions that the trading partner ________ and that ________ the benefits the trading partner receives from the trade.
A) observes; affect
B) observes; do not affect
C) cannot observe; affect
D) cannot observe; do not affect
A) observes; affect
B) observes; do not affect
C) cannot observe; affect
D) cannot observe; do not affect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A salesperson works for a car dealership for 40 hours per week,but may choose not to work hard all of the time.The dealership's owner cannot observe the salesperson's effort,but can observe the number of cars sold.The salesperson's personal cost of working at the dealership is C(H)= 1,200 + H2,where H is the number of hours during which he works hard.The corresponding marginal cost of effort is MC = 2H.Without any effort,the salesperson will,on average,generate a profit of $1,200.With each hour of high effort,he has a 5 percent chance of selling a car.Each car sale generates a profit of $900.How much surplus does the relationship generate?
A) $506.25
B) $906.25
C) $1,518.75
D) $2,212.50
A) $506.25
B) $906.25
C) $1,518.75
D) $2,212.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A salesperson works for a car dealership for 40 hours per week,but may choose not to work hard all of the time.The dealership's owner cannot observe the salesperson's effort,but can observe the number of cars sold.The salesperson's personal cost of working at the dealership is C(H)= 1,200 + H2,where H is the number of hours during which he works hard.The corresponding marginal cost of effort is MC = 2H.Without any effort,the salesperson will,on average,generate a profit of $1,200.With each hour of high effort,he has a 5 percent chance of selling a car.Each car sale generates a profit of $900.Suppose the owner gives the salesperson $1,200 in base pay plus a bonus of $500 for each car he sells.How many hours of hard work will the salesperson choose?
A) 20
B) 22.5
C) 12.5
D) 25
A) 20
B) 22.5
C) 12.5
D) 25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
________ has occurred if the manager of a firm takes an action that furthers her own interests at the expense of the firm's profits.
A) Incentive scheming
B) Adverse selection
C) Signaling
D) Moral hazard
A) Incentive scheming
B) Adverse selection
C) Signaling
D) Moral hazard

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
When one party to a transaction takes actions that a trading partner cannot observe but that nonetheless affect that trading partner,this is called:
A) signaling.
B) screening.
C) moral hazard.
D) adverse selection.
A) signaling.
B) screening.
C) moral hazard.
D) adverse selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A salesperson works for a car dealership for 40 hours per week,but may choose not to work hard all of the time.The dealership's owner cannot observe the salesperson's effort,but can observe the number of cars sold.The salesperson's personal cost of working at the dealership is C(H)= 1,200 + H2,where H is the number of hours during which he works hard.The corresponding marginal cost of effort is MC = 2H.Without any effort,the salesperson will,on average,generate a profit of $1,200.With each hour of high effort,he has a 5 percent chance of selling a car.Each car sale generates a profit of $900.What is the efficient number of hours of hard work?
A) 22.5
B) 20
C) 40
D) 27.5
A) 22.5
B) 20
C) 40
D) 27.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following explains why a compensation contract designed to combat employee moral hazard that features strong incentives might be worse than having no incentive scheme at all?
A) If performance depends on factors other than just the employee's effort, the strong incentives create large costs associated with risk bearing.
B) Employers are generally pretty skilled at measuring the aspects of job performance in which they are the most interested.
C) Generally, an employee's effort and ability are the only two determinants of the employee's performance.
D) This is a trick question; in the presence of moral hazard, even a poorly-designed incentive scheme is better than no incentive scheme.
A) If performance depends on factors other than just the employee's effort, the strong incentives create large costs associated with risk bearing.
B) Employers are generally pretty skilled at measuring the aspects of job performance in which they are the most interested.
C) Generally, an employee's effort and ability are the only two determinants of the employee's performance.
D) This is a trick question; in the presence of moral hazard, even a poorly-designed incentive scheme is better than no incentive scheme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
One way to confront an individual employee with the full benefits and costs of their actions is through:
A) ownership.
B) an incentive scheme.
C) moral hazard.
D) screening.
A) ownership.
B) an incentive scheme.
C) moral hazard.
D) screening.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Figure 21.2 shows the benefit functions for low-ability workers and high-ability workers (A and B),along with one indifference curve for each worker type (C and D).The employer cannot observe worker type directly but has created two positions,E and F,as a screening mechanism.Which of the following is true? 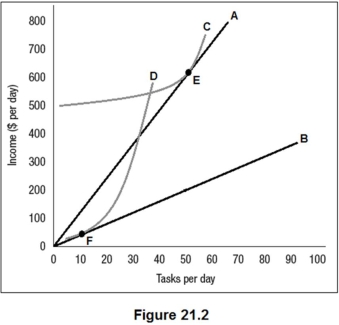
A) The employer will lose money on the low-ability workers hired but earn profit on the high-ability workers hired.
B) The employer will earn profit on all workers hired.
C) The employer will break even on all workers hired.
D) The employer will lose money on all workers hired.

A) The employer will lose money on the low-ability workers hired but earn profit on the high-ability workers hired.
B) The employer will earn profit on all workers hired.
C) The employer will break even on all workers hired.
D) The employer will lose money on all workers hired.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In situations where there is a potential for moral hazard,the increased efficiency achieved through incentive schemes is:
A) due to the reduction in resources that are dedicated to observing behavior.
B) not certain, because incentive schemes can also create costs.
C) easily achieved because incentive schemes are easy to design and yield predictable results.
D) controversial because it usually comes at the expense of equity.
A) due to the reduction in resources that are dedicated to observing behavior.
B) not certain, because incentive schemes can also create costs.
C) easily achieved because incentive schemes are easy to design and yield predictable results.
D) controversial because it usually comes at the expense of equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A salesperson works for a car dealership for 40 hours per week,but may choose not to work hard all of the time.The dealership's owner cannot observe the salesperson's effort,but can observe the number of cars sold.The salesperson's personal cost of working at the dealership is C(H)= 1,200 + H2,where H is the number of hours during which he works hard.The corresponding marginal cost of effort is MC = 2H.Without any effort,the salesperson will,on average,generate a profit of $1,200.With each hour of high effort,he has a 5 percent chance of selling a car.Each car sale generates a profit of $900.Which of the following is an incentive scheme that leads to the efficient effort level and allows the owner to keep all of the surplus?
A) $900 in base pay with a $1,177.50 bonus for each car he sells
B) $900 in base pay with a $900 bonus for each car he sells
C) $600 in base pay with a $1,000 bonus for each car he sells
D) $1,177.50 in base pay with a $900 bonus for each car he sells
A) $900 in base pay with a $1,177.50 bonus for each car he sells
B) $900 in base pay with a $900 bonus for each car he sells
C) $600 in base pay with a $1,000 bonus for each car he sells
D) $1,177.50 in base pay with a $900 bonus for each car he sells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In order to induce desirable behavior,one might employ _______,which is a contract or compensation policy that ties rewards or punishments to performance.
A) signaling
B) an incentive scheme
C) nudges
D) advantageous selection
A) signaling
B) an incentive scheme
C) nudges
D) advantageous selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is NOT a potential source of incentives covered in the textbook?
A) Cultural norms
B) Performance-based pay
C) Ownership rights
D) Informal understandings
A) Cultural norms
B) Performance-based pay
C) Ownership rights
D) Informal understandings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is NOT a potential source of incentives covered in the textbook?
A) Compensation contracts
B) Promotion
C) Reputational considerations
D) Peer pressure
A) Compensation contracts
B) Promotion
C) Reputational considerations
D) Peer pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Suppose research reveals that college graduates have higher employment rates and higher wages,but a significant proportion of college graduates who get jobs do so in fields other than the field in which they earned their degree.How could this be evidence of signaling? What is the counter-argument?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
George Akerloff theorized that adverse selection in the used car market could be so bad that the market completely unravels and no good used cars are offered for sale.But,of course,there probably are some good used cars offered for sale in real used car markets.What methods have developed in the used car market to overcome this problem of asymmetric information and to prevent market unraveling?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Explain the differences and similarities between screening and signaling.Is one better than the other?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Give an example of the potential for moral hazard that exists in the following relationships: (a)a film actress and her agent; (b)a employee hired by a large firm to manage one retail location; and (c)a college student and a professor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Explain in your own words how the government can create Pareto efficiency by mandating participation in a social health insurance program.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



