Deck 19: Nuclear Chemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/128
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Nuclear Chemistry
1
When atoms of beryllium-9 are bombarded with alpha particles, neutrons are produced. What new isotope is also formed
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
2
Alpha particles are identical to
A) protons.
B) helium atoms.
C) hydrogen atoms.
D) helium nuclei.
E) electrons.
A) protons.
B) helium atoms.
C) hydrogen atoms.
D) helium nuclei.
E) electrons.
helium nuclei.
3
Consider the following decay series:  What is the symbol for the product labeled as Y
What is the symbol for the product labeled as Y
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
 What is the symbol for the product labeled as Y
What is the symbol for the product labeled as YA)
B)
C)
D)
E)
4
Sulfur-35 decays by beta emission. The decay product is
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is characteristic of a nuclear reaction
I. Electrons in atomic orbitals are involved in the breaking and forming of bonds
II. Elements are converted from one to another
III. Reaction rates are typically not affected by catalysts
IV. Atoms are rearranged by the breaking and forming of chemical bonds
A) I and II
B) I, II, and III
C) III and IV
D) II and III
E) I, II, III, and IV
I. Electrons in atomic orbitals are involved in the breaking and forming of bonds
II. Elements are converted from one to another
III. Reaction rates are typically not affected by catalysts
IV. Atoms are rearranged by the breaking and forming of chemical bonds
A) I and II
B) I, II, and III
C) III and IV
D) II and III
E) I, II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Consider the following decay series: 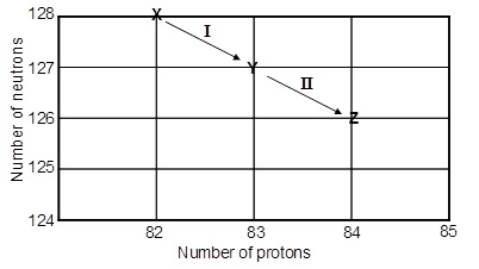 What type of nuclear process occurs at the transformation labeled I
What type of nuclear process occurs at the transformation labeled I
A) aemission
B) bemission
C) positron emission
D) electron capture
E) gamma radiation
 What type of nuclear process occurs at the transformation labeled I
What type of nuclear process occurs at the transformation labeled IA) aemission
B) bemission
C) positron emission
D) electron capture
E) gamma radiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
List the number of protons, neutrons, and nucleons (protons + neutrons), in that order, for an isotope with the symbol: Cs
A) 137, 55, 192
B) 55, 137, 192
C) 55, 82, 137
D) 82, 55, 137
E) 82, 137, 219
A) 137, 55, 192
B) 55, 137, 192
C) 55, 82, 137
D) 82, 55, 137
E) 82, 137, 219

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Consider the following decay series: 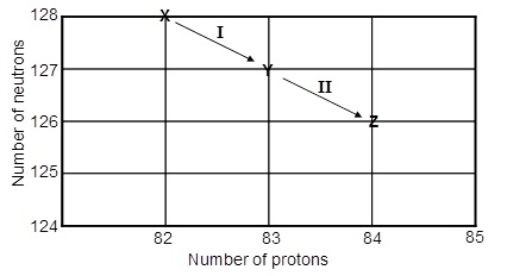 What type of nuclear process occurs at the transformation labeled II
What type of nuclear process occurs at the transformation labeled II
A) aemission
B) bemission
C) positron emission
D) electron capture
E) gamma radiation
 What type of nuclear process occurs at the transformation labeled II
What type of nuclear process occurs at the transformation labeled IIA) aemission
B) bemission
C) positron emission
D) electron capture
E) gamma radiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following represents a rule for balancing a nuclear equation
I. The total number of protons plus neutrons in the products and reactants must be the same
II. The total number of each type of element in the products and reactants must be the same
III. The total number of nuclear charges in the products and reactants must be the same
IV. The total number of each type of elementary particle in the products and reactants must be the same
A) I, II, III, and IV
B) I, II, and IV
C) I, III, and IV
D) III and IV
E) I and III
I. The total number of protons plus neutrons in the products and reactants must be the same
II. The total number of each type of element in the products and reactants must be the same
III. The total number of nuclear charges in the products and reactants must be the same
IV. The total number of each type of elementary particle in the products and reactants must be the same
A) I, II, III, and IV
B) I, II, and IV
C) I, III, and IV
D) III and IV
E) I and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
As a result of beta decay, the product nucleus is
A) one atomic number lower than the original element.
B) two atomic numbers higher than the original element.
C) one atomic number higher than the original element.
D) two atomic numbers lower than the original element.
E) four atomic numbers lower than the original element.
A) one atomic number lower than the original element.
B) two atomic numbers higher than the original element.
C) one atomic number higher than the original element.
D) two atomic numbers lower than the original element.
E) four atomic numbers lower than the original element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The only stable isotope of iodine is iodine-127. Predict the mode of decay of
A) alpha emission
B) beta emission
C) positron emission
D) electron capture
A) alpha emission
B) beta emission
C) positron emission
D) electron capture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Beta particles are identical to
A) protons.
B) helium atoms.
C) hydrogen atoms.
D) helium nuclei.
E) electrons.
A) protons.
B) helium atoms.
C) hydrogen atoms.
D) helium nuclei.
E) electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Consider the following decay series: 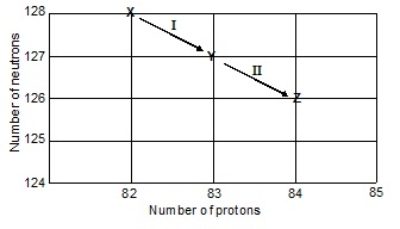 What is the complete element symbol for the product labeled Y
What is the complete element symbol for the product labeled Y
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
 What is the complete element symbol for the product labeled Y
What is the complete element symbol for the product labeled YA)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
As a result of alpha emission, the product nucleus is
A) one atomic number lower than the original element.
B) two atomic numbers higher than the original element.
C) one atomic number higher than the original element.
D) two atomic numbers lower than the original element.
E) four atomic numbers lower than the original element.
A) one atomic number lower than the original element.
B) two atomic numbers higher than the original element.
C) one atomic number higher than the original element.
D) two atomic numbers lower than the original element.
E) four atomic numbers lower than the original element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Consider the following decay series: Which type of nuclear process occurs in steps a and b, respectively
A) aemission, a emission
B) aemission, b emission
C) bemission, positron emission
D) bemission, a emission
E) positron emission, b emission
A) aemission, a emission
B) aemission, b emission
C) bemission, positron emission
D) bemission, a emission
E) positron emission, b emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consider the following decay series: 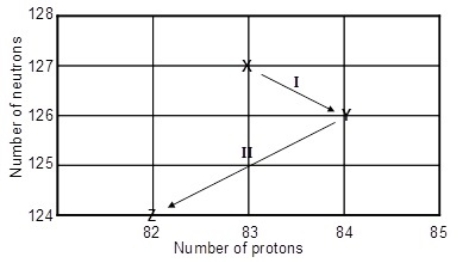 What type of nuclear process occurs at the transformation labeled I
What type of nuclear process occurs at the transformation labeled I
A) aemission
B) bemission
C) positron emission
D) electron capture
E) gamma radiation
 What type of nuclear process occurs at the transformation labeled I
What type of nuclear process occurs at the transformation labeled IA) aemission
B) bemission
C) positron emission
D) electron capture
E) gamma radiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
List the number of protons, neutrons, and nucleons (protons + neutrons), in that order, for an isotope with the symbol: Ba
A) 56, 81, 137
B) 81, 56, 137
C) 56, 137, 193
D) 137, 56, 193
E) 81, 137, 218
A) 56, 81, 137
B) 81, 56, 137
C) 56, 137, 193
D) 137, 56, 193
E) 81, 137, 218

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Consider the following decay series: Which type of nuclear process occurs in steps c and d, respectively
A) aemission, a emission
B) aemission, b emission
C) bemission, positron emission
D) bemission, a emission
E) positron emission, b emission
A) aemission, a emission
B) aemission, b emission
C) bemission, positron emission
D) bemission, a emission
E) positron emission, b emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Consider the following decay series:  What type of nuclear process occurs at the transformation labeled II
What type of nuclear process occurs at the transformation labeled II
A) aemission
B) bemission
C) positron emission
D) electron capture
E) gamma radiation
 What type of nuclear process occurs at the transformation labeled II
What type of nuclear process occurs at the transformation labeled IIA) aemission
B) bemission
C) positron emission
D) electron capture
E) gamma radiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Radium-226 decays by alpha emission. What is its decay product
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What fraction of radioactive atoms remains in a sample after six half-lives
A) zero
B) 1/6
C) 1/16
D) 1/32
E) 1/64
A) zero
B) 1/6
C) 1/16
D) 1/32
E) 1/64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
1 joule equals
A) 1 kg m
B) 1 g m2 s2
C) 1 kg m2/s
D) 1 g m2/s
E) 1 kg m2/s2
A) 1 kg m
B) 1 g m2 s2
C) 1 kg m2/s
D) 1 g m2/s
E) 1 kg m2/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following nuclear processes results in an increase of atomic number in the product element formed
I. Alpha emission
II. Beta emission
III. Positron emission
IV. Electron capture
A) I and II
B) III and IV
C) I, II, and III
D) II only
E) IV only
I. Alpha emission
II. Beta emission
III. Positron emission
IV. Electron capture
A) I and II
B) III and IV
C) I, II, and III
D) II only
E) IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The energy equivalent of a mass defect of - 0.1710 amu is which of the following
A) - 5.130 x 107 J
B) - 1.539 x 1016 J
C) - 2.556 x 10-8 J
D) - 2.556 x 10-11 J
E) - 8.519 x 10-20 J
A) - 5.130 x 107 J
B) - 1.539 x 1016 J
C) - 2.556 x 10-8 J
D) - 2.556 x 10-11 J
E) - 8.519 x 10-20 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The energy equivalent of a mass defect of - 0.1620 amu is which of the following
A) - 1.458 x 1016 J
B) - 2.421 x 10-8 J
C) - 2.421 x 10-11 J
D) - 2.421 x 1013 J
E) - 1.458 x 10-11 J
A) - 1.458 x 1016 J
B) - 2.421 x 10-8 J
C) - 2.421 x 10-11 J
D) - 2.421 x 1013 J
E) - 1.458 x 10-11 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Determine how much energy is released when polonium-210 decays according to . [Atomic masses: polonium-210 = 209.982857 amu; helium-4 = 4.002603 amu; lead-206 = 205.974449 amu]
A) 4.14 * 109 kJ/mol
B) 7.20 * 1011 kJ/mol
C) 5.22 * 108 kJ/mol
D) 4.66 * 109 kJ/mol
E) 6.43 * 1012 kJ/mol
A) 4.14 * 109 kJ/mol
B) 7.20 * 1011 kJ/mol
C) 5.22 * 108 kJ/mol
D) 4.66 * 109 kJ/mol
E) 6.43 * 1012 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Find the nuclear binding energy of uranium-234 (atomic mass = 234.040947 amu) in units of joules per nucleon. [Data: neutron mass = 1.674928 * 10-24 g; proton mass = 1.672623 * 10-24 g; electron mass = 9.109387 * 10-28 g; NA = 6.0221367 * 1023 /mol; c = 2.99792458 * 108 m/s]
A) 2.97 * 10-10 J/nucleon
B) 1.22 * 10-12 J/nucleon
C) 3.04 * 10-10 J/nucleon
D) 1.30 * 10-12 J/nucleon
E) 1.41 * 10-12 J/nucleon
F) 1.27 * 10-12 J/nucleon
A) 2.97 * 10-10 J/nucleon
B) 1.22 * 10-12 J/nucleon
C) 3.04 * 10-10 J/nucleon
D) 1.30 * 10-12 J/nucleon
E) 1.41 * 10-12 J/nucleon
F) 1.27 * 10-12 J/nucleon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the nuclear binding energy per nucleon, in joules, for (atomic mass 24.985839 amu)
[Data: (atomic mass) = 1.007825 amu; (mass) = 1.008665 amu; 1 kg = 6.022 * 1026 amu; c = 3.00 * 108 m/s]
A) 0.22076 J/nucleon
B) 3.30 * 10-11 J/nucleon
C) 1.32 * 10-12 J/nucleon
D) 0.999 J/nucleon
E) None of the above.
[Data: (atomic mass) = 1.007825 amu; (mass) = 1.008665 amu; 1 kg = 6.022 * 1026 amu; c = 3.00 * 108 m/s]
A) 0.22076 J/nucleon
B) 3.30 * 10-11 J/nucleon
C) 1.32 * 10-12 J/nucleon
D) 0.999 J/nucleon
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following nuclear processes does not change the mass number in the product element formed
I. Alpha emission
II. Beta emission
III. Positron emission
IV. Electron capture
A) I and II
B) III and IV
C) I, II, and III
D) II, III, and IV
E) IV only
I. Alpha emission
II. Beta emission
III. Positron emission
IV. Electron capture
A) I and II
B) III and IV
C) I, II, and III
D) II, III, and IV
E) IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A balanced nuclear equation representing the alpha emission of curium-242 is which of the following
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Determine how much energy is released when thorium-230 decays according to . [Atomic masses: thorium-230 = 230.033127 amu; helium-4 = 4.002603 amu; radium-226 = 226.025403 amu]
A) 3.98 * 109 kJ/mol
B) 4.60 * 108 kJ/mol
C) 7.20 * 1011 kJ/mol
D) 4.90 * 109 kJ/mol
E) 7.15 * 1011 kJ/mol
A) 3.98 * 109 kJ/mol
B) 4.60 * 108 kJ/mol
C) 7.20 * 1011 kJ/mol
D) 4.90 * 109 kJ/mol
E) 7.15 * 1011 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Calculate the energy released in joules when one mole of polonium-214 decays according to the equation [Atomic masses: Pb-210 = 209.98284 amu, Po-214 = 213.99519 amu, He-4 = 4.00260 amu.]
A) 8.78 * 1014 J/mol
B) 7.2 * 1014 J/mol
C) 8.78 * 1011 J/mol
D) -9.75 * 10-3 J/mol
E) 1.46 * 10-9 J/mol
A) 8.78 * 1014 J/mol
B) 7.2 * 1014 J/mol
C) 8.78 * 1011 J/mol
D) -9.75 * 10-3 J/mol
E) 1.46 * 10-9 J/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What fraction of radioactive atoms remains in a sample after five half-lives
A) zero
B) 1/6
C) 1/16
D) 1/32
E) 1/64
A) zero
B) 1/6
C) 1/16
D) 1/32
E) 1/64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A balanced nuclear equation representing the beta emission of iodine-131 is which of the following
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The isotope with the greatest nuclear binding energy per nucleon is
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Carbon-11 is a radioactive isotope of carbon. Its half-life is 20.3 minutes. What fraction of the initial number of carbon-11 atoms in a sample will remain after 81 minutes
A) 1/16
B) 1/4
C) 1/2
D) 1/32
E) 1/8
A) 1/16
B) 1/4
C) 1/2
D) 1/32
E) 1/8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The only stable isotope of aluminum is aluminum-27. What type of radioactive decay should be expected from
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Find the nuclear binding energy of potassium-40 (atomic mass = 39.9632591 amu) in units of joules per nucleon. [Data: neutron mass = 1.674928 * 10-24 g; proton mass = 1.672623 * 10-24g; electron mass = 9.109387 * 10-28 g; NA = 6.0221367 * 1023 /mol; c = 2.99792458 * 108 m/s]
A) 1.37 * 10-12 J/nucleon
B) 5.48 * 10-11 J/nucleon
C) 5.64 * 10-11 J/nucleon
D) 1.41 * 10-12 J/nucleon
E) 2.97 * 10-12 J/nucleon
A) 1.37 * 10-12 J/nucleon
B) 5.48 * 10-11 J/nucleon
C) 5.64 * 10-11 J/nucleon
D) 1.41 * 10-12 J/nucleon
E) 2.97 * 10-12 J/nucleon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A typical radius of an atomic nucleus is about
A) 100 µm
B) 5000 mm
C) 100 nm
D) 5 * 10-3 pm
E) 500 pm
A) 100 µm
B) 5000 mm
C) 100 nm
D) 5 * 10-3 pm
E) 500 pm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following nuclear processes results in an increase in the number of neutrons in the product element
I. Alpha emission
II. Beta emission
III. Positron emission
IV. Electron capture
A) I and II
B) III and IV
C) I, II, and III
D) II, III, and IV
E) I, II, III, and IV
I. Alpha emission
II. Beta emission
III. Positron emission
IV. Electron capture
A) I and II
B) III and IV
C) I, II, and III
D) II, III, and IV
E) I, II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What would the atom ratio of 206Pb to 238U be in a uranium mineral from a rock that is 1.0 * 109 years old? t1/2(238U) = 4.5 * 109 yr.
A) 0.14
B) 0.16
C) 0.22
D) 0.86
E) 1.16
A) 0.14
B) 0.16
C) 0.22
D) 0.86
E) 1.16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The heaviest known isotope of hydrogen is called tritium, H . It decays by beta emission, and has a half-life of 12.3 years. What fraction of a tritium sample will remain after 5.20 years
A) 0.0210
B) 0.746
C) 3.41
D) 0.254
E) 0.423
A) 0.0210
B) 0.746
C) 3.41
D) 0.254
E) 0.423

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The half-life of 90Sr is 29 years. What fraction of the atoms in a sample of 90Sr would remain 175 years later
A) 0.17
B) 0.12
C) 0.062
D) 0.015
E) 0.50
A) 0.17
B) 0.12
C) 0.062
D) 0.015
E) 0.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In passing through matter, alpha particles lose energy chiefly by causing
A) fermentation.
B) neutralization.
C) ionization.
D) condensation.
E) carbonation.
A) fermentation.
B) neutralization.
C) ionization.
D) condensation.
E) carbonation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Cobalt-60 is a beta emitter with a half-life of 5.3 years. Approximately what fraction of the cobalt-60 atoms in a particular sample will remain after 32 years
A) 1/6
B) 1/8
C) 1/16
D) 1/32
E) 1/64
A) 1/6
B) 1/8
C) 1/16
D) 1/32
E) 1/64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The energy released by the sun is the result of
A) natural radioactivity.
B) nuclear fusion.
C) combustion of hydrogen.
D) photosynthesis.
E) nuclear fission.
A) natural radioactivity.
B) nuclear fusion.
C) combustion of hydrogen.
D) photosynthesis.
E) nuclear fission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The radioisotope potassium-40 decays to argon-40 by positron emission with a half-life of 1.3 * 109 yr. A sample of moon rock was found to contain 78 argon-40 atoms for every 22 potassium-40 atoms. The age of the rock is
A) 8.1 * 10-10 yr.
B) 2.4 * 109 yr.
C) 2.8 * 109 yr.
D) 4.6 * 109 yr.
E) 6.8 * 109 yr.
A) 8.1 * 10-10 yr.
B) 2.4 * 109 yr.
C) 2.8 * 109 yr.
D) 4.6 * 109 yr.
E) 6.8 * 109 yr.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Charcoal found under a stone at Stonehenge, England, has a carbon-14 activity that is 0.60 that of new wood. How old is the charcoal (The half-life of carbon-14 is 5,730 years.)
A) Less than 5,730 yr
B) Between 5,730 and 11,460 yr
C) Between 11,460 and 17,190 yr
D) More than 17,190 yr
A) Less than 5,730 yr
B) Between 5,730 and 11,460 yr
C) Between 11,460 and 17,190 yr
D) More than 17,190 yr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A rock contains 0.37 mg of Pb-206 and 0.95 mg of U-238. The half-life of the decay series U-238 Pb-206 is 4.5 * 109 yr. Assuming no Pb-206 was present in the rock initially, how old is the rock
A) 1.7 * 109 yr
B) 5.2 * 109 yr
C) 2.7 * 106 yr
D) 4.5 * 109 yr
E) 2.4 * 109 yr
A) 1.7 * 109 yr
B) 5.2 * 109 yr
C) 2.7 * 106 yr
D) 4.5 * 109 yr
E) 2.4 * 109 yr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The Rb-87/Sr-87 method of dating rocks is often used by geologists: t1/2 = 6.0 * 1010 yr.Estimate the age of a rock sample in which the present-day mole ratio of Rb-87 to Sr-87 is 36:1.
A) 2.4 * 109 yr
B) 1.7 * 109 yr
C) 3.1 * 1011 yr
D) 4.1 * 10-11 yr
E) 3.6 * 1011 yr
A) 2.4 * 109 yr
B) 1.7 * 109 yr
C) 3.1 * 1011 yr
D) 4.1 * 10-11 yr
E) 3.6 * 1011 yr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If 24% of a certain radioisotope decays in 6.5 years, what is the half-life of this isotope
A) 3.9 yr
B) 16 yr
C) 0.22 yr
D) 2.2 yr
E) 3.2 yr
A) 3.9 yr
B) 16 yr
C) 0.22 yr
D) 2.2 yr
E) 3.2 yr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A rock contains 0.37 mg of Pb-206 and 0.95 mg of U-238. Approximately how many U-238 atoms were in the rock when it was formed billions of years ago (The half life for 238U 206Pb is 4.5 * 109 yr.)
A) 1.32 atoms
B) 5.8 * 10-6 atoms
C) 2.4 * 1018 atoms
D) 3.5 * 1018 atoms
E) 3.5 * 1021 atoms
A) 1.32 atoms
B) 5.8 * 10-6 atoms
C) 2.4 * 1018 atoms
D) 3.5 * 1018 atoms
E) 3.5 * 1021 atoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
How old is a bottle of wine if the tritium (3H) content is 25% that of a new wine? The half-life of tritium is 12.5 years.
A) 0.25 yr
B) 3.1 yr
C) 25 yr
D) 38 yr
E) 50. yr
A) 0.25 yr
B) 3.1 yr
C) 25 yr
D) 38 yr
E) 50. yr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Cobalt-60 is a beta emitter with a half-life of 5.3 years. Approximately what fraction of cobalt-60 atoms will remain in a particular sample after 26.5 years
A) 1/5
B) 1/16
C) 1/26
D) 1/32
E) 1/64
A) 1/5
B) 1/16
C) 1/26
D) 1/32
E) 1/64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which type of nuclear process requires an extremely high temperature (millions of degrees)
A) beta decay
B) fission reaction
C) fusion reaction
D) alpha decay
E) positron emission
A) beta decay
B) fission reaction
C) fusion reaction
D) alpha decay
E) positron emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What role does cadmium metal (Cd) play in a nuclear reactor
A) slows down the fission neutrons (moderator)
B) transfers heat from the reactor to the heat exchanger (primary coolant)
C) controls chain reaction (control rods)
D) transfers heat from the condenser to the environment (cooling tower)
E) undergoes fission (fuel rods)
A) slows down the fission neutrons (moderator)
B) transfers heat from the reactor to the heat exchanger (primary coolant)
C) controls chain reaction (control rods)
D) transfers heat from the condenser to the environment (cooling tower)
E) undergoes fission (fuel rods)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which one of the following statements about fission and fusion is false
A) Fission occurs among the heaviest isotopes, whereas fusion occurs more readily for light isotopes.
B) For a fission reaction the mass defect (Dm) is negative, whereas for fusion Dm is positive.
C) In order for fusion reactions to occur, temperatures must be in the millions of degrees.
D) The fission of Pu-239 atoms produces a great number of isotopes of a large number of elements.
E) Neutron-induced fission processes can occur at room temperature, rather than at millions of degrees.
A) Fission occurs among the heaviest isotopes, whereas fusion occurs more readily for light isotopes.
B) For a fission reaction the mass defect (Dm) is negative, whereas for fusion Dm is positive.
C) In order for fusion reactions to occur, temperatures must be in the millions of degrees.
D) The fission of Pu-239 atoms produces a great number of isotopes of a large number of elements.
E) Neutron-induced fission processes can occur at room temperature, rather than at millions of degrees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If 12% of a certain radioisotope decays in 5.2 years, what is the half-life of this isotope
A) 0.59 yr
B) 1.7 yr
C) 22 yr
D) 28 yr
E) 32 yr
A) 0.59 yr
B) 1.7 yr
C) 22 yr
D) 28 yr
E) 32 yr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Estimate the age of a bottled wine that has a tritium, 3H, content 60% that of freshly bottled wine. Tritium decays by beta decay and has a half-life of 12.3 yr.
A) 0.029 yr
B) 7.4 yr
C) 9.1 yr
D) 16 yr
E) 35 yr
A) 0.029 yr
B) 7.4 yr
C) 9.1 yr
D) 16 yr
E) 35 yr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Polonium-208 is an alpha emitter with a half-life of 2.90 years. How many milligrams of polonium from an original sample of 2.00 mg will remain after 8.00 years
A) 0.147 mg
B) 0.296 mg
C) 0.725 mg
D) 6.77 mg
E) 1.90 mg
A) 0.147 mg
B) 0.296 mg
C) 0.725 mg
D) 6.77 mg
E) 1.90 mg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which isotope, when bombarded with nitrogen-15, yields the artificial isotope dubnium-260 plus 4 neutrons
A) californium-245
B) thorium-257
C) nobelium-245
D) californium-249
E) dubnium-249
A) californium-245
B) thorium-257
C) nobelium-245
D) californium-249
E) dubnium-249

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Present-day plant life has a carbon-14 decay rate of 16 disintegrations per minute (dpm) per gram of carbon. If a contemporary wooden chair were somehow preserved for the next 3,900 years, what 14C decay rate should be expected from the wood used to make the chair (t1/2 = 5,730 yr)
A) 26 dpm
B) 12 dpm
C) 11 dpm
D) 10 dpm
E) 8 dpm
A) 26 dpm
B) 12 dpm
C) 11 dpm
D) 10 dpm
E) 8 dpm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In the following reaction, identify X .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The dose unit of ionizing radiation is called the rad. The rad is defined in terms of
A) the half-life of a radioisotope.
B) the energy deposited per gram of an object.
C) the biological damage produced.
D) the accumulation of fission products.
E) the number of ions per centimeter.
A) the half-life of a radioisotope.
B) the energy deposited per gram of an object.
C) the biological damage produced.
D) the accumulation of fission products.
E) the number of ions per centimeter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
How many 14C atoms are in a charcoal sample that has a decay rate of 3,500 disintegrations per min? (For 14C, t1/2 = 5,730 yr.)
A) 2.9 * 107 atoms
B) 8.0 * 10-7 atoms
C) 1.4 * 1014 atoms
D) 1.5 * 1013 atoms
E) 6.02 * 1020 atoms
A) 2.9 * 107 atoms
B) 8.0 * 10-7 atoms
C) 1.4 * 1014 atoms
D) 1.5 * 1013 atoms
E) 6.02 * 1020 atoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Decay of lutetium-167 by electron capture yields
A) ytterbium-167.
B) lutetium-166.
C) thulium-163.
D) tantalum-171.
E) hafnium-167.
A) ytterbium-167.
B) lutetium-166.
C) thulium-163.
D) tantalum-171.
E) hafnium-167.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which isotope, when bombarded with oxygen-18, yields the artificial isotope seaborgium-263 plus 4 neutrons
A) nobelium-245
B) radium-259
C) californium-245
D) nobelium-249
E) californium-249
A) nobelium-245
B) radium-259
C) californium-245
D) nobelium-249
E) californium-249

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
List the different types of nuclear radiation (alpha, beta, gamma) in order of increasing penetrating power.
A) alpha < beta < gamma
B) beta < alpha < gamma
C) gamma < alpha < beta
D) gamma < beta < alpha
E) alpha < gamma < beta
A) alpha < beta < gamma
B) beta < alpha < gamma
C) gamma < alpha < beta
D) gamma < beta < alpha
E) alpha < gamma < beta

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is an example of a free radical
A) H3O+
B) H2O2
C) HO2-
D) HO2·
E) H2O
A) H3O+
B) H2O2
C) HO2-
D) HO2·
E) H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The carbon-14 activity of some ancient Indian corn was found to be 7.0 disintegrations per minute (dpm) per gram of carbon. If present-day plant life has 16 dpm per gram of carbon, how old is the Indian corn? (t1/2 = 5,730 yr)
A) 6,800 yr
B) 2,500 yr
C) 4,700 yr
D) 10,000 yr
E) 7,200 yr
A) 6,800 yr
B) 2,500 yr
C) 4,700 yr
D) 10,000 yr
E) 7,200 yr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The half-life of 14C is 5,730 yr. Assuming some charcoal from a campfire 29,000 years old was found, what fraction of the original C-14 would remain today
A) 3.0 * 10-2
B) 0.197
C) 3.51
D) 33.3
E) None of these.
A) 3.0 * 10-2
B) 0.197
C) 3.51
D) 33.3
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
List the given types of nuclear radiation (cosmic rays, medical and dental X rays, and nuclear waste) in order of how much each contributes to the average yearly dose of nuclear radiation for Americans
A) cosmic rays < medical and dental X rays < nuclear waste
B) medical and dental X rays < cosmic rays < nuclear waste
C) nuclear waste < cosmic rays < medical and dental X rays
D) cosmic rays < nuclear waste < medical and dental X rays
E) medical and dental X rays < nuclear waste < cosmic rays
A) cosmic rays < medical and dental X rays < nuclear waste
B) medical and dental X rays < cosmic rays < nuclear waste
C) nuclear waste < cosmic rays < medical and dental X rays
D) cosmic rays < nuclear waste < medical and dental X rays
E) medical and dental X rays < nuclear waste < cosmic rays

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Gamma-rays cause radiation damage when they interact with matter by producing
A) ions and free radicals.
B) isotopes.
C) daughter products.
D) oxidation.
E) reduction.
A) ions and free radicals.
B) isotopes.
C) daughter products.
D) oxidation.
E) reduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In the following reaction, identify X.
A) 7b
B) 3a
C) 4n
D)
E) 15p
A) 7b
B) 3a
C) 4n
D)
E) 15p

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Decay of silicon-27 by positron emission yields
A) magnesium-23.
B) sulfur-31.
C) phosphorus-27.
D) silicon-26.
E) aluminum-27.
A) magnesium-23.
B) sulfur-31.
C) phosphorus-27.
D) silicon-26.
E) aluminum-27.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In the following reaction, identify X.
A) a
B) n
C) p
D) e
E) b
A) a
B) n
C) p
D) e
E) b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Rubidium-87 decays by beta decay with a half-life of 4.9 * 1010 yr. How many 87Rb atoms are in a moon rock sample that has a rubidium decay rate of 3,500 disintegrations per hour
A) 9.0 * 1016 atoms
B) 4.3 * 10-4 atoms
C) 2.2 * 1018 atoms
D) 2.5 * 1014 atoms
E) 1.7 * 1014 atoms
A) 9.0 * 1016 atoms
B) 4.3 * 10-4 atoms
C) 2.2 * 1018 atoms
D) 2.5 * 1014 atoms
E) 1.7 * 1014 atoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Decay of tin-110 by electron capture yields
A) tin-109.
B) cadmium-106.
C) indium-110.
D) antimony-110.
E) tellurium-114.
A) tin-109.
B) cadmium-106.
C) indium-110.
D) antimony-110.
E) tellurium-114.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Petroleum is a fossil fuel containing many different carbon compounds. If the carbon atoms in petroleum have been in the ground for 100 million years, what fraction of the initial 14C atoms is still there? (t1/2 = 5,370 yr)
A) 0
B) 1 * 10-10
C) 5.7 * 10-5
D) 1.0 * 10-3
E) 5.7 * 10-1
A) 0
B) 1 * 10-10
C) 5.7 * 10-5
D) 1.0 * 10-3
E) 5.7 * 10-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A sample of a radioisotope shows an activity of 999 disintegrations per minute due to beta decay. If after 1.10 years the activity is 952 disintegrations per minute, what is the half-life of this radioisotope
A) 4.38 * 10-2 yr
B) 11.4 yr
C) 0.25 yr
D) 15.8 yr
E) 9.1 yr
A) 4.38 * 10-2 yr
B) 11.4 yr
C) 0.25 yr
D) 15.8 yr
E) 9.1 yr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



