Deck 6: Elasticity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/255
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Elasticity
1
Most demand curves are relatively elastic in the upper-left portion because the original price
A) and quantity from which the percentage changes in price and quantity are calculated are both large.
B) and quantity from which the percentage changes in price and quantity are calculated are both small.
C) from which the percentage price change is calculated is small and the original quantity from which the percentage change in quantity is calculated is large.
D) from which the percentage price change is calculated is large and the original quantity from which the percentage change in quantity is calculated is small.
A) and quantity from which the percentage changes in price and quantity are calculated are both large.
B) and quantity from which the percentage changes in price and quantity are calculated are both small.
C) from which the percentage price change is calculated is small and the original quantity from which the percentage change in quantity is calculated is large.
D) from which the percentage price change is calculated is large and the original quantity from which the percentage change in quantity is calculated is small.
from which the percentage price change is calculated is large and the original quantity from which the percentage change in quantity is calculated is small.
2
The basic formula for the price elasticity of demand coefficient is
A) absolute decline in quantity demanded/absolute increase in price.
B) percentage change in quantity demanded/percentage change in price.
C) absolute decline in price/absolute increase in quantity demanded.
D) percentage change in price/percentage change in quantity demanded.
A) absolute decline in quantity demanded/absolute increase in price.
B) percentage change in quantity demanded/percentage change in price.
C) absolute decline in price/absolute increase in quantity demanded.
D) percentage change in price/percentage change in quantity demanded.
percentage change in quantity demanded/percentage change in price.
3
If the demand for product X is inelastic, a 4 percent decrease in the price of X will
A) decrease the quantity of X demanded by more than 4 percent.
B) decrease the quantity of X demanded by less than 4 percent.
C) increase the quantity of X demanded by more than 4 percent.
D) increase the quantity of X demanded by less than 4 percent.
A) decrease the quantity of X demanded by more than 4 percent.
B) decrease the quantity of X demanded by less than 4 percent.
C) increase the quantity of X demanded by more than 4 percent.
D) increase the quantity of X demanded by less than 4 percent.
increase the quantity of X demanded by less than 4 percent.
4
Suppose we find that the price elasticity of demand for a product is 3.5 when its price is increased by 2 percent. We can conclude that quantity demanded
A) increased by 7 percent.
B) decreased by 7 percent.
C) decreased by 9 percent.
D) decreased by 1.75 percent.
A) increased by 7 percent.
B) decreased by 7 percent.
C) decreased by 9 percent.
D) decreased by 1.75 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The demand for a product is inelastic with respect to price if
A) consumers are largely unresponsive to a per unit price change.
B) the elasticity coefficient is greater than 1.
C) a drop in price is accompanied by a decrease in the quantity demanded.
D) a drop in price is accompanied by an increase in the quantity demanded.
A) consumers are largely unresponsive to a per unit price change.
B) the elasticity coefficient is greater than 1.
C) a drop in price is accompanied by a decrease in the quantity demanded.
D) a drop in price is accompanied by an increase in the quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A leftward shift in the supply curve of product X will increase equilibrium price to a greater extent the
A) more elastic the supply curve.
B) larger the elasticity of demand coefficient.
C) more elastic the demand for the product.
D) more inelastic the demand for the product.
A) more elastic the supply curve.
B) larger the elasticity of demand coefficient.
C) more elastic the demand for the product.
D) more inelastic the demand for the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Suppose Aiyanna's Pizzeria currently faces a linear demand curve and is charging a very high price per pizza and doing very little business. Aiyanna now decides to lower pizza prices by 5 percent per week for an indefinite period of time. We can expect that each successive week,
A) demand will become more price elastic.
B) price elasticity of demand will not change as price is lowered.
C) demand will become less price elastic.
D) the elasticity of supply will increase.
A) demand will become more price elastic.
B) price elasticity of demand will not change as price is lowered.
C) demand will become less price elastic.
D) the elasticity of supply will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Suppose that as the price of Y falls from $2.00 to $1.90, the quantity of Y demanded increases from 110 to 118. Then the absolute value of the price elasticity (using the midpoint formula) is
A) 4.00.
B) 2.09.
C) 1.37.
D) 3.94.
A) 4.00.
B) 2.09.
C) 1.37.
D) 3.94.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The larger the coefficient of price elasticity of demand for a product, the
A) larger the resulting price change for an increase in supply.
B) more rapid the rate at which the marginal utility of that product diminishes.
C) less competitive will be the industry supplying that product.
D) smaller the resulting price change for an increase in supply.
A) larger the resulting price change for an increase in supply.
B) more rapid the rate at which the marginal utility of that product diminishes.
C) less competitive will be the industry supplying that product.
D) smaller the resulting price change for an increase in supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The price elasticity of demand is generally
A) negative, but the minus sign is ignored.
B) positive, but the plus sign is ignored.
C) positive for normal goods and negative for inferior goods.
D) positive because price and quantity demanded are inversely related.
A) negative, but the minus sign is ignored.
B) positive, but the plus sign is ignored.
C) positive for normal goods and negative for inferior goods.
D) positive because price and quantity demanded are inversely related.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The price elasticity of demand of a straight-line demand curve is
A) elastic in high-price ranges and inelastic in low-price ranges.
B) elastic but does not change at various points on the curve.
C) inelastic but does not change at various points on the curve.
D) 1 at all points on the curve.
A) elastic in high-price ranges and inelastic in low-price ranges.
B) elastic but does not change at various points on the curve.
C) inelastic but does not change at various points on the curve.
D) 1 at all points on the curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The price elasticity of demand coefficient measures
A) buyer responsiveness to price changes.
B) the extent to which a demand curve shifts as incomes change.
C) the slope of the demand curve.
D) how far business executives can stretch their fixed costs.
A) buyer responsiveness to price changes.
B) the extent to which a demand curve shifts as incomes change.
C) the slope of the demand curve.
D) how far business executives can stretch their fixed costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If the demand for bacon is relatively elastic, a 10 percent decline in the price of bacon will
A) decrease the amount demanded by more than 10 percent.
B) increase the amount demanded by more than 10 percent.
C) decrease the amount demanded by less than 10 percent.
D) increase the amount demanded by less than 10 percent.
A) decrease the amount demanded by more than 10 percent.
B) increase the amount demanded by more than 10 percent.
C) decrease the amount demanded by less than 10 percent.
D) increase the amount demanded by less than 10 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The price of product X is reduced from $100 to $90 and, as a result, the quantity demanded increases from 50 to 60 units. Therefore, demand for X in this price range
A) has declined.
B) is of unit elasticity.
C) is inelastic.
D) is elastic.
A) has declined.
B) is of unit elasticity.
C) is inelastic.
D) is elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If the price elasticity of demand for a product is 2.5, then a price cut from $2.00 to $1.80 will
A) increase the quantity demanded by about 2.5 percent.
B) decrease the quantity demanded by about 2.5 percent.
C) increase the quantity demanded by about 25 percent.
D) increase the quantity demanded by about 250 percent.
A) increase the quantity demanded by about 2.5 percent.
B) decrease the quantity demanded by about 2.5 percent.
C) increase the quantity demanded by about 25 percent.
D) increase the quantity demanded by about 250 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is not characteristic of the demand for a commodity that is elastic?
A) The relative change in quantity demanded is greater than the relative change in price.
B) Buyers are relatively sensitive to price changes.
C) Total revenue increases if price is increased.
D) The elasticity coefficient is greater than one.
A) The relative change in quantity demanded is greater than the relative change in price.
B) Buyers are relatively sensitive to price changes.
C) Total revenue increases if price is increased.
D) The elasticity coefficient is greater than one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
For a linear demand curve,
A) elasticity is constant along the curve.
B) elasticity is unity at every point on the curve.
C) demand is elastic at relatively low prices.
D) demand is elastic at relatively high prices.
A) elasticity is constant along the curve.
B) elasticity is unity at every point on the curve.
C) demand is elastic at relatively low prices.
D) demand is elastic at relatively high prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A perfectly inelastic demand schedule
A) rises upward and to the right but has a constant slope.
B) can be represented by a line parallel to the vertical axis.
C) cannot be shown on a two-dimensional graph.
D) can be represented by a line parallel to the horizontal axis.
A) rises upward and to the right but has a constant slope.
B) can be represented by a line parallel to the vertical axis.
C) cannot be shown on a two-dimensional graph.
D) can be represented by a line parallel to the horizontal axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If a firm can sell 3,000 units of product A at $10 per unit and 5,000 at $8, then
A) the price elasticity of demand is 0.44.
B) A is a complementary good.
C) the price elasticity of demand is 2.25.
D) A is an inferior good.
A) the price elasticity of demand is 0.44.
B) A is a complementary good.
C) the price elasticity of demand is 2.25.
D) A is an inferior good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The price elasticity of demand for widgets is 0.80. Assuming no change in the demand curve for widgets, a 16 percent increase in sales implies a
A) 1 percent reduction in price.
B) 12 percent reduction in price.
C) 20 percent reduction in price.
D) 40 percent reduction in price.
A) 1 percent reduction in price.
B) 12 percent reduction in price.
C) 20 percent reduction in price.
D) 40 percent reduction in price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When the percentage change in price is greater than the resulting percentage change in quantity demanded,
A) a decrease in price will increase total revenue.
B) demand may be either elastic or inelastic.
C) an increase in price will increase total revenue.
D) demand is elastic.
A) a decrease in price will increase total revenue.
B) demand may be either elastic or inelastic.
C) an increase in price will increase total revenue.
D) demand is elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The concept of price elasticity of demand measures
A) the slope of the demand curve.
B) the number of buyers in a market.
C) the extent to which the demand curve shifts as the result of a price decline.
D) the sensitivity of consumer purchases to price changes.
A) the slope of the demand curve.
B) the number of buyers in a market.
C) the extent to which the demand curve shifts as the result of a price decline.
D) the sensitivity of consumer purchases to price changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If demand for a product is elastic, the value of the price elasticity coefficient is
A) zero.
B) greater than one.
C) equal to one.
D) less than one.
A) zero.
B) greater than one.
C) equal to one.
D) less than one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A firm can sell as much as it wants at a constant price. Demand is thus
A) perfectly inelastic.
B) perfectly elastic.
C) relatively inelastic.
D) relatively elastic.
A) perfectly inelastic.
B) perfectly elastic.
C) relatively inelastic.
D) relatively elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Answer the question on the basis of the following demand schedule. 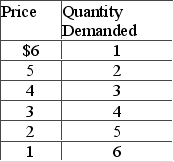 The price elasticity of demand is unity
The price elasticity of demand is unity
A) throughout the entire price range, because the slope of the demand curve is constant.
B) in the $4-$3 price range only.
C) over the entire $3-$1 price range.
D) over the entire $6-$4 price range.
 The price elasticity of demand is unity
The price elasticity of demand is unityA) throughout the entire price range, because the slope of the demand curve is constant.
B) in the $4-$3 price range only.
C) over the entire $3-$1 price range.
D) over the entire $6-$4 price range.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose the price of local cable TV service increased from $16.20 to $19.80 and as a result the number of cable subscribers decreased from 224,000 to 176,000. Along this portion of the demand curve, price elasticity of demand is
A) 0.8.
B) 1.2.
C) 1.6.
D) 8.0.
A) 0.8.
B) 1.2.
C) 1.6.
D) 8.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The price elasticity of demand for beef is about 0.60. Other things equal, this means that a 20 percent increase in the price of beef will cause the quantity of beef demanded to
A) increase by approximately 12 percent.
B) decrease by approximately 12 percent.
C) decrease by approximately 32 percent.
D) decrease by approximately 26 percent.
A) increase by approximately 12 percent.
B) decrease by approximately 12 percent.
C) decrease by approximately 32 percent.
D) decrease by approximately 26 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Suppose the price elasticity coefficients of demand are 1.43, 0.67, 1.11, and 0.29 for products W, X, Y, and Z, respectively. A 1 percent decrease in price will increase total revenue in the cases of
A) W and Y.
B) Y and Z.
C) X and Z.
D) Z and W.
A) W and Y.
B) Y and Z.
C) X and Z.
D) Z and W.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Answer the question on the basis of the following demand schedule. 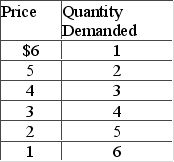 Which of the following is correct?
Which of the following is correct?
A) Although the slope of the demand curve is constant, price elasticity declines as we move from high to low price ranges.
B) Although the slope of the demand curve is constant, price elasticity increases as we move from high to low price ranges.
C) Although the demand curve is convex to the origin, price elasticity of demand is constant throughout.
D) A steep slope means demand is inelastic; a flat slope means demand is elastic.
 Which of the following is correct?
Which of the following is correct?A) Although the slope of the demand curve is constant, price elasticity declines as we move from high to low price ranges.
B) Although the slope of the demand curve is constant, price elasticity increases as we move from high to low price ranges.
C) Although the demand curve is convex to the origin, price elasticity of demand is constant throughout.
D) A steep slope means demand is inelastic; a flat slope means demand is elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A demand curve that is parallel to the horizontal axis is
A) perfectly inelastic.
B) perfectly elastic.
C) relatively inelastic.
D) relatively elastic.
A) perfectly inelastic.
B) perfectly elastic.
C) relatively inelastic.
D) relatively elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In which price range of the accompanying demand schedule is demand elastic? 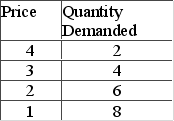
A) $4-$3
B) $3-$2
C) $2-$1
D) below $1

A) $4-$3
B) $3-$2
C) $2-$1
D) below $1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Answer the question on the basis of the following demand schedule. 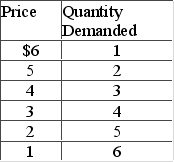 The price elasticity of demand is relatively inelastic
The price elasticity of demand is relatively inelastic
A) in the $6-$4 price range.
B) over the entire $6-$1 price range.
C) in the $3-$1 price range.
D) in the $6-$5 price range only.
 The price elasticity of demand is relatively inelastic
The price elasticity of demand is relatively inelasticA) in the $6-$4 price range.
B) over the entire $6-$1 price range.
C) in the $3-$1 price range.
D) in the $6-$5 price range only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A perfectly inelastic demand curve
A) has a price elasticity coefficient greater than unity.
B) has a price elasticity coefficient of unity throughout.
C) graphs as a line parallel to the vertical axis.
D) graphs as a line parallel to the horizontal axis.
A) has a price elasticity coefficient greater than unity.
B) has a price elasticity coefficient of unity throughout.
C) graphs as a line parallel to the vertical axis.
D) graphs as a line parallel to the horizontal axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A) If the relative change in price is greater than the relative change in the quantity demanded associated with it, demand is inelastic.
B) In the range of prices in which demand is elastic, total revenue will diminish as price decreases.
C) Total revenue will not change if price varies within a range where the elasticity coefficient is unity.
D) Demand tends to be elastic at high prices and inelastic at low prices.
A) If the relative change in price is greater than the relative change in the quantity demanded associated with it, demand is inelastic.
B) In the range of prices in which demand is elastic, total revenue will diminish as price decreases.
C) Total revenue will not change if price varies within a range where the elasticity coefficient is unity.
D) Demand tends to be elastic at high prices and inelastic at low prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Answer the question on the basis of the following demand schedule. 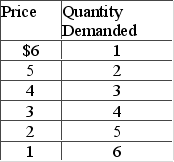 If this demand schedule were graphed, we would find that
If this demand schedule were graphed, we would find that
A) its slope diminishes as we move southeast down the curve.
B) its slope diminishes as we move northwest up the curve.
C) its slope is constant throughout.
D) the data are inconsistent with the law of demand.
 If this demand schedule were graphed, we would find that
If this demand schedule were graphed, we would find thatA) its slope diminishes as we move southeast down the curve.
B) its slope diminishes as we move northwest up the curve.
C) its slope is constant throughout.
D) the data are inconsistent with the law of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If quantity demanded is completely unresponsive to price changes, demand is
A) perfectly inelastic.
B) perfectly elastic.
C) relatively inelastic.
D) relatively elastic.
A) perfectly inelastic.
B) perfectly elastic.
C) relatively inelastic.
D) relatively elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the price of hand calculators falls from $10 to $9 and, as a result, the quantity demanded increases from 100 to 125, then
A) demand is price elastic.
B) demand is price inelastic.
C) demand is unit elastic with respect to price.
D) not enough information is given to make a statement about elasticity.
A) demand is price elastic.
B) demand is price inelastic.
C) demand is unit elastic with respect to price.
D) not enough information is given to make a statement about elasticity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If a firm's demand for labor is elastic, a union-negotiated wage increase will
A) necessarily be inflationary.
B) cause the firm's total payroll to increase.
C) cause the firm's total payroll to decline.
D) cause a shortage of labor.
A) necessarily be inflationary.
B) cause the firm's total payroll to increase.
C) cause the firm's total payroll to decline.
D) cause a shortage of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Answer the question on the basis of the following demand schedule. 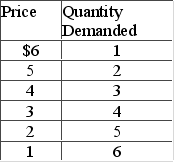 The price elasticity of demand is relatively elastic
The price elasticity of demand is relatively elastic
A) in the $6-$4 price range.
B) over the entire $6-$1 price range.
C) in the $3-$1 price range.
D) in the $6-$5 price range only.
 The price elasticity of demand is relatively elastic
The price elasticity of demand is relatively elasticA) in the $6-$4 price range.
B) over the entire $6-$1 price range.
C) in the $3-$1 price range.
D) in the $6-$5 price range only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In which of the following instances will total revenue decline?
A) Price rises and supply is elastic.
B) Price falls and demand is elastic.
C) Price rises and demand is inelastic.
D) Price rises and demand is elastic.
A) Price rises and supply is elastic.
B) Price falls and demand is elastic.
C) Price rises and demand is inelastic.
D) Price rises and demand is elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In which of the following cases will total revenue increase?
A) Price falls and demand is inelastic.
B) Price falls and supply is elastic.
C) Price rises and demand is inelastic.
D) Price rises and demand is elastic.
A) Price falls and demand is inelastic.
B) Price falls and supply is elastic.
C) Price rises and demand is inelastic.
D) Price rises and demand is elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If a firm finds that it can sell $13,000 worth of a product when its price is $5 per unit and $11,000 worth of it when its price is $6, then
A) the demand for the product is elastic in the $6-$5 price range.
B) the demand for the product must have increased.
C) elasticity of demand is 0.74.
D) the demand for the product is inelastic in the $6-$5 price range.
A) the demand for the product is elastic in the $6-$5 price range.
B) the demand for the product must have increased.
C) elasticity of demand is 0.74.
D) the demand for the product is inelastic in the $6-$5 price range.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the price elasticity of demand for a product is unity, a decrease in price will
A) have no effect upon the amount purchased.
B) increase the quantity demanded and increase total revenue.
C) increase the quantity demanded but decrease total revenue.
D) increase the quantity demanded, but total revenue will be unchanged.
A) have no effect upon the amount purchased.
B) increase the quantity demanded and increase total revenue.
C) increase the quantity demanded but decrease total revenue.
D) increase the quantity demanded, but total revenue will be unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If the University Chamber Music Society decides to raise ticket prices to provide more funds to finance concerts, the Society is assuming that the demand for tickets is
A) parallel to the horizontal axis.
B) shifting to the left.
C) inelastic.
D) elastic.
A) parallel to the horizontal axis.
B) shifting to the left.
C) inelastic.
D) elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The demand schedules for such products as eggs, bread, and electricity tend to be
A) perfectly price elastic.
B) of unit price elasticity.
C) relatively price inelastic.
D) relatively price elastic.
A) perfectly price elastic.
B) of unit price elasticity.
C) relatively price inelastic.
D) relatively price elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is correct?
A) If the demand for a product is inelastic, a change in price will cause total revenue to change in the opposite direction.
B) If the demand for a product is inelastic, a change in price will cause total revenue to change in the same direction.
C) If the demand for a product is inelastic, a change in price may cause total revenue to change in either the opposite or the same direction.
D) The price elasticity coefficient applies to demand, but not to supply.
A) If the demand for a product is inelastic, a change in price will cause total revenue to change in the opposite direction.
B) If the demand for a product is inelastic, a change in price will cause total revenue to change in the same direction.
C) If the demand for a product is inelastic, a change in price may cause total revenue to change in either the opposite or the same direction.
D) The price elasticity coefficient applies to demand, but not to supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The total-revenue test for elasticity
A) is equally applicable to both demand and supply.
B) does not apply to demand, because price and quantity are inversely related.
C) does not apply to supply, because price and total revenue have a positive correlation.
D) applies to the short-run supply curve but not to the long-run supply curve.
A) is equally applicable to both demand and supply.
B) does not apply to demand, because price and quantity are inversely related.
C) does not apply to supply, because price and total revenue have a positive correlation.
D) applies to the short-run supply curve but not to the long-run supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Other things the same, if a price change causes total revenue to change in the opposite direction, demand is
A) perfectly inelastic.
B) relatively elastic.
C) relatively inelastic.
D) of unit elasticity.
A) perfectly inelastic.
B) relatively elastic.
C) relatively inelastic.
D) of unit elasticity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If the demand for farm products is price inelastic, a good harvest will cause farm revenues to
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) be unchanged.
D) either increase or decrease, depending on what happens to supply.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) be unchanged.
D) either increase or decrease, depending on what happens to supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Gigantic State University raises tuition for the purpose of increasing its revenue so that more faculty can be hired. GSU is assuming that the demand for education at GSU is
A) decreasing.
B) relatively elastic.
C) perfectly elastic.
D) relatively inelastic.
A) decreasing.
B) relatively elastic.
C) perfectly elastic.
D) relatively inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is correct?
A) If demand is elastic, an increase in price will increase total revenue.
B) If demand is elastic, a decrease in price will decrease total revenue.
C) If demand is elastic, a decrease in price will increase total revenue.
D) If demand is inelastic, an increase in price will decrease total revenue.
A) If demand is elastic, an increase in price will increase total revenue.
B) If demand is elastic, a decrease in price will decrease total revenue.
C) If demand is elastic, a decrease in price will increase total revenue.
D) If demand is inelastic, an increase in price will decrease total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
We would expect
A) the demand for Coca-Cola to be less price elastic than the demand for soft drinks in general.
B) the demand for Coca-Cola to be more price elastic than the demand for soft drinks in general.
C) no relationship between the price elasticity of demand for Coca-Cola and the price elasticity of demand for soft drinks in general.
D) none of the other answers to hold true.
A) the demand for Coca-Cola to be less price elastic than the demand for soft drinks in general.
B) the demand for Coca-Cola to be more price elastic than the demand for soft drinks in general.
C) no relationship between the price elasticity of demand for Coca-Cola and the price elasticity of demand for soft drinks in general.
D) none of the other answers to hold true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The state legislature has cut Gigantic State University's appropriations. GSU's Board of Regents decides to increase tuition and fees to compensate for the loss of revenue. The board is assuming that the
A) demand for education at GSU is elastic.
B) demand for education at GSU is inelastic.
C) coefficient of price elasticity of demand for education at GSU is unity.
D) coefficient of price elasticity of demand for education at GSU is greater than unity.
A) demand for education at GSU is elastic.
B) demand for education at GSU is inelastic.
C) coefficient of price elasticity of demand for education at GSU is unity.
D) coefficient of price elasticity of demand for education at GSU is greater than unity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose that the price of peanuts falls from $3 to $2 per bushel and that, as a result, the total revenue received by peanut farmers changes from $16 to $14 billion. Thus,
A) the demand for peanuts is elastic.
B) the demand for peanuts is inelastic.
C) the demand curve for peanuts has shifted to the right.
D) no inference can be made as to the elasticity of demand for peanuts.
A) the demand for peanuts is elastic.
B) the demand for peanuts is inelastic.
C) the demand curve for peanuts has shifted to the right.
D) no inference can be made as to the elasticity of demand for peanuts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The elasticity of demand for a product is likely to be greater,
A) if the product is a necessity, rather than a luxury good.
B) the greater the amount of time over which buyers adjust to a price change.
C) the smaller the proportion of one's income spent on the product.
D) the smaller the number of substitute products available.
A) if the product is a necessity, rather than a luxury good.
B) the greater the amount of time over which buyers adjust to a price change.
C) the smaller the proportion of one's income spent on the product.
D) the smaller the number of substitute products available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The narrower the definition of a product,
A) the larger the number of substitutes and the greater the price elasticity of demand.
B) the smaller the number of substitutes and the greater the price elasticity of demand.
C) the larger the number of substitutes and the smaller the price elasticity of demand.
D) the smaller the number of substitutes and the smaller the price elasticity of demand.
A) the larger the number of substitutes and the greater the price elasticity of demand.
B) the smaller the number of substitutes and the greater the price elasticity of demand.
C) the larger the number of substitutes and the smaller the price elasticity of demand.
D) the smaller the number of substitutes and the smaller the price elasticity of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Suppose the price elasticity of demand for bread is 0.20. If the price of bread falls by 10 percent, the quantity demanded will increase by
A) 2 percent and total expenditures on bread will rise.
B) 2 percent and total expenditures on bread will fall.
C) 20 percent and total expenditures on bread will fall.
D) 20 percent and total expenditures on bread will rise.
A) 2 percent and total expenditures on bread will rise.
B) 2 percent and total expenditures on bread will fall.
C) 20 percent and total expenditures on bread will fall.
D) 20 percent and total expenditures on bread will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A manufacturer of frozen pizzas found that total revenue decreased when price was lowered from $5 to $4. It was also found that total revenue decreased when price was raised from $5 to $6. Thus,
A) the demand for pizza is elastic above $5 and inelastic below $5.
B) the demand for pizza is elastic both above and below $5.
C) the demand for pizza is inelastic above $5 and elastic below $5.
D) $5 is not the equilibrium price of pizza.
A) the demand for pizza is elastic above $5 and inelastic below $5.
B) the demand for pizza is elastic both above and below $5.
C) the demand for pizza is inelastic above $5 and elastic below $5.
D) $5 is not the equilibrium price of pizza.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The more time consumers have to adjust to a change in price,
A) the smaller will be the price elasticity of demand.
B) the greater will be the price elasticity of demand.
C) the more likely the product is a normal good.
D) the more likely the product is an inferior good.
A) the smaller will be the price elasticity of demand.
B) the greater will be the price elasticity of demand.
C) the more likely the product is a normal good.
D) the more likely the product is an inferior good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The Illinois Central Railroad once asked the Illinois Commerce Commission for permission to increase its commuter rates by 20 percent. The railroad argued that declining revenues made this rate increase essential. Opponents of the rate increase contended that the railroad's revenues would fall because of the rate hike. It can be concluded that
A) both groups felt that the demand was elastic but for different reasons.
B) both groups felt that the demand was inelastic but for different reasons.
C) the railroad felt that the demand for passenger service was inelastic and opponents of the rate increase felt it was elastic.
D) the railroad felt that the demand for passenger service was elastic and opponents of the rate increase felt it was inelastic.
A) both groups felt that the demand was elastic but for different reasons.
B) both groups felt that the demand was inelastic but for different reasons.
C) the railroad felt that the demand for passenger service was inelastic and opponents of the rate increase felt it was elastic.
D) the railroad felt that the demand for passenger service was elastic and opponents of the rate increase felt it was inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Suppose the supply of product X is perfectly inelastic. If there is an increase in the demand for this product, equilibrium price
A) will decrease, but equilibrium quantity will increase.
B) and quantity will both decrease.
C) will increase, but equilibrium quantity will decline.
D) will increase, but equilibrium quantity will be unchanged.
A) will decrease, but equilibrium quantity will increase.
B) and quantity will both decrease.
C) will increase, but equilibrium quantity will decline.
D) will increase, but equilibrium quantity will be unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The main determinant of elasticity of supply is the
A) number of close substitutes for the product available to consumers.
B) amount of time the producer has to adjust inputs in response to a price change.
C) urgency of consumer wants for the product.
D) number of uses for the product.
A) number of close substitutes for the product available to consumers.
B) amount of time the producer has to adjust inputs in response to a price change.
C) urgency of consumer wants for the product.
D) number of uses for the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The demand for autos is likely to be
A) less price elastic than the demand for Honda Accords.
B) more price elastic than the demand for Honda Accords.
C) of the same price elasticity as the demand for Honda Accords.
D) perfectly inelastic.
A) less price elastic than the demand for Honda Accords.
B) more price elastic than the demand for Honda Accords.
C) of the same price elasticity as the demand for Honda Accords.
D) perfectly inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The elasticity of supply of product X is unitary if the price of X rises by
A) 5 percent and quantity supplied rises by 7 percent.
B) 8 percent and quantity supplied rises by 8 percent.
C) 10 percent and quantity supplied stays the same.
D) 7 percent and quantity supplied rises by 5 percent.
A) 5 percent and quantity supplied rises by 7 percent.
B) 8 percent and quantity supplied rises by 8 percent.
C) 10 percent and quantity supplied stays the same.
D) 7 percent and quantity supplied rises by 5 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The supply of product X is perfectly inelastic if the price of X rises by
A) 5 percent and quantity supplied rises by 7 percent.
B) 8 percent and quantity supplied rises by 8 percent.
C) 10 percent and quantity supplied stays the same.
D) 7 percent and quantity supplied rises by 5 percent.
A) 5 percent and quantity supplied rises by 7 percent.
B) 8 percent and quantity supplied rises by 8 percent.
C) 10 percent and quantity supplied stays the same.
D) 7 percent and quantity supplied rises by 5 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If the supply of product X is perfectly elastic, an increase in the demand for it will increase
A) equilibrium quantity but reduce equilibrium price.
B) equilibrium quantity, but equilibrium price will be unchanged.
C) equilibrium price but reduce equilibrium quantity.
D) equilibrium price, but equilibrium quantity will be unchanged.
A) equilibrium quantity but reduce equilibrium price.
B) equilibrium quantity, but equilibrium price will be unchanged.
C) equilibrium price but reduce equilibrium quantity.
D) equilibrium price, but equilibrium quantity will be unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
For an increase in demand, the price effect is smallest and the quantity effect is largest
A) when supply is least elastic.
B) in the long run.
C) in the short run.
D) in the immediate market period.
A) when supply is least elastic.
B) in the long run.
C) in the short run.
D) in the immediate market period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The demand for a necessity whose cost is a small portion of one's total income is
A) perfectly price inelastic.
B) perfectly price elastic.
C) relatively price inelastic.
D) relatively price elastic.
A) perfectly price inelastic.
B) perfectly price elastic.
C) relatively price inelastic.
D) relatively price elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Price elasticity of demand is generally
A) greater in the long run than in the short run.
B) greater in the short run than in the long run.
C) the same in both the short run and the long run.
D) greater for "necessities" than it is for "luxuries."
A) greater in the long run than in the short run.
B) greater in the short run than in the long run.
C) the same in both the short run and the long run.
D) greater for "necessities" than it is for "luxuries."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose that the price of product X rises by 20 percent and the quantity supplied of X increases by 15 percent. The coefficient of price elasticity of supply for good X is
A) negative, and therefore X is an inferior good.
B) positive, and therefore X is a normal good.
C) less than 1, and therefore supply is inelastic.
D) more than 1, and therefore supply is elastic.
A) negative, and therefore X is an inferior good.
B) positive, and therefore X is a normal good.
C) less than 1, and therefore supply is inelastic.
D) more than 1, and therefore supply is elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Suppose the price of a product rises and the total revenue of sellers increases.
A) It can be concluded that the demand for the product is elastic.
B) It can be concluded that the supply of the product is elastic.
C) It can be concluded that the supply of the product is inelastic.
D) No conclusion can be reached with respect to the elasticity of supply.
A) It can be concluded that the demand for the product is elastic.
B) It can be concluded that the supply of the product is elastic.
C) It can be concluded that the supply of the product is inelastic.
D) No conclusion can be reached with respect to the elasticity of supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following generalizations is not correct?
A) The larger an item is in one's budget, the greater the price elasticity of demand.
B) The price elasticity of demand is greater for necessities than it is for luxuries.
C) The larger the number of close substitutes available, the greater will be the price elasticity of demand for a particular product.
D) The price elasticity of demand is greater the longer the time period under consideration.
A) The larger an item is in one's budget, the greater the price elasticity of demand.
B) The price elasticity of demand is greater for necessities than it is for luxuries.
C) The larger the number of close substitutes available, the greater will be the price elasticity of demand for a particular product.
D) The price elasticity of demand is greater the longer the time period under consideration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The demand for a luxury good whose purchase would exhaust a big portion of one's income is
A) perfectly price inelastic.
B) perfectly price elastic.
C) relatively price inelastic.
D) relatively price elastic.
A) perfectly price inelastic.
B) perfectly price elastic.
C) relatively price inelastic.
D) relatively price elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A supply curve that is a vertical straight line indicates that
A) production costs for this product cannot be calculated.
B) the relationship between price and quantity supplied is inverse.
C) a change in price will have no effect on the quantity supplied.
D) an unlimited amount of the product will be supplied at a constant price.
A) production costs for this product cannot be calculated.
B) the relationship between price and quantity supplied is inverse.
C) a change in price will have no effect on the quantity supplied.
D) an unlimited amount of the product will be supplied at a constant price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
It takes a considerable amount of time to increase the production of pork. This implies that
A) a change in the demand for pork will not affect its price in the short run.
B) the short-run supply curve for pork is less elastic than the long-run supply curve for pork.
C) an increase in the demand for pork will elicit a larger supply response in the short run than in the long run.
D) the long-run supply curve for pork is less elastic than the short-run supply curve for pork.
A) a change in the demand for pork will not affect its price in the short run.
B) the short-run supply curve for pork is less elastic than the long-run supply curve for pork.
C) an increase in the demand for pork will elicit a larger supply response in the short run than in the long run.
D) the long-run supply curve for pork is less elastic than the short-run supply curve for pork.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The supply of product X is elastic if the price of X rises by
A) 5 percent and quantity supplied rises by 7 percent.
B) 8 percent and quantity supplied rises by 8 percent.
C) 10 percent and quantity supplied remains the same.
D) 7 percent and quantity supplied rises by 5 percent.
A) 5 percent and quantity supplied rises by 7 percent.
B) 8 percent and quantity supplied rises by 8 percent.
C) 10 percent and quantity supplied remains the same.
D) 7 percent and quantity supplied rises by 5 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If price and total revenue vary in opposite directions, demand is
A) perfectly inelastic.
B) perfectly elastic.
C) relatively inelastic.
D) relatively elastic.
A) perfectly inelastic.
B) perfectly elastic.
C) relatively inelastic.
D) relatively elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Supply curves tend to be
A) perfectly elastic in the long run because consumer demand will have sufficient time to adjust fully to changes in supply.
B) more elastic in the long run because there is time for firms to enter or leave the industry.
C) perfectly inelastic in the long run because the law of scarcity imposes absolute limits on production.
D) less elastic in the long run because there is time for firms to enter or leave an industry.
A) perfectly elastic in the long run because consumer demand will have sufficient time to adjust fully to changes in supply.
B) more elastic in the long run because there is time for firms to enter or leave the industry.
C) perfectly inelastic in the long run because the law of scarcity imposes absolute limits on production.
D) less elastic in the long run because there is time for firms to enter or leave an industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The supply of product X is inelastic (but not perfectly inelastic) if the price of X rises by
A) 5 percent and quantity supplied rises by 7 percent.
B) 8 percent and quantity supplied rises by 8 percent.
C) 10 percent and quantity supplied remains the same.
D) 7 percent and quantity supplied rises by 5 percent.
A) 5 percent and quantity supplied rises by 7 percent.
B) 8 percent and quantity supplied rises by 8 percent.
C) 10 percent and quantity supplied remains the same.
D) 7 percent and quantity supplied rises by 5 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The price elasticity of supply measures how
A) easily labor and capital can be substituted for one another in the production process.
B) responsive the quantity supplied of X is to changes in the price of X.
C) responsive the quantity supplied of Y is to changes in the price of X.
D) responsive quantity supplied is to a change in incomes.
A) easily labor and capital can be substituted for one another in the production process.
B) responsive the quantity supplied of X is to changes in the price of X.
C) responsive the quantity supplied of Y is to changes in the price of X.
D) responsive quantity supplied is to a change in incomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 255 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



