Deck 6: Qualitative and Quantitative Measurement
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/82
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Qualitative and Quantitative Measurement
1
Professor Leon Loopy's survey question asked students to indicate their class standing as one of the following: first year,second year,third year,fourth year,or graduate.He measured the variable at what level of measurement?
A)Nominal
B)Ordinal
C)Interval
D)Ratio
E)None of the above
A)Nominal
B)Ordinal
C)Interval
D)Ratio
E)None of the above
Ordinal
2
Which one of the following is FALSE?
A)Ordinal measures have the properties of interval measures.
B)Interval measures have the properties of nominal measures.
C)Ratio measures have the properties of ordinal measures.
D)Ordinal measures have the properties of nominal measures.
E)All are true.
A)Ordinal measures have the properties of interval measures.
B)Interval measures have the properties of nominal measures.
C)Ratio measures have the properties of ordinal measures.
D)Ordinal measures have the properties of nominal measures.
E)All are true.
Ordinal measures have the properties of interval measures.
3
How do qualitative and quantitative ideas about validity differ?
●Qualitative researchers have developed several methods that serve as substitutes for the quantitative approach to validity.These emphasize covering the insider's view to others.Historical researchers use internal and external criticisms to determine whether the evidence they have is real or they believe it to be.Qualitative researchers adhere to the core principle of validity,to be truthful (i.e.,avoid false or distorted accounts).They try to create a tight fit between their understanding,ideas,and statements about the social world and what is actually occurring in it.Instead of validity,qualitative researchers use the terms credibility (internal validity)and transferability (external validity).
●Quantitative researchers consider validity to mean "true" or "correct." They use several types of measurement validity.At its core,measurement validity refers to how well an empirical indicator and the conceptual definition of the construct that the indicator is supposed to measure "fit" together.The better the "fit," the greater the measurement validity.
●Quantitative researchers consider validity to mean "true" or "correct." They use several types of measurement validity.At its core,measurement validity refers to how well an empirical indicator and the conceptual definition of the construct that the indicator is supposed to measure "fit" together.The better the "fit," the greater the measurement validity.
4
During the conceptualization process,a quantitative researcher should
A)look for multiple dimensions of a construct.
B)ignore definitions of other scientists,because it creates confusion.
C)avoid thinking about measuring the concept.
D)use vague,general definitions to protect a definition from criticism.
E)include a mix of unrelated ideas in his or her definition.
A)look for multiple dimensions of a construct.
B)ignore definitions of other scientists,because it creates confusion.
C)avoid thinking about measuring the concept.
D)use vague,general definitions to protect a definition from criticism.
E)include a mix of unrelated ideas in his or her definition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Professor Helga Hightower developed a new measure of intelligence.She then tested two groups of people.One group scored low on existing IQ tests.The other scored very high.Those who scored low on old tests usually scored low on her new test; those who scored very high on old tests usually scored high on the new test.Her new measure has
A)concurrent validity.
B)face validity.
C)content validity.
D)internal validity.
E)statistical validity.
A)concurrent validity.
B)face validity.
C)content validity.
D)internal validity.
E)statistical validity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How does standardization make comparisons easier?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
How do reliability and validity differ? How do they complement each other? Can a measure be reliable but invalid? How?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Name the levels of measurement and explain how they differ.Give examples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is NOT measured at a higher level than the nominal level?
A)Temperature
B)Student grades
C)Personal income in a year
D)Religious affiliation
E)The number of members in a club
A)Temperature
B)Student grades
C)Personal income in a year
D)Religious affiliation
E)The number of members in a club

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What are the main distinctions between qualitative and quantitative approaches to measurement?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Identify and explain the four ways social scientific researchers may increase the reliability of measures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
How does a researcher use the conceptual definition of a construct in operationalization and conceptualization?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A social researcher takes an abstract idea and develops a clear conceptual definition for it.This is called
A)androtempration.
B)conceptualization.
C)operationalization.
D)replication.
E)triangulation.
A)androtempration.
B)conceptualization.
C)operationalization.
D)replication.
E)triangulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What are the differences among face,content,and criterion validity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Explain the difference between the logic of a scale and an index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Most social scientists do not accept a person's height in centimetres and millimetres as a measure of her or his intelligence because it lacks
A)precision.
B)reliability.
C)accuracy.
D)validity.
E)all of the above.
A)precision.
B)reliability.
C)accuracy.
D)validity.
E)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is an example of a continuous variable?
A)Income bracket
B)Temperature measured in degrees Fahrenheit
C)Religious identification
D)Gender
E)Socioeconomic status
A)Income bracket
B)Temperature measured in degrees Fahrenheit
C)Religious identification
D)Gender
E)Socioeconomic status

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Undergraduate student Millie Magnificent developed a way to measure sexist attitudes.It worked such that a person with a score of zero truly had a neutral attitude.Also,a person who had a score of 50 had exactly double the score of someone with a score of 25.She created a(n)
A)nominal variable.
B)interval variable.
C)ratio variable.
D)ordinal variable.
E)none of the above.
A)nominal variable.
B)interval variable.
C)ratio variable.
D)ordinal variable.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Create three example items,using the Likert Scale,that have mutually exclusive and exhaustive categories and no problem with the response set.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which sequence illustrates the progression of quantitative measurement steps?
A)Conceptualization,conceptual definition,operational definition,and measurement in the empirical world
B)Conceptual definition,conceptualization,operational definition,and measurement in the empirical world
C)Operational definition,conceptualization,conceptual definition,and measurement in the empirical world
D)Conceptual definition,operationalization,conceptualization,and empirical world measurement
E)Conceptualization,operationalization,conceptual definition,and empirical world measurement
A)Conceptualization,conceptual definition,operational definition,and measurement in the empirical world
B)Conceptual definition,conceptualization,operational definition,and measurement in the empirical world
C)Operational definition,conceptualization,conceptual definition,and measurement in the empirical world
D)Conceptual definition,operationalization,conceptualization,and empirical world measurement
E)Conceptualization,operationalization,conceptual definition,and empirical world measurement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Patrick Paddywagon,owner of the Paddywagon Automobile Supermarket,wanted to find out the kinds of cars he should push to graduating college students.He asked 100 university seniors to rate 10 aspects of 11 models his dealership sold: style,fuel economy,engineering,safety,performance,prestige,comfort,price,selection or options,and interior size.Each car was rated on the 10 aspects from 0 (poor)to 5 (excellent).Each student also rated the importance of each aspect (1 = unimportant,2 = moderate importance,3 = very important).Then each aspect rating was weighed (multiplied)by its importance rating.Next,everything was added together for a score.Each car received a score of 0 to 150.What measurement technique did Patrick use in his study?
A)Interval measure
B)Graphic rating scale
C)Likert scale
D)Predictive scale
E)An index
A)Interval measure
B)Graphic rating scale
C)Likert scale
D)Predictive scale
E)An index

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Dr.Aaron Adamson uses telephone surveys to measure life satisfaction across Canada.When Dr.Adamson and his research assistants phone participants,they ask them to report responses to questions by indicating whether they "strongly agree," "agree," "strongly disagree," or "disagree." Which of the following is he using?
A)Standard scale
B)An index
C)Graphic rating scale
D)Likert scale
E)None of the above
A)Standard scale
B)An index
C)Graphic rating scale
D)Likert scale
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is measured at the ordinal level?
A)George weighs the same as Harry.
B)Mary weighs less than Janet.
C)Martha weighs 8 pounds more than Ruth.
D)Sam weighs twice as much as his dog.
E)Henry and Charlie weigh 150 lbs.
A)George weighs the same as Harry.
B)Mary weighs less than Janet.
C)Martha weighs 8 pounds more than Ruth.
D)Sam weighs twice as much as his dog.
E)Henry and Charlie weigh 150 lbs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Professor Richard Rockabilly developed a measure of an ideal rock group.He added together ratings of six factors: clear beat in music,on-stage performance excitement,new electronic sound,dress and appearance of performers,distinctiveness of sound,and degree to which lyrics were relevant.He rated 25 groups on the six factors to get an overall measure of each rock group.He created a(n)
A)index.
B)scale.
C)measure of central tendency.
D)statistic.
E)item analysis.
A)index.
B)scale.
C)measure of central tendency.
D)statistic.
E)item analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Use the letters marking parts of the diagram of the measurement process to identify the following part: Operational definition of the dependent variable. 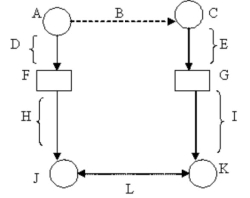
A)F
B)G
C)K
D)J
E)L

A)F
B)G
C)K
D)J
E)L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What level of measurement is the Likert scale appropriate for measuring?
A)Nominal
B)Ordinal
C)Interval
D)Ratio
E)none of the above.
A)Nominal
B)Ordinal
C)Interval
D)Ratio
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Dr.Jim Jennings studies the relationship between age and levels of activity.Jim measures levels of activity by documenting the number of steps his subjects take each day.What has Jim done by creating this measure of activity levels?
A)Conceptualized an operation
B)Standardized a variable
C)Operationalized a concept
D)Operationalized a definition
E)None of the above
A)Conceptualized an operation
B)Standardized a variable
C)Operationalized a concept
D)Operationalized a definition
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Professor Ethan Enright developed a measure of an ideal place to live.He added together measures of many factors: tax rate,quality of school system,cultural and recreational opportunities,pollution,traffic congestion,crime rate,and health-care availability for 50 Canadian cities to get a score for each.Dr.Enright created a(n)
A)index.
B)scale.
C)measure of central tendency.
D)statistic.
E)item analysis.
A)index.
B)scale.
C)measure of central tendency.
D)statistic.
E)item analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Qualitative researchers do not place the same emphasis on reliability as quantitative researchers do.What do qualitative researchers aspire to that is similar to reliability?
A)Credibility
B)Truthfulness
C)Validity
D)Transferability
E)Consistency
A)Credibility
B)Truthfulness
C)Validity
D)Transferability
E)Consistency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When a researcher seeks to validate a measure by comparing it with a "tried and true" pre-existing measure,this type of validity is called
A)face.
B)predictive.
C)criterion.
D)concurrent.
E)content.
A)face.
B)predictive.
C)criterion.
D)concurrent.
E)content.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the problem with this measure of university student age? Please indicate your age:
(i)17 to 18 years old
(ii)19 to 20 years old
(iii)21 to 22 years old
A)Its attributes are mutually exclusive.
B)Its attributes are not exhaustive.
C)Its attributes are exhaustive.
D)Its attributes are double-barrelled.
E)There is nothing wrong with it.
(i)17 to 18 years old
(ii)19 to 20 years old
(iii)21 to 22 years old
A)Its attributes are mutually exclusive.
B)Its attributes are not exhaustive.
C)Its attributes are exhaustive.
D)Its attributes are double-barrelled.
E)There is nothing wrong with it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following concepts pertains to the fit between conceptual and operational definitions?
A)Measurement validity
B)Statistical validity
C)Interval measures
D)Standardization
E)Reliability
A)Measurement validity
B)Statistical validity
C)Interval measures
D)Standardization
E)Reliability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following lists contains all variables?
A)Female,Catholic,educational level
B)Accountant,professor,carpenter
C)Occupation,number of children,rate of divorce
D)21 years old,married,middle class
E)Frequency of attending religious services,Chinese ethnicity,farmer
A)Female,Catholic,educational level
B)Accountant,professor,carpenter
C)Occupation,number of children,rate of divorce
D)21 years old,married,middle class
E)Frequency of attending religious services,Chinese ethnicity,farmer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What level of measurement is being used in the statement,"A fox terrier is smaller than a Russian wolfhound,but bigger than a Chihuahua."
A)Nominal
B)Ordinal
C)Internal
D)Ratio
E)None of the above
A)Nominal
B)Ordinal
C)Internal
D)Ratio
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following statements about the role of a conceptual definition in variable measurement is true?
A)Value judgments never play a role.
B)There is agreement among researchers about the single best definition for all concepts,and we just have to find it.
C)Good definitions are ones that are explicit and clear.
D)Never provide an example for a definition.
E)Conceptual definitions should never contain multiple dimensions.
A)Value judgments never play a role.
B)There is agreement among researchers about the single best definition for all concepts,and we just have to find it.
C)Good definitions are ones that are explicit and clear.
D)Never provide an example for a definition.
E)Conceptual definitions should never contain multiple dimensions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Professor Tak Tanaka developed a new measure of fear of crime.His conceptual definition was this: "The degree of emotional,behavioural,or mental response to a real or imagined theft of property or attack on one's person or family members." He then developed one question for a survey to measure his concept: "Do you lock your car doors when you park to go shopping?" What is the major problem with his measure?
A)Reliability
B)Content validity
C)Face validity
D)Internal validity
E)Representative validity
A)Reliability
B)Content validity
C)Face validity
D)Internal validity
E)Representative validity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Mildred Magnificent got on the scale at 7:00 a.m.and weighed 295 pounds.At 7:02 a.m.she again got on the scale and weighed 200 pounds.At 7:04 a.m.she weighed 499 pounds.The measurement of Mildred's weight has problems with
A)reliability.
B)induction.
C)standardization
D)conceptualization.
E)precision.
A)reliability.
B)induction.
C)standardization
D)conceptualization.
E)precision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The two subtypes of criterion validity are __________ validity and __________ validity.
A)content; predictive
B)face; content
C)concurrent; predictive
D)internal; external
E)concurrent; measurement
A)content; predictive
B)face; content
C)concurrent; predictive
D)internal; external
E)concurrent; measurement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which sort of hypothesis are researchers interested in testing at the level of operational definitions?
A)Grounded
B)Variable
C)Conceptual
D)Empirical
E)Abstract
A)Grounded
B)Variable
C)Conceptual
D)Empirical
E)Abstract

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which type of measurement validity is the easiest to achieve?
A)Concurrent
B)Face
C)Content
D)Criterion
E)Predictive
A)Concurrent
B)Face
C)Content
D)Criterion
E)Predictive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When comparing qualitative and a quantitative approaches to measurement,operationalization in the qualitative approach involves which of the following?
A)More of an "after-the-fact" description based on what was observed in the data than based on a preplanned idea
B)A researcher taking a carefully developed theoretical definition and developing specific empirical indicators of it for use when later gathering data
C)A process that comes after careful conceptualization; operationalization never comes before careful conceptualization in qualitative research
D)There is no difference between qualitative and quantitative operationalization.
E)There is no operationalization in qualitative research.
A)More of an "after-the-fact" description based on what was observed in the data than based on a preplanned idea
B)A researcher taking a carefully developed theoretical definition and developing specific empirical indicators of it for use when later gathering data
C)A process that comes after careful conceptualization; operationalization never comes before careful conceptualization in qualitative research
D)There is no difference between qualitative and quantitative operationalization.
E)There is no operationalization in qualitative research.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Define the following:
conceptual definition
conceptual definition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Define the following:
concurrent validity
concurrent validity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Define the following:
dependability
dependability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Define the following:
continuous variables
continuous variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Use the letters marking parts of the diagram of the measurement process to identify the following part: Conceptualization of the dependent variable. 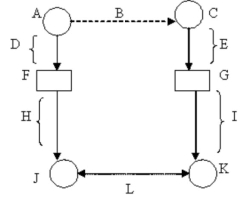
A)E
B)I
C)H
D)D
E)F

A)E
B)I
C)H
D)D
E)F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
For quantitative researchers,validity means truthfulness.It refers to the bridge between a concept and the data.Qualitative researchers are also concerned with truthfulness,but do not discuss it in terms of "validity." What term do qualitative researchers use to discuss the truth-value of their research?
A)Accuracy
B)Authenticity
C)Consistency
D)Reliability
E)Standardization
A)Accuracy
B)Authenticity
C)Consistency
D)Reliability
E)Standardization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Define the following:
conceptualization
conceptualization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Minako Wada,a graduate student in sociology,considers herself to be an atheist.She is asked to complete a survey on international students' experiences in Canada.The question on religious affiliation asks participants to identify their religious affiliation and includes the following categories:
a.Catholic
b.Protestant
c.Jewish
d.Muslim
e.Hindu
f.Buddhist
g.Shinto
What is wrong with this question?
A)The response categories are not mutually exclusive.
B)The response categories are not exhaustive.
C)The response categories are not ranked.
D)All of the above are problems.
E)None of the above.
a.Catholic
b.Protestant
c.Jewish
d.Muslim
e.Hindu
f.Buddhist
g.Shinto
What is wrong with this question?
A)The response categories are not mutually exclusive.
B)The response categories are not exhaustive.
C)The response categories are not ranked.
D)All of the above are problems.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Define the following:
authenticity
authenticity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the letters marking parts of the diagram of the measurement process to identify the following parts: Conceptual definition of the dependent variable. 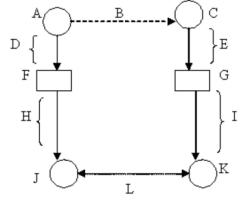
A)K
B)G
C)B
D)A
E)C

A)K
B)G
C)B
D)A
E)C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The following question appeared on the Canadian Community Health Survey,a survey administered to all Canadians 18 years of age and older: To what age category do you belong?
a.18-24
b.25-34
c.35-44
d.45-54
e.55-65
f.65+
What is wrong with this question?
A)The response categories are not exhaustive.
B)The response categories are not mutually exclusive.
C)The response categories are not labelled with life course stages,e.g.,middle age,senior.
D)All of the above are problems.
E)None of the above.
a.18-24
b.25-34
c.35-44
d.45-54
e.55-65
f.65+
What is wrong with this question?
A)The response categories are not exhaustive.
B)The response categories are not mutually exclusive.
C)The response categories are not labelled with life course stages,e.g.,middle age,senior.
D)All of the above are problems.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Define the following:
criterion validity
criterion validity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Define the following:
conceptual hypothesis
conceptual hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Define the following:
empirical hypothesis
empirical hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Use the letters marking parts of the diagram of the measurement process to identify the following part: Empirical hypothesis. 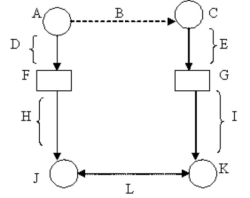
A)L
B)B
C)H
D)G
E)C

A)L
B)B
C)H
D)G
E)C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Define the following:
discrete variables
discrete variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Define the following:
content validity
content validity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Define the following:
exhaustive attributes
exhaustive attributes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Define the following:
credibility
credibility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Define the following:
ordinal-level measurement
ordinal-level measurement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Define the following:
index
index

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Define the following:
measurement validity
measurement validity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Define the following:
nominal-level measurement
nominal-level measurement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Define the following:
mutually exclusive attributes
mutually exclusive attributes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Define the following:
ratio-level measurement
ratio-level measurement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Define the following:
external validity
external validity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Define the following:
standardization
standardization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Define the following:
interval-level measurement
interval-level measurement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Define the following:
multiple indicators
multiple indicators

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Define the following:
statistical validity
statistical validity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Define the following:
internal validity
internal validity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Define the following:
levels of measurement
levels of measurement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Define the following:
scale
scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Define the following:
operational definition
operational definition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Define the following:
Likert scale
Likert scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Define the following:
reliability
reliability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Define the following:
face validity
face validity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Define the following:
predictive validity
predictive validity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Define the following:
operationalization
operationalization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



