Deck 12: Scheduling Operations
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/42
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Scheduling Operations
1
According to Goldratt,
A) an hour lost at the bottleneck is an hour lost for the entire system.
B) a product coming out of a non-bottleneck is precious and should not be wasted.
C) maximizing the efficiency of all resources would generate money for the company.
D) utilization, productivity, and operating expenses are the three vital metrics of a process.
A) an hour lost at the bottleneck is an hour lost for the entire system.
B) a product coming out of a non-bottleneck is precious and should not be wasted.
C) maximizing the efficiency of all resources would generate money for the company.
D) utilization, productivity, and operating expenses are the three vital metrics of a process.
an hour lost at the bottleneck is an hour lost for the entire system.
2
The reason(s)for batch scheduling being a complex management problem is/are
A) irregular flow of units with many starts and stops.
B) layout of the batch process by machine group or skills into work centers.
C) batches result in inventory or people waiting in queues.
D) all of the above.
A) irregular flow of units with many starts and stops.
B) layout of the batch process by machine group or skills into work centers.
C) batches result in inventory or people waiting in queues.
D) all of the above.
all of the above.
3
Which of the following statements concerning scheduling is INCORRECT?
A) Scheduling decisions allocate available capacity to jobs, activities, tasks, or customers.
B) Scheduling is typically performed prior to aggregate planning.
C) Scheduling results in a time-phased plan, representing what is to be done, when it should be done, who will do the work, and the equipment required for the work.
D) Scheduling seeks to resolve several conflicting objectives, including high efficiency, low inventories, and good customer service.
A) Scheduling decisions allocate available capacity to jobs, activities, tasks, or customers.
B) Scheduling is typically performed prior to aggregate planning.
C) Scheduling results in a time-phased plan, representing what is to be done, when it should be done, who will do the work, and the equipment required for the work.
D) Scheduling seeks to resolve several conflicting objectives, including high efficiency, low inventories, and good customer service.
Scheduling is typically performed prior to aggregate planning.
4
Which of the following statements is NOT true about the theory of constraints (TOC)?
A) It was developed by Goldratt in his book "The Goal."
B) Operations should help to increase sales, as long as capacity is available.
C) Identifying the bottleneck in a process is critical for improving the overall flow through the process.
D) Increased utilization of a non-bottleneck would improve the operating performance in a factory.
A) It was developed by Goldratt in his book "The Goal."
B) Operations should help to increase sales, as long as capacity is available.
C) Identifying the bottleneck in a process is critical for improving the overall flow through the process.
D) Increased utilization of a non-bottleneck would improve the operating performance in a factory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is a performance measure for a Gantt chart?
A) Makespan.
B) Machine utilization.
C) Sum of the wait times for each job.
D) All of the above.
A) Makespan.
B) Machine utilization.
C) Sum of the wait times for each job.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The overriding problem in batch scheduling is
A) regulating input.
B) controlling output.
C) managing queues.
D) assigning labor.
A) regulating input.
B) controlling output.
C) managing queues.
D) assigning labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Given the following information: 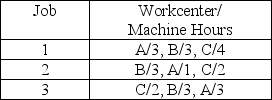 Use a Gantt chart to schedule the jobs in order 1,2,3 and assume that jobs cannot be split.What is the makespan?
Use a Gantt chart to schedule the jobs in order 1,2,3 and assume that jobs cannot be split.What is the makespan?
A) 12
B) 9
C) 14
D) 3
 Use a Gantt chart to schedule the jobs in order 1,2,3 and assume that jobs cannot be split.What is the makespan?
Use a Gantt chart to schedule the jobs in order 1,2,3 and assume that jobs cannot be split.What is the makespan?A) 12
B) 9
C) 14
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Scheduling deals with which three conflicting objectives?
A) High efficiency, high profits, and short lead time.
B) High profits, low inventories, and good customer service.
C) Low inventories, high efficiency, and good customer service.
D) Low inventories, good customer service, and short lead time.
A) High efficiency, high profits, and short lead time.
B) High profits, low inventories, and good customer service.
C) Low inventories, high efficiency, and good customer service.
D) Low inventories, good customer service, and short lead time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is NOT determined by Gantt charting?
A) The waiting time of each job.
B) Makespan of all jobs.
C) Resource utilization.
D) Finite capacity scheduling.
A) The waiting time of each job.
B) Makespan of all jobs.
C) Resource utilization.
D) Finite capacity scheduling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Shortest processing time (SPT)rule means
A) the job with the least processing time is worked on next.
B) the job needed at the bottleneck is worked on next.
C) the same as critical ratio.
D) none of the above.
A) the job with the least processing time is worked on next.
B) the job needed at the bottleneck is worked on next.
C) the same as critical ratio.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Scheduling systems answer all the following questions EXCEPT
A) What delivery date do I promise?
B) How much will the schedule cost?
C) When should I start each particular activity or task?
D) How do I make sure that the job is completed on time?
A) What delivery date do I promise?
B) How much will the schedule cost?
C) When should I start each particular activity or task?
D) How do I make sure that the job is completed on time?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Theory of constraints,as it applies to business systems,is based on which of the following premises?
A) A business has the obligation to consider its responsibility to society.
B) The goal of a business is to make money now and in the future.
C) The goal of a business is to make inventory.
D) The goal of a business is to eliminate all constraints.
A) A business has the obligation to consider its responsibility to society.
B) The goal of a business is to make money now and in the future.
C) The goal of a business is to make inventory.
D) The goal of a business is to eliminate all constraints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements is NOT true about finite capacity scheduling (FCS)?
A) FCS is an extension of Gantt chart methods.
B) FCS requires that jobs be loaded backward from due dates to determine the capacity required at each work center.
C) FCS assumes that jobs are scheduled through a number of work centers, each with one or more machines.
D) In FCS, attention is paid to scarce resources to facilitate job flow and to improve the performance of the shop.
A) FCS is an extension of Gantt chart methods.
B) FCS requires that jobs be loaded backward from due dates to determine the capacity required at each work center.
C) FCS assumes that jobs are scheduled through a number of work centers, each with one or more machines.
D) In FCS, attention is paid to scarce resources to facilitate job flow and to improve the performance of the shop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Critical ratio is
A) the ratio of processing time to idle time of the process.
B) the ratio of remaining time until due date to the remaining processing time.
C) greater than 1 if the job is behind schedule.
D) all of the above.
A) the ratio of processing time to idle time of the process.
B) the ratio of remaining time until due date to the remaining processing time.
C) greater than 1 if the job is behind schedule.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the language of theory of constraints,inventory is
A) the rate at which the system generates money through sales.
B) equal to the number of orders shipped.
C) the raw material value of any goods being held in inventory.
D) the sales of the plant minus the cost of raw materials used to produce those sales.
A) the rate at which the system generates money through sales.
B) equal to the number of orders shipped.
C) the raw material value of any goods being held in inventory.
D) the sales of the plant minus the cost of raw materials used to produce those sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Aggregate planning and scheduling differ in that
A) the former ensures that capacity is efficiently used, whereas the latter is the acquisition of resources.
B) the former is short term, whereas the latter is medium term.
C) the former is last in the hierarchy of capacity planning decisions, and the latter is first.
D) the former deals with acquiring resources, and the latter deals with allocating resources.
A) the former ensures that capacity is efficiently used, whereas the latter is the acquisition of resources.
B) the former is short term, whereas the latter is medium term.
C) the former is last in the hierarchy of capacity planning decisions, and the latter is first.
D) the former deals with acquiring resources, and the latter deals with allocating resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
For services,the most common priority dispatch rule is
A) critical ratio.
B) preemptive rule.
C) first come, first served.
D) shortest processing time.
A) critical ratio.
B) preemptive rule.
C) first come, first served.
D) shortest processing time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A bottleneck is
A) a resource that has the maximum capacity in the facility.
B) a resource whose capacity is less than the capacity of all other resources and whose capacity is less than the demand placed on it.
C) a resource that blocks labor productivity.
D) a resource that has the fastest processing time.
A) a resource that has the maximum capacity in the facility.
B) a resource whose capacity is less than the capacity of all other resources and whose capacity is less than the demand placed on it.
C) a resource that blocks labor productivity.
D) a resource that has the fastest processing time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Lead time for completion of a job is a function of
A) capacity and demand.
B) capacity and priority decisions.
C) capacity and supply decisions.
D) none of the above.
A) capacity and demand.
B) capacity and priority decisions.
C) capacity and supply decisions.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The theory of constraints (TOC)is
A) a strategic technique primarily used to reduce waste.
B) a strategic technique used to help firms effectively improve the rate at which raw materials are converted to finished goods and then money through sales.
C) a strategic technique used to balance capacity across all resources.
D) all of the above.
A) a strategic technique primarily used to reduce waste.
B) a strategic technique used to help firms effectively improve the rate at which raw materials are converted to finished goods and then money through sales.
C) a strategic technique used to balance capacity across all resources.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
First come,first served is widely used in both service and manufacturing firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Starting with a due date and scheduling a job through work centers so that the job finishes at each work center just in time for the next center is called
A) forward scheduling.
B) backward scheduling.
C) theory of constraints scheduling.
D) batch scheduling.
A) forward scheduling.
B) backward scheduling.
C) theory of constraints scheduling.
D) batch scheduling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A bottleneck should never be blocked or starved.Non-bottlenecks must function to keep the bottleneck at full utilization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A manufacturer of water filtration pumps is most likely to use which of the following?
A) A prioritization rule based on the price the customer paid.
B) A prioritization formula comparing time left before the job is due to the remaining processing time.
C) A prioritization formula based on the first come, first served rule.
D) All of the above.
A) A prioritization rule based on the price the customer paid.
B) A prioritization formula comparing time left before the job is due to the remaining processing time.
C) A prioritization formula based on the first come, first served rule.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the critical ratio of a job is greater than 1,the job is late.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following statements about batch scheduling is INCORRECT?
A) Dispatching is used to determine the job priority at a work center.
B) The priority of a job, once determined, does not change as it progresses through the production process.
C) Finite scheduling in batch systems recognizes the limited processing capacity of the facility and does not allocate more capacity than is available.
D) The theory of constraints argues that scheduling can be improved by increasing capacity at bottleneck operations.
A) Dispatching is used to determine the job priority at a work center.
B) The priority of a job, once determined, does not change as it progresses through the production process.
C) Finite scheduling in batch systems recognizes the limited processing capacity of the facility and does not allocate more capacity than is available.
D) The theory of constraints argues that scheduling can be improved by increasing capacity at bottleneck operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is a tactic for reducing demand pressure on a process bottleneck?
A) Place a quality inspection point immediately before the bottleneck.
B) Decrease the size of batches run through the bottleneck (assuming setup required).
C) Increase inventory levels at the non-bottleneck resources.
D) All of the above.
A) Place a quality inspection point immediately before the bottleneck.
B) Decrease the size of batches run through the bottleneck (assuming setup required).
C) Increase inventory levels at the non-bottleneck resources.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Concerning dispatching rules,which of the following is correct?
A) SPT is good at meeting due dates.
B) CR is good at efficiency and high throughput.
C) SPT is good at moving small jobs quickly through the process.
D) All of the above.
A) SPT is good at meeting due dates.
B) CR is good at efficiency and high throughput.
C) SPT is good at moving small jobs quickly through the process.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The greater the workload on a process,the less time jobs spend waiting in queues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Finite capacity scheduling
A) is an extension of the theory of constraints.
B) requires that jobs be scheduled whole (they cannot be split).
C) schedules jobs through a number of work centers, each with one or more machines.
D) has all of the above properties.
A) is an extension of the theory of constraints.
B) requires that jobs be scheduled whole (they cannot be split).
C) schedules jobs through a number of work centers, each with one or more machines.
D) has all of the above properties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The theory of constraints says that
A) queues should not be allowed to form in the plant.
B) bottleneck resources should be idle whenever possible.
C) the bottleneck is the most critical resource.
D) labor expense reduction should be the primary goal.
A) queues should not be allowed to form in the plant.
B) bottleneck resources should be idle whenever possible.
C) the bottleneck is the most critical resource.
D) labor expense reduction should be the primary goal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is NOT typically addressed by advanced planning and scheduling (APS)software?
A) Finite capacity scheduling.
B) Constraint-based scheduling.
C) Plant-floor level job dispatching.
D) All of the above are addressed by APS.
A) Finite capacity scheduling.
B) Constraint-based scheduling.
C) Plant-floor level job dispatching.
D) All of the above are addressed by APS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When scheduling in the short run,there is a trade-off between which of the following?
A) Efficiency and inventory levels.
B) Efficiency and customer service.
C) Inventory levels and quality.
D) Inventory levels and customer service.
A) Efficiency and inventory levels.
B) Efficiency and customer service.
C) Inventory levels and quality.
D) Inventory levels and customer service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A manufacturing company could increase the output rate of the bottleneck by running larger batches at the bottleneck (assuming another bottleneck in the plant does not interfere).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Finite capacity scheduling can be used to identify the bottleneck in a given process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Given no constraints,how many possible sequences are there if five jobs are in the queue for an operation?
A) 24
B) 25
C) 120
D) 720
A) 24
B) 25
C) 120
D) 720

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Under the theory of constraints,throughput is defined as the difference between the sales and the operating expenses of a plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The shortest process time (SPT)rule is better at meeting due dates when compared to the critical ratio rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The three most important metrics according to the theory of constraints are
A) throughput, utilization, and inventory.
B) inventory, efficiency, and utilization.
C) efficiency, utilization, and operating expenses.
D) throughput, inventory, and operating expenses.
A) throughput, utilization, and inventory.
B) inventory, efficiency, and utilization.
C) efficiency, utilization, and operating expenses.
D) throughput, inventory, and operating expenses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A bottleneck is the work center that has capacity greater than the demand placed on it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The preemptive rule in a manufacturing setting is based on remaining time until the due date and the remaining processing time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What are the steps that could be taken at a bottleneck resource to increase its capacity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



