Deck 14: Labour Markets and Income Inequality
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/119
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Labour Markets and Income Inequality
1
If you choose to stay in school beyond the compulsory minimum period,you are
A)realizing the benefits of your investment in human capital.
B)delaying your investment in human capital.
C)refusing to invest in your human capital.
D)investing further in your human capital.
E)wasting your time from an economic standpoint.
A)realizing the benefits of your investment in human capital.
B)delaying your investment in human capital.
C)refusing to invest in your human capital.
D)investing further in your human capital.
E)wasting your time from an economic standpoint.
investing further in your human capital.
2
One or two generations ago,fewer Canadians completed post-secondary training and education.One explanation for this is
A)a decrease in demand for more education in recent years.
B)wage differentials due to formal education have diminished over time.
C)a negative relationship between the acquisition of human capital and overall earnings.
D)the relative wage of more highly educated people has increased in recent years.
E)that the opportunity cost of post-secondary education has increased.
A)a decrease in demand for more education in recent years.
B)wage differentials due to formal education have diminished over time.
C)a negative relationship between the acquisition of human capital and overall earnings.
D)the relative wage of more highly educated people has increased in recent years.
E)that the opportunity cost of post-secondary education has increased.
the relative wage of more highly educated people has increased in recent years.
3
Other things being equal,individuals working in relatively risky working conditions generally
A)earn higher wages due to the greater relative demand for these individuals.
B)earn higher wages due to the reduced supply of risk-taking individuals.
C)earn lower wages because of the scarcity of these jobs.
D)do not concern economists as these situations are uncommon.
E)work in perfectly competitive labour markets.
A)earn higher wages due to the greater relative demand for these individuals.
B)earn higher wages due to the reduced supply of risk-taking individuals.
C)earn lower wages because of the scarcity of these jobs.
D)do not concern economists as these situations are uncommon.
E)work in perfectly competitive labour markets.
earn higher wages due to the reduced supply of risk-taking individuals.
4
In terms of human capital,which of the following is the best example of an inherited skill?
A)a neurosurgeon who can perform brain surgery after many years of training
B)a retail worker who is able to work overtime each week
C)a worker who exercises is healthier and therefore more productive
D)a salesman doubles his sales after taking a training course
E)a music teacher who can carry a tune for the school choir
A)a neurosurgeon who can perform brain surgery after many years of training
B)a retail worker who is able to work overtime each week
C)a worker who exercises is healthier and therefore more productive
D)a salesman doubles his sales after taking a training course
E)a music teacher who can carry a tune for the school choir

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Labour-market discrimination results in a
A)lower supply in discriminating occupations and a higher supply in non-discriminating occupations.
B)higher supply in discriminating occupations and a lower supply in non-discriminating occupations.
C)lower supply in all occupations.
D)lower demand in all occupations.
E)higher demand in both occupations.
A)lower supply in discriminating occupations and a higher supply in non-discriminating occupations.
B)higher supply in discriminating occupations and a lower supply in non-discriminating occupations.
C)lower supply in all occupations.
D)lower demand in all occupations.
E)higher demand in both occupations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In recent years,some business schools in Canada have begun charging tuition of close to $35 000 per year for a graduate degree,whereas Arts faculties charge much lower tuition for their graduate degrees.Students are prepared to pay the high tuition in a business school because
A)the expected payoff in terms of higher future wages is large.
B)the cost of providing the business education is far higher than the cost of the Arts education.
C)the marginal revenue product of a business degree is lower than the marginal revenue product of an Arts degree.
D)the marginal cost of a business degree is less than the marginal benefit of a business degree.
E)they recognize that the investment in human capital is not worthwhile.
A)the expected payoff in terms of higher future wages is large.
B)the cost of providing the business education is far higher than the cost of the Arts education.
C)the marginal revenue product of a business degree is lower than the marginal revenue product of an Arts degree.
D)the marginal cost of a business degree is less than the marginal benefit of a business degree.
E)they recognize that the investment in human capital is not worthwhile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Wage differentials due to cross-worker differences in human capital
A)are not justifiable on efficiency grounds.
B)will persist in competitive equilibrium.
C)are not an important source of observed wage differentials.
D)are an example of economic distortions due to monopoly power.
E)exist because of distortions in labour markets.
A)are not justifiable on efficiency grounds.
B)will persist in competitive equilibrium.
C)are not an important source of observed wage differentials.
D)are an example of economic distortions due to monopoly power.
E)exist because of distortions in labour markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The table below shows the labour demand and labour supply schedules in a competitive labour market.
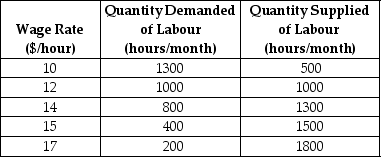 TABLE 14-1
TABLE 14-1
Refer to Table 14-1.In a competitive labour market that clears,the equilibrium employment level would be
A)400 units.
B)500 units.
C)800 units.
D)1000 units.
E)1300 units.
 TABLE 14-1
TABLE 14-1Refer to Table 14-1.In a competitive labour market that clears,the equilibrium employment level would be
A)400 units.
B)500 units.
C)800 units.
D)1000 units.
E)1300 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The table below shows the labour demand and labour supply schedules in a competitive labour market.
 TABLE 14-1
TABLE 14-1
Refer to Table 14-1.If the wage rate is $15 per hour,how many hours per month are supplied to this market but are not actually employed?
A)0
B)400
C)1000
D)1100
E)1500
 TABLE 14-1
TABLE 14-1Refer to Table 14-1.If the wage rate is $15 per hour,how many hours per month are supplied to this market but are not actually employed?
A)0
B)400
C)1000
D)1100
E)1500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
During recessions,individual investment in higher education typically ________ due to the relatively ________ opportunity cost of time spent in university.
A)rises; high
B)rises; low
C)falls; high
D)falls; low
E)stays constant; constant
A)rises; high
B)rises; low
C)falls; high
D)falls; low
E)stays constant; constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In a perfectly competitive labour market,all workers would earn the same wage if
A)the world was fair.
B)workers' education and experience were identical.
C)all jobs had the same working conditions.
D)regional variables mattered.
E)jobs and workers were identical in every way.
A)the world was fair.
B)workers' education and experience were identical.
C)all jobs had the same working conditions.
D)regional variables mattered.
E)jobs and workers were identical in every way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If labour markets were perfectly competitive,
A)all workers would eventually earn the same wage.
B)all workers would achieve the same levels of education and experience.
C)working conditions would be the same for all jobs.
D)wage differentials could still exist because of differences in workers and jobs.
E)discrimination could not create wage differentials.
A)all workers would eventually earn the same wage.
B)all workers would achieve the same levels of education and experience.
C)working conditions would be the same for all jobs.
D)wage differentials could still exist because of differences in workers and jobs.
E)discrimination could not create wage differentials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A typical firm hiring in a perfectly competitive labour market faces a marginal cost curve for labour that is
A)horizontal.
B)vertical.
C)equal to the supply curve of the firm.
D)parallel to the firm's marginal cost curve for its product.
E)downward sloping.
A)horizontal.
B)vertical.
C)equal to the supply curve of the firm.
D)parallel to the firm's marginal cost curve for its product.
E)downward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Labour-market discrimination,which keeps one group of workers out of elite (E)occupations and limits them to ordinary (O)occupations,will have which of the following effects?
A)a decrease in supply and higher wages in the E occupations
B)more employment in the E occupations
C)a decrease in supply and lower wages in the O occupations
D)more unemployment in the E occupations
E)a decrease in supply and higher wages in the O occupation
A)a decrease in supply and higher wages in the E occupations
B)more employment in the E occupations
C)a decrease in supply and lower wages in the O occupations
D)more unemployment in the E occupations
E)a decrease in supply and higher wages in the O occupation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
One attempt to provide some minimum level of human capital for all citizens is a system of
A)compulsory and publicly financed education.
B)income taxation.
C)unionism.
D)comparable worth.
E)minimum wages.
A)compulsory and publicly financed education.
B)income taxation.
C)unionism.
D)comparable worth.
E)minimum wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
One possible reason for wage differentials is that
A)there are competitive forces operating in labour markets.
B)discrimination affects labour-market outcomes.
C)working conditions are the same for most jobs.
D)workers have more-or-less equal skills.
E)there is only a single national labour market.
A)there are competitive forces operating in labour markets.
B)discrimination affects labour-market outcomes.
C)working conditions are the same for most jobs.
D)workers have more-or-less equal skills.
E)there is only a single national labour market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Investment in human capital can be very costly to the individual,but it can also generate large returns.Canadian census data from 2007 show that average employment income for a university graduate is approximately ________ of the average employment income of a worker with no more than a high school diploma.
A)50%
B)125%
C)200%
D)300%
E)400%
A)50%
B)125%
C)200%
D)300%
E)400%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
All of the following are classified as human capital EXCEPT
A)education.
B)training.
C)gender.
D)health.
E)experience.
A)education.
B)training.
C)gender.
D)health.
E)experience.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Labour-market discrimination,which keeps one group of workers out of elite (E)occupations and limits them to ordinary (O)occupations,will have which of the following effects?
A)a decrease in supply and lower wages in the O occupations
B)an increase in supply and lower wages in the E occupations
C)an increase in supply and higher wages in the E occupations
D)a decrease in supply and lower wages in the E occupations
E)an increase in supply and lower wages in the O occupations
A)a decrease in supply and lower wages in the O occupations
B)an increase in supply and lower wages in the E occupations
C)an increase in supply and higher wages in the E occupations
D)a decrease in supply and lower wages in the E occupations
E)an increase in supply and lower wages in the O occupations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The table below shows the labour demand and labour supply schedules in a competitive labour market.
 TABLE 14-1
TABLE 14-1
Refer to Table 14-1.In this labour market,if the wage rate is $10 per hour,how many hours of labour per month are actually employed?
A)0
B)500
C)1000
D)1300
E)1850
 TABLE 14-1
TABLE 14-1Refer to Table 14-1.In this labour market,if the wage rate is $10 per hour,how many hours of labour per month are actually employed?
A)0
B)500
C)1000
D)1300
E)1850

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Some types of discrimination in the labour market will be limited by
A)the minimum wage.
B)entry of of discriminating firms into the market.
C)an increase in the number of individuals discriminated against.
D)the desire of firms to maximize profits.
E)greater monopoly power in the market.
A)the minimum wage.
B)entry of of discriminating firms into the market.
C)an increase in the number of individuals discriminated against.
D)the desire of firms to maximize profits.
E)greater monopoly power in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Suppose an island economy has only two labour markets - fishing (high skill)and farming (low skill).There are 1000 males and 1000 females in the labour force.There is an equal distribution of skilled and non-skilled workers among each sex. 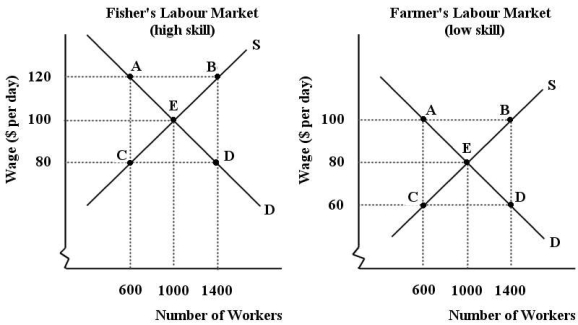 FIGURE 14-1
FIGURE 14-1
Refer to Figure 14-1.Suppose the employers in the fishers labour market begin to discriminate against male workers.Which of the following can we expect to occur in the farmers labour market?
A)There will be an equal flow of workers between the two markets,equilibrium will remain at point E and the wage at $80 per day.
B)The demand for labour curve shifts to the right until a new equilibrium is reached at point B and the wage rises to $100 per day.
C)The labour supply curve shifts to the left until a new equilibrium is reached at point A and the wage rises to $100 per day.
D)The demand for labour curve shifts to the left until a new equilibrium is reached at point C and the wage falls to $60 per day.
E)The labour supply curve shifts to the right until a new equilibrium is reached at point D and the wage falls to $60 per day.
 FIGURE 14-1
FIGURE 14-1Refer to Figure 14-1.Suppose the employers in the fishers labour market begin to discriminate against male workers.Which of the following can we expect to occur in the farmers labour market?
A)There will be an equal flow of workers between the two markets,equilibrium will remain at point E and the wage at $80 per day.
B)The demand for labour curve shifts to the right until a new equilibrium is reached at point B and the wage rises to $100 per day.
C)The labour supply curve shifts to the left until a new equilibrium is reached at point A and the wage rises to $100 per day.
D)The demand for labour curve shifts to the left until a new equilibrium is reached at point C and the wage falls to $60 per day.
E)The labour supply curve shifts to the right until a new equilibrium is reached at point D and the wage falls to $60 per day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A labour union can most easily raise the wages received by its members by
A)increasing the demand for the product.
B)decreasing the supply of labour from its members.
C)raising employment.
D)increasing the demand for labour.
E)improving productivity.
A)increasing the demand for the product.
B)decreasing the supply of labour from its members.
C)raising employment.
D)increasing the demand for labour.
E)improving productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the 1950s and 1960s,Arvida,Quebec,was basically a one-company town where Alcan was the sole buyer of labour services.This is a good example of
A)pure monopoly.
B)monopolistic competition.
C)oligopoly.
D)monopsony.
E)union power.
A)pure monopoly.
B)monopolistic competition.
C)oligopoly.
D)monopsony.
E)union power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Evidence suggests that some of the observed average female-male wage differential can be explained by
A)the nature of the jobs and differences in acquired human capital.
B)differences in the innate abilities between men and women.
C)higher marginal revenue product for female workers.
D)the labour-force participation rate of adult women being above that of adult men.
E)None of the above can explain part of the wage differentials.
A)the nature of the jobs and differences in acquired human capital.
B)differences in the innate abilities between men and women.
C)higher marginal revenue product for female workers.
D)the labour-force participation rate of adult women being above that of adult men.
E)None of the above can explain part of the wage differentials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If there is discrimination against some workers in market A but no discrimination in market B,then we can predict
1)a decrease in supply and higher wages in the A occupations.;
2)more employment in the A occupations.;
3)more unemployment in the B occupations if there is a binding minimum wage.
A)1 only
B)2 only
C)3 only
D)1 and 2
E)1 and 3
1)a decrease in supply and higher wages in the A occupations.;
2)more employment in the A occupations.;
3)more unemployment in the B occupations if there is a binding minimum wage.
A)1 only
B)2 only
C)3 only
D)1 and 2
E)1 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
As a seller of labour services,a labour union is a form of
A)monopoly.
B)monopsony.
C)oligopoly.
D)monopolistic competitor.
E)illegal cartel.
A)monopoly.
B)monopsony.
C)oligopoly.
D)monopolistic competitor.
E)illegal cartel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Suppose that a professional association strengthened the limits to entry into their profession and at the same time lengthened its required apprenticeship program.The likely effect would be that
A)the supply curve for labour would shift to the left.
B)the supply curve for labour would shift to the right.
C)both the demand and supply curves for labour would shift to the left.
D)the demand curve for labour would shift to the right.
E)there would be an increase in the quantity of labour supplied.
A)the supply curve for labour would shift to the left.
B)the supply curve for labour would shift to the right.
C)both the demand and supply curves for labour would shift to the left.
D)the demand curve for labour would shift to the right.
E)there would be an increase in the quantity of labour supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Certain professions limit the number of students who are eligible to enroll in their programs in university - engineering,architecture,dentistry,and law,for example.Other things being equal,what is one predicted effect of such restrictions?
A)increased wages across all segments of the labour market
B)decreased wages across all segments of the labour market
C)decreased wages in the labour market outside of these professions
D)increased wages in the labour market outside of these professions
E)there will be no effect on any wages
A)increased wages across all segments of the labour market
B)decreased wages across all segments of the labour market
C)decreased wages in the labour market outside of these professions
D)increased wages in the labour market outside of these professions
E)there will be no effect on any wages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If competitive labour market E discriminates against one group of workers and market O does not,we can predict an increase in
A)employment in market E.
B)wages in market E.
C)wages in market O.
D)the welfare of the average worker.
E)economy-wide wage rates.
A)employment in market E.
B)wages in market E.
C)wages in market O.
D)the welfare of the average worker.
E)economy-wide wage rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If there is only a single buyer in the labour market,that buyer is called
A)a monopolist.
B)a monopsonist.
C)an oligopolist.
D)an oligopsonist.
E)a single-product firm.
A)a monopolist.
B)a monopsonist.
C)an oligopolist.
D)an oligopsonist.
E)a single-product firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Suppose market E discriminates against one group of workers and market O does not.Unemployment in market O would result if
A)the free-market equilibrium wage in market O is below the legal minimum wage.
B)some workers are unwilling to work in E-market jobs.
C)there is no statutory minimum wage.
D)the supply curve in market O shifts to the left and wages are slow to adjust.
E)the demand curve in market O shifts to the right and wages are slow to adjust.
A)the free-market equilibrium wage in market O is below the legal minimum wage.
B)some workers are unwilling to work in E-market jobs.
C)there is no statutory minimum wage.
D)the supply curve in market O shifts to the left and wages are slow to adjust.
E)the demand curve in market O shifts to the right and wages are slow to adjust.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Suppose an island economy has only two labour markets - fishing (high skill)and farming (low skill).There are 1000 males and 1000 females in the labour force.There is an equal distribution of skilled and non-skilled workers among each sex.  FIGURE 14-1
FIGURE 14-1
Refer to Figure 14-1.Suppose the employers in the fishers labour market begin to discriminate against male workers,and we move to a new equilibrium in each market.In the absence of any government intervention in these markets,what forces might we expect to see over time?
1)All female workers will migrate to the fishers labour market due to the higher wage.
2)The discriminatory wage differential will tend to be eliminated by the pursuit of profit.
3)Some firm owners in the fishing labour market will find it profitable to hire high-skill males,thus reducing the wage differential.
A)1 only
B)2 only
C)3 only
D)1 and 2
E)2 and 3
 FIGURE 14-1
FIGURE 14-1Refer to Figure 14-1.Suppose the employers in the fishers labour market begin to discriminate against male workers,and we move to a new equilibrium in each market.In the absence of any government intervention in these markets,what forces might we expect to see over time?
1)All female workers will migrate to the fishers labour market due to the higher wage.
2)The discriminatory wage differential will tend to be eliminated by the pursuit of profit.
3)Some firm owners in the fishing labour market will find it profitable to hire high-skill males,thus reducing the wage differential.
A)1 only
B)2 only
C)3 only
D)1 and 2
E)2 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
To a monopsonist in a labour market,the average cost curve of labour
A)lies above the supply curve of labour.
B)lies below the supply curve of labour.
C)is the supply curve of labour,which lies below the marginal cost curve for labour.
D)is the marginal cost curve of labour when the supply curve is upward sloping.
E)coincides with the marginal cost curve of labour only below the profit-maximizing wage rate.
A)lies above the supply curve of labour.
B)lies below the supply curve of labour.
C)is the supply curve of labour,which lies below the marginal cost curve for labour.
D)is the marginal cost curve of labour when the supply curve is upward sloping.
E)coincides with the marginal cost curve of labour only below the profit-maximizing wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Suppose an island economy has only two labour markets - fishing (high skill)and farming (low skill).There are 1000 males and 1000 females in the labour force.There is an equal distribution of skilled and non-skilled workers among each sex.  FIGURE 14-1
FIGURE 14-1
Refer to Figure 14-1.Suppose the employers in the fishers labour market begin to discriminate against male workers.Which of the following can we expect to occur in the fishers labour market?
A)There will be an equal flow of workers between the two markets,equilibrium will remain at point E and the wage at $100 per day.
B)The demand for labour curve shifts to the right until a new equilibrium is reached at point B and the wage rises to $120 per day.
C)The labour supply curve shifts to the left until a new equilibrium is reached at point A and the wage rises to $120 per day.
D)The demand for labour curve shifts to the left until a new equilibrium is reached at point C and the wage falls to $80 per day.
E)The labour supply curve shifts to the right until a new equilibrium is reached at point D and the wage falls to $80 per day.
 FIGURE 14-1
FIGURE 14-1Refer to Figure 14-1.Suppose the employers in the fishers labour market begin to discriminate against male workers.Which of the following can we expect to occur in the fishers labour market?
A)There will be an equal flow of workers between the two markets,equilibrium will remain at point E and the wage at $100 per day.
B)The demand for labour curve shifts to the right until a new equilibrium is reached at point B and the wage rises to $120 per day.
C)The labour supply curve shifts to the left until a new equilibrium is reached at point A and the wage rises to $120 per day.
D)The demand for labour curve shifts to the left until a new equilibrium is reached at point C and the wage falls to $80 per day.
E)The labour supply curve shifts to the right until a new equilibrium is reached at point D and the wage falls to $80 per day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The following statements describe the adverse effects suffered by groups subject to labour-market discrimination.Which of the statements is false?
A)They will be more likely to experience spells of unemployment.
B)Their children's ability and willingness to invest in human capital will be less on average than those of children of other groups.
C)They will receive lower wages on average than other groups.
D)Their human capital will increase.
E)The discriminatory wage differentials will persist as long as the discrimination exists.
A)They will be more likely to experience spells of unemployment.
B)Their children's ability and willingness to invest in human capital will be less on average than those of children of other groups.
C)They will receive lower wages on average than other groups.
D)Their human capital will increase.
E)The discriminatory wage differentials will persist as long as the discrimination exists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Suppose a labour union enters a competitive labour market and is successful in raising wages above the competitive equilibrium level.In this situation,
A)each firm in the industry will face a horizontal supply curve for labour at the union wage,up to the maximum quantity of labour that is prepared to work at that wage.
B)those workers already employed will earn a lower wage than before.
C)employment in the industry will surely increase.
D)the market supply curve for labour will be upward sloping over its entire range.
E)the number of firms in the industry will increase and the demand for labour curve will shift to the right,causing a subsequent increase in the wage.
A)each firm in the industry will face a horizontal supply curve for labour at the union wage,up to the maximum quantity of labour that is prepared to work at that wage.
B)those workers already employed will earn a lower wage than before.
C)employment in the industry will surely increase.
D)the market supply curve for labour will be upward sloping over its entire range.
E)the number of firms in the industry will increase and the demand for labour curve will shift to the right,causing a subsequent increase in the wage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Certain professions limit the number of students who are eligible to enroll in their programs in university - engineering,architecture,dentistry,and law,for example.What is the predicted effect of such a policy in each of these professions?
A)An increase in supply and a wage that is lower than it otherwise would be.
B)A reduction in supply and a wage that is lower than it otherwise would be.
C)An increase in supply and a wage that is higher than it otherwise would be.
D)A reduction in supply and a wage that is higher than it otherwise would be.
E)These professions are a relatively small portion of the labour market and so there will be no detectible change in wages.
A)An increase in supply and a wage that is lower than it otherwise would be.
B)A reduction in supply and a wage that is lower than it otherwise would be.
C)An increase in supply and a wage that is higher than it otherwise would be.
D)A reduction in supply and a wage that is higher than it otherwise would be.
E)These professions are a relatively small portion of the labour market and so there will be no detectible change in wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Suppose an island economy has only two labour markets - fishing (high skill)and farming (low skill).There are 1000 males and 1000 females in the labour force.There is an equal distribution of skilled and non-skilled workers among each sex.  FIGURE 14-1
FIGURE 14-1
Refer to Figure 14-1.The two labour markets are each in a ________ equilibrium at point E.The wage differential between the industries is a(n)________ wage differential.
A)non-competitive; discriminatory
B)competitive; temporary
C)competitive; equilibrium
D)non-competitive; temporary
E)competitive; discriminatory
 FIGURE 14-1
FIGURE 14-1Refer to Figure 14-1.The two labour markets are each in a ________ equilibrium at point E.The wage differential between the industries is a(n)________ wage differential.
A)non-competitive; discriminatory
B)competitive; temporary
C)competitive; equilibrium
D)non-competitive; temporary
E)competitive; discriminatory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
For a monopsonist in a labour market,the firm's MC curve for labour lies ________ the competitive supply curve for labour; just as the marginal revenue curve for a monopolist lies ________ the demand curve for its product.
A)below; below
B)below; above
C)above; above
D)above; below
A)below; below
B)below; above
C)above; above
D)above; below

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A profit-maximizing monopsonist in a labour market will continue to hire labour until the
A)hourly wage of the labour is equated with its marginal cost.
B)hourly wage of the labour is equated with its average cost.
C)marginal revenue product of labour equals its marginal cost.
D)marginal cost of labour equals its average revenue.
E)marginal product of labour is maximized.
A)hourly wage of the labour is equated with its marginal cost.
B)hourly wage of the labour is equated with its average cost.
C)marginal revenue product of labour equals its marginal cost.
D)marginal cost of labour equals its average revenue.
E)marginal product of labour is maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Suppose your firm is a monopsonist hiring only one variable input.If you want to maximize profits,you will purchase that variable input up to the point where the
A)demand curve intersects the supply curve of the input.
B)MRP curve for the input intersects the marginal cost curve for the input.
C)wage rate is the highest.
D)marginal product of that input equals the price of one unit of the input.
E)cost of the input equals the profit generated by the employment of that input.
A)demand curve intersects the supply curve of the input.
B)MRP curve for the input intersects the marginal cost curve for the input.
C)wage rate is the highest.
D)marginal product of that input equals the price of one unit of the input.
E)cost of the input equals the profit generated by the employment of that input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
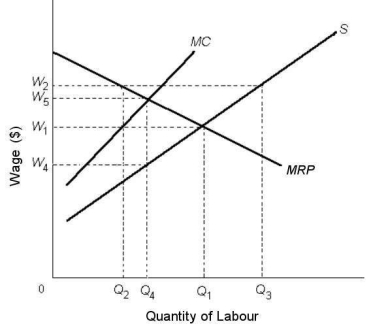 FIGURE 14-2
FIGURE 14-2Refer to Figure 14-2.Suppose the labour market is initially in a monopsonistic equilibrium.If a strong union is then formed and establishes a minimum wage of W1,
A)employment will decrease to Q2.
B)the wage rate and employment will both increase to their competitive levels.
C)the wage rate will increase but employment will decrease.
D)there will be an effect on either wages or employment but not both.
E)the wage rate will decrease but employment will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
 FIGURE 14-2
FIGURE 14-2Refer to Figure 14-2.Suppose the labour market is perfectly competitive.If a minimum wage of W4 is then established,the predicted change in the wage is
A)an increase in the wage paid.
B)a decrease in the wage paid.
C)no change in the wage paid.
D)a decrease equal to W1 - W4.
E)an increase equal to W1 - W4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The diagram below shows the supply and demand for labour in a hypothetical town in northern British Columbia,with only one employer,a logging company. 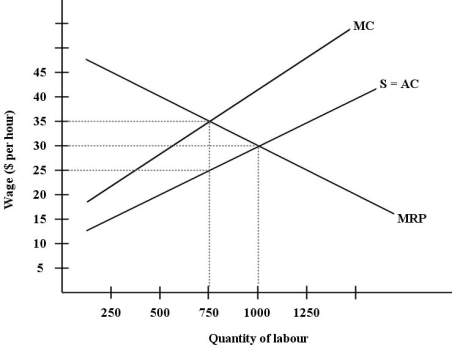 FIGURE 14-4
FIGURE 14-4
Refer to Figure 14-4.The wage paid by this monopsonistic firm will be ________ and employment will be ________.
A)below $25 per hour; below 750 units of labour
B)between $25 and $35 per hour; between 750 and 1000 units of labour
C)$30 per hour; 1000 units of labour
D)$25 per hour; 750 units of labour
E)$35 per hour; 750 units of labour
 FIGURE 14-4
FIGURE 14-4Refer to Figure 14-4.The wage paid by this monopsonistic firm will be ________ and employment will be ________.
A)below $25 per hour; below 750 units of labour
B)between $25 and $35 per hour; between 750 and 1000 units of labour
C)$30 per hour; 1000 units of labour
D)$25 per hour; 750 units of labour
E)$35 per hour; 750 units of labour

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Consider a small,remote town with only one employer - a gold mining company.Suppose the current work force is 875 workers,each of whom is paid $6000 per month.In order to attract one additional worker,the employer must increase the wage to $6025 per month.The marginal cost of this additional worker is
A)$21 875 per month.
B)$21 900 per month.
C)$27 900 per month.
D)$5.25 million per month.
E)$5.28 million per month.
A)$21 875 per month.
B)$21 900 per month.
C)$27 900 per month.
D)$5.25 million per month.
E)$5.28 million per month.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If we compare the wage rate and the level of employment achieved in a competitive labour market with those in a monopsonistic labour market,the latter will generate
A)a lower level of employment and a higher wage rate.
B)a higher level of employment and a lower wage.
C)a higher level of employment and a higher wage rate.
D)a lower level of employment and a lower wage.
E)the same outcomes as in a competitive labour market.
A)a lower level of employment and a higher wage rate.
B)a higher level of employment and a lower wage.
C)a higher level of employment and a higher wage rate.
D)a lower level of employment and a lower wage.
E)the same outcomes as in a competitive labour market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Suppose that the professional association of dentists reduces entry into their profession by lengthening the required training program.The likely effect is that
A)the supply curve of dentists will shift to the left.
B)the supply curve of dentists will shift to the right.
C)both the demand and supply curves for dentists will shift to the left.
D)the demand curve for dentists will shift to the right.
E)there will be an increase in the quantity of dentists supplied.
A)the supply curve of dentists will shift to the left.
B)the supply curve of dentists will shift to the right.
C)both the demand and supply curves for dentists will shift to the left.
D)the demand curve for dentists will shift to the right.
E)there will be an increase in the quantity of dentists supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
 FIGURE 14-2
FIGURE 14-2Refer to Figure 14-2.If the labour market were in a monopsonistic equilibrium,the predicted wage and number of workers employed would be
A)W4 and Q4.
B)W5 and Q4.
C)W2 and Q1.
D)W1 and Q2.
E)W1 and Q3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
 FIGURE 14-2
FIGURE 14-2Refer to Figure 14-2.Suppose the labour market is perfectly competitive.If a minimum wage of W5 were then established,the predicted effect would be which one of the following?
A)Q2 workers would be employed and unemployment would equal Q2Q3.
B)Employment would fall by the amount Q1Q4.
C)Employment would remain the same as in a competitive market.
D)Q3 workers would now be employed.
E)Q4 workers would be employed and there would be no unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The three diagrams below show the supply and demand for teenage babysitters in one local area.The initial supply curve is S0 in all cases. 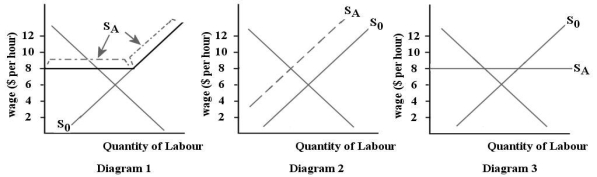 FIGURE 14-3
FIGURE 14-3
Refer to Figure 14-3.Suppose all of the teenage babysitters in one local area form an association and set a minimum age of 16 for working as a babysitter.Which diagram illustrates the new supply curve (SA)for babysitters?
A)diagram 1
B)diagram 2
C)diagram 3
D)none of the diagrams
E)any of the diagrams
 FIGURE 14-3
FIGURE 14-3Refer to Figure 14-3.Suppose all of the teenage babysitters in one local area form an association and set a minimum age of 16 for working as a babysitter.Which diagram illustrates the new supply curve (SA)for babysitters?
A)diagram 1
B)diagram 2
C)diagram 3
D)none of the diagrams
E)any of the diagrams

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Consider a monopsonistic labour market.One hundred units of labour will be supplied if the wage rate is $12,and 101 units of labour will be supplied if the wage rate is $14.The marginal cost of the 101st worker is
A)$14.
B)$140.
C)$214.
D)$1414.
E)Not enough information to know.
A)$14.
B)$140.
C)$214.
D)$1414.
E)Not enough information to know.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
 FIGURE 14-2
FIGURE 14-2Refer to Figure 14-2.In a perfectly competitive labour market,the equilibrium wage rate and the quantity of labour employed would be
A)W4 and Q4.
B)W2 and Q2.
C)W5 and Q5.
D)W1 and Q1.
E)W5 and Q4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
 FIGURE 14-2
FIGURE 14-2Refer to Figure 14-2.Suppose the labour market is in a monopsonistic equilibrium.If a minimum wage is then imposed at W5,the effect would be to
A)increase employment only.
B)waste policy effort,as there would be no effect whatsoever in the labour market.
C)increase wages and maintain employment but create a pool of unemployed workers.
D)increase wages and create a shortage of workers.
E)decrease wages but employment would remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Suppose we have a labour market with a monopsony employer in a town.Now suppose that all workers form a union and negotiate a wage with the employer.We refer to this as a situation of
A)double monopsony.
B)collective bargaining.
C)union-wage premium.
D)bilateral monopoly.
E)monopsony.
A)double monopsony.
B)collective bargaining.
C)union-wage premium.
D)bilateral monopoly.
E)monopsony.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
For a monopsonist that faces an upward-sloping labour supply curve,the marginal cost of labour curve will be ________ the supply curve because ________.
A)below; the increased wage necessary to attract an extra worker is paid to that worker alone
B)above; the increased wage necessary to attract an extra worker must be paid to everyone already employed
C)above; the average wage exceeds the marginal wage when the average wage is rising
D)the same as; the marginal cost of labour equals the average cost of labour
E)below; the extra labour supplied is less capable than previous units of labour supplied
A)below; the increased wage necessary to attract an extra worker is paid to that worker alone
B)above; the increased wage necessary to attract an extra worker must be paid to everyone already employed
C)above; the average wage exceeds the marginal wage when the average wage is rising
D)the same as; the marginal cost of labour equals the average cost of labour
E)below; the extra labour supplied is less capable than previous units of labour supplied

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Suppose that a regional health authority is the only employer of nurses,and further,suppose that nurses are not unionized.The 625 currently employed nurses are paid $27 per hour.To attract an additional nurse,the employer must increase the wage to $28 per hour.The marginal cost of this additional worker is
A)$653.
B)$28.
C)$17 500.
D)$17 528.
E)$27.
A)$653.
B)$28.
C)$17 500.
D)$17 528.
E)$27.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Consider a wage-setting union in an otherwise competitive labour market.If the union sets a wage above the competitive level,the effect will be
A)to raise wages for all workers who wish to work in the industry.
B)to increase the amount of employment in the industry.
C)to create a group of workers who would like to obtain jobs in the industry but cannot do so.
D)a level of employment which is the same as that at the competitive equilibrium wage.
E)to cause the labour supply curve to shift to the right.
A)to raise wages for all workers who wish to work in the industry.
B)to increase the amount of employment in the industry.
C)to create a group of workers who would like to obtain jobs in the industry but cannot do so.
D)a level of employment which is the same as that at the competitive equilibrium wage.
E)to cause the labour supply curve to shift to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The three diagrams below show the supply and demand for teenage babysitters in one local area.The initial supply curve is S0 in all cases.  FIGURE 14-3
FIGURE 14-3
Refer to Figure 14-3.Suppose all of the teenage babysitters in one local area form an association and set a minimum acceptable wage of $8 per hour.Which diagram illustrates the new supply curve (SA)for babysitters?
A)diagram 1
B)diagram 2
C)diagram 3
D)none of the diagrams
E)any of the diagrams
 FIGURE 14-3
FIGURE 14-3Refer to Figure 14-3.Suppose all of the teenage babysitters in one local area form an association and set a minimum acceptable wage of $8 per hour.Which diagram illustrates the new supply curve (SA)for babysitters?
A)diagram 1
B)diagram 2
C)diagram 3
D)none of the diagrams
E)any of the diagrams

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Consider a monopsonistic labour market.Ten units of labour will be supplied if the wage rate is $12,and 11 units of labour will be supplied if the wage rate is $14.The marginal cost of the eleventh worker is
A)$2.
B)$12.
C)between $12 and $14.
D)$14.
E)more than $14.
A)$2.
B)$12.
C)between $12 and $14.
D)$14.
E)more than $14.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Suppose there is a competitive market for retail workers at a large shopping mall that is large enough to constitute its own labour market.The labour demand curve is QD = 1000 - 20(w).The labour supply curve is QS = 400 + 40(w).Suppose that a union now successfully organizes the workers at this mall and obtains a wage rate of $11 (but does not affect the demand curve).The number of workers employed after unionization is
A)400.
B)780.
C)880.
D)1000.
E)Not determinable from the information provided.
A)400.
B)780.
C)880.
D)1000.
E)Not determinable from the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A legislated minimum wage is comparable to
A)bilateral monopoly.
B)a black-market price.
C)a rent control.
D)a price ceiling.
E)a price floor.
A)bilateral monopoly.
B)a black-market price.
C)a rent control.
D)a price ceiling.
E)a price floor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
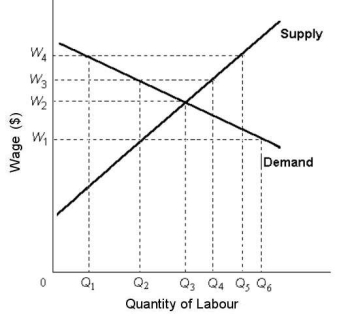 FIGURE 14-5
FIGURE 14-5Refer to Figure 14-5.Suppose this labour market is competitive.If a minimum wage of W4 is then imposed,the number of unemployed workers would be
A)0Q1.
B)Q5 - Q1.
C)Q3 - Q1.
D)0Q3.
E)0Q5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The diagram below shows the supply and demand for labour in a hypothetical town in northern British Columbia,with only one employer,a logging company.  FIGURE 14-4
FIGURE 14-4
Refer to Figure 14-4.Suppose this labour market is in a monopsonistic equilibrium.Then,suppose the provincial government of British Columbia imposes a minimum wage for employees in this industry of $38 per hour.What will be the effects on wages and employment?
A)wages will rise by $8 per hour and employment will fall below 750 units of labour
B)wages will rise by $3 per hour and employment will fall by 125 units of labour
C)wages will rise by $8 per hour and employment will remain unchanged
D)wages will rise by $13 per hour and employment will fall below 750 units of labour
E)wages will rise by $8 per hour and employment will fall by between 0 and 250 units of labour
 FIGURE 14-4
FIGURE 14-4Refer to Figure 14-4.Suppose this labour market is in a monopsonistic equilibrium.Then,suppose the provincial government of British Columbia imposes a minimum wage for employees in this industry of $38 per hour.What will be the effects on wages and employment?
A)wages will rise by $8 per hour and employment will fall below 750 units of labour
B)wages will rise by $3 per hour and employment will fall by 125 units of labour
C)wages will rise by $8 per hour and employment will remain unchanged
D)wages will rise by $13 per hour and employment will fall below 750 units of labour
E)wages will rise by $8 per hour and employment will fall by between 0 and 250 units of labour

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If a minimum wage is set above the free-market equilibrium wage in a competitive labour market,the labour market will experience an increase in wages and
A)employment will increase.
B)employment will decrease.
C)there will be no unemployment.
D)employment will remain the same.
E)there is an unpredictable effect on employment.
A)employment will increase.
B)employment will decrease.
C)there will be no unemployment.
D)employment will remain the same.
E)there is an unpredictable effect on employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The diagram below shows the supply and demand for labour in a hypothetical town in northern British Columbia,with only one employer,a logging company.  FIGURE 14-4
FIGURE 14-4
Refer to Figure 14-4.Compared to the outcome in a competitive labour market,the wage and employment outcome in this town's monopsonistic labour market are as follows:
A)wages are lower by $5 per hour and employment is lower by 250 units of labour.
B)wages and employment are both the same as the competitive outcome.
C)wages are higher by $10 per hour and employment is lower by 250 units of labour.
D)wages are lower by $10 per hour and employment is the same as the competitive outcome.
E)wages are the same as the competitive outcome and employment is higher by 250 units of labour.
 FIGURE 14-4
FIGURE 14-4Refer to Figure 14-4.Compared to the outcome in a competitive labour market,the wage and employment outcome in this town's monopsonistic labour market are as follows:
A)wages are lower by $5 per hour and employment is lower by 250 units of labour.
B)wages and employment are both the same as the competitive outcome.
C)wages are higher by $10 per hour and employment is lower by 250 units of labour.
D)wages are lower by $10 per hour and employment is the same as the competitive outcome.
E)wages are the same as the competitive outcome and employment is higher by 250 units of labour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The diagram below shows the supply and demand for labour in a hypothetical town in northern British Columbia,with only one employer,a logging company.  FIGURE 14-4
FIGURE 14-4
Refer to Figure 14-4.Suppose the workers in this town form a union to negotiate the wage rate with the firm.Economists refer to this situation as
A)a monopoly.
B)a unionized monopoly.
C)a competitive labour market.
D)a monopolistic labour market.
E)a bilateral monopoly.
 FIGURE 14-4
FIGURE 14-4Refer to Figure 14-4.Suppose the workers in this town form a union to negotiate the wage rate with the firm.Economists refer to this situation as
A)a monopoly.
B)a unionized monopoly.
C)a competitive labour market.
D)a monopolistic labour market.
E)a bilateral monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
 FIGURE 14-5
FIGURE 14-5Refer to Figure 14-5.Suppose this labour market is perfectly competitive.If a minimum wage of W1 is then imposed,the quantity of labour hired would be
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.
D)Q4.
E)Q5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Suppose there is a competitive market for retail workers at a large shopping mall that is large enough to constitute its own labour market.The labour demand curve is QD = 1000 - 20(w).The labour supply curve is QS = 400 + 40(w).Suppose that a union now successfully organizes the workers at this mall and obtains a wage rate of $13 (but does not affect the position of the demand curve).One result is
A)an increase in employment of 20 workers.
B)an increase in employment of 60 workers.
C)a decrease in employment of 100 workers.
D)a decrease in employment of 140 workers.
E)a decrease in employment of 60 workers.
A)an increase in employment of 20 workers.
B)an increase in employment of 60 workers.
C)a decrease in employment of 100 workers.
D)a decrease in employment of 140 workers.
E)a decrease in employment of 60 workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following statements about a legislated minimum wage is true?
A)In a competitive labour market,(if effective)it may increase wages and will increase employment.
B)In a monopsonistic labour market,(if effective)it may increase wage rates but it must decrease employment.
C)In a monopsonistic labour market,if set equal to the competitive wage,will increase wages and employment.
D)It will have the same wage and employment effects in competitive and monopsonistic labour markets.
E)It will have no effect if the market is monopsonistic.
A)In a competitive labour market,(if effective)it may increase wages and will increase employment.
B)In a monopsonistic labour market,(if effective)it may increase wage rates but it must decrease employment.
C)In a monopsonistic labour market,if set equal to the competitive wage,will increase wages and employment.
D)It will have the same wage and employment effects in competitive and monopsonistic labour markets.
E)It will have no effect if the market is monopsonistic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Suppose there is a competitive market for retail workers at a large shopping mall that is large enough to constitute its own labour market.The labour demand curve is QD = 1000 - 20(w).The labour supply curve is QS = 400 + 40(w).Suppose that a union now successfully organizes the workers at this mall and obtains a wage rate of $11 (but does not affect the demand curve).One result is
A)an increase in employment of 20 workers.
B)an increase in employment of 40 workers.
C)a decrease in employment of 20 workers.
D)a decrease in employment of 40 workers.
E)a decrease in employment of 60 workers.
A)an increase in employment of 20 workers.
B)an increase in employment of 40 workers.
C)a decrease in employment of 20 workers.
D)a decrease in employment of 40 workers.
E)a decrease in employment of 60 workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
 FIGURE 14-5
FIGURE 14-5Refer to Figure 14-5.If this labour market were perfectly competitive,the predicted wage and employment level would be
A)W1 and Q2.
B)W2 and Q3.
C)W3 and Q2.
D)W3 and Q4.
E)W4 and Q5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A legislated minimum wage is said to be binding when
A)it is below an industry's free-market equilibrium wage.
B)an industry is poorly organized and composed largely of unskilled labour.
C)it raises wage rates in an industry above the free-market equilibrium level.
D)it decreases the turnover rate among employees.
E)it is enforced by legal authorities.
A)it is below an industry's free-market equilibrium wage.
B)an industry is poorly organized and composed largely of unskilled labour.
C)it raises wage rates in an industry above the free-market equilibrium level.
D)it decreases the turnover rate among employees.
E)it is enforced by legal authorities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Suppose there is a competitive market for retail workers at a large shopping mall that is large enough to constitute its own labour market.The labour demand curve is QD = 1000 - 20(w).The labour supply curve is QS = 400 + 40(w).Suppose that a union now successfully organizes the workers at this mall and obtains a wage rate of $11 (but does not affect the demand curve).The number of unemployed workers in this mall labour market becomes
A)20.
B)40.
C)60.
D)80.
E)100.
A)20.
B)40.
C)60.
D)80.
E)100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The diagram below shows the supply and demand for labour in a hypothetical town in northern British Columbia,with only one employer,a logging company.  FIGURE 14-4
FIGURE 14-4
Refer to Figure 14-4.Suppose this labour market is in a monopsonistic equilibrium.Then,suppose the provincial government of British Columbia imposes a minimum wage for employees in this industry of $30 per hour.What will be the effects on wages and employment?
A)wages will fall by $5 per hour and employment will increase by 250 units of labour
B)wages will not change and employment will increase by 250 units of labour
C)wages will rise by $5 per hour and employment will increase by 250 units of labour
D)wages will not change and employment will change by between 0 and 250 units of labour
E)wages will not change and employment will not change
 FIGURE 14-4
FIGURE 14-4Refer to Figure 14-4.Suppose this labour market is in a monopsonistic equilibrium.Then,suppose the provincial government of British Columbia imposes a minimum wage for employees in this industry of $30 per hour.What will be the effects on wages and employment?
A)wages will fall by $5 per hour and employment will increase by 250 units of labour
B)wages will not change and employment will increase by 250 units of labour
C)wages will rise by $5 per hour and employment will increase by 250 units of labour
D)wages will not change and employment will change by between 0 and 250 units of labour
E)wages will not change and employment will not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Suppose there is a competitive market for retail workers at a large shopping mall that is large enough to constitute its own labour market.The labour demand curve is QD = 1000 - 20(w).The labour supply curve is QS = 400 + 40(w).Suppose that a union now successfully organizes the workers at this mall and obtains a wage rate of $11 (but does not affect the demand curve).The number of workers who wish to work at the new wage is
A)400.
B)440.
C)780.
D)840.
E)1000.
A)400.
B)440.
C)780.
D)840.
E)1000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The diagram below shows the supply and demand for labour in a hypothetical town in northern British Columbia,with only one employer,a logging company.  FIGURE 14-4
FIGURE 14-4
Refer to Figure 14-4.Suppose this labour market is in a monopsonistic equilibrium.Then,suppose the workers form a union and negotiate a higher wage with the firm.In this case the wage will be ________ and the employment will be ________.
A)above $35 per hour; less than 750 units of labour
B)between $25 and $35 per hour; between 750 and 1000 units of labour
C)above $25 per hour; above or below 750 units of labour,depending on the negotiated wage
D)$30 per hour; 1000 units of labour
E)$35 per hour; 750 units of labour
 FIGURE 14-4
FIGURE 14-4Refer to Figure 14-4.Suppose this labour market is in a monopsonistic equilibrium.Then,suppose the workers form a union and negotiate a higher wage with the firm.In this case the wage will be ________ and the employment will be ________.
A)above $35 per hour; less than 750 units of labour
B)between $25 and $35 per hour; between 750 and 1000 units of labour
C)above $25 per hour; above or below 750 units of labour,depending on the negotiated wage
D)$30 per hour; 1000 units of labour
E)$35 per hour; 750 units of labour

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
 FIGURE 14-5
FIGURE 14-5Refer to Figure 14-5.Suppose this labour market is competitive.If a minimum wage of W4 is then imposed,the quantity of labour supplied would be
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.
D)Q4.
E)Q5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
 FIGURE 14-5
FIGURE 14-5Refer to Figure 14-5.Suppose this labour market is competitive.If a minimum wage of W3 is then imposed,the quantity of labour hired would be
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.
D)Q4.
E)Q5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Suppose there is a competitive market for retail workers at a large shopping mall that is large enough to constitute its own labour market.The labour demand curve is QD = 1000 - 20(w).The labour supply curve is QS = 400 + 40(w).What is the equilibrium level of employment?
A)20
B)40
C)400
D)800
E)1000
A)20
B)40
C)400
D)800
E)1000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



