Deck 21: Tax Aspects of Corporate Financing
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/8
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Tax Aspects of Corporate Financing
1
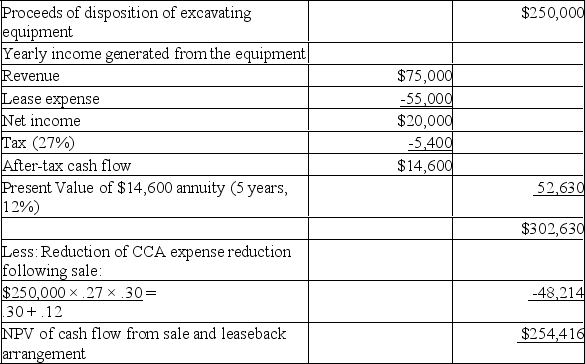
Jet Dry Inc.is undergoing a sale/leaseback arrangement on a piece of its excavating equipment.The equipment is a class 38 (30%)asset,with a fair market value of $250,000 (which is lower than the original cost).The equipment currently generates $75,000 in annual pre-tax revenue.Jet Dry Inc.will sell the equipment at FMV.
Under the leasing terms,the lease agreement will be for five years,with no residual value at the end of the term.The annual leasing cost will be $55,000 per year.
The UCC relating to this piece of equipment is $150,000.Other assets will remain in the asset pool,and there is sufficient UCC in the class that recapture will not occur as a result of the sale.
The company is subject to a corporate tax rate of 27% and achieves a 12% after-tax rate of return.
Required:
Calculate the net present value of the cash flow that will result from this sale-and-leaseback arrangement.(Round all numbers to zero decimal places.)
Under the leasing terms,the lease agreement will be for five years,with no residual value at the end of the term.The annual leasing cost will be $55,000 per year.
The UCC relating to this piece of equipment is $150,000.Other assets will remain in the asset pool,and there is sufficient UCC in the class that recapture will not occur as a result of the sale.
The company is subject to a corporate tax rate of 27% and achieves a 12% after-tax rate of return.
Required:
Calculate the net present value of the cash flow that will result from this sale-and-leaseback arrangement.(Round all numbers to zero decimal places.)
2
Which of the following statements regarding debt and equity financing is FALSE?
A)Interest payments on debt financing are deductible by the corporation for tax purposes.
B)Interest income from debt financing is taxable in the hands of the investor.
C)Dividend payments on equity financing are deductible by the corporation for tax purposes.
D)Dividends are paid from after-tax corporate income.
A)Interest payments on debt financing are deductible by the corporation for tax purposes.
B)Interest income from debt financing is taxable in the hands of the investor.
C)Dividend payments on equity financing are deductible by the corporation for tax purposes.
D)Dividends are paid from after-tax corporate income.
C
3
Andrea Houser recently inherited $500,000.She would like to invest the money and receive an annual after-tax return of $30,000 on the investment income.She has a number of investment alternatives available to her.Based on the combination of federal and provincial rates in her province,she would pay 45% tax on interest,28% tax on eligible dividends,37% tax on non-eligible dividends,and 23% tax (rounded)on capital gains.
Required:
A)Calculate how much taxable income Andrea would need to receive in (i)interest,(ii)eligible dividends,(iii)non-eligible dividends,and (iv)capital gains in order to realize a $30,000 after-tax return.(Round all answers to zero decimal places.)
B)What is Andrea's pre-tax rate of return on each of the investments? (Round all answers to one decimal place.)
C)Calculate Andrea's after-tax rate of return (rounded to zero decimal places)on each of the investments,using her tax rates given in the problem to arrive at your answers.
Required:
A)Calculate how much taxable income Andrea would need to receive in (i)interest,(ii)eligible dividends,(iii)non-eligible dividends,and (iv)capital gains in order to realize a $30,000 after-tax return.(Round all answers to zero decimal places.)
B)What is Andrea's pre-tax rate of return on each of the investments? (Round all answers to one decimal place.)
C)Calculate Andrea's after-tax rate of return (rounded to zero decimal places)on each of the investments,using her tax rates given in the problem to arrive at your answers.
A)
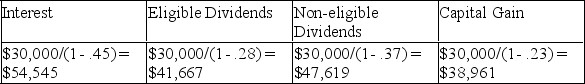 B)
B)
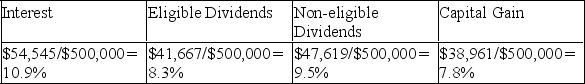 C)Andrea's after-tax rate of return will be 6% (rounded for each alternative),since she is seeking $30,000,after-tax,from her investment.$30,000/$500,000 = 6%
C)Andrea's after-tax rate of return will be 6% (rounded for each alternative),since she is seeking $30,000,after-tax,from her investment.$30,000/$500,000 = 6%
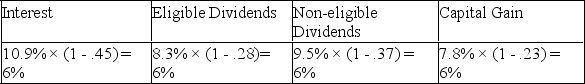
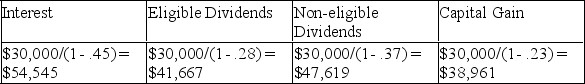 B)
B)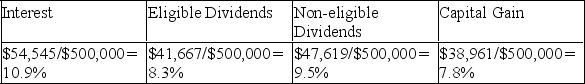 C)Andrea's after-tax rate of return will be 6% (rounded for each alternative),since she is seeking $30,000,after-tax,from her investment.$30,000/$500,000 = 6%
C)Andrea's after-tax rate of return will be 6% (rounded for each alternative),since she is seeking $30,000,after-tax,from her investment.$30,000/$500,000 = 6%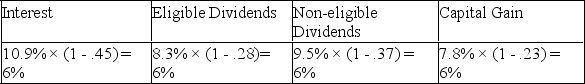
4
Mary is deciding where to invest $10,000.Based on her decision,she will either receive a 5% capital gain or a 7% non-eligible dividend as her return on investment.Mary's marginal tax rates are 45% on regular income,37% on non-eligible dividends,28% on eligible dividends,and 23% (rounded)on capital gains.Which of the following is TRUE?
A)Mary will receive a higher after-tax rate of return on the capital gain due to the higher tax rate for non-eligible dividends.
B)Mary will receive an after-tax rate of return of 5% on the capital gain and 7% on the non-eligible dividends.
C)Mary will receive an after-tax rate of return of 3.85% on the capital gain and 4.41% on the non-eligible dividends.
D)There is no difference in the after-tax rate of return on the two investments.
A)Mary will receive a higher after-tax rate of return on the capital gain due to the higher tax rate for non-eligible dividends.
B)Mary will receive an after-tax rate of return of 5% on the capital gain and 7% on the non-eligible dividends.
C)Mary will receive an after-tax rate of return of 3.85% on the capital gain and 4.41% on the non-eligible dividends.
D)There is no difference in the after-tax rate of return on the two investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
With regard to debt and equity securities,which of the following statements is TRUE? (Assume the corporations are not in the business of lending money.)
A)A premium on an equity issue has a tax impact on the issuing corporation.
B)A discount on an equity issue has a tax impact on the issuing corporation.
C)A premium on a debt security is taxed in the hands of an issuing corporation that is not in the business of lending money.
D)A discount on a debt security is fully or partially deductible for tax purposes, depending on the discount rate.
A)A premium on an equity issue has a tax impact on the issuing corporation.
B)A discount on an equity issue has a tax impact on the issuing corporation.
C)A premium on a debt security is taxed in the hands of an issuing corporation that is not in the business of lending money.
D)A discount on a debt security is fully or partially deductible for tax purposes, depending on the discount rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Silver Photo Studios Inc.requires $50,000 capital for a proposed expansion.Simon Silver,the company's president and CEO,is trying to decide whether to issue preferred shares with a fixed dividend rate of 5%,or to borrow from the bank at a rate of 7%.The company pays a corporate tax rate of 27%.
Required:
A)Determine the amount of corporate income that would be required to finance (i)the interest in the bank loan and (ii)the dividends on the preferred shares.
B)Calculate the actual cost (as a %)of the debt and the actual cost (as a %)of issuing the preferred shares.
Required:
A)Determine the amount of corporate income that would be required to finance (i)the interest in the bank loan and (ii)the dividends on the preferred shares.
B)Calculate the actual cost (as a %)of the debt and the actual cost (as a %)of issuing the preferred shares.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Joe Genius of ABC Corporation is considering whether to engage in a financial lease or to purchase a large capital asset.If Joe purchases the asset,he will use debt financing.Which of the following accurately describes the similarities in the tax treatment of leasing and purchasing with debt?
A)Both methods allow for deductions which reduces taxable income.
B)The after-tax net present value of the two methods will usually be identical.
C)The timing of cash payments and tax savings is the same under both alternatives.
D)Capital cost allowance is always expensed for both alternatives.
A)Both methods allow for deductions which reduces taxable income.
B)The after-tax net present value of the two methods will usually be identical.
C)The timing of cash payments and tax savings is the same under both alternatives.
D)Capital cost allowance is always expensed for both alternatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
During the year,The Light Corporation paid $550,000 in preferred share dividends to ABC Inc.Both companies are Canadian corporations.Which of the following is TRUE?
A)ABC Inc.is subject to Part VI.1 tax.
B)The Light Corporation is subject to Part VI.1 tax.
C)Neither corporation is subject to Part VI.1 tax.
D)Both corporations are subject to Part VI.1 tax.
A)ABC Inc.is subject to Part VI.1 tax.
B)The Light Corporation is subject to Part VI.1 tax.
C)Neither corporation is subject to Part VI.1 tax.
D)Both corporations are subject to Part VI.1 tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



