Deck 14: Interest Rate and Currency Swaps
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Interest Rate and Currency Swaps
1
A swap bank has identified two companies with mirror-image financing needs-they both want to borrow equivalent amounts for the same amount of time.Company X has agreed to one leg of the swap but company Y is "playing hard to get."
A)The swap bank could just sell the company X side of the swap.
B)Company X should lobby Y to "get on board."
C)Company Y should calculate the QSD and subtract that from their best outside offer.
D)none of the options
A)The swap bank could just sell the company X side of the swap.
B)Company X should lobby Y to "get on board."
C)Company Y should calculate the QSD and subtract that from their best outside offer.
D)none of the options
A
2
An interest-only single currency interest rate swap
A)is also known as a plain vanilla swap.
B)is also known as an interest rate swap.
C)is about as simple as swaps can get.
D)all of the options
A)is also known as a plain vanilla swap.
B)is also known as an interest rate swap.
C)is about as simple as swaps can get.
D)all of the options
D
3
A swap bank
A)can act as a broker,bringing together counterparties to a swap.
B)can act as a dealer,standing ready to buy and sell swaps.
C)can act as a broker,bringing together counterparties to a swap and standing ready to buy and sell swaps.
D)only sometimes acts as a broker,bringing together counterparties to a swap,but never ever acts as a dealer,standing ready to buy and sell swaps.
A)can act as a broker,bringing together counterparties to a swap.
B)can act as a dealer,standing ready to buy and sell swaps.
C)can act as a broker,bringing together counterparties to a swap and standing ready to buy and sell swaps.
D)only sometimes acts as a broker,bringing together counterparties to a swap,but never ever acts as a dealer,standing ready to buy and sell swaps.
C
4
Company X wants to borrow $10,000,000 floating for 5 years; company Y wants to borrow $10,000,000 fixed for 5 years.Their external borrowing opportunities are shown here: A swap bank proposes the following interest only swap:
X will pay the swap bank annual payments on $10,000,000 with the coupon rate of LIBOR ? 0.15 percent; in exchange the swap bank will pay to company X interest payments on $10,000,000 at a fixed rate of 9.90 percent.What is the value of this swap to company X?
A)Company X will lose money on the deal.
B)Company X will save 25 basis points per year on $10,000,000 = $25,000 per year.
C)Company X will only break even on the deal.
D)Company X will save 5 basis points per year on $10,000,000 = $5,000 per year.
X will pay the swap bank annual payments on $10,000,000 with the coupon rate of LIBOR ? 0.15 percent; in exchange the swap bank will pay to company X interest payments on $10,000,000 at a fixed rate of 9.90 percent.What is the value of this swap to company X?
A)Company X will lose money on the deal.
B)Company X will save 25 basis points per year on $10,000,000 = $25,000 per year.
C)Company X will only break even on the deal.
D)Company X will save 5 basis points per year on $10,000,000 = $5,000 per year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Company X wants to borrow $10,000,000 floating for 5 years; company Y wants to borrow $10,000,000 fixed for 5 years.Their external borrowing opportunities are shown here: A swap bank proposes the following interest only swap:
X will pay the swap bank annual payments on $10,000,000 with the coupon rate of LIBOR; in exchange the swap bank will pay to company X interest payments on $10,000,000 at a fixed rate of 10.05 percent.Y will pay the swap bank interest payments on $10,000,000 at a fixed rate of 10.30 percent and the swap bank will pay Y annual payments on $10,000,000 with the coupon rate of LIBOR ? 0.15 percent.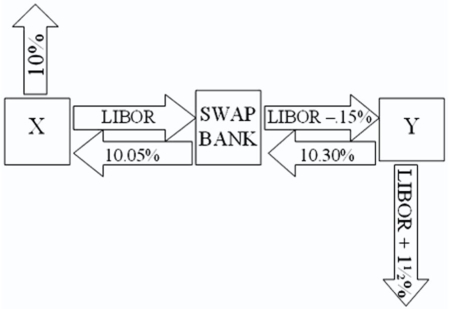 What is the value of this swap to the swap bank?
What is the value of this swap to the swap bank?
A)The swap bank will earn 40 basis points per year on $10,000,000 = $40,000 per year.
B)The swap bank will earn 10 basis points per year on $10,000,000 = $10,000 per year.
C)The swap bank will lose money.
D)none of the options
X will pay the swap bank annual payments on $10,000,000 with the coupon rate of LIBOR; in exchange the swap bank will pay to company X interest payments on $10,000,000 at a fixed rate of 10.05 percent.Y will pay the swap bank interest payments on $10,000,000 at a fixed rate of 10.30 percent and the swap bank will pay Y annual payments on $10,000,000 with the coupon rate of LIBOR ? 0.15 percent.
 What is the value of this swap to the swap bank?
What is the value of this swap to the swap bank?A)The swap bank will earn 40 basis points per year on $10,000,000 = $40,000 per year.
B)The swap bank will earn 10 basis points per year on $10,000,000 = $10,000 per year.
C)The swap bank will lose money.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The size of the swap market (as of mid-year 2015)is
A)measured by notational principal.
B)over 23 trillion dollars.
C)measured by notational principal and over 23 trillion dollars.
D)none of the options
A)measured by notational principal.
B)over 23 trillion dollars.
C)measured by notational principal and over 23 trillion dollars.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Suppose the quote for a five-year swap with semiannual payments is 8.50-8.60 percent.This means
A)the swap bank will pay semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.60 percent against receiving six-month dollar LIBOR
B)the swap bank will receive semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.50 percent against paying six-month dollar LIBOR.
C)if the swap bank is successful in getting counterparties to both legs of the swap at these prices,he will have an annual profit of ten basis points.
D)none of the options
A)the swap bank will pay semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.60 percent against receiving six-month dollar LIBOR
B)the swap bank will receive semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.50 percent against paying six-month dollar LIBOR.
C)if the swap bank is successful in getting counterparties to both legs of the swap at these prices,he will have an annual profit of ten basis points.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The term interest rate swap
A)refers to a "single-currency interest rate swap" shortened to "interest rate swap."
B)involves "counterparties" who make a contractual agreement to exchange cash flows at periodic intervals.
C)can be "fixed-for-floating rate" or "fixed-for-fixed rate."
D)all of the options
A)refers to a "single-currency interest rate swap" shortened to "interest rate swap."
B)involves "counterparties" who make a contractual agreement to exchange cash flows at periodic intervals.
C)can be "fixed-for-floating rate" or "fixed-for-fixed rate."
D)all of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Examples of "single-currency interest rate swap" and "cross-currency interest rate swap" are:
A)fixed-for-floating rate interest rate swap,where one counterparty exchanges the interest payments of a floating-rate debt obligations for fixed-rate interest payments of the other counter party.
B)fixed-for-fixed rate debt service (currency swap),where one counterparty exchanges the debt service obligations of a bond denominated in one currency for the debt service obligations of the other counterparty denominated in another currency.
C)fixed-for-floating rate interest rate swap,where one counterparty exchanges the interest payments of a floating-rate debt obligations for fixed-rate interest payments of the other counter party,as well as fixed-for-fixed rate debt service (currency swap),where one counterparty exchanges the debt service obligations of a bond denominated in one currency for the debt service obligations of the other counterparty denominated in another currency.
D)none of the options
A)fixed-for-floating rate interest rate swap,where one counterparty exchanges the interest payments of a floating-rate debt obligations for fixed-rate interest payments of the other counter party.
B)fixed-for-fixed rate debt service (currency swap),where one counterparty exchanges the debt service obligations of a bond denominated in one currency for the debt service obligations of the other counterparty denominated in another currency.
C)fixed-for-floating rate interest rate swap,where one counterparty exchanges the interest payments of a floating-rate debt obligations for fixed-rate interest payments of the other counter party,as well as fixed-for-fixed rate debt service (currency swap),where one counterparty exchanges the debt service obligations of a bond denominated in one currency for the debt service obligations of the other counterparty denominated in another currency.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Company X wants to borrow $10,000,000 floating for 5 years; company Y wants to borrow $10,000,000 fixed for 5 years.Their external borrowing opportunities are shown here: A swap bank proposes the following interest only swap:
X will pay the swap bank annual payments on $10,000,000 with the coupon rate of LIBOR ? 0.15 percent; in exchange the swap bank will pay to company X interest payments on $10,000,000 at a fixed rate of 9.90 percent.Y will pay the swap bank interest payments on $10,000,000 at a fixed rate of 10.30 percent and the swap bank will pay Y annual payments on $10,000,000 with the coupon rate of LIBOR ? 0.15 percent.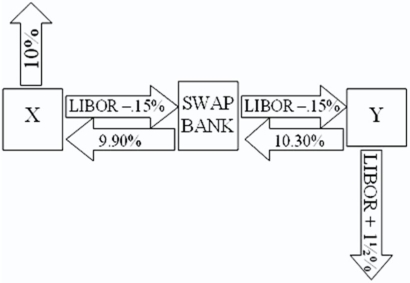 What is the value of this swap to the swap bank?
What is the value of this swap to the swap bank?
A)The swap bank will lose money on the deal.
B)The swap bank will earn 40 basis points per year on $10,000,000 = $40,000 per year.
C)The swap bank will break even.
D)none of the options
X will pay the swap bank annual payments on $10,000,000 with the coupon rate of LIBOR ? 0.15 percent; in exchange the swap bank will pay to company X interest payments on $10,000,000 at a fixed rate of 9.90 percent.Y will pay the swap bank interest payments on $10,000,000 at a fixed rate of 10.30 percent and the swap bank will pay Y annual payments on $10,000,000 with the coupon rate of LIBOR ? 0.15 percent.
 What is the value of this swap to the swap bank?
What is the value of this swap to the swap bank?A)The swap bank will lose money on the deal.
B)The swap bank will earn 40 basis points per year on $10,000,000 = $40,000 per year.
C)The swap bank will break even.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A swap bank makes the following quotes for 5-year swaps and AAA-rated firms: USD Euro
A)The bank stands ready to pay $5.2 percent against receiving dollar LIBOR on 5-year loans.
B)The bank stands ready to receive €7 percent against receiving dollar LIBOR on 5-year loans.
C)The bank stands ready to pay €7 percent against receiving dollar LIBOR on 5-year loans.
D)none of the options
A)The bank stands ready to pay $5.2 percent against receiving dollar LIBOR on 5-year loans.
B)The bank stands ready to receive €7 percent against receiving dollar LIBOR on 5-year loans.
C)The bank stands ready to pay €7 percent against receiving dollar LIBOR on 5-year loans.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which combination of the following statements is true about a swap bank? (i)it is a generic term to describe a financial institution that facilitates swaps between counterparties
(ii)it can be an international commercial bank
(iii)it can be an investment bank
(iv)it can be a merchant bank
(v)it can be an independent operator
A)(i)and (ii)
B)(i),(ii)and (iii)
C)(i),(ii),(iii)and (iv)
D)(i),(ii),(iii),(iv)and (v)
(ii)it can be an international commercial bank
(iii)it can be an investment bank
(iv)it can be a merchant bank
(v)it can be an independent operator
A)(i)and (ii)
B)(i),(ii)and (iii)
C)(i),(ii),(iii)and (iv)
D)(i),(ii),(iii),(iv)and (v)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Suppose the quote for a five-year swap with semiannual payments is 8.50-8.60 percent.This means
A)the swap bank will pay semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.50 percent against receiving six-month dollar LIBOR.
B)the swap bank will receive semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.60 percent against paying six-month dollar LIBOR.
C)the swap bank will pay semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.50 percent against receiving six-month dollar LIBOR,and the swap bank will receive semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.60 percent against paying six-month dollar LIBOR.
D)none of the options
A)the swap bank will pay semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.50 percent against receiving six-month dollar LIBOR.
B)the swap bank will receive semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.60 percent against paying six-month dollar LIBOR.
C)the swap bank will pay semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.50 percent against receiving six-month dollar LIBOR,and the swap bank will receive semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.60 percent against paying six-month dollar LIBOR.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The primary reasons for a counterparty to use a currency swap are
A)to hedge and to speculate.
B)to play in the futures and forward markets.
C)to obtain debt financing in the swapped currency at an interest cost reduction brought about through comparative advantages each counterparty has in its national capital market,and the benefit of hedging long-run exchange rate exposure.
D)to hedge and to speculate,as well as to play in the futures and forward markets.
A)to hedge and to speculate.
B)to play in the futures and forward markets.
C)to obtain debt financing in the swapped currency at an interest cost reduction brought about through comparative advantages each counterparty has in its national capital market,and the benefit of hedging long-run exchange rate exposure.
D)to hedge and to speculate,as well as to play in the futures and forward markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Company X wants to borrow $10,000,000 floating for 5 years; company Y wants to borrow $10,000,000 fixed for 5 years.Their external borrowing opportunities are shown here: A swap bank proposes the following interest only swap:
Y will pay the swap bank annual payments on $10,000,000 with a fixed rate of rate of 9.90 percent.In exchange the swap bank will pay to company Y interest payments on $10,000,000 at LIBOR ? 0.15 percent; What is the value of this swap to company Y?
A)Company Y will save 15 basis points per year on $10,000,000 = $15,000 per year.
B)Company Y will save 45 basis points per year on $10,000,000 = $45,000 per year.
C)Company Y will save 5 basis points per year on $10,000,000 = $5,000 per year.
D)Company Y will only break even on the deal.
Y will pay the swap bank annual payments on $10,000,000 with a fixed rate of rate of 9.90 percent.In exchange the swap bank will pay to company Y interest payments on $10,000,000 at LIBOR ? 0.15 percent; What is the value of this swap to company Y?
A)Company Y will save 15 basis points per year on $10,000,000 = $15,000 per year.
B)Company Y will save 45 basis points per year on $10,000,000 = $45,000 per year.
C)Company Y will save 5 basis points per year on $10,000,000 = $5,000 per year.
D)Company Y will only break even on the deal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A swap bank has identified two companies with mirror-image financing needs (they both want to borrow equivalent amounts for the same amount of time.Company X has agreed to one leg of the swap but company Y is "playing hard to get."
A)If the swap bank has already contracted one leg of the swap,they should be anxious to offer better terms to company Y to just get the deal done.
B)The swap bank could just sell the company X side of the swap.
C)Company X should lobby Y to "get on board."
D)If the swap bank has already contracted one leg of the swap,they should be anxious to offer better terms to company Y to just get the deal done,and the swap bank could just sell the company X side of the swap.
A)If the swap bank has already contracted one leg of the swap,they should be anxious to offer better terms to company Y to just get the deal done.
B)The swap bank could just sell the company X side of the swap.
C)Company X should lobby Y to "get on board."
D)If the swap bank has already contracted one leg of the swap,they should be anxious to offer better terms to company Y to just get the deal done,and the swap bank could just sell the company X side of the swap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose the quote for a five-year swap with semiannual payments is 8.50−8.60 percent in dollars and 6.60−6.80 percent in euro against six-month dollar LIBOR.This means
A)the swap bank will enter into a currency swap in which it would pay semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.50 percent against receiving semiannual fixed-rate euro payments of 6.80.
B)the swap bank will enter into a currency swap in which it would pay semiannual fixed-rate euro payments of 6.60 percent against receiving semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.60.
C)the swap bank will enter into a currency swap in which it would pay semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.50 percent against receiving semiannual fixed-rate euro payments of 6.80,and the swap bank will enter into a currency swap in which it would pay semiannual fixed-rate euro payments of 6.60 percent against receiving semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.60.
D)none of the options
A)the swap bank will enter into a currency swap in which it would pay semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.50 percent against receiving semiannual fixed-rate euro payments of 6.80.
B)the swap bank will enter into a currency swap in which it would pay semiannual fixed-rate euro payments of 6.60 percent against receiving semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.60.
C)the swap bank will enter into a currency swap in which it would pay semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.50 percent against receiving semiannual fixed-rate euro payments of 6.80,and the swap bank will enter into a currency swap in which it would pay semiannual fixed-rate euro payments of 6.60 percent against receiving semiannual fixed-rate dollar payments of 8.60.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Company X wants to borrow $10,000,000 floating for 5 years; company Y wants to borrow $10,000,000 fixed for 5 years.Their external borrowing opportunities are shown here: A swap bank is involved and quotes the following rates five-year dollar interest rate swaps at 10.05 percent?10.45 percent against LIBOR flat. 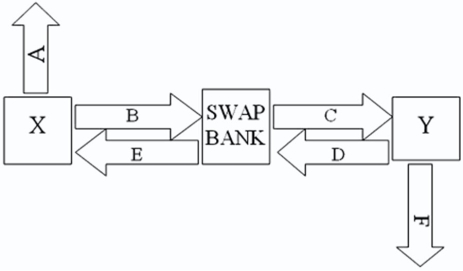 Assume both X and Y agree to the swap bank's terms.Fill in the values for A,B,C,D,E,& F on the diagram.
Assume both X and Y agree to the swap bank's terms.Fill in the values for A,B,C,D,E,& F on the diagram.
A)A = LIBOR; B = 10.45%; C = 10.05%; D = LIBOR; E = LIBOR; F = 12%
B)A = 10%; B = 10.45%; C = 10.05%; D = LIBOR; E = LIBOR; F = LIBOR + 1½%
C)A = 10%; B = 10.45%; C = LIBOR; D = LIBOR; E = 10.05%; F = LIBOR + 1½%
D)A = 10%; B = LIBOR; C = LIBOR; D = 10.45%; E = 10.05%; F = LIBOR + 1½%
 Assume both X and Y agree to the swap bank's terms.Fill in the values for A,B,C,D,E,& F on the diagram.
Assume both X and Y agree to the swap bank's terms.Fill in the values for A,B,C,D,E,& F on the diagram.A)A = LIBOR; B = 10.45%; C = 10.05%; D = LIBOR; E = LIBOR; F = 12%
B)A = 10%; B = 10.45%; C = 10.05%; D = LIBOR; E = LIBOR; F = LIBOR + 1½%
C)A = 10%; B = 10.45%; C = LIBOR; D = LIBOR; E = 10.05%; F = LIBOR + 1½%
D)A = 10%; B = LIBOR; C = LIBOR; D = 10.45%; E = 10.05%; F = LIBOR + 1½%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Company X and company Y have mirror-image financing needs (they both want to borrow equivalent amounts for the same amount of time.Company X has a AAA credit rating,but company Y's credit standing is considerably lower.
A)Company X should demand most of the QSD in any swap with Y as compensation for default risk.
B)Since Y has a poor credit rating,it would not be a participant in the swap market.
C)Company X should more readily agree to a swap involving Y if there is also a swap bank providing credit risk intermediation.
D)Company X should demand most of the QSD in any swap with Y as compensation for default risk,and Company X should more readily agree to a swap involving Y if there is also a swap bank providing credit risk intermediation.
A)Company X should demand most of the QSD in any swap with Y as compensation for default risk.
B)Since Y has a poor credit rating,it would not be a participant in the swap market.
C)Company X should more readily agree to a swap involving Y if there is also a swap bank providing credit risk intermediation.
D)Company X should demand most of the QSD in any swap with Y as compensation for default risk,and Company X should more readily agree to a swap involving Y if there is also a swap bank providing credit risk intermediation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the swap market,which position potentially carries greater risks,broker or dealer?
A)Broker
B)Dealer
C)They are the same swaps,therefore the same risks.
D)none of the options
A)Broker
B)Dealer
C)They are the same swaps,therefore the same risks.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Company X wants to borrow $10,000,000 floating for 5 years; company Y wants to borrow $10,000,000 fixed for 5 years.Their external borrowing opportunities are shown below.
A swap bank is involved and quotes the following rates five-year dollar interest rate swaps at 10.05 percent -10.45 percent against LIBOR flat.
Assume company Y has agreed,but company X will only agree to the swap if the bank offers better terms.
What are the absolute best terms the bank can offer X,given that it already booked Y?
A)10.45% ?10.45% against LIBOR flat.
B)10.45%?10.05% against LIBOR flat.
C)10.50%?10.50% against LIBOR flat.
D)none of the options
A swap bank is involved and quotes the following rates five-year dollar interest rate swaps at 10.05 percent -10.45 percent against LIBOR flat.
Assume company Y has agreed,but company X will only agree to the swap if the bank offers better terms.
What are the absolute best terms the bank can offer X,given that it already booked Y?

A)10.45% ?10.45% against LIBOR flat.
B)10.45%?10.05% against LIBOR flat.
C)10.50%?10.50% against LIBOR flat.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Company X wants to borrow $10,000,000 floating for 1 year; company Y wants to borrow £5,000,000 fixed for 1 year.The spot exchange rate is $2 = £1 and IRP calculates the one-year forward rate as $2.00 × (1.08)/£1.00 × (1.06)= $2.0377/£1.Their external borrowing opportunities are: A swap bank wants to design a profitable interest-only fixed-for-fixed currency swap.In order for X and Y to be interested,they can face no exchange rate risk.
What must the values of A and B in the graph shown above be in order for the swap to be of interest to firms X and Y?
A)A = £7%; B = $9%.
B)A = $8%; B = £6%.
C)A = $7%; B = £7%.
D)A = $8%; B = £8%.
What must the values of A and B in the graph shown above be in order for the swap to be of interest to firms X and Y?
A)A = £7%; B = $9%.
B)A = $8%; B = £6%.
C)A = $7%; B = £7%.
D)A = $8%; B = £8%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Pricing a currency swap after inception involves
A)finding the difference between the present values of the payments streams the party will receive in one currency and pay in the other currency,converted to a common currency.
B)sending a market order to a swap dealer.
C)finding the sum of the present values of the payments streams that each party will receive in one currency and pay in the other currency,converted to a common currency.
D)none of the options
A)finding the difference between the present values of the payments streams the party will receive in one currency and pay in the other currency,converted to a common currency.
B)sending a market order to a swap dealer.
C)finding the sum of the present values of the payments streams that each party will receive in one currency and pay in the other currency,converted to a common currency.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Consider the dollar- and euro-based borrowing opportunities of companies A and B. A is a U.S.-based MNC with AAA credit; B is an Italian firm with AAA credit.Firm A wants to borrow €1,000,000 for one year and B wants to borrow $2,000,000 for one year.The spot exchange rate is $2.00 = €1.00 and the one-year forward rate is given by IRP as = .
Suppose they agree to the swap shown here.Is this mutually beneficial swap equally fair to both parties?![<strong>Consider the dollar- and euro-based borrowing opportunities of companies A and B. \begin{array}{ccc} & € \text { borrowing } & \$ \text { borrowing } \\ \mathrm{A} & € 7 \% & \$ 8 \% \\ \mathrm{~B} & € 6 \% & \$ 9 \% \end{array} A is a U.S.-based MNC with AAA credit; B is an Italian firm with AAA credit.Firm A wants to borrow €1,000,000 for one year and B wants to borrow $2,000,000 for one year.The spot exchange rate is $2.00 = €1.00 and the one-year forward rate is given by IRP as \frac { \$ 2.00 \times ( 1.08 ) } { € 1.00 \times ( 1.06 ) } = \frac { \$ 2.0377 } { € 1.00 } . Suppose they agree to the swap shown here.Is this mutually beneficial swap equally fair to both parties? </strong> A)Yes,QSD = [€7% ? €6% × $2.00/€1.00] ? ($8% ? $9%)= $2% + $1% = $3%. B)No,company A borrows at 6 percent in euro but company B borrows at 8 percent in dollars. C)Yes,A will be better off by €1 percent on €1m; B by 1 percent on $2m and $2.00 = €1.00. D)No,company A saves 1 percent in euro but company B saves only 1 percent in dollars when the spot exchange rate is $2.00 = €1.00-A is twice as better off as B.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f120_6541_926a_0720fc146700_TB2600_00.jpg)
A)Yes,QSD = [€7% ? €6% × $2.00/€1.00] ? ($8% ? $9%)= $2% + $1% = $3%.
B)No,company A borrows at 6 percent in euro but company B borrows at 8 percent in dollars.
C)Yes,A will be better off by €1 percent on €1m; B by 1 percent on $2m and $2.00 = €1.00.
D)No,company A saves 1 percent in euro but company B saves only 1 percent in dollars when the spot exchange rate is $2.00 = €1.00-A is twice as better off as B.
Suppose they agree to the swap shown here.Is this mutually beneficial swap equally fair to both parties?
![<strong>Consider the dollar- and euro-based borrowing opportunities of companies A and B. \begin{array}{ccc} & € \text { borrowing } & \$ \text { borrowing } \\ \mathrm{A} & € 7 \% & \$ 8 \% \\ \mathrm{~B} & € 6 \% & \$ 9 \% \end{array} A is a U.S.-based MNC with AAA credit; B is an Italian firm with AAA credit.Firm A wants to borrow €1,000,000 for one year and B wants to borrow $2,000,000 for one year.The spot exchange rate is $2.00 = €1.00 and the one-year forward rate is given by IRP as \frac { \$ 2.00 \times ( 1.08 ) } { € 1.00 \times ( 1.06 ) } = \frac { \$ 2.0377 } { € 1.00 } . Suppose they agree to the swap shown here.Is this mutually beneficial swap equally fair to both parties? </strong> A)Yes,QSD = [€7% ? €6% × $2.00/€1.00] ? ($8% ? $9%)= $2% + $1% = $3%. B)No,company A borrows at 6 percent in euro but company B borrows at 8 percent in dollars. C)Yes,A will be better off by €1 percent on €1m; B by 1 percent on $2m and $2.00 = €1.00. D)No,company A saves 1 percent in euro but company B saves only 1 percent in dollars when the spot exchange rate is $2.00 = €1.00-A is twice as better off as B.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f120_6541_926a_0720fc146700_TB2600_00.jpg)
A)Yes,QSD = [€7% ? €6% × $2.00/€1.00] ? ($8% ? $9%)= $2% + $1% = $3%.
B)No,company A borrows at 6 percent in euro but company B borrows at 8 percent in dollars.
C)Yes,A will be better off by €1 percent on €1m; B by 1 percent on $2m and $2.00 = €1.00.
D)No,company A saves 1 percent in euro but company B saves only 1 percent in dollars when the spot exchange rate is $2.00 = €1.00-A is twice as better off as B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Company X wants to borrow $10,000,000 floating for 5 years; company Y wants to borrow £5,000,000 fixed for 5 years.The exchange rate is $2 = £1 and is not expected to change over the next 5 years.Their external borrowing opportunities are: A swap bank proposes the following interest-only swap: Company X will pay the swap bank annual payments on $10,000,000 at an interest rate of $9.80 percent; in exchange the swap bank will pay to company X interest payments on £5,000,000 at a fixed rate of 10.5 percent.Y will pay the swap bank interest payments on £5,000,000 at a fixed rate of 12.80 percent and the swap bank will pay Y annual payments on $10,000,000 with the coupon rate of 12 percent. 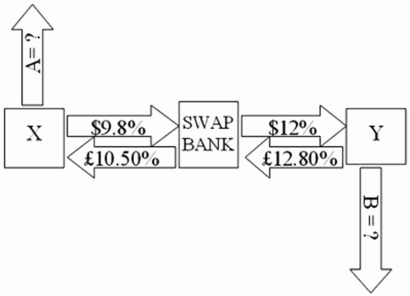 If company X takes on the swap,what external actions should they engage in?
If company X takes on the swap,what external actions should they engage in?
A)They should borrow $10,000,000 at $10 percent.
B)They should borrow £5,000,000 at 10.50 percent interest-only for five years; translate pounds to dollars at the spot rate.
C)They should borrow £5,000,000 at £10.50 percent interest-only for five years; translate pounds to dollars at the spot rate; enter long position in a forward contract to buy £5,000,000 in five years.
D)none of the options
 If company X takes on the swap,what external actions should they engage in?
If company X takes on the swap,what external actions should they engage in?A)They should borrow $10,000,000 at $10 percent.
B)They should borrow £5,000,000 at 10.50 percent interest-only for five years; translate pounds to dollars at the spot rate.
C)They should borrow £5,000,000 at £10.50 percent interest-only for five years; translate pounds to dollars at the spot rate; enter long position in a forward contract to buy £5,000,000 in five years.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In a currency swap,
A)it may be the case that two counterparties have equivalent credit ratings.
B)it may be the case that firms have a comparative advantage in borrowing in their domestic markets.
C)it may be the case that two counterparties have equivalent credit ratings,and it may also be the case that firms have a comparative advantage in borrowing in their domestic markets.
D)none of the options
A)it may be the case that two counterparties have equivalent credit ratings.
B)it may be the case that firms have a comparative advantage in borrowing in their domestic markets.
C)it may be the case that two counterparties have equivalent credit ratings,and it may also be the case that firms have a comparative advantage in borrowing in their domestic markets.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Compute the payments due in the second year on a three-year amortizing swap from company B to company A.Company A and company B both want to borrow £1,000,000 for three years.A wants to borrow floating and B wants to borrow fixed.A and B agree to split the QSD.
A)B pays £402,114.80 to A
B)B pays £100,000 to A
C)B pays £69,788.52 to A
D)none of the options
A)B pays £402,114.80 to A
B)B pays £100,000 to A
C)B pays £69,788.52 to A
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Swaps are said to offer market completeness.
A)This means that all types of debt instruments are not regularly available for all borrowers.Thus interest rate swap markets assist in tailoring financing to the type desired by a particular borrower.
B)In that the swap market offers price discovery to the market
C)Because you can trade across both currencies and fixed and floating market segments
D)none of the options
A)This means that all types of debt instruments are not regularly available for all borrowers.Thus interest rate swap markets assist in tailoring financing to the type desired by a particular borrower.
B)In that the swap market offers price discovery to the market
C)Because you can trade across both currencies and fixed and floating market segments
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Company X wants to borrow $10,000,000 for 5 years; company Y wants to borrow £5,000,000 for 5 years.The exchange rate is $2 = £1 and is not expected to change over the next 5 years.Their external borrowing opportunities are shown here: A swap bank proposes the following interest only swap:
X will pay the swap bank annual payments on $10,000,000 with the coupon rate of 9.80 percent; in exchange the swap bank will pay to company X interest payments on £5,000,000 at a fixed rate of 10.5 percent.Y will pay the swap bank interest payments on £5,000,000 at a fixed rate of 12.80 percent and the swap bank will pay Y annual payments on $10,000,000 with the coupon rate of 12 percent.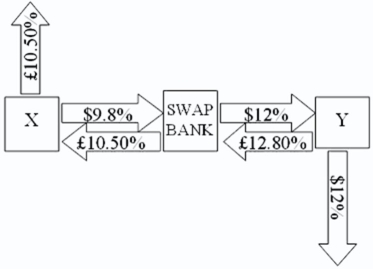 What is the value of this swap to the swap bank?
What is the value of this swap to the swap bank?
A)The swap bank will earn 10 basis points per year; the only risk is default risk.
B)The swap bank will earn 10 basis points per year but has exchange rate risk: dollar-denominated income and pound-denominated costs and default risk.
C)The swap bank will earn 10 basis points per year but has exchange rate risk: pound-denominated income and dollar-denominated costs and default risk.
D)The swap bank will earn 20 basis points per year in dollars but has exchange rate risk: pound-denominated income and dollar-denominated costs and default risk.
X will pay the swap bank annual payments on $10,000,000 with the coupon rate of 9.80 percent; in exchange the swap bank will pay to company X interest payments on £5,000,000 at a fixed rate of 10.5 percent.Y will pay the swap bank interest payments on £5,000,000 at a fixed rate of 12.80 percent and the swap bank will pay Y annual payments on $10,000,000 with the coupon rate of 12 percent.
 What is the value of this swap to the swap bank?
What is the value of this swap to the swap bank?A)The swap bank will earn 10 basis points per year; the only risk is default risk.
B)The swap bank will earn 10 basis points per year but has exchange rate risk: dollar-denominated income and pound-denominated costs and default risk.
C)The swap bank will earn 10 basis points per year but has exchange rate risk: pound-denominated income and dollar-denominated costs and default risk.
D)The swap bank will earn 20 basis points per year in dollars but has exchange rate risk: pound-denominated income and dollar-denominated costs and default risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Floating-for-floating currency swaps
A)have different reference rates for the different currencies: e.g.dollar LIBOR versus euro LIBOR.
B)do not exist.
C)offer the swap bank a built-in hedge.
D)none of the options
A)have different reference rates for the different currencies: e.g.dollar LIBOR versus euro LIBOR.
B)do not exist.
C)offer the swap bank a built-in hedge.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A is a U.S.-based MNC with AAA credit; B is an Italian firm with AAA credit.Firm A wants to borrow €1,000,000 for one year and B wants to borrow $2,000,000 for one year.The spot exchange rate is $2.00 = €1.00,a swap bank makes the following quotes for 1-year swaps and AAA-rated firms against USD LIBOR. USD Euro
The firms external borrowing opportunities are
A)Firm A does 2 swaps with the swap bank,$ at bid and € at ask.Firm B does 2 swaps with the swap bank,$ at ask and € at bid.Firms A and B would each save 90bp and the swap bank would earn 20bp.
B)There is no mutually beneficial swap at these prices.
C)Firm A does 2 swaps with the swap bank,$ at ask and € at bid.Firm B does 2 swaps with the swap bank,$ at bid and € at ask.Firms A and B would each save 90bp and the swap bank would earn 20bp.
D)none of the options
The firms external borrowing opportunities are
A)Firm A does 2 swaps with the swap bank,$ at bid and € at ask.Firm B does 2 swaps with the swap bank,$ at ask and € at bid.Firms A and B would each save 90bp and the swap bank would earn 20bp.
B)There is no mutually beneficial swap at these prices.
C)Firm A does 2 swaps with the swap bank,$ at ask and € at bid.Firm B does 2 swaps with the swap bank,$ at bid and € at ask.Firms A and B would each save 90bp and the swap bank would earn 20bp.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Consider the dollar- and euro-based borrowing opportunities of companies A and B. A is a U.S.-based MNC with AAA credit; B is an Italian firm with AAA credit.Firm A wants to borrow €1,000,000 for one year and B wants to borrow $2,000,000 for one year.The spot exchange rate is $2.00 = €1.00 and the one-year forward rate is given by IRP as $2.00 × (1.08)/€1.00 × (1.06)= $2.0377/€1.
Is there a mutually beneficial swap?
A)No,QSD = 0
B)Yes,QSD = 2% = (7% ? 6%)? (8% ? 9%)= 1% ? (?1%)
C)Yes,QSD = [€7% ? €6%] × $2.00/€1.00 ? ($8% ? $9%)= $2% + $1% = $3%
D)Yes,QSD = [€7% ? €6%] ? ($8% ? $9%)× €1.00/$2.00 = €1½%
Is there a mutually beneficial swap?
A)No,QSD = 0
B)Yes,QSD = 2% = (7% ? 6%)? (8% ? 9%)= 1% ? (?1%)
C)Yes,QSD = [€7% ? €6%] × $2.00/€1.00 ? ($8% ? $9%)= $2% + $1% = $3%
D)Yes,QSD = [€7% ? €6%] ? ($8% ? $9%)× €1.00/$2.00 = €1½%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When an interest-only swap is established on an amortizing basis,
A)the debt service exchanges decrease periodically through time as the hypothetical notational principal is amortized.
B)the debt service exchanges are the same each year,but the level of interest and principal changes as the loans amortize.
C)there is no such thing as an amortizing interest-only swap.
D)none of the options
A)the debt service exchanges decrease periodically through time as the hypothetical notational principal is amortized.
B)the debt service exchanges are the same each year,but the level of interest and principal changes as the loans amortize.
C)there is no such thing as an amortizing interest-only swap.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Company X wants to borrow $10,000,000 floating for 5 years; company Y wants to borrow $10,000,000 fixed for 5 years.Their external borrowing opportunities are shown here: Design a mutually beneficial interest only swap for X and Y with a notational principal of $10 million by having appropriate values for;
A = Company X's external borrowing rate
B = Company Y's payment to X (rate)C = Company X's payment to Y (rate)D = Company Y's external borrowing rate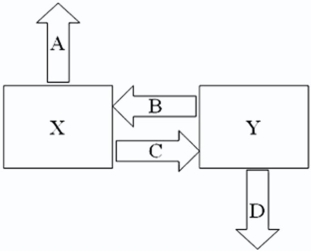
A.A = 10%; B = 11.75%; C = LIBOR - .25%; D = LIBOR + 1.5%
B.A = 10%; B = 10%; C = LIBOR - .25%; D = LIBOR + 1.5%
C.A = LIBOR; B = 10%; C = LIBOR - .25%; D = 12%
D.A = LIBOR; B = LIBOR; C = LIBOR - .25%; D = 12%
A)Option a
B)Option b
C)Option c
D)Option d
A = Company X's external borrowing rate
B = Company Y's payment to X (rate)C = Company X's payment to Y (rate)D = Company Y's external borrowing rate

A.A = 10%; B = 11.75%; C = LIBOR - .25%; D = LIBOR + 1.5%
B.A = 10%; B = 10%; C = LIBOR - .25%; D = LIBOR + 1.5%
C.A = LIBOR; B = 10%; C = LIBOR - .25%; D = 12%
D.A = LIBOR; B = LIBOR; C = LIBOR - .25%; D = 12%
A)Option a
B)Option b
C)Option c
D)Option d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Company X wants to borrow $10,000,000 floating for 1 year; company Y wants to borrow £5,000,000 fixed for 1 year.The spot exchange rate is $2 = £1 and IRP calculates the one-year forward rate as $2.00 × (1.08)/£1.00 × (1.06)= $2.0377/£1.Their external borrowing opportunities are: A swap bank wants to design a profitable interest-only fixed-for-fixed currency swap.In order for X and Y to be interested,they can face no exchange rate risk.
Company X
A)is probably British.
B)is probably American.
C)has a comparative advantage in borrowing pounds.
D)is probably British,and has a comparative advantage in borrowing pounds.
Company X
A)is probably British.
B)is probably American.
C)has a comparative advantage in borrowing pounds.
D)is probably British,and has a comparative advantage in borrowing pounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Suppose ABC Investment Banker Ltd.,is quoting swap rates as follows: 7.50 − 7.85 annually against six-month dollar LIBOR for dollars,and 11.00 percent−11.30 percent annually against six-month dollar LIBOR for British pound sterling.ABC would enter into a $/£ currency swap in which:
A)it would pay annual fixed-rate dollar payments of 7.5 percent in return for receiving annual fixed-rate £ payments at 11.3 percent.
B)it will receive annual fixed-rate dollar payments at 7.85 percent against paying annual fixed-rate £ payments at 11 percent.
C)it would pay annual fixed-rate dollar payments of 7.5 percent in return for receiving annual fixed-rate £ payments at 11.3 percent,and it will receive annual fixed-rate dollar payments at 7.85 percent against paying annual fixed-rate £ payments at 11 percent.
D)none of the options
A)it would pay annual fixed-rate dollar payments of 7.5 percent in return for receiving annual fixed-rate £ payments at 11.3 percent.
B)it will receive annual fixed-rate dollar payments at 7.85 percent against paying annual fixed-rate £ payments at 11 percent.
C)it would pay annual fixed-rate dollar payments of 7.5 percent in return for receiving annual fixed-rate £ payments at 11.3 percent,and it will receive annual fixed-rate dollar payments at 7.85 percent against paying annual fixed-rate £ payments at 11 percent.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Company X wants to borrow $10,000,000 floating for 5 years; company Y wants to borrow £5,000,000 fixed for 5 years.The exchange rate is $2 = £1 and is not expected to change over the next 5 years.Their external borrowing opportunities are A swap bank wants to design a profitable interest-only fixed-for-fixed currency swap.In order for X and Y to be interested,they can face no exchange rate risk. 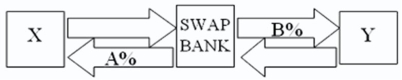 What must the values of A and B in the graph shown above be in order for the swap to be of interest to firms X and Y?
What must the values of A and B in the graph shown above be in order for the swap to be of interest to firms X and Y?
A)A = $10.50%; B = £12%.
B)A = $10%; B = £13%.
C)A = $12%; B = £13%.
D)A = £10.50%; B = $12%.
 What must the values of A and B in the graph shown above be in order for the swap to be of interest to firms X and Y?
What must the values of A and B in the graph shown above be in order for the swap to be of interest to firms X and Y?A)A = $10.50%; B = £12%.
B)A = $10%; B = £13%.
C)A = $12%; B = £13%.
D)A = £10.50%; B = $12%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Compute the payments due in the first year on a three-year amortizing swap from company B to company A.Company A and company B both want to borrow £1,000,000 for three years.A wants to borrow floating and B wants to borrow fixed.A and B agree to split the QSD.
A)B pays £402,114.80 to A
B)B pays £100,000 to A
C)B pays £69,788.52 to A
D)none of the options
A)B pays £402,114.80 to A
B)B pays £100,000 to A
C)B pays £69,788.52 to A
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Use the following information to calculate the quality spread differential (QSD).
A)0.50 percent
B)1.00 percent
C)1.50 percent
D)2.00 percent
A)0.50 percent
B)1.00 percent
C)1.50 percent
D)2.00 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Pricing an interest-only single currency swap after inception involves
A)sending a market order to a swap dealer.
B)finding the difference between the present values of the payments streams the party will receive and pay.
C)finding the sum of the present values of the payments streams that each party will receive in one currency and pay in the other currency,converted to a common currency.
D)none of the options
A)sending a market order to a swap dealer.
B)finding the difference between the present values of the payments streams the party will receive and pay.
C)finding the sum of the present values of the payments streams that each party will receive in one currency and pay in the other currency,converted to a common currency.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Nominal differences in currency swaps
A)can be explained by the set of international parity relationships.
B)can be explained by the credit risk differentials.
C)can be explained by the quality spread differential.
D)disappear when controlling for volatility.
A)can be explained by the set of international parity relationships.
B)can be explained by the credit risk differentials.
C)can be explained by the quality spread differential.
D)disappear when controlling for volatility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In an interest-only currency swap
A)the counterparties must raise the actual notational principal in their home markets; then exchange it for the foreign currency they desire.They must also hedge with forward contracts on the currency.
B)the counterparties periodically exchange the amortized portions of the notational principals.
C)the counterparties must raise the actual notational principal in their home markets; then exchange it for the foreign currency they desire.They must also hedge with forward contracts on the currency.Additionally,the counterparties periodically exchange the amortized portions of the notational principals.
D)none of the options
A)the counterparties must raise the actual notational principal in their home markets; then exchange it for the foreign currency they desire.They must also hedge with forward contracts on the currency.
B)the counterparties periodically exchange the amortized portions of the notational principals.
C)the counterparties must raise the actual notational principal in their home markets; then exchange it for the foreign currency they desire.They must also hedge with forward contracts on the currency.Additionally,the counterparties periodically exchange the amortized portions of the notational principals.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In an efficient market without barriers to capital flows,the cost-savings argument of the QSD is difficult to accept,because
A)it implies that an arbitrage opportunity exists because of some mispricing of the default risk premiums on different types of debt instruments.
B)it implies that an arbitrage opportunity exists because of some mispricing of the exchange rates on different maturities of forward contracts.
C)it implies that an arbitrage opportunity exists because of some mispricing of the default risk premiums on different types of debt instruments,and it implies that an arbitrage opportunity exists because of some mispricing of the exchange rates on different maturities of forward contracts.
D)none of the options
A)it implies that an arbitrage opportunity exists because of some mispricing of the default risk premiums on different types of debt instruments.
B)it implies that an arbitrage opportunity exists because of some mispricing of the exchange rates on different maturities of forward contracts.
C)it implies that an arbitrage opportunity exists because of some mispricing of the default risk premiums on different types of debt instruments,and it implies that an arbitrage opportunity exists because of some mispricing of the exchange rates on different maturities of forward contracts.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Consider a plain vanilla interest rate swap.Firm A can borrow at 8 percent fixed or can borrow floating at LIBOR.Firm B is somewhat less creditworthy and can borrow at 10 percent fixed or can borrow floating at LIBOR + 1 percent.Eun wants to borrow floating and Resnick prefers to borrow fixed.Both corporations wish to borrow $10 million for 5 years.Which of the following swaps is mutually beneficial to each party and meets their financing needs?
A)Firm A borrows $10 million externally for 5 years at LIBOR; agrees to swap LIBOR to firm B for 8 ½ percent fixed for 5 years on a notational principal of $5 million; B borrows $10 million externally at 10 percent.
B)A borrows $10 million externally for 5 years at LIBOR; agrees to pay 8½ percent to B for LIBOR fixed for 5 years on a notational principal of $5 million; B borrows $10 million externally at 10 percent.
C)Since the QSD = 0 there is no mutually beneficial swap.
D)A borrows $10 million externally at 8 percent fixed for 5 years; agrees to swap LIBOR to B for 8½ percent fixed for 5 years on a notational principal of $5 million; B borrows $10 million externally at LIBOR + 1 percent.
A)Firm A borrows $10 million externally for 5 years at LIBOR; agrees to swap LIBOR to firm B for 8 ½ percent fixed for 5 years on a notational principal of $5 million; B borrows $10 million externally at 10 percent.
B)A borrows $10 million externally for 5 years at LIBOR; agrees to pay 8½ percent to B for LIBOR fixed for 5 years on a notational principal of $5 million; B borrows $10 million externally at 10 percent.
C)Since the QSD = 0 there is no mutually beneficial swap.
D)A borrows $10 million externally at 8 percent fixed for 5 years; agrees to swap LIBOR to B for 8½ percent fixed for 5 years on a notational principal of $5 million; B borrows $10 million externally at LIBOR + 1 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When a swap bank serves as a broker,
A)the swap bank stands willing to accept either side of a swap.
B)the swap bank matches counterparties but does not assume any risk of the swap.
C)the swap bank receives a commission for matching buyers and sellers.
D)none of the options
A)the swap bank stands willing to accept either side of a swap.
B)the swap bank matches counterparties but does not assume any risk of the swap.
C)the swap bank receives a commission for matching buyers and sellers.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When a swap bank serves as a dealer,
A)the swap bank stands willing to accept either side of a swap.
B)the swap bank matches counterparties but does not assume any risk of the swap.
C)the swap bank receives a commission for matching buyers and sellers.
D)none of the options
A)the swap bank stands willing to accept either side of a swap.
B)the swap bank matches counterparties but does not assume any risk of the swap.
C)the swap bank receives a commission for matching buyers and sellers.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Consider a bank that has entered into a five-year swap on a notational balance of $10,000,000 with a corporate customer who has agreed to pay a fixed payment of 10 percent in exchange for LIBOR.As of the fourth reset date,determine the price of the swap from the bank's point of view assuming that the fixed-rate side of the swap has increased to 11 percent.LIBOR is at 5 percent.
A)$909,090.91 gain.
B)$90,090.09 loss.
C)No loss or no gain since maturity has not arrived.
D)$90,090.09 gain.
A)$909,090.91 gain.
B)$90,090.09 loss.
C)No loss or no gain since maturity has not arrived.
D)$90,090.09 gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which combination of the following represent the risks that a swap dealer confronts. (i)interest rate risk
(ii)basis risk
(iii)exchange rate risk
(iv)political risk
(v)sovereign risk
A)(i),(ii),(iii),and (v)
B)(i),(iii),and (iv)
C)(iii),(iv),and (iv)
D)(i),(ii),(iii),(iv),and (v)
(ii)basis risk
(iii)exchange rate risk
(iv)political risk
(v)sovereign risk
A)(i),(ii),(iii),and (v)
B)(i),(iii),and (iv)
C)(iii),(iv),and (iv)
D)(i),(ii),(iii),(iv),and (v)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A major that can be eliminated through a swap is exchange rate risk.
A)But only to the extent that a foreign counterparty will not default in a currency swap.
B)But only if the bid-ask spreads are wide.
C)But swaps can be less efficient in this than just trading at the expected spot exchange rates each year.
D)none of the options
A)But only to the extent that a foreign counterparty will not default in a currency swap.
B)But only if the bid-ask spreads are wide.
C)But swaps can be less efficient in this than just trading at the expected spot exchange rates each year.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A major risk faced by a swap dealer is credit risk.This is
A)the probability that a counterparty will default.
B)the probability that both counterparties default.
C)the probability floating rates will move against the dealer.
D)none of the options
A)the probability that a counterparty will default.
B)the probability that both counterparties default.
C)the probability floating rates will move against the dealer.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Some of the risks that a swap dealer confronts are "basis risk" and "sovereign risk." Select the definitions that best describe each.
A)"Basis risk" refers to the probability that a country will impose exchange restrictions on a currency involved in a swap,and "sovereign risk" refers to a situation in which the floating rates of the two counterparties are not pegged to the same index.
B)"Basis risk" refers to a situation in which the floating rates of the two counterparties are not pegged to the same index and "sovereign risk" refers to the probability that a country will impose exchange restrictions on a currency involved in a swap.
C)"Basis risk" refers to interest rate changing unfavorably before the swap bank can lay off to an opposing counterparty the other side of an interest rate swap entered into with a counter party,and "sovereign risk" refers to the probability that a country will impose exchange restrictions on a currency involved in a swap.
D)"Basis risk" refers to the risk of fluctuating exchange rates,and "sovereign risk" refers to a situation in which the floating rates of the two counterparties are not pegged to the same index.
A)"Basis risk" refers to the probability that a country will impose exchange restrictions on a currency involved in a swap,and "sovereign risk" refers to a situation in which the floating rates of the two counterparties are not pegged to the same index.
B)"Basis risk" refers to a situation in which the floating rates of the two counterparties are not pegged to the same index and "sovereign risk" refers to the probability that a country will impose exchange restrictions on a currency involved in a swap.
C)"Basis risk" refers to interest rate changing unfavorably before the swap bank can lay off to an opposing counterparty the other side of an interest rate swap entered into with a counter party,and "sovereign risk" refers to the probability that a country will impose exchange restrictions on a currency involved in a swap.
D)"Basis risk" refers to the risk of fluctuating exchange rates,and "sovereign risk" refers to a situation in which the floating rates of the two counterparties are not pegged to the same index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Consider fixed-for-fixed currency swap.Firm A is a U.S.-based multinational.Firm B is a U.K.-based multinational.Firm A wants to finance a £2 million expansion in Great Britain.Firm B wants to finance a $4 million expansion in the U.S.The spot exchange rate is £1.00 = $2.00.Firm A can borrow dollars at 10 percent and pounds sterling at 12 percent.Firm B can borrow dollars at 9 percent and pounds sterling at 11 percent.Which of the following swaps is mutually beneficial to each party and meets their financing needs? Neither party should face exchange rate risk.
A)There is no mutually beneficial swap that has neither party facing exchange rate risk.
B)Firm A should borrow $4 million in dollars,pay 11 percent in pounds to Firm B,who in turn borrows 2 million pounds and pays 8 percent in dollars to A.
C)Firm A should borrow $2 million in dollars,pay 11 percent in pounds to Firm B,who in turn borrows 4 million pounds and pays 8 percent in dollars to A.
D)Firm A should borrow $4 million in dollars,pay 11 percent in pounds to Firm B,who in turn borrows 2 million pounds and pays 10 percent in dollars to A.
A)There is no mutually beneficial swap that has neither party facing exchange rate risk.
B)Firm A should borrow $4 million in dollars,pay 11 percent in pounds to Firm B,who in turn borrows 2 million pounds and pays 8 percent in dollars to A.
C)Firm A should borrow $2 million in dollars,pay 11 percent in pounds to Firm B,who in turn borrows 4 million pounds and pays 8 percent in dollars to A.
D)Firm A should borrow $4 million in dollars,pay 11 percent in pounds to Firm B,who in turn borrows 2 million pounds and pays 10 percent in dollars to A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Consider a fixed for fixed currency swap.The Dow Corporation is a U.S.-based multinational.The Jones Corporation is a U.K.-based multinational.Dow wants to finance a £2 million expansion in Great Britain.Jones wants to finance a $4 million expansion in the U.S.The spot exchange rate is £1.00 = $2.00.Dow can borrow dollars at $10 percent and pounds sterling at 12 percent.Jones can borrow dollars at 9 percent and pounds sterling at 10 percent.Assuming that the swap bank is willing to take on exchange rate risk,but the other counterparties are not,which of the following swaps is mutually beneficial to each party and meets their financing needs?
A)Dow should borrow $4 million in dollars externally at $10 percent; pay £11¾ percent in pounds to the swap bank on a notational principal of £2 million; receive $10 percent from the swap bank on a notational principal of $4 million.Jones,borrows £2 million pounds externally at £10 percent; pays $8¾ percent to the swap bank on a notational principal of $4 million and receives £10 percent in pounds from the swap bank on a notational principal of £2 million.
B)Dow should borrow $4 million in dollars externally at $10 percent; pay £11½ percent in pounds to the swap bank on a notational principal of £2 million; receive $10 percent from the swap bank on a notational principal of $4 million.Jones,borrows £2 million pounds externally at £10 percent; pays $8½ percent to the swap bank on a notational principal of $4 million and receives £10 percent in pounds from the swap bank on a notational principal of £2 million.
C)Dow should borrow $4 million in dollars externally at $10 percent; pay £11 percent in pounds to the swap bank on a notational principal of £2 million; receive $8 percent from the swap bank on a notational principal of $4 million.Jones,borrows £2 million pounds externally at £10 percent; pays $10 percent to the swap bank on a notational principal of $4 million and receives £11 percent in pounds from the swap bank on a notational principal of £2 million.
D)There is no swap that is possible.
A)Dow should borrow $4 million in dollars externally at $10 percent; pay £11¾ percent in pounds to the swap bank on a notational principal of £2 million; receive $10 percent from the swap bank on a notational principal of $4 million.Jones,borrows £2 million pounds externally at £10 percent; pays $8¾ percent to the swap bank on a notational principal of $4 million and receives £10 percent in pounds from the swap bank on a notational principal of £2 million.
B)Dow should borrow $4 million in dollars externally at $10 percent; pay £11½ percent in pounds to the swap bank on a notational principal of £2 million; receive $10 percent from the swap bank on a notational principal of $4 million.Jones,borrows £2 million pounds externally at £10 percent; pays $8½ percent to the swap bank on a notational principal of $4 million and receives £10 percent in pounds from the swap bank on a notational principal of £2 million.
C)Dow should borrow $4 million in dollars externally at $10 percent; pay £11 percent in pounds to the swap bank on a notational principal of £2 million; receive $8 percent from the swap bank on a notational principal of $4 million.Jones,borrows £2 million pounds externally at £10 percent; pays $10 percent to the swap bank on a notational principal of $4 million and receives £11 percent in pounds from the swap bank on a notational principal of £2 million.
D)There is no swap that is possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A major risk faced by a swap dealer is sovereign risk.This is
A)the probability that a sovereign counterparty will default.
B)the probability that a country will impose exchange restrictions on a currency involved in an existing swap.
C)the probability governments will intervene to support an exchange rate.
D)none of the options
A)the probability that a sovereign counterparty will default.
B)the probability that a country will impose exchange restrictions on a currency involved in an existing swap.
C)the probability governments will intervene to support an exchange rate.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
XYZ Corporation enters into a 6-year interest rate swap with a swap bank in which it agrees to pay the swap bank a fixed-rate of 9 percent annually on a notional amount of SFr10,000,000 and receive LIBOR −½ percent.As of the third reset date (i.e.,midway through the 6-year agreement),calculate the price of the swap,assuming that the fixed-rate at which XYZ can borrow has increased to 10 percent.
A)SFr248,685
B)SFr900,000
C)SFr2,700,000
D)SFr7,300,000
A)SFr248,685
B)SFr900,000
C)SFr2,700,000
D)SFr7,300,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Floating-for-floating currency swaps
A)have reference rates that are different for the different currencies (e.g.,dollar LIBOR versus euro LIBOR).
B)have reference rates that can be the same but have different frequencies.
C)have reference rates that are different for the different currencies (e.g.,dollar LIBOR versus euro LIBOR),and the reference rates can be the same but have different frequencies.
D)none of the options
A)have reference rates that are different for the different currencies (e.g.,dollar LIBOR versus euro LIBOR).
B)have reference rates that can be the same but have different frequencies.
C)have reference rates that are different for the different currencies (e.g.,dollar LIBOR versus euro LIBOR),and the reference rates can be the same but have different frequencies.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Find the all-in-cost of a swap to a party that has agreed to borrow $5 million at 5 percent externally and pays LIBOR + ½ percent on a notational principal of $5 million in exchange for fixed rate payments of 6 percent.
A)LIBOR + ½ percent
B)LIBOR
C)LIBOR − ½ percent
D)none of the options
A)LIBOR + ½ percent
B)LIBOR
C)LIBOR − ½ percent
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A major risk faced by a swap dealer is exchange rate risk.This is
A)the probability that a foreign counterparty will default in a currency swap.
B)the probability that either counterparty defaults in a currency swap.
C)the probability exchange rates will move against the dealer.
D)none of the options
A)the probability that a foreign counterparty will default in a currency swap.
B)the probability that either counterparty defaults in a currency swap.
C)the probability exchange rates will move against the dealer.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A major risk faced by a swap dealer is mismatch risk.This is
A)the probability floating rates and exchange rates will not move together.
B)the difficulty in finding a second counterparty for a swap that the bank has agreed to take with another party.
C)the probability that both counterparties default.
D)none of the options
A)the probability floating rates and exchange rates will not move together.
B)the difficulty in finding a second counterparty for a swap that the bank has agreed to take with another party.
C)the probability that both counterparties default.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Amortizing currency swaps
A)decrease the debt service exchanges periodically through time as the hypothetical notational principal is amortized.
B)incorporate an amortization feature in which periodically the amortized portions of the notational principals are re-exchanged.
C)decrease the debt service exchanges periodically through time as the hypothetical notational principal is amortized.Additionally,amortizing currency swaps incorporate an amortization feature in which periodically the amortized portions of the notational principals are re-exchanged.
D)none of the options
A)decrease the debt service exchanges periodically through time as the hypothetical notational principal is amortized.
B)incorporate an amortization feature in which periodically the amortized portions of the notational principals are re-exchanged.
C)decrease the debt service exchanges periodically through time as the hypothetical notational principal is amortized.Additionally,amortizing currency swaps incorporate an amortization feature in which periodically the amortized portions of the notational principals are re-exchanged.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Consider the situation of firm A and firm B.The current exchange rate is $1.50/€.Firm A is a U.S.MNC and wants to borrow €40 million for 2 years.Firm B is a French MNC and wants to borrow $60 million for 2 years.Their borrowing opportunities are as shown; both firms have AAA credit ratings.
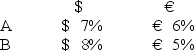 If firm B could use the forward exchange markets to redenominate a 2-year €40m 5 percent euro loan into a 2-year USD-denominated loan,what would be the interest rate?
If firm B could use the forward exchange markets to redenominate a 2-year €40m 5 percent euro loan into a 2-year USD-denominated loan,what would be the interest rate?
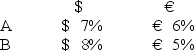 If firm B could use the forward exchange markets to redenominate a 2-year €40m 5 percent euro loan into a 2-year USD-denominated loan,what would be the interest rate?
If firm B could use the forward exchange markets to redenominate a 2-year €40m 5 percent euro loan into a 2-year USD-denominated loan,what would be the interest rate?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Consider the situation of firm A and firm B.The current exchange rate is $1.50/€.Firm A is a U.S.MNC and wants to borrow €40 million for 2 years.Firm B is a French MNC and wants to borrow $60 million for 2 years.Their borrowing opportunities are as shown; both firms have AAA credit ratings.
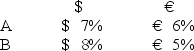 What are the IRP 1-year and 2-year forward exchange rates?
What are the IRP 1-year and 2-year forward exchange rates?
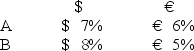 What are the IRP 1-year and 2-year forward exchange rates?
What are the IRP 1-year and 2-year forward exchange rates?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Suppose that you are a swap bank and you notice that interest rates on coupon bonds are as shown.Develop the 3-year bid price of a euro swap quoted against flat USD LIBOR.The current spot exchange rate is $1.50 per €1.00.The size of the swap is €40 million versus $60 million. In other words,what will you be willing to pay in euro against receiving USD LIBOR?
A)7 percent
B)6 percent
C)5 percent
D)none of the options
A)7 percent
B)6 percent
C)5 percent
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Consider the situation of firm A and firm B.The current exchange rate is $1.50/€.Firm A is a U.S.MNC and wants to borrow €40 million for 2 years.Firm B is a French MNC and wants to borrow $60 million for 2 years.Their borrowing opportunities are as shown; both firms have AAA credit ratings.
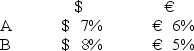 Explain how firm A could use the forward exchange markets to redenominate a 2-year $60m 7 percent USD loan into a 2-year euro denominated loan.
Explain how firm A could use the forward exchange markets to redenominate a 2-year $60m 7 percent USD loan into a 2-year euro denominated loan.
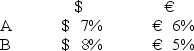 Explain how firm A could use the forward exchange markets to redenominate a 2-year $60m 7 percent USD loan into a 2-year euro denominated loan.
Explain how firm A could use the forward exchange markets to redenominate a 2-year $60m 7 percent USD loan into a 2-year euro denominated loan.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
You are the debt manager for a U.S.-based multinational.You need to borrow €100,000,000 for five years.You can either borrow the €100,000,000 directly in Germany or borrow dollars in the U.S.and enter into a combined interest rate and currency swap with a swap bank.One risk that you face by using the swap that you do not face by borrowing euros directly is
A)exchange rate risk.
B)sovereign risk.
C)credit risk.
D)interest rate risk.
A)exchange rate risk.
B)sovereign risk.
C)credit risk.
D)interest rate risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Consider the situation of firm A and firm B.The current exchange rate is $1.50/€.Firm A is a U.S.MNC and wants to borrow €40 million for 2 years.Firm B is a French MNC and wants to borrow $60 million for 2 years.Their borrowing opportunities are as shown; both firms have AAA credit ratings.
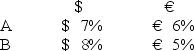 If firm A could use the forward exchange markets to redenominate a 2-year $60m 7 percent USD loan into a 2-year euro denominated loan,what would be the interest rate?
If firm A could use the forward exchange markets to redenominate a 2-year $60m 7 percent USD loan into a 2-year euro denominated loan,what would be the interest rate?
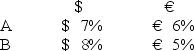 If firm A could use the forward exchange markets to redenominate a 2-year $60m 7 percent USD loan into a 2-year euro denominated loan,what would be the interest rate?
If firm A could use the forward exchange markets to redenominate a 2-year $60m 7 percent USD loan into a 2-year euro denominated loan,what would be the interest rate?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose that the swap that you proposed is now 4 years old (i.e.,there is exactly one year to go on the swap).The fourth payment has already been made.If the spot exchange rate prevailing in year 4 is $1.8778 = €1 and the 1-year forward exchange rate prevailing in year 4 is $1.95 = €1,what is the value of the swap to the party paying dollars? If the swap were initiated today the correct rates would be as shown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Consider the situation of firm A and firm B.The current exchange rate is $1.50/€.Firm A is a U.S.MNC and wants to borrow €40 million for 2 years.Firm B is a French MNC and wants to borrow $60 million for 2 years.Their borrowing opportunities are as shown; both firms have AAA credit ratings.
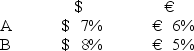 Explain how this opportunity affects which swap firm B will be willing to participate in.
Explain how this opportunity affects which swap firm B will be willing to participate in.
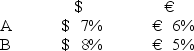 Explain how this opportunity affects which swap firm B will be willing to participate in.
Explain how this opportunity affects which swap firm B will be willing to participate in.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Suppose that you are a swap bank and you notice that interest rates on zero coupon bonds are as shown.Develop the 3-year bid price of a dollar swap quoted against flat USD LIBOR. In other words,what will you be willing to pay in euro against receiving USD LIBOR?
A)5 percent
B)4 percent
C)3 percent
D)2 percent
A)5 percent
B)4 percent
C)3 percent
D)2 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
With regard to a swap bank acting as a dealer in swap transactions,interest rate risk refers to
A)the risk that arises from the situation in which the floating-rates of the two counterparties are not pegged to the same index.
B)the risk that interest rates changing unfavorably before the swap bank can lay off to an opposing counterparty on the other side of an interest rate swap entered into with the first counterparty.
C)the risk the swap bank faces from fluctuating exchange rates during the time it takes for the bank to lay off a swap it undertakes with one counterparty with an opposing transaction.
D)the risk that a counterparty will default.
A)the risk that arises from the situation in which the floating-rates of the two counterparties are not pegged to the same index.
B)the risk that interest rates changing unfavorably before the swap bank can lay off to an opposing counterparty on the other side of an interest rate swap entered into with the first counterparty.
C)the risk the swap bank faces from fluctuating exchange rates during the time it takes for the bank to lay off a swap it undertakes with one counterparty with an opposing transaction.
D)the risk that a counterparty will default.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Come up with a swap (principal + interest)for two parties A and B who have the following borrowing opportunities.
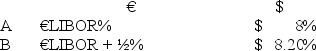 The current exchange rate is $1.60 = €1.00.Company "A" wishes to borrow $1,000,000 for 5 years and "B" wants to borrow €625,000 for 5 years.You are a swap dealer.Quote A and B a swap that makes money for all parties and eliminates exchange rate risk for both A and B.Firms A and B are more concerned with what currency that they borrow in than whether the debt is fixed or floating.
The current exchange rate is $1.60 = €1.00.Company "A" wishes to borrow $1,000,000 for 5 years and "B" wants to borrow €625,000 for 5 years.You are a swap dealer.Quote A and B a swap that makes money for all parties and eliminates exchange rate risk for both A and B.Firms A and B are more concerned with what currency that they borrow in than whether the debt is fixed or floating.
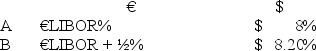 The current exchange rate is $1.60 = €1.00.Company "A" wishes to borrow $1,000,000 for 5 years and "B" wants to borrow €625,000 for 5 years.You are a swap dealer.Quote A and B a swap that makes money for all parties and eliminates exchange rate risk for both A and B.Firms A and B are more concerned with what currency that they borrow in than whether the debt is fixed or floating.
The current exchange rate is $1.60 = €1.00.Company "A" wishes to borrow $1,000,000 for 5 years and "B" wants to borrow €625,000 for 5 years.You are a swap dealer.Quote A and B a swap that makes money for all parties and eliminates exchange rate risk for both A and B.Firms A and B are more concerned with what currency that they borrow in than whether the debt is fixed or floating.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Consider the situation of firm A and firm B.The current exchange rate is $1.50/€.Firm A is a U.S.MNC and wants to borrow €40 million for 2 years.Firm B is a French MNC and wants to borrow $60 million for 2 years.Their borrowing opportunities are as shown; both firms have AAA credit ratings.
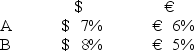 Devise a direct swap for A and B that has no swap bank.Show their external borrowing.
Devise a direct swap for A and B that has no swap bank.Show their external borrowing. 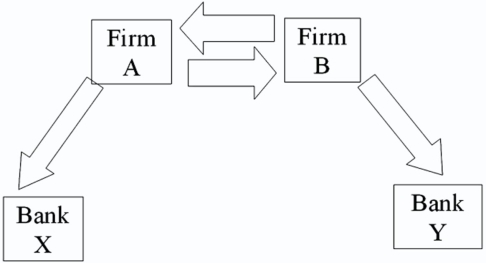
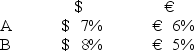 Devise a direct swap for A and B that has no swap bank.Show their external borrowing.
Devise a direct swap for A and B that has no swap bank.Show their external borrowing. 

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Suppose that you are a swap bank and you notice that interest rates on zero coupon bonds are as shown.Develop the 3-year bid price of a euro swap quoted against flat USD LIBOR. In other words,what will you be willing to pay in euro against receiving USD LIBOR?
A)5 percent
B)4 percent
C)3 percent
D)2 percent
A)5 percent
B)4 percent
C)3 percent
D)2 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Suppose that the swap that you proposed is now 4 years old (i.e.,there is exactly one year to go on the swap).If the spot exchange rate prevailing in year 4 is $1.8778 = €1 and the 1-year forward exchange rate prevailing in year 4 is $1.95 = €1,what is the value of the swap to the party paying dollars? If the swap were initiated today the correct rates would be as shown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Come up with a swap (exchange of interest and principal)for parties A and B who have the following borrowing opportunities.
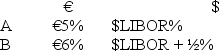 The current exchange rate is $1.60 = €1.00.Company "A" is in Milan,Italy and wishes to borrow $1,000,000 at a floating rate for 5 years and company "B" is a U.S.firm that wants to borrow €625,000 for 5 years at a fixed rate of interest.You are a swap dealer.Quote A and B a swap that makes money for all parties and eliminates exchange rate risk for both A and B.
The current exchange rate is $1.60 = €1.00.Company "A" is in Milan,Italy and wishes to borrow $1,000,000 at a floating rate for 5 years and company "B" is a U.S.firm that wants to borrow €625,000 for 5 years at a fixed rate of interest.You are a swap dealer.Quote A and B a swap that makes money for all parties and eliminates exchange rate risk for both A and B.
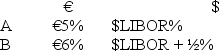 The current exchange rate is $1.60 = €1.00.Company "A" is in Milan,Italy and wishes to borrow $1,000,000 at a floating rate for 5 years and company "B" is a U.S.firm that wants to borrow €625,000 for 5 years at a fixed rate of interest.You are a swap dealer.Quote A and B a swap that makes money for all parties and eliminates exchange rate risk for both A and B.
The current exchange rate is $1.60 = €1.00.Company "A" is in Milan,Italy and wishes to borrow $1,000,000 at a floating rate for 5 years and company "B" is a U.S.firm that wants to borrow €625,000 for 5 years at a fixed rate of interest.You are a swap dealer.Quote A and B a swap that makes money for all parties and eliminates exchange rate risk for both A and B.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Consider the situation of firm A and firm B.The current exchange rate is $1.50/€.Firm A is a U.S.MNC and wants to borrow €40 million for 2 years.Firm B is a French MNC and wants to borrow $60 million for 2 years.Their borrowing opportunities are as shown; both firms have AAA credit ratings.
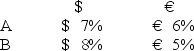 Explain how firm B could use the forward exchange markets to redenominate a 2-year €40m 5 percent euro loan into a 2-year USD-denominated loan.
Explain how firm B could use the forward exchange markets to redenominate a 2-year €40m 5 percent euro loan into a 2-year USD-denominated loan.
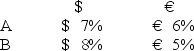 Explain how firm B could use the forward exchange markets to redenominate a 2-year €40m 5 percent euro loan into a 2-year USD-denominated loan.
Explain how firm B could use the forward exchange markets to redenominate a 2-year €40m 5 percent euro loan into a 2-year USD-denominated loan.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
With regard to a swap bank acting as a dealer in swap transactions,mismatch risk refers to
A)the risk that arises from the situation in which the floating-rates of the two counterparties are not pegged to the same index.
B)the risk that interest rates changing unfavorably before the swap bank can lay off to an opposing counterparty on the other side of an interest rate swap entered into with the first counterparty.
C)the risk the swap bank faces from fluctuating exchange rates during the time it takes for the bank to lay off a swap it undertakes with one counterparty with an opposing transaction.
D)the risk that it may be difficult or impossible to find an exact opposite match for a swap the bank has agreed take.
A)the risk that arises from the situation in which the floating-rates of the two counterparties are not pegged to the same index.
B)the risk that interest rates changing unfavorably before the swap bank can lay off to an opposing counterparty on the other side of an interest rate swap entered into with the first counterparty.
C)the risk the swap bank faces from fluctuating exchange rates during the time it takes for the bank to lay off a swap it undertakes with one counterparty with an opposing transaction.
D)the risk that it may be difficult or impossible to find an exact opposite match for a swap the bank has agreed take.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Consider the situation of firm A and firm B.The current exchange rate is $1.50/€.Firm A is a U.S.MNC and wants to borrow €40 million for 2 years.Firm B is a French MNC and wants to borrow $60 million for 2 years.Their borrowing opportunities are as shown; both firms have AAA credit ratings.
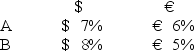 Explain how this opportunity affects which swap firm A will be willing to participate in.
Explain how this opportunity affects which swap firm A will be willing to participate in.
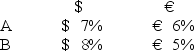 Explain how this opportunity affects which swap firm A will be willing to participate in.
Explain how this opportunity affects which swap firm A will be willing to participate in.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Consider the situation of firm A and firm B.The current exchange rate is $1.50/€.Firm A is a U.S.MNC and wants to borrow €40 million for 2 years.Firm B is a French MNC and wants to borrow $60 million for 2 years.Their borrowing opportunities are as shown; both firms have AAA credit ratings.
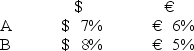 Act as a swap bank and quote bid and ask prices to A and B that are attractive to A and B and promise to make at least 20bp for your firm.
Act as a swap bank and quote bid and ask prices to A and B that are attractive to A and B and promise to make at least 20bp for your firm.

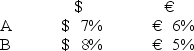 Act as a swap bank and quote bid and ask prices to A and B that are attractive to A and B and promise to make at least 20bp for your firm.
Act as a swap bank and quote bid and ask prices to A and B that are attractive to A and B and promise to make at least 20bp for your firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Consider the situation of firm A and firm B.The current exchange rate is $1.50/€.Firm A is a U.S.MNC and wants to borrow €40 million for 2 years.Firm B is a French MNC and wants to borrow $60 million for 2 years.Their borrowing opportunities are as shown; both firms have AAA credit ratings.
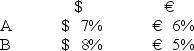 Show how your proposed swap would work for firm A.(e.g.,if you were acting as an agent for the swap bank,try to "sell" firm A on your swap)
Show how your proposed swap would work for firm A.(e.g.,if you were acting as an agent for the swap bank,try to "sell" firm A on your swap)
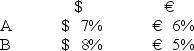 Show how your proposed swap would work for firm A.(e.g.,if you were acting as an agent for the swap bank,try to "sell" firm A on your swap)
Show how your proposed swap would work for firm A.(e.g.,if you were acting as an agent for the swap bank,try to "sell" firm A on your swap)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



