Deck 11: Analysis of Quantitative Data
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/91
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Analysis of Quantitative Data
1
Discuss the concepts of control variables and trivariate tables.What are three limitations of trivariate tables?
● In order to meet all the conditions needed for causality,researchers want to "control for" or see whether an alternative explanation explains away a causal relationship.If an alternative explanation explains a relationship,then the bivariate relationship is spurious.Alternative explanations are operationalized as third variables,which are called control variables because they control for alternative explanations.
● A trivariate table has a bivariate table of the independent and dependent variable for each category of the control variable.These new tables are called partials.The number of partials depends on the number of categories in the control variable.Partial tables look like bivariate tables,but they use a subset of the cases.Only cases with a specific value on the control variable are in the partial.Thus,it is possible to break apart a bivariate table to form partials,or combine the partials to restore the initial bivariate table.
● Trivariate tables have three limitations.First,they are difficult to interpret if a control variable has numerous categories.Second,control variables can be at any level of measurement,but interval or ratio control variables must be grouped (i.e.,converted to an ordinal level),and how cases are grouped can affect the interpretation of effects.Finally,the total number of cases is a limiting factor because the cases are divided among cells in partials.
● A trivariate table has a bivariate table of the independent and dependent variable for each category of the control variable.These new tables are called partials.The number of partials depends on the number of categories in the control variable.Partial tables look like bivariate tables,but they use a subset of the cases.Only cases with a specific value on the control variable are in the partial.Thus,it is possible to break apart a bivariate table to form partials,or combine the partials to restore the initial bivariate table.
● Trivariate tables have three limitations.First,they are difficult to interpret if a control variable has numerous categories.Second,control variables can be at any level of measurement,but interval or ratio control variables must be grouped (i.e.,converted to an ordinal level),and how cases are grouped can affect the interpretation of effects.Finally,the total number of cases is a limiting factor because the cases are divided among cells in partials.
2
Is a Type I or Type II error more likely if a 0.05 level is used? Explain.
● Type I error: Falsely accepting the null hypothesis when in fact there is a causal relationship (usually occurs at a more precise level such as at the 0.01 level)
● Type II error: Indicates a relationship when in fact no causal relationship exists (random factors actually caused the results and usually occurs at the 0.10 level)
● 0.05 level is a compromise between Type I and Type II errors.
● Type II error: Indicates a relationship when in fact no causal relationship exists (random factors actually caused the results and usually occurs at the 0.10 level)
● 0.05 level is a compromise between Type I and Type II errors.
3
Describe each of the three measures of central tendency.What are the main differences between them? How are they affected by a normal versus a skewed distribution of data?
● Mean: A measure of central tendency for one variable that indicates the arithmetic average (i.e.,the sum of all scores divided by the total number of scores)
● Median: A measure of central tendency for one variable indicating the point or score at which half the cases are higher and half are lower
● Mode: A measure of central tendency for one variable that indicates the most frequent or common score
● Skewed distribution: If the frequency distribution forms a "normal" or bell-shaped curve (normal distribution),the three measures of central tendency equal each other.If the distribution is a skewed distribution (i.e.,more cases are in the upper or lower scores),then the three will not be equal.If most cases have lower scores with a few extreme high scores,the mean will be the highest,the median in the middle,and the mode the lowest.If most cases have higher scores with a few extremely low scores,the mean will be the lowest,the median in the middle,and the mode the highest.
● Median: A measure of central tendency for one variable indicating the point or score at which half the cases are higher and half are lower
● Mode: A measure of central tendency for one variable that indicates the most frequent or common score
● Skewed distribution: If the frequency distribution forms a "normal" or bell-shaped curve (normal distribution),the three measures of central tendency equal each other.If the distribution is a skewed distribution (i.e.,more cases are in the upper or lower scores),then the three will not be equal.If most cases have lower scores with a few extreme high scores,the mean will be the highest,the median in the middle,and the mode the lowest.If most cases have higher scores with a few extremely low scores,the mean will be the lowest,the median in the middle,and the mode the highest.
4
A researcher wants to express the middle of a distribution of numbers whereby half the cases are higher and half the cases are lower than the middle value.What statistical measure should the researcher use?
A)Mean
B)Median
C)Mode
D)Standard deviation
E)Correlation
A)Mean
B)Median
C)Mode
D)Standard deviation
E)Correlation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Calculate the mean for the following six shoe sizes: 9,10,10,8,12,11.
A)8
B)8)5
C)9
D)9)5
E)10
A)8
B)8)5
C)9
D)9)5
E)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Describe four ways a researcher can display information about univariate statistics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which neighbourhood(s)has an income distribution resembling a skewed curve?
A)Glenbrook
B)Meadowbrook
C)Elmbrook
D)Glenbrook and Elmbrook
E)Meadowbrook and Elmbrook
A)Glenbrook
B)Meadowbrook
C)Elmbrook
D)Glenbrook and Elmbrook
E)Meadowbrook and Elmbrook

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Describe,as simply as possible,what is meant by the statement "It is statistically significant at the 0.05 level."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What are two ways in which statistical relationships can be described? Provide an example for each one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Why is knowing the variability or dispersion of a variable as important as knowing its central tendency? How is variation measured?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A "codebook" is
A)only used in existing statistics research.
B)a document that tells the researcher where variables are located in the data file and what numbers go with what variable attributes.
C)the set of instructions that tell interviewers or experimenters how to treat respondents or subjects.
D)an unnecessary part of data analysis since computers were invented.
E)a sheet of paper with a grid of 80 columns corresponding to data card columns,with rows representing an individual card.
A)only used in existing statistics research.
B)a document that tells the researcher where variables are located in the data file and what numbers go with what variable attributes.
C)the set of instructions that tell interviewers or experimenters how to treat respondents or subjects.
D)an unnecessary part of data analysis since computers were invented.
E)a sheet of paper with a grid of 80 columns corresponding to data card columns,with rows representing an individual card.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An elementary school teacher has three classes.She finds the following mean and standard deviations for student IQ scores. 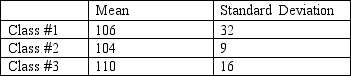 She knows she is most effective when the students all have similar IQ levels.Which class is she likely to be most effective with?
She knows she is most effective when the students all have similar IQ levels.Which class is she likely to be most effective with?
A)Class #1
B)Class #2
C)Class #3
D)Classes #1 and #2 equally
E)Classes #1 and #3 equally
 She knows she is most effective when the students all have similar IQ levels.Which class is she likely to be most effective with?
She knows she is most effective when the students all have similar IQ levels.Which class is she likely to be most effective with?A)Class #1
B)Class #2
C)Class #3
D)Classes #1 and #2 equally
E)Classes #1 and #3 equally

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
You discover that the years of marriage before a divorce for nine whites and nine nonwhites are as follows: Whites 12,1,8,9,10,17,3,6,6
Non-Whites 1,9,15,18,11,13,14,7,3
Which statement about this data is true?
A)There is no difference in the range for the two groups.
B)The median years of marriage prior to divorce is three years longer for whites than nonwhites.
C)The mean years of marriage prior to divorce are the same for both groups.
D)On average,nonwhites stay married longer prior to divorce than whites.
E)The mode for the two groups is the same.
Non-Whites 1,9,15,18,11,13,14,7,3
Which statement about this data is true?
A)There is no difference in the range for the two groups.
B)The median years of marriage prior to divorce is three years longer for whites than nonwhites.
C)The mean years of marriage prior to divorce are the same for both groups.
D)On average,nonwhites stay married longer prior to divorce than whites.
E)The mode for the two groups is the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which neighbourhood(s)has an income distribution resembling a normal curve?
A)Glenbrook
B)Meadowbrook
C)Elmbrook
D)Glenbrook and Elmbrook
E)Meadowbrook and Elmbrook
A)Glenbrook
B)Meadowbrook
C)Elmbrook
D)Glenbrook and Elmbrook
E)Meadowbrook and Elmbrook

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Calculate the median for the following six shoe sizes: 9,10,10,8,12,11.
A)8
B)8)5
C)9
D)9)5
E)10
A)8
B)8)5
C)9
D)9)5
E)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Explain how a researcher codes,enters,and cleans data so that it can be used for statistical analysis.What procedures are involved in each of these steps?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What are five measures of association that are useful when interpreting bivariate statistics? Describe each one and also specify which level of data each one is applicable to.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Calculate the mode for the following six shoe sizes: 9,10,10,8,12,11.
A)8
B)8)5
C)9
D)9)5
E)10
A)8
B)8)5
C)9
D)9)5
E)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Describe each of the three techniques researchers use when deciding whether a relationship exists between two variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which neighbourhood(s)has the greatest differences in family income?
A)Glenbrook
B)Meadowbrook
C)Elmbrook
D)Glenbrook and Elmbrook
E)Meadowbrook and Elmbrook
A)Glenbrook
B)Meadowbrook
C)Elmbrook
D)Glenbrook and Elmbrook
E)Meadowbrook and Elmbrook

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Susan weighs 140 pounds.You learn that for the women in her sorority the mean weight is 130 pounds,the median is 125,the mode is 120,and the standard deviation is 10 pounds.What is Susan's z-score in the distribution weight in the sorority?
A)zero
B)1
C)2
D)1)5
E)-1
A)zero
B)1
C)2
D)1)5
E)-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which neighbourhood(s)has the highest number of families with the lowest incomes?
A)Glenbrook
B)Meadowbrook
C)Elmbrook
D)Glenbrook and Elmbrook
E)Meadowbrook and Elmbrook
A)Glenbrook
B)Meadowbrook
C)Elmbrook
D)Glenbrook and Elmbrook
E)Meadowbrook and Elmbrook

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What type of relationship exists between level of violence and level of education?
A)There is no relationship.
B)There is a negative relationship.
C)There is a positive relationship.
D)There is a nonlinear relationship.
E)There is a recursive relationship.
A)There is no relationship.
B)There is a negative relationship.
C)There is a positive relationship.
D)There is a nonlinear relationship.
E)There is a recursive relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
How many individuals with 17+ years of education engaged in a level of violence defined as medium?
A)20
B)180
C)160
D)55
E)5
A)20
B)180
C)160
D)55
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What does it mean if someone tells you that they calculated a correlation of -0.75?
A)There is a strong negative relationship between two ratio or interval level variables.
B)There is statistical independence between the two variables.
C)The variables that were used were measured at the nominal level and the relationship between them is strong.
D)The researcher looked at two ordinal-level variables and found no relationship between them.
E)The person made an error in calculation: correlations can never be negative numbers.
A)There is a strong negative relationship between two ratio or interval level variables.
B)There is statistical independence between the two variables.
C)The variables that were used were measured at the nominal level and the relationship between them is strong.
D)The researcher looked at two ordinal-level variables and found no relationship between them.
E)The person made an error in calculation: correlations can never be negative numbers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the true situation in the world is that there is no causal relationship,but a researcher states that there is a causal relationship,what error occurs?
A)Type I
B)Type II
C)Falsely reject the null hypothesis
D)Falsely accept the null hypothesis
E)A and C
A)Type I
B)Type II
C)Falsely reject the null hypothesis
D)Falsely accept the null hypothesis
E)A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which neighbourhood(s)has the 50th percentile of education as a college education?
A)Glenbrook
B)Meadowbrook
C)Elmbrook
D)Glenbrook and Elmbrook
E)Meadowbrook and Elmbrook
A)Glenbrook
B)Meadowbrook
C)Elmbrook
D)Glenbrook and Elmbrook
E)Meadowbrook and Elmbrook

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Among the violent offenders in the following table,what is the ratio of males to females? 
A)1 male to 1 female,or 1:1
B)2 males to 3 females,or 2:3
C)4 males to 1 female,or 4:1
D)2 males to 1 female,or 2:1

A)1 male to 1 female,or 1:1
B)2 males to 3 females,or 2:3
C)4 males to 1 female,or 4:1
D)2 males to 1 female,or 2:1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which neighbourhood(s)has a small number of very high income people and a greater proportion of families earning $26,000?
A)Glenbrook
B)Meadowbrook
C)Elmbrook
D)Glenbrook and Elmbrook
E)Meadowbrook and Elmbrook
A)Glenbrook
B)Meadowbrook
C)Elmbrook
D)Glenbrook and Elmbrook
E)Meadowbrook and Elmbrook

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which neighbourhood(s)has the smallest differences in family income?
A)Glenbrook
B)Meadowbrook
C)Elmbrook
D)Glenbrook and Elmbrook
E)Meadowbrook and Elmbrook
A)Glenbrook
B)Meadowbrook
C)Elmbrook
D)Glenbrook and Elmbrook
E)Meadowbrook and Elmbrook

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Your research assistant finds a positive relationship between mother's education and income at age 40.The relationship remained after controlling for the family's social class.This means that
A)social class is really the causal variable.
B)social class does not have an impact on the relationship.
C)the original relationship is spurious.
D)income is caused by neither the mother's education level nor her social class.
E)the mother's education has no effect on her future income.
A)social class is really the causal variable.
B)social class does not have an impact on the relationship.
C)the original relationship is spurious.
D)income is caused by neither the mother's education level nor her social class.
E)the mother's education has no effect on her future income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following research topics is an example of multivariate analysis?
A)An analysis of the ages of all women who are corporate executives
B)An analysis of the relationship between age,sex,and type of restaurant frequented in Saskatoon
C)An analysis of the relationship between undergraduate majors and level of position held in a major corporation
D)An analysis of the relationship between type of offense and length of prison sentence
E)The relationship between socio-economic status and annual income
A)An analysis of the ages of all women who are corporate executives
B)An analysis of the relationship between age,sex,and type of restaurant frequented in Saskatoon
C)An analysis of the relationship between undergraduate majors and level of position held in a major corporation
D)An analysis of the relationship between type of offense and length of prison sentence
E)The relationship between socio-economic status and annual income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following tells how well a set of variables explains a dependent variable?
A)Z-score
B)Standard deviation
C)Chi-square
D)R-squared
E)Gamma
A)Z-score
B)Standard deviation
C)Chi-square
D)R-squared
E)Gamma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which neighbourhood(s)has the greatest variation in years of education?
A)Glenbrook
B)Meadowbrook
C)Elmbrook
D)Glenbrook and Elmbrook
E)Meadowbrook and Elmbrook
A)Glenbrook
B)Meadowbrook
C)Elmbrook
D)Glenbrook and Elmbrook
E)Meadowbrook and Elmbrook

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the true situation in the world is that there is a causal relationship,but a researcher states that there is no causal relationship,what error occurs?
A)Type I
B)Type II
C)Falsely reject the null hypothesis
D)Falsely accept the null hypothesis
E)B and D
A)Type I
B)Type II
C)Falsely reject the null hypothesis
D)Falsely accept the null hypothesis
E)B and D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Fatima Fashionista wears a size 2 blazer.She went to her favourite clothing store and found that the mean size of the store's stock of blazers is a size 10 with a standard deviation of 4 sizes.What is her z-score in the distribution of the store's blazers?
A)zero
B)1
C)2
D)-1.5
E)-2
A)zero
B)1
C)2
D)-1.5
E)-2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Connie and Tom both received 75 percent on the social research methods final exam.The mean for all women who took the test was 80 percent and the median was 75 percent with a standard deviation of 5 percent.The mean and median for the men was 65 percent with a standard deviation of 10 percent.What is the z-score for Connie and Tom relative to those of their own sex?
A)Connie's z-score is +1 and Tom's is -2,so Connie did better.
B)Connie's z-score is -1 and Tom's is +1,so Tom did better.
C)Both Connie and Tom have the same z-score,1.
D)Connie's z-score is 0 and Tom's is +1,so he did worse.
E)Connie's z-score is -2 and Tom's is -1,so Tom did better.
A)Connie's z-score is +1 and Tom's is -2,so Connie did better.
B)Connie's z-score is -1 and Tom's is +1,so Tom did better.
C)Both Connie and Tom have the same z-score,1.
D)Connie's z-score is 0 and Tom's is +1,so he did worse.
E)Connie's z-score is -2 and Tom's is -1,so Tom did better.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In which neighbourhood(s)do half the families have incomes of $28,000 or more?
A)Glenbrook
B)Meadowbrook
C)Elmbrook
D)Glenbrook and Elmbrook
E)Meadowbrook and Elmbrook
A)Glenbrook
B)Meadowbrook
C)Elmbrook
D)Glenbrook and Elmbrook
E)Meadowbrook and Elmbrook

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
All the sales representatives at Acadia Insurance are female,and their mean annual salary is $60,000 with a standard deviation of $5000.All customer account managers are male and they have a mean salary of $80,000 with a standard deviation of $15,000.Heather knows she is one standard deviation above the mean of the sales representatives.She wants to transfer to become the first female customer account manager and will begin at her same salary.After she transfers,compared to the customer account managers her salary will be at what z-score?
A)-2
B)-1
C)0
D)+1
E)+2
A)-2
B)-1
C)0
D)+1
E)+2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What feature of experimental research allows it to demonstrate causality without control variables?
A)Experimental researchers cannot demonstrate causality without control variables.
B)Experimental researchers eliminate alternative explanations by choosing a research design that physically controls potential alternative explanations for results.
C)Experimental researchers eliminate alternative explanations by testing temporal order and association.
D)Experimental researchers can be assured causal relationships are not spurious because they use random sampling procedures.
E)Experimental researchers make use of partials instead of control variables in order to demonstrate causality.
A)Experimental researchers cannot demonstrate causality without control variables.
B)Experimental researchers eliminate alternative explanations by choosing a research design that physically controls potential alternative explanations for results.
C)Experimental researchers eliminate alternative explanations by testing temporal order and association.
D)Experimental researchers can be assured causal relationships are not spurious because they use random sampling procedures.
E)Experimental researchers make use of partials instead of control variables in order to demonstrate causality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Define the following:
codebook
codebook

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Usually,when constructing a scattergram,the __________ goes on the X axis and the __________ goes on the Y axis.
A)independent variable; dependent variable
B)dependent variable; independent variable
C)form; direction
D)direction; form
E)control variable; causal variable
A)independent variable; dependent variable
B)dependent variable; independent variable
C)form; direction
D)direction; form
E)control variable; causal variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Define the following:
bivariate statistics
bivariate statistics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What do social scientific researchers call the process of checking the categories of all variables for impossible codes?
A)Possible code cleaning
B)Contingency cleaning
C)Wild code checking
D)A and B
E)A and C
A)Possible code cleaning
B)Contingency cleaning
C)Wild code checking
D)A and B
E)A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Define the following:
code sheet
code sheet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which measure of association can never take a negative value?
A)Lambda
B)Gamma
C)Tau
D)Rho
E)Chi-square
A)Lambda
B)Gamma
C)Tau
D)Rho
E)Chi-square

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Define the following:
cell of a table
cell of a table

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following statements about the following numbers is true: 2,7,6,9,4,6,2,8?
A)The median is a whole number
B)The distribution is bimodal
C)The mean is higher than half of the numbers in the distribution
D)A and B
E)A and C
A)The median is a whole number
B)The distribution is bimodal
C)The mean is higher than half of the numbers in the distribution
D)A and B
E)A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Define the following:
contingency cleaning
contingency cleaning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Define the following:
body of a table
body of a table

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Define the following:
control variable
control variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Define the following:
bar chart
bar chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Define the following:
bimodal
bimodal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Professor Quincy Quacker found a statistically significant relationship between variable X and variable Y.It is statistically significant at the 0.05 level.What does this mean?
A)There are 95 chances in 100 that the results are true.
B)There is a 5 percent chance that the results are true.
C)If 100 samples were drawn,results like these could be obtained by pure random chance 10 percent of the time.
D)A person could be 95 percent sure that the results of the study were a reflection of the population if random sampling was used.
E)A and D.
A)There are 95 chances in 100 that the results are true.
B)There is a 5 percent chance that the results are true.
C)If 100 samples were drawn,results like these could be obtained by pure random chance 10 percent of the time.
D)A person could be 95 percent sure that the results of the study were a reflection of the population if random sampling was used.
E)A and D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Define the following:
correlation
correlation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is an example of a multivariate statistic?
A)Multiple regression
B)Standard deviation
C)Z-score
D)Chi-square
E)Age
A)Multiple regression
B)Standard deviation
C)Z-score
D)Chi-square
E)Age

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What should you see in a scattergram if the bivariate relationship depicted in the scattergram is characterized by a high level of precision?
A)Data points widely spread around the line
B)Data points hugging the line
C)A low number of data points
D)A high number of data points
E)A curved line
A)Data points widely spread around the line
B)Data points hugging the line
C)A low number of data points
D)A high number of data points
E)A curved line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Define the following:
contingency table
contingency table

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following cannot be learned from a scattergram?
A)Form
B)Intensity
C)Direction
D)Precision
E)None of the above
A)Form
B)Intensity
C)Direction
D)Precision
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
After administering a measure for Generalized Anxiety Disorder to eight-hundred randomly sampled participants,Dr.Winkler calculated the mean GAD-scores for men and for women.Dr.Winkler found the mean GAD-score for men was higher than the mean-GAD score for women,but concluded that the difference between the two means was not statistically significant.What is the difference between the sample means tell us about the relationship between the mean GAD-scores of men and women in the population?
A)The mean GAD-score for men is higher than the mean GAD-score for women in the population
B)The mean GAD-score for women is higher than the mean GAD-score for men in the population
C)There is no difference between the mean GAD-score for men and the mean GAD-score for women in the population
D)The mean GAD-score for men is equal to or higher than the mean GAD-score for women in the population,but not lower
E)The difference in sample means tells us nothing about the difference in population means
A)The mean GAD-score for men is higher than the mean GAD-score for women in the population
B)The mean GAD-score for women is higher than the mean GAD-score for men in the population
C)There is no difference between the mean GAD-score for men and the mean GAD-score for women in the population
D)The mean GAD-score for men is equal to or higher than the mean GAD-score for women in the population,but not lower
E)The difference in sample means tells us nothing about the difference in population means

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Define the following:
histogram
histogram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Define the following:
percentile
percentile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Define the following:
partials
partials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Define the following:
pie chart
pie chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Define the following:
mean
mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Define the following:
median
median

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Define the following:
cross-tabulation
cross-tabulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Define the following:
multimodal
multimodal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Define the following:
direct entry method
direct entry method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Define the following:
mode
mode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Define the following:
marginals
marginals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Define the following:
descriptive statistics
descriptive statistics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Define the following:
independence
independence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Define the following:
frequency distribution
frequency distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Define the following:
normal distribution
normal distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Define the following:
linear relationship
linear relationship

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Define the following:
level of statistical significance
level of statistical significance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Define the following:
curvilinear relationship
curvilinear relationship

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Define the following:
multiple regression
multiple regression

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Define the following:
measure of association
measure of association

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



