Deck 29: A: Central Nervous System Smoke on the Brain
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/107
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 29: A: Central Nervous System Smoke on the Brain
1
Do you believe that addiction is an illness? Use your knowledge of the physiology of addiction to support your answer.
Answers will vary.One example is that addiction is associated with alterations in brain chemistry and in the levels of certain neurotransmitters and receptors.Since these are altered from what is normal,addiction is an illness and affects one's mental health.
2
Does knowing more about the physiology of addiction change your attitudes about it? Provide examples of how addiction affects the brain and body.
Answers will vary.One example is that after prolonged use,drugs of abuse change the structure and function of the brain in ways that can wreak havoc on user's lives.
3
When smoking,nicotine passes from the lungs to the _______.
A) heart
B) bloodstream
C) white blood cells
D) blastocysts
E) stomach
A) heart
B) bloodstream
C) white blood cells
D) blastocysts
E) stomach
B
4
The central nervous system is composed of the _______ and the _______.
A) spinal cord, peripheral nerves
B) sensory nerves; motor nerves
C) interneurons; motor nerves
D) brain; spinal cord
E) cerebral; spinal cord
A) spinal cord, peripheral nerves
B) sensory nerves; motor nerves
C) interneurons; motor nerves
D) brain; spinal cord
E) cerebral; spinal cord

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
People who receive a sharp blow to the elbow will sometimes feel their pinky and third finger go numb.The injury that causes this happens to the ________.
A) central nervous system
B) peripheral nervous system
C) sensory neurons
D) motor neurons
E) spinal cord
A) central nervous system
B) peripheral nervous system
C) sensory neurons
D) motor neurons
E) spinal cord

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Sensory receptors in your skin belong to the _______.
A) central nervous system
B) spinal cord
C) peripheral nervous system
D) effector system
E) None of the above.
A) central nervous system
B) spinal cord
C) peripheral nervous system
D) effector system
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Sensory neurons and motor neurons are part of the _______.
A) peripheral nervous system
B) cerebral cortex
C) limbic system
D) cerebellum
E) C and D
A) peripheral nervous system
B) cerebral cortex
C) limbic system
D) cerebellum
E) C and D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Sensory input is received by the _______ nervous system.
A) central
B) polar
C) involuntary
D) peripheral
E) cerebral
A) central
B) polar
C) involuntary
D) peripheral
E) cerebral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When you jerk your hand away from a hot surface,the path taken from stimulus to action is _______.
A) central nervous system to peripheral nervous system
B) peripheral nervous system to central nervous system
C) central nervous system to peripheral nervous system and back to central nervous system
D) peripheral nervous system to central nervous system and back to peripheral nervous system
E) None of the above.
A) central nervous system to peripheral nervous system
B) peripheral nervous system to central nervous system
C) central nervous system to peripheral nervous system and back to central nervous system
D) peripheral nervous system to central nervous system and back to peripheral nervous system
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Suppose you are walking on the beach and step on a piece of broken glass.Describe the path that nervous impulses would take in causing you to jerk your foot up.Make sure to describe the kinds of cells involved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Most of a neuron's organelles are contained in the _______.
A) myelin sheath vacuole
B) axon
C) cell body
D) axon hillock
E) synaptic cleft
A) myelin sheath vacuole
B) axon
C) cell body
D) axon hillock
E) synaptic cleft

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following correctly lists the steps by which nicotine from cigarettes reaches the pleasure centers of the brain?
A) Nicotine moves to the lungs, travels to the brain, is absorbed into the bloodstream, and travels throughout the body.
B) Nicotine moves to the lungs, is absorbed into the bloodstream, and travels to the brain and the rest of the body.
C) Nicotine is absorbed into the bloodstream, moves to the lungs, and travels to the brain and the rest of the body.
D) Nicotine is absorbed into the bloodstream and travels simultaneously to the lungs, brain, and rest of the body.
E) None of the above.
A) Nicotine moves to the lungs, travels to the brain, is absorbed into the bloodstream, and travels throughout the body.
B) Nicotine moves to the lungs, is absorbed into the bloodstream, and travels to the brain and the rest of the body.
C) Nicotine is absorbed into the bloodstream, moves to the lungs, and travels to the brain and the rest of the body.
D) Nicotine is absorbed into the bloodstream and travels simultaneously to the lungs, brain, and rest of the body.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
_______ control contractions of skeletal muscle.
A) Interneurons
B) Glial cells
C) Potassium ions
D) Motor neurons
E) Skeletal neurons
A) Interneurons
B) Glial cells
C) Potassium ions
D) Motor neurons
E) Skeletal neurons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An example of an effector cell is_______.
A) a motor neuron
B) a sensory neuron
C) a muscle cell
D) A and D
E) A and B
A) a motor neuron
B) a sensory neuron
C) a muscle cell
D) A and D
E) A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The nervous system is composed of two parts,the _______ and the _______.
A) sensory; central
B) central; peripheral
C) central; peripheral
D) motor; central
E) brain; nerves
A) sensory; central
B) central; peripheral
C) central; peripheral
D) motor; central
E) brain; nerves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Muscle cells that respond to signals from the central nervous system are examples of _______.
A) sensory receptors
B) peripheral nervous system
C) central nervous system
D) effector cells
E) None of the above.
A) sensory receptors
B) peripheral nervous system
C) central nervous system
D) effector cells
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A difference between the central and peripheral nervous systems is that _________.
A) the peripheral nervous system contains neurons, unlike the central nervous system
B) the peripheral nervous system is not involved in regulating body functions
C) the neurons of central nervous system use neurotransmitters
D) the central nervous system only contains receiving neurons
E) None of the above.
A) the peripheral nervous system contains neurons, unlike the central nervous system
B) the peripheral nervous system is not involved in regulating body functions
C) the neurons of central nervous system use neurotransmitters
D) the central nervous system only contains receiving neurons
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The general flow of information through the nervous system is from _____ to _____ to _____.
A) sensory receptors; the brain; the peripheral nervous system
B) the central nervous system; the brain; effector cells
C) the peripheral nervous system; the central nervous system; effector cells
D) the peripheral nervous system; effector cells; the central nervous system
E) the central nervous system; the peripheral nervous system; effector cells
A) sensory receptors; the brain; the peripheral nervous system
B) the central nervous system; the brain; effector cells
C) the peripheral nervous system; the central nervous system; effector cells
D) the peripheral nervous system; effector cells; the central nervous system
E) the central nervous system; the peripheral nervous system; effector cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The central nervous system consists of ________ ,whereas the peripheral nervous system consists of _______.
A) the brain, spinal cord, and other nervous tissue; peripheral nerves
B) the brain and spinal cord; effector cells
C) all nervous tissue; effector cells
D) the brain and spinal cord; peripheral nerves
E) effector cells; sensory cells
A) the brain, spinal cord, and other nervous tissue; peripheral nerves
B) the brain and spinal cord; effector cells
C) all nervous tissue; effector cells
D) the brain and spinal cord; peripheral nerves
E) effector cells; sensory cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The ___________ connects the peripheral nervous system to the rest of the central nervous system.
A) brain
B) brain stem
C) cerebrum
D) cerebellum
E) spinal cord
A) brain
B) brain stem
C) cerebrum
D) cerebellum
E) spinal cord

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Sensory neurons _______.
A) convey information to the central nervous system
B) are part of the peripheral nervous system
C) are part of the central nervous system
D) A and B
E) A, B, and C
A) convey information to the central nervous system
B) are part of the peripheral nervous system
C) are part of the central nervous system
D) A and B
E) A, B, and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Use the diagram to answer Questions 31-35.
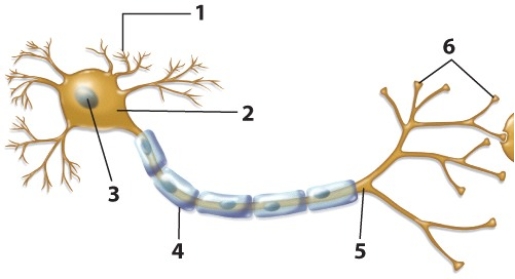
Which of the following gives the name and number of the labeled structure that transmits nerve signals along the length of the neuron?
A) cell body/2
B) myelin sheath/3
C) myelin sheath/4
D) axon/5
E) axon/6

Which of the following gives the name and number of the labeled structure that transmits nerve signals along the length of the neuron?
A) cell body/2
B) myelin sheath/3
C) myelin sheath/4
D) axon/5
E) axon/6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
An axon is to a telephone line as myelin is to _______.
A) a telephone
B) a telephone switchboard
C) rubber wire insulation
D) telephone poles
E) a telephone jack
A) a telephone
B) a telephone switchboard
C) rubber wire insulation
D) telephone poles
E) a telephone jack

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
________ are a fatty layer insulating neurons and increasing efficiency.
A) Axon hillocks
B) Cell bodies
C) Dendrites
D) Axon terminals
E) Myelin sheaths
A) Axon hillocks
B) Cell bodies
C) Dendrites
D) Axon terminals
E) Myelin sheaths

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The support cells protecting neurons are called _______ cells.
A) glial
B) myelin
C) axial
D) neuroblasts
E) axons
A) glial
B) myelin
C) axial
D) neuroblasts
E) axons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Sensory input comes into a neuron at the _______.
A) axon hillocks
B) cell bodies
C) dendrites
D) axon terminals
E) myelin sheaths
A) axon hillocks
B) cell bodies
C) dendrites
D) axon terminals
E) myelin sheaths

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is an action potential?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Use the diagram to answer Questions 31-35.

Which of the labeled structures is the cell body?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Which of the labeled structures is the cell body?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Axon is to electrical cord as _________ is to electrical plug.
A) sensory neuron
B) motor neuron
C) myelin
D) axon terminal
E) A and B
A) sensory neuron
B) motor neuron
C) myelin
D) axon terminal
E) A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Motor neurons _______.
A) control the contraction of skeletal muscle
B) control the contraction of cardiac muscle
C) are part of the central nervous system
D) A and B
E) A, B, and C
A) control the contraction of skeletal muscle
B) control the contraction of cardiac muscle
C) are part of the central nervous system
D) A and B
E) A, B, and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the role of the myelin sheath in a neuron?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When a neuron is activated,it goes from having _______ internal charge to having _______ internal charge.
A) a positive; a more positive
B) a negative; a more negative
C) a positive; a negative
D) a negative; a positive
E) a positive; no
A) a positive; a more positive
B) a negative; a more negative
C) a positive; a negative
D) a negative; a positive
E) a positive; no

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When a neuron is activated,_______ ions rush into the cell.
A) chloride
B) boron
C) sodium
D) potassium
E) phosphate
A) chloride
B) boron
C) sodium
D) potassium
E) phosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Two neurons interact with each other at the _______.
A) axon hillocks
B) cell bodies
C) dendrites
D) axon terminals
E) myelin sheaths
A) axon hillocks
B) cell bodies
C) dendrites
D) axon terminals
E) myelin sheaths

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Use the diagram to answer Questions 31-35.

Which of the following gives the name and number of the labeled structure that insulates the axon and makes neuronal signaling more efficient?
A) axon/6
B) axon/4
C) myelin sheath/4
D) myelin sheath/6
E) cell body/3

Which of the following gives the name and number of the labeled structure that insulates the axon and makes neuronal signaling more efficient?
A) axon/6
B) axon/4
C) myelin sheath/4
D) myelin sheath/6
E) cell body/3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Use the diagram to answer Questions 31-35.

Which of the labeled structures are the dendrites?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6

Which of the labeled structures are the dendrites?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The root word in dendrite means "tree." Explain why this is an appropriate name.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The nucleus of a neuron is found in the _______.
A) axon hillocks
B) cell body
C) dendrites
D) axon terminals
E) myelin sheaths
A) axon hillocks
B) cell body
C) dendrites
D) axon terminals
E) myelin sheaths

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A bundle of specialized cells that transmit information are called _______.
A) an interneuron
B) the central nervous system
C) a cell body
D) the corpus luteus
E) a nerve
A) an interneuron
B) the central nervous system
C) a cell body
D) the corpus luteus
E) a nerve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Use the diagram to answer Questions 31-35.

Which of the following gives the name and number of the labeled structure(s)that communicate(s)with the next cell in the signaling pathway?
A) dendrites/1
B) axon terminals/1
C) dendrites/6
D) axon terminals/6
E) cell body/3

Which of the following gives the name and number of the labeled structure(s)that communicate(s)with the next cell in the signaling pathway?
A) dendrites/1
B) axon terminals/1
C) dendrites/6
D) axon terminals/6
E) cell body/3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is NOT part of the limbic system?
A) prefrontal cortex
B) hypothalamus
C) hippocampus
D) amygdala
E) thalamus
A) prefrontal cortex
B) hypothalamus
C) hippocampus
D) amygdala
E) thalamus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The part of the brain that receives and interprets sensory input is the _______.
A) thalamus
B) brain stem
C) cerebrum
D) cerebellum
E) pons
A) thalamus
B) brain stem
C) cerebrum
D) cerebellum
E) pons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is the diencephalon?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Explain the steps required for smoking to cause a feeling of pleasure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The amygdala processes _______.
A) temperature fluctuations
B) input from the olfactory nerves
C) fear and anxiety
D) the sex drive
E) memory and learning
A) temperature fluctuations
B) input from the olfactory nerves
C) fear and anxiety
D) the sex drive
E) memory and learning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Release of dopamine in the brain leads to feelings of _______.
A) anxiety
B) lethargy
C) pleasure
D) fear
E) loathing
A) anxiety
B) lethargy
C) pleasure
D) fear
E) loathing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Action potentials travel down axons because _______.
A) sensory signals stimulate axons at many points along their lengths
B) potassium moves rapidly down the length of the axon, triggering action potentials as it does so
C) sodium moves rapidly down the length of the axon, triggering action potentials as it does so
D) positive sodium ions entering the neuron at one spot trigger an action potential at a neighboring spot on the membrane
E) positive potassium ions entering the neuron at one spot trigger an action potential at a neighboring spot on the membrane
A) sensory signals stimulate axons at many points along their lengths
B) potassium moves rapidly down the length of the axon, triggering action potentials as it does so
C) sodium moves rapidly down the length of the axon, triggering action potentials as it does so
D) positive sodium ions entering the neuron at one spot trigger an action potential at a neighboring spot on the membrane
E) positive potassium ions entering the neuron at one spot trigger an action potential at a neighboring spot on the membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An action potential at one point along a neuron's membrane ends when _______.
A) sodium channels open and sodium enters the neuron
B) sodium channels open and sodium exits the neuron
C) potassium channels open and potassium enters the neuron
D) potassium channels open and potassium exits the neuron
E) sodium channels close and sodium is pumped out of the neuron
A) sodium channels open and sodium enters the neuron
B) sodium channels open and sodium exits the neuron
C) potassium channels open and potassium enters the neuron
D) potassium channels open and potassium exits the neuron
E) sodium channels close and sodium is pumped out of the neuron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The largest part of the forebrain is the _______.
A) thalamus
B) brain stem
C) cerebrum
D) cerebellum
E) pons
A) thalamus
B) brain stem
C) cerebrum
D) cerebellum
E) pons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Nicotine causes a release of _______ in the brain.
A) melatonin
B) boron
C) neurons
D) dopamine
E) ephedrine
A) melatonin
B) boron
C) neurons
D) dopamine
E) ephedrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The proper path for an action potential is _________.
A) axon terminals to axon to dendrites
B) axon to axon terminals to dendrites
C) dendrites to axon terminals to axon
D) dendrites to axon to axon terminals
E) Either A or D
A) axon terminals to axon to dendrites
B) axon to axon terminals to dendrites
C) dendrites to axon terminals to axon
D) dendrites to axon to axon terminals
E) Either A or D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The region of the brain involved in learning and memory is the _______.
A) pons
B) cerebellum
C) thalamus
D) medulla
E) hippocampus
A) pons
B) cerebellum
C) thalamus
D) medulla
E) hippocampus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An action potential begins when,in response to a stimulus,_______.
A) sodium channels open and sodium enters the neuron
B) sodium channels open and sodium exits the neuron
C) potassium channels open and potassium enters the neuron
D) potassium channels open and potassium exits the neuron
E) sodium channels close and sodium is pumped out of the neuron
A) sodium channels open and sodium enters the neuron
B) sodium channels open and sodium exits the neuron
C) potassium channels open and potassium enters the neuron
D) potassium channels open and potassium exits the neuron
E) sodium channels close and sodium is pumped out of the neuron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In the propagation of an action potential,the entering of ________ into the neuron stimulates _________.
A)sodium ions; entering of more sodium ions
B)potassium ions; entering of sodium ions
C)sodium ions; entering of potassium ions
D)A and C.
E)None of the above.
A)sodium ions; entering of more sodium ions
B)potassium ions; entering of sodium ions
C)sodium ions; entering of potassium ions
D)A and C.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The region of the brain that regulates homeostatic functions and includes the thalamus and hypothalamus is the _______.
A) diencephalon
B) encephalartos
C) medulla
D) parietal lobe
E) pons
A) diencephalon
B) encephalartos
C) medulla
D) parietal lobe
E) pons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The arrival of an action potential at an axon terminal stimulates _______.
A) the release of sodium ions
B) the uptake of neurotransmitters
C) the release of neurotransmitters
D) A and B
E) A and C
A) the release of sodium ions
B) the uptake of neurotransmitters
C) the release of neurotransmitters
D) A and B
E) A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An action potential is best defined as _______.
A) the difference in charge across a resting neuron due to the distribution of ions across the neuron's membrane
B) the opening of sodium channels in response to a stimulus
C) the closing of sodium channels and the opening of potassium channels
D) an electrical signal within a neuron caused by the movement of ions
E) None of the above.
A) the difference in charge across a resting neuron due to the distribution of ions across the neuron's membrane
B) the opening of sodium channels in response to a stimulus
C) the closing of sodium channels and the opening of potassium channels
D) an electrical signal within a neuron caused by the movement of ions
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A resting neuron _______.
A) is more positively charged on the outside of its membrane than on the inside
B) is more negatively charged on the outside of its membrane than on the inside
C) is positively charged on both sides of the membrane
D) is negatively charged on both sides of the membrane
E) is electrically neutral
A) is more positively charged on the outside of its membrane than on the inside
B) is more negatively charged on the outside of its membrane than on the inside
C) is positively charged on both sides of the membrane
D) is negatively charged on both sides of the membrane
E) is electrically neutral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Compare an action potential to the sodium potassium pump.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What are the parts of the limbic system?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The primary neurotransmitter of addiction is _______.
A) acetylcholine (Ach)
B) nicotine
C) dopamine
D) egotamine
E) GABA
A) acetylcholine (Ach)
B) nicotine
C) dopamine
D) egotamine
E) GABA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Use the diagram to answer Questions 62-68.
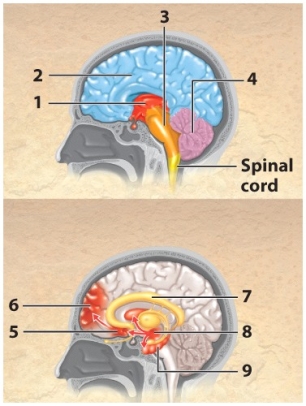
This is the limbic system.
A) 5
B) 6
C) 7
D) 8
E) 9

This is the limbic system.
A) 5
B) 6
C) 7
D) 8
E) 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Neurotransmitters are released _______.
A) into the next neuron
B) into the synaptic cleft
C) right before an action potential reaches the synaptic region
D) whenever magnesium ions enter the neuron
E) into interneuron vesicles
A) into the next neuron
B) into the synaptic cleft
C) right before an action potential reaches the synaptic region
D) whenever magnesium ions enter the neuron
E) into interneuron vesicles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When you step on a nail,a series of electrical signals are generated that tell you to raise your foot,but also that signal pain and tell you to change your balance and strengthen your other leg.Explain this,using the following terms: peripheral nervous system,pain neuron,central nervous system,motor neuron,axon terminal,synaptic cleft,action potential,and neurotransmitter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the diagram to answer Questions 62-68.

This region is involved in memory,learning,and the processing of emotions.
A) 4
B) 6
C) 7
D) 8
E) 9

This region is involved in memory,learning,and the processing of emotions.
A) 4
B) 6
C) 7
D) 8
E) 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The region between two neurons is known as the _______.
A) synapse
B) axon canyon
C) synaptic cleft
D) neurotransmitter
E) synaptic vacuole
A) synapse
B) axon canyon
C) synaptic cleft
D) neurotransmitter
E) synaptic vacuole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
List and describe the steps by which a neuron transmits an action potential (AP)to a neighboring cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the diagram to answer Questions 62-68.

This is the brain stem.
A) 1
B) 3
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7

This is the brain stem.
A) 1
B) 3
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Use the diagram to answer Question 78.
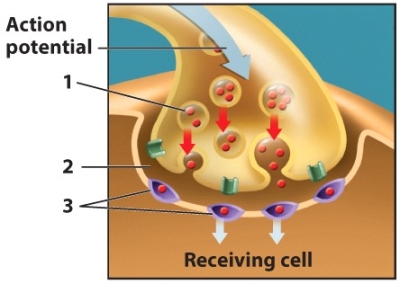
Structures 1,2,and 3 on the diagram are,in order,_______.
A) neurotransmitter receptor, synaptic cleft, synapse
B) neurotransmitter, neurotransmitter receptor, synaptic cleft
C) dopamine, synaptic cleft, VTA
D) neurotransmitter, synaptic cleft, sodium channel
E) neurotransmitter, synaptic cleft, neurotransmitter receptor

Structures 1,2,and 3 on the diagram are,in order,_______.
A) neurotransmitter receptor, synaptic cleft, synapse
B) neurotransmitter, neurotransmitter receptor, synaptic cleft
C) dopamine, synaptic cleft, VTA
D) neurotransmitter, synaptic cleft, sodium channel
E) neurotransmitter, synaptic cleft, neurotransmitter receptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The synaptic cleft is the area where _______.
A) an axon terminal nearly touches a receiving neuron
B) the electrical charge of an action potential moves through an axon to the receiving neuron
C) neurotransmitters are released to stimulate a receiving neuron
D) A and C
E) B and C
A) an axon terminal nearly touches a receiving neuron
B) the electrical charge of an action potential moves through an axon to the receiving neuron
C) neurotransmitters are released to stimulate a receiving neuron
D) A and C
E) B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Use the diagram to answer Questions 62-68.

This is the prefrontal cortex.
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7

This is the prefrontal cortex.
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
It is TRUE to say that _______.
A)sodium ions; entering of more sodium ions
B)potassium ions; entering of sodium ions
C)sodium ions; entering of potassium ions
D)A and C.
E)None of the above.
A)sodium ions; entering of more sodium ions
B)potassium ions; entering of sodium ions
C)sodium ions; entering of potassium ions
D)A and C.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Use the diagram to answer Questions 62-68.

This region controls higher-level functions like thinking.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

This region controls higher-level functions like thinking.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A pharmaceutical company is developing an anti-addiction drug that lowers dopamine reception in the limbic system.This drug will most likely _________.
A)work very well because the limbic system is one of the main centers of the brain responsible for addiction
B)not work very well because lowered dopamine release is caused by most drugs of abuse
C)work very well because reducing dopamine sensitivity should help people break their addiction
D)not work very well because many different regions in the brain are involved in addiction
E)A and C.
A)work very well because the limbic system is one of the main centers of the brain responsible for addiction
B)not work very well because lowered dopamine release is caused by most drugs of abuse
C)work very well because reducing dopamine sensitivity should help people break their addiction
D)not work very well because many different regions in the brain are involved in addiction
E)A and C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The primary neurotransmitter of addiction is produced in the _______ and affects the _______.
A) prefrontal cortex; limbic system
B) nucleus accumbens; limbic system and prefrontal cortex
C) cerebellum; nucleus accumbens, prefrontal cortex, and limbic system
D) ventral tegmental area; nucleus accumbens, prefrontal cortex, and limbic system
E) ventral tegmental area; hippocampus
A) prefrontal cortex; limbic system
B) nucleus accumbens; limbic system and prefrontal cortex
C) cerebellum; nucleus accumbens, prefrontal cortex, and limbic system
D) ventral tegmental area; nucleus accumbens, prefrontal cortex, and limbic system
E) ventral tegmental area; hippocampus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Use the diagram to answer Questions 62-68.

This region controls movement,coordination,and balance.
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7

This region controls movement,coordination,and balance.
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The ________ is responsible for conscious thought,whereas the ________ is involved with coordination of movement.
A) brainstem; cerebellum
B) cerebrum; cerebellum
C) limbic system; ventral tegumental area
D) cerebrum; diencephalon
E) limbic system; prefrontal cortex
A) brainstem; cerebellum
B) cerebrum; cerebellum
C) limbic system; ventral tegumental area
D) cerebrum; diencephalon
E) limbic system; prefrontal cortex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Use the diagram to answer Questions 62-68.

This is the diencephalon.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

This is the diencephalon.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What is a neurotransmitter?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The _________ is sometimes referred to as the "old brain" because it is evolutionarily the oldest and controls basic body functions like heart rate and unconscious breathing.
A) cerebellum
B) cerebrum
C) cerebral cortex
D) brain stem
E) ventral tegumental area
A) cerebellum
B) cerebrum
C) cerebral cortex
D) brain stem
E) ventral tegumental area

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



