Deck 12: MRP and ERP
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/89
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: MRP and ERP
1
The bill of materials indicates how much material will be needed to produce the quantities on a given master production schedule.
False
2
Net requirements equal gross requirements minus safety stock.
False
3
The master production schedule states which end items are to be produced, in addition to when and how many.
True
4
Initially, a master production schedule - the output from MRP - may not represent a feasible schedule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The inventory records contain information on the status of each item by time period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
MRP is used within most MRP II and ERP systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
MRP, considering inventory position, bills of material, open purchase orders and lead times guarantees a feasible production plan if the inputs to MRP are accurate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The gross requirements value for any given component is equal to the net requirements of that component's immediate parent multiplied by the quantity per parent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The bill of materials contains information on lead times and current inventory position on every component required to produce the end item.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The gross requirements at one level of an MRP plan determine the gross requirements at the next lower level continuing on down to the lowest levels shown on the bill of material.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The term pegging refers to identifying the parent items that have generated a given set of material requirements for a part or subassembly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A net-change MRP system is one that is updated periodically but not less frequently than once a week.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A bill of materials contains a listing of all the assemblies, parts, and materials needed to produce one unit of an end item.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An assembly-time chart indicates gross and net requirements taking into account the current available inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Low level coding represents items less than $18 per unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The master schedule needs to be for a period long enough to cover the stacked or cumulative lead time necessary to produce the end items.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Lumpy demand for components results primarily from the periodic scheduling of batch production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
MRP II did not replace or improve the basic MRP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Independent demand tends to be more 'lumpy' than dependent demand meaning that we need large quantities followed by periods of no demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
MRP works best if the inventory items have dependent demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In MRP, EOQ models tend to be less useful for materials at the lowest levels than for upper level assemblies of the bill of materials since higher-level assemblies have larger dollar investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
MRP really doesn't apply to services since raw material isn't required.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
ERP implementation requires support and a direct mandate from the CEO because it impacts so many different functional areas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Capacity requirements planning (CRP) is an important feature in MRP+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Before a schedule receipt can take place, and order must be placed with a vendor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
MRP II is simply an improved version of MRP that processes faster and can plan for a larger number of end items.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
ERP represents an expanded effort to integrate standardized record-keeping that shares information among different areas of an organization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Lot-for-lot ordering in MRP eliminates the holding costs for parts that are carried over to other periods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
MRP output reports are divided into two main groups - daily and weekly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
ERP began in manufacturing organizations but has spread into service organizations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Load reports show capacity requirements for departments or work centers which may be more or less than the capacity available in that work center.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
As long as a forecast is plus or minus 10%, MRP works well.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Back flushing takes place after the production has been completed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Lot-for-lot ordering in MRP provides coverage for some predetermined number of periods using forecasted demand to extend beyond the orders already received for those periods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
One of the primary output reports of MRP concerns changes to planned orders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Project Management approaches can help in a conversion to an ERP system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
One reason that accurate bills of material are important is that errors at one level become magnified at lower levels because of the multiplication process used by MRP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
ERP automates the tasks involved in performing a business process, such as order fulfillment and financial reporting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Safety time is sometimes used in MRP rather than safety stock quantities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A regenerative MRP system is one that is updated continuously - every time there is a schedule change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A computer-based information system designed to handle ordering and scheduling of dependent-demand inventories is:
A)computer aided manufacturing (CAM)
B)computer integrated manufacturing (CIM)
C)economic order quantity (EOQ)
D)material requirements planning (MRP)
E)economic run size (ERS)
A)computer aided manufacturing (CAM)
B)computer integrated manufacturing (CIM)
C)economic order quantity (EOQ)
D)material requirements planning (MRP)
E)economic run size (ERS)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following most closely describes dependent demand?
A)demand generated by suppliers
B)estimates of demand using regression analysis of independent variables
C)derived demand
D)demands placed on suppliers by their customers
E)net material requirements
A)demand generated by suppliers
B)estimates of demand using regression analysis of independent variables
C)derived demand
D)demands placed on suppliers by their customers
E)net material requirements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Under lot-for-lot, order sizes for component parts are essentially determined directly from which one of the following?
A)gross requirements
B)net requirements
C)economic order quantity
D)gross requirements - net requirements
E)net requirements - amount on-hand
A)gross requirements
B)net requirements
C)economic order quantity
D)gross requirements - net requirements
E)net requirements - amount on-hand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In an MRP master schedule, the planning horizon is often separated into a series of times periods called:
A)pegging
B)lead times
C)stacked lead times
D)time buckets
E)firm, fixed and frozen
A)pegging
B)lead times
C)stacked lead times
D)time buckets
E)firm, fixed and frozen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The development and application of MRP depended upon two developments: (1) the recognition of the difference between independent and dependent demand, and (2):
A)computers
B)development of the EOQ model
C)inventory control systems
D)blanket purchase orders
E)the internet
A)computers
B)development of the EOQ model
C)inventory control systems
D)blanket purchase orders
E)the internet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In MRP, under lot-for-lot ordering, "planned-order receipts" are:
A)identical to "scheduled receipts"
B)identical to "planned-order releases"
C)open orders (that is, ordered before the first time bucket, but not delivered yet)
D)"gross requirements"
E)available to promise inventory
A)identical to "scheduled receipts"
B)identical to "planned-order releases"
C)open orders (that is, ordered before the first time bucket, but not delivered yet)
D)"gross requirements"
E)available to promise inventory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Periodic updating of an MRP system to account for all changes which have occurred within a given time interval is called:
A)pegging
B)planned order release
C)net change
D)regenerative
E)exception report
A)pegging
B)planned order release
C)net change
D)regenerative
E)exception report

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In MRP, "scheduled receipts" are:
A)identical to "planned-order receipts"
B)identical to "planned-order releases"
C)open orders (that is, ordered before the first time bucket, but not delivered yet)
D)"net requirements"
E)available to promise inventory
A)identical to "planned-order receipts"
B)identical to "planned-order releases"
C)open orders (that is, ordered before the first time bucket, but not delivered yet)
D)"net requirements"
E)available to promise inventory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A visual depiction of the subassemblies and components that are needed to produce and/or assemble a product is called a(n):
A)assembly time chart
B)product structure tree
C)MRP II
D)pegging
E)Gantt chart
A)assembly time chart
B)product structure tree
C)MRP II
D)pegging
E)Gantt chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The MRP input stating which end items are to be produced, when they are needed, and what quantities are needed, is the:
A)master schedule
B)bill-of-materials
C)inventory-records
D)assembly-time chart
E)net-requirements chart
A)master schedule
B)bill-of-materials
C)inventory-records
D)assembly-time chart
E)net-requirements chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which one of the following most closely describes net material requirements?
A)gross requirements - amount on-hand - scheduled receipts
B)gross requirements - planned receipts
C)gross requirements - order releases + amount on-hand
D)gross requirements - planned order releases
E)gross requirements - amount on-hand + planned order releases
A)gross requirements - amount on-hand - scheduled receipts
B)gross requirements - planned receipts
C)gross requirements - order releases + amount on-hand
D)gross requirements - planned order releases
E)gross requirements - amount on-hand + planned order releases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The MRP input listing the assemblies, subassemblies, parts, and raw materials needed to produce one unit of finished product is the:
A)master production schedule
B)bill-of-materials
C)inventory-records
D)assembly-time chart
E)net-requirements chart
A)master production schedule
B)bill-of-materials
C)inventory-records
D)assembly-time chart
E)net-requirements chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The identification of parent items is called:
A)Paternity
B)Pegging
C)Requirement I.D.
D)Relationship tracking
E)Master Scheduling
A)Paternity
B)Pegging
C)Requirement I.D.
D)Relationship tracking
E)Master Scheduling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The output of MRP is:
A)gross requirements
B)net requirements
C)a schedule of requirements for all parts and end items
D)inventory reorder points
E)economic order quantities and reorder points
A)gross requirements
B)net requirements
C)a schedule of requirements for all parts and end items
D)inventory reorder points
E)economic order quantities and reorder points

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
An MRP system whose records are updated continuously is referred to as a(n):
A)regenerative system
B)batch-type system
C)Plossl-Wright system
D)net-change system
E)gross-change system
A)regenerative system
B)batch-type system
C)Plossl-Wright system
D)net-change system
E)gross-change system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
ERP implementation probably won't require:
A)cross functional teams
B)just a few weeks to install
C)intensive training
D)high funding for both initial cost and maintenance
E)frequent upgrades after installation
A)cross functional teams
B)just a few weeks to install
C)intensive training
D)high funding for both initial cost and maintenance
E)frequent upgrades after installation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The MRP input storing information on the status of each item by time period (e.g., scheduled receipts, lead time, lot size) is the:
A)master production schedule
B)bill-of-materials
C)inventory-records
D)assembly-time chart
E)net-requirements chart
A)master production schedule
B)bill-of-materials
C)inventory-records
D)assembly-time chart
E)net-requirements chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which one of the following is not an input in an MRP system?
A)planned-order schedules
B)bill of materials
C)master production schedule
D)inventory records
E)All are inputs.
A)planned-order schedules
B)bill of materials
C)master production schedule
D)inventory records
E)All are inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which is true of a net-change system?
A)It is a batch-type system which is updated periodically.
B)It is usually run at the beginning of each month.
C)The basic production plan is modified to reflect changes as they occur.
D)It is used to authorize the execution of planned orders.
E)It indicates the amount and timing of future changes.
A)It is a batch-type system which is updated periodically.
B)It is usually run at the beginning of each month.
C)The basic production plan is modified to reflect changes as they occur.
D)It is used to authorize the execution of planned orders.
E)It indicates the amount and timing of future changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In MRP, the gross requirements of a given component part are calculated from:
A)net requirements + amount on-hand.
B)gross requirements of the immediate parent.
C)planned orders of the end item.
D)net requirements of end item.
E)planned orders of the immediate parent.
A)net requirements + amount on-hand.
B)gross requirements of the immediate parent.
C)planned orders of the end item.
D)net requirements of end item.
E)planned orders of the immediate parent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following lot sizing methods does not attempt to balance ordering (or setup) and holding costs?
A)economic order quantity
B)economic run size
C)lot-for-lot
D)part-period
E)all of the above
A)economic order quantity
B)economic run size
C)lot-for-lot
D)part-period
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The _________ of ERP makes it valuable as a strategic planning tool.
A)Internet base
B)Rapid Batch capability
C)Employee focus
D)Real-time aspect
E)Database structure
A)Internet base
B)Rapid Batch capability
C)Employee focus
D)Real-time aspect
E)Database structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following is not usually necessary in order to have an effective MRP system?
A)a computer and software
B)an accurate bill of materials
C)lot-for-lot ordering
D)an up-to-date master schedule
E)integrity of file data
A)a computer and software
B)an accurate bill of materials
C)lot-for-lot ordering
D)an up-to-date master schedule
E)integrity of file data

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A recent effort to expand the scope of production resource planning by involving other functional areas in the planning process has been:
A)material requirements planning
B)capacity requirements planning
C)manufacturing resources planning
D)Just-In-Time planning
E)multifunctional relationships planning
A)material requirements planning
B)capacity requirements planning
C)manufacturing resources planning
D)Just-In-Time planning
E)multifunctional relationships planning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Given the following data, construct a material requirements plan which will result in 100 units of Parent #1 (P1) at the beginning of week 6, and 200 units of Parent #2 (P2) at the beginning of week 8:
B.
B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which one of the following most closely describes the MRP approach that is used for components or subassemblies to compensate for variations in lead time?
A)pegging
B)safety stock
C)increased order sizes
D)safety time
E)low-level coding
A)pegging
B)safety stock
C)increased order sizes
D)safety time
E)low-level coding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If 40 Ps are needed, and on-hand inventory consists of 15 Ps and 10 each of all other components and subassemblies, how many Cs are needed?
A)340
B)350
C)380
D)400
E)590
A)340
B)350
C)380
D)400
E)590

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of these items would be most likely to have dependent demand?
A)Xbox batteries
B)toy trains
C)flowers
D)chocolate chip cookies
E)wrist watches
A)Xbox batteries
B)toy trains
C)flowers
D)chocolate chip cookies
E)wrist watches

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Develop a material requirements plan for end item P and its components, given the tree below.Assume that all lead times are one week, and that lot-for-lot ordering is used except for item F, which is ordered in multiples of 400 units.
One hundred units of P should be available at the start of week 4 and at the start of week 8.Beginning inventories are: 20 P, 100 A, and 200F.
Scheduled receipts are: 800 F at the start of week 1.
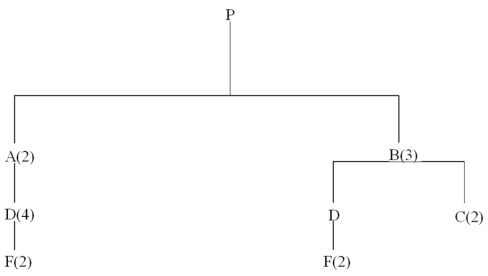
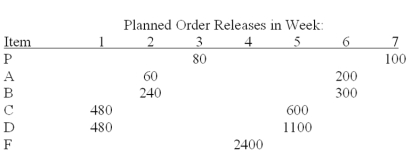
One hundred units of P should be available at the start of week 4 and at the start of week 8.Beginning inventories are: 20 P, 100 A, and 200F.
Scheduled receipts are: 800 F at the start of week 1.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The multiplication process used by MRP to determine lower level requirements is called:
A)time-phasing
B)pegging
C)netting
D)projecting
E)exploding
A)time-phasing
B)pegging
C)netting
D)projecting
E)exploding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which statement concerning MRP II is false?
A)It is basically a computerized system.
B)It can handle complex planning and scheduling quickly.
C)It involves other functional areas in the production planning process.
D)It involves capacity planning.
E)It produces a production plan which includes all resources required.
A)It is basically a computerized system.
B)It can handle complex planning and scheduling quickly.
C)It involves other functional areas in the production planning process.
D)It involves capacity planning.
E)It produces a production plan which includes all resources required.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If 17 Ps are needed, and on-hand inventory consists of 10 As, 15 Bs, 20 Cs, 12 Ms, and 5 Ns, how many Cs are needed?
A)48
B)144
C)192
D)212
E)272
A)48
B)144
C)192
D)212
E)272

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When MRP II systems include feedback, they are known as:
A)MRPIII
B)Enterprise resource planning
C)Circular MRP
D)Feasible MRP
E)Closed Loop MRP
A)MRPIII
B)Enterprise resource planning
C)Circular MRP
D)Feasible MRP
E)Closed Loop MRP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The following is a list of components required to produce one unit of end item P:
P: 2 A's, 3 B's, 3 C's
A: 5 M's, 2 R's
B: 1 D, 3 N's.
C: 1 T, 4 N's
M: 1 N
Determine the number of N's that will be needed to make 60 P's in each of these cases:
(A) There are currently 10 P's on hand.
(B) On-hand inventory consists of 15 P's, 10A's, 20 B's, 10 C's, 100 N's, 300 T's, and 200 M's.
P: 2 A's, 3 B's, 3 C's
A: 5 M's, 2 R's
B: 1 D, 3 N's.
C: 1 T, 4 N's
M: 1 N
Determine the number of N's that will be needed to make 60 P's in each of these cases:
(A) There are currently 10 P's on hand.
(B) On-hand inventory consists of 15 P's, 10A's, 20 B's, 10 C's, 100 N's, 300 T's, and 200 M's.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Given the following information, construct a product tree diagram and develop a material requirements plan that will lead to 400 units of product P being available at the start of week 7.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Using the product tree shown, determine the following:
(A) the quantity of component K that will be needed to assemble 80 units of P, assuming no on-hand inventory of any components exists.
(B) the quantity of component K needed to assemble 80 units of P, given on-hand inventory of 30 A's, 50 B's and 20 C's.
(A) the quantity of component K that will be needed to assemble 80 units of P, assuming no on-hand inventory of any components exists.
(B) the quantity of component K needed to assemble 80 units of P, given on-hand inventory of 30 A's, 50 B's and 20 C's.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
End item Alpha's product structure tree and inventory information are as follows:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
_______ is choosing how many to order or make.
A)Quantity determination
B)Package sizing
C)Lot sizing
D)Grouping
E)Aggregation
A)Quantity determination
B)Package sizing
C)Lot sizing
D)Grouping
E)Aggregation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of these products would be most likely to have dependent demand?
A)refrigerators
B)automobile engines
C)televisions
D)brownies
E)automobiles
A)refrigerators
B)automobile engines
C)televisions
D)brownies
E)automobiles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If 17 Ps are needed, and no on-hand inventory exists for any items, how many Cs will be needed?
A)8
B)16
C)136
D)204
E)272
A)8
B)16
C)136
D)204
E)272

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



