Deck 19: Ecosystem Essentials
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/128
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Ecosystem Essentials
1
The study of the distribution of plants and animals, the diverse spatial patterns they create, and the physical and biological processes that produce Earth's species richness is called
A) biology.
B) ecology.
C) geoarchaeology.
D) biogeography.
A) biology.
B) ecology.
C) geoarchaeology.
D) biogeography.
D
2
Of the total energy intercepted at Earth's surface and available for work, only about ________ is actually fixed by photosynthesis.
A) 1%
B) 5%
C) 10%
D) 15%
A) 1%
B) 5%
C) 10%
D) 15%
A
3
Photosynthesis involves
A) the release of stored carbon dioxide in a process using sunlight.
B) the union of carbon dioxide and hydrogen in the presence of sunlight, and the release of oxygen.
C) a process known as respiration.
D) important reactions within the stems and roots of plants.
A) the release of stored carbon dioxide in a process using sunlight.
B) the union of carbon dioxide and hydrogen in the presence of sunlight, and the release of oxygen.
C) a process known as respiration.
D) important reactions within the stems and roots of plants.
B
4
An ecosystem is a(n) ________ system in terms of energy, and a(n) ________ system in terms of matter.
A) open; open
B) open; closed
C) closed; open
D) closed; closed
A) open; open
B) open; closed
C) closed; open
D) closed; closed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An organism capable of synthesizing its own food and inorganic substances using sunlight or chemical energy is known as a(n)
A) heterotroph.
B) autotroph.
C) primary consumer.
D) secondary consumer.
A) heterotroph.
B) autotroph.
C) primary consumer.
D) secondary consumer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A self-regulating association of living plants and animals and their nonliving physical environment is termed a(n)
A) ecosystem.
B) ecotone.
C) community.
D) niche.
A) ecosystem.
B) ecotone.
C) community.
D) niche.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Chlorophyll absorbs only the ________ and ________ wavelengths for photochemical operations.
A) orange-red; violet-blue
B) violet-blue; green-yellow
C) orange-red; green-yellow
D) yellow-red; violet-green
A) orange-red; violet-blue
B) violet-blue; green-yellow
C) orange-red; green-yellow
D) yellow-red; violet-green

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The Earth's biosphere
A) consists of only terrestrial organisms, while the hydrosphere includes aquatic and marine organisms.
B) only includes the biotic components of an ecosystem, with the abiotic components being considered part of the lithosphere, hydrosphere, or atmosphere, respectively.
C) is more a theoretical construct than an observable sphere of study.
D) extends from the ocean floor to an altitude of approximately 8 km (5 mi) into the atmosphere.
A) consists of only terrestrial organisms, while the hydrosphere includes aquatic and marine organisms.
B) only includes the biotic components of an ecosystem, with the abiotic components being considered part of the lithosphere, hydrosphere, or atmosphere, respectively.
C) is more a theoretical construct than an observable sphere of study.
D) extends from the ocean floor to an altitude of approximately 8 km (5 mi) into the atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is not a abiotic component of an ecosystem?
A) plants
B) sunlight
C) precipitation
D) mineral nutrients
A) plants
B) sunlight
C) precipitation
D) mineral nutrients

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A study of the spatial distribution of the coast redwood (Sequoia sempervirens) and the environmental factors that control that distribution would be an example of a topic studied in
A) biogeography.
B) ecology.
C) pedology.
D) plant biology.
A) biogeography.
B) ecology.
C) pedology.
D) plant biology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Autotrophs that dwell in dark caves, in wells, or on the ocean floor often depend on which of the following biogeochemical processes?
A) chemosynthesis
B) photosynthesis
C) nutrient leaching
D) nitrogen fixing
A) chemosynthesis
B) photosynthesis
C) nutrient leaching
D) nitrogen fixing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Today, there are over 270,000 plant species with conductive tissues and material flow systems known as
A) blue-green algae.
B) cyanobacteria.
C) xeriphytes.
D) vascular plants.
A) blue-green algae.
B) cyanobacteria.
C) xeriphytes.
D) vascular plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The study of the interrelationships between organisms and their environment is called
A) biology.
B) ecology.
C) pedology.
D) biogeography.
A) biology.
B) ecology.
C) pedology.
D) biogeography.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Light g C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ is the generalized equation for
A) respiration.
B) photosynthesis.
C) chemosynthesis.
D) transpiration.
A) respiration.
B) photosynthesis.
C) chemosynthesis.
D) transpiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ g 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + heat energy is the generalized equation for
A) respiration.
B) photosynthesis.
C) chemosynthesis.
D) transpiration.
A) respiration.
B) photosynthesis.
C) chemosynthesis.
D) transpiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Chlorophyll reflects predominately ________ wavelengths of visible light.
A) red
B) blue
C) green
D) indigo
A) red
B) blue
C) green
D) indigo

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A study of the dietary requirements of African bush elephants (Loxodonta africana) in a savanna environment, and the role the elephants play in that environment, would be an example of a topic studied in
A) biogeography.
B) ecology.
C) pedology.
D) plant biology.
A) biogeography.
B) ecology.
C) pedology.
D) plant biology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The gaseous oxygen in the Earth's atmosphere was produced as a by-product of
A) volcanic outgassing.
B) photochemical reactions breaking down ozone (O₃) to form oxygen (O₂).
C) photosynthesis.
D) decay of organic matter.
A) volcanic outgassing.
B) photochemical reactions breaking down ozone (O₃) to form oxygen (O₂).
C) photosynthesis.
D) decay of organic matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is not a biotic component of an ecosystem?
A) plants
B) animals
C) bacteria
D) mineral nutrients
A) plants
B) animals
C) bacteria
D) mineral nutrients

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The openings on the surfaces of plant leaves through which gases move into and out of are known as
A) chlorophyll.
B) stomata.
C) guard cells.
D) chloroplasts.
A) chlorophyll.
B) stomata.
C) guard cells.
D) chloroplasts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Energy flows through an ecosystem along an idealized unidirectional pathway called a
A) food web.
B) niche order.
C) trophic cascade.
D) food chain.
A) food web.
B) niche order.
C) trophic cascade.
D) food chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How is atmospheric nitrogen converted to a usable form in the biosphere?
A) Atmospheric nitrogen is directly available to plants and animals.
B) It is absorbed into plants via stomata and converted within the plant to a usable form.
C) Bacteria within root nodules of legumes chemically combine the atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates and ammonia.
D) Atmospheric nitrogen is completely unavailable to plants and animals and, as a result, synthetic fertilizers must be used.
A) Atmospheric nitrogen is directly available to plants and animals.
B) It is absorbed into plants via stomata and converted within the plant to a usable form.
C) Bacteria within root nodules of legumes chemically combine the atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates and ammonia.
D) Atmospheric nitrogen is completely unavailable to plants and animals and, as a result, synthetic fertilizers must be used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The net dry weight of all organic material in an ecosystem is known as
A) net primary productivity.
B) biomass.
C) net photosynthesis.
D) compensation point.
A) net primary productivity.
B) biomass.
C) net photosynthesis.
D) compensation point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The net photosynthesis for an entire ecosystem is known as the
A) net primary productivity.
B) compensation point.
C) net photosynthesis.
D) free air CO₂ enrichment.
A) net primary productivity.
B) compensation point.
C) net photosynthesis.
D) free air CO₂ enrichment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Organisms that share the same feeding level (e.g. primary producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, etc.) are said to be at the same
A) food web.
B) niche order.
C) trophic level.
D) food pyramid.
A) food web.
B) niche order.
C) trophic level.
D) food pyramid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Approximately ________ of the light energy arriving at the surface of a leaf is useful to chlorophyll.
A) 5%
B) 10%
C) 25%
D) 50%
A) 5%
B) 10%
C) 25%
D) 50%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Respiration involves
A) the use of heat energy to react carbon dioxide with water to produce oxygen.
B) a chemical reaction between carbohydrates and oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and heat energy.
C) a photochemical reaction involving carbon dioxide and water to produce carbohydrates and oxygen.
D) a photochemical reaction involving carbon dioxide and oxygen to produce water and oxygen.
A) the use of heat energy to react carbon dioxide with water to produce oxygen.
B) a chemical reaction between carbohydrates and oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and heat energy.
C) a photochemical reaction involving carbon dioxide and water to produce carbohydrates and oxygen.
D) a photochemical reaction involving carbon dioxide and oxygen to produce water and oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The break-even point between the production and consumption of organic material is termed
A) net primary productivity.
B) compensation point.
C) net photosynthesis.
D) free air CO₂ enrichment.
A) net primary productivity.
B) compensation point.
C) net photosynthesis.
D) free air CO₂ enrichment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The difference between the photosynthetic production of carbohydrates and the respiration loss of carbohydrates is known as
A) net primary productivity.
B) compensation point.
C) net photosynthesis.
D) free air CO₂ enrichment.
A) net primary productivity.
B) compensation point.
C) net photosynthesis.
D) free air CO₂ enrichment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is not correct regarding nitrogen.
A) The atmosphere contains about 78% nitrogen.
B) Bacterial action is key to the nitrogen cycle.
C) Atmospheric nitrogen is accessible directly to most organisms.
D) Nitrogen is very important to organisms.
A) The atmosphere contains about 78% nitrogen.
B) Bacterial action is key to the nitrogen cycle.
C) Atmospheric nitrogen is accessible directly to most organisms.
D) Nitrogen is very important to organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A ________ is a complex network of interconnected food chains with multidirectional branches.
A) food web
B) niche order
C) trophic level
D) food pyramid
A) food web
B) niche order
C) trophic level
D) food pyramid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is the largest carbon sinks?
A) the atmosphere
B) fossil fuels and oil shales
C) dead organic matter
D) the oceans
A) the atmosphere
B) fossil fuels and oil shales
C) dead organic matter
D) the oceans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In which of the following marine/aquatic ecosystems would one tend to find the highest net primary productivity?
A) open ocean
B) boreal forest
C) algal beds and reefs
D) upwelling zone
A) open ocean
B) boreal forest
C) algal beds and reefs
D) upwelling zone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
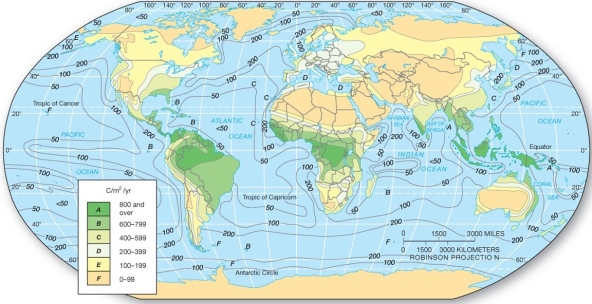
In which of the following areas would one tend to find the highest net primary productivity?
A) northern Brazil
B) central Australia
C) western Canada
D) Euroasia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In which of the following terrestrial ecosystems would one tend to find the lowest net primary productivity?
A) extreme desert
B) woodland and shrubland
C) tundra
D) cultivated lands
A) extreme desert
B) woodland and shrubland
C) tundra
D) cultivated lands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Photosynthesis converts
A) heat energy, carbon dioxide, and water into carbohydrates and oxygen.
B) heat energy, oxygen, and carbohydrates into carbon dioxide and water.
C) light energy, carbon dioxide, and water into carbohydrates and oxygen.
D) light energy, oxygen, and carbohydrates into carbon dioxide and water.
A) heat energy, carbon dioxide, and water into carbohydrates and oxygen.
B) heat energy, oxygen, and carbohydrates into carbon dioxide and water.
C) light energy, carbon dioxide, and water into carbohydrates and oxygen.
D) light energy, oxygen, and carbohydrates into carbon dioxide and water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A dead zone refers to
A) terrestrial areas in which excessive nitrogen fertilizer has essentially burned the soil, preventing plants and microorganisms from living there.
B) oligotrophic areas in water bodies that cannot support life due to lack of nutrients.
C) an ecosystem that was cleared of all vegetation for slash and burn agriculture.
D) hypoxic areas in water bodies that limit marine and aquatic life.
A) terrestrial areas in which excessive nitrogen fertilizer has essentially burned the soil, preventing plants and microorganisms from living there.
B) oligotrophic areas in water bodies that cannot support life due to lack of nutrients.
C) an ecosystem that was cleared of all vegetation for slash and burn agriculture.
D) hypoxic areas in water bodies that limit marine and aquatic life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In which of the following terrestrial ecosystems would one tend to find the highest net primary productivity?
A) temperate grassland
B) boreal forest
C) tropical seasonal forest
D) tundra and alpine region
A) temperate grassland
B) boreal forest
C) tropical seasonal forest
D) tundra and alpine region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is incorrect regarding the spatial variability of net primary productivity?
A) At temperate and high latitudes, the rate of carbon fixing is seasonally variable.
B) Productivity rates are constantly high throughout the year in the tropics.
C) Net primary productivity is highest in the fall and winter in temperate and high latitude areas.
D) Productivity rates in deserts is much less than that of tropical regions.
A) At temperate and high latitudes, the rate of carbon fixing is seasonally variable.
B) Productivity rates are constantly high throughout the year in the tropics.
C) Net primary productivity is highest in the fall and winter in temperate and high latitude areas.
D) Productivity rates in deserts is much less than that of tropical regions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Together, three natural elements make up 99% of the Earth's biomass. Which of the following is not one of those three elements?
A) oxygen (O)
B) hydrogen (H)
C) nitrogen (N)
D) carbon (C)
A) oxygen (O)
B) hydrogen (H)
C) nitrogen (N)
D) carbon (C)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In food webs, toxic chemicals tend to accumulate and concentrate most in the
A) top carnivores.
B) herbivores.
C) omnivores.
D) autotrophs.
A) top carnivores.
B) herbivores.
C) omnivores.
D) autotrophs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
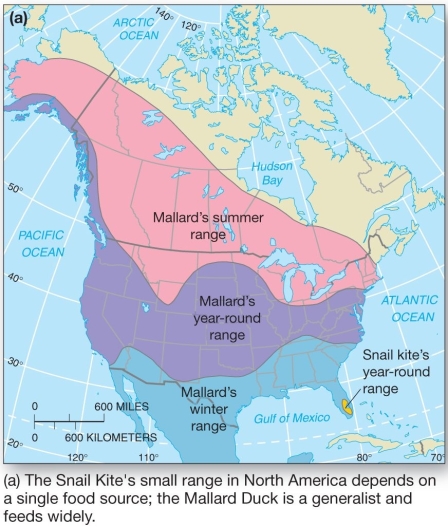
The snail kite (Rostrhamus sociabilis) is a specialist that feeds on only one specific type of snail. By comparison, the Mallard Duck (Anas platyrhynchos) is a generalist that feeds on diverse food sources. Whereas the snail kite has a very limited range, the Mallard Duck has a very broad range. The snail kite's diet is an example of a(n)
A) limiting factor.
B) range of tolerance.
C) ecological niche.
D) habitat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
________ refers to the biotic and abiotic characteristics in the environment that determine species distribution.
A) Limiting factor
B) Range of tolerance
C) Ecological niche
D) Habitat
A) Limiting factor
B) Range of tolerance
C) Ecological niche
D) Habitat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Lichen are made up of algae and fungi living together. In this relationship, the alga is the produce and for source for the fungus and the fungus provides structure and physical support for the alga. This is an example of which symbiotic relationship?
A) parasitism
B) mutualism
C) commensalism
D) amensalism
A) parasitism
B) mutualism
C) commensalism
D) amensalism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Currently, approximately ________ of cultivated acreage in the United States and Canada is planted for animal consumption
A) 15%
B) 30%
C) 50%
D) 65%
A) 15%
B) 30%
C) 50%
D) 65%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Only about ________ of the kilocalories in a trophic level is passed to the next trophic level (e.g. from autotroph to primary consumer).
A) 5%
B) 10%
C) 15%
D) 20%
A) 5%
B) 10%
C) 15%
D) 20%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The environment in which an organism resides or is biologically adapted to live is called a(n)
A) ecotone.
B) habitat.
C) community.
D) niche.
A) ecotone.
B) habitat.
C) community.
D) niche.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A consumer, such as a bear, that eats both producers (plants) and consumers (animals) is a
A) herbivore.
B) carnivore.
C) omnivore.
D) detritivore.
A) herbivore.
B) carnivore.
C) omnivore.
D) detritivore.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Mistletoe (Phoradendron) infest many taxa of plants, often causing the branches of the host species to become swollen and distorted and making the trees more susceptible to insect infestations. This is an example of which symbiotic relationship?
A) parasitism
B) mutualism
C) commensalism
D) amensalism
A) parasitism
B) mutualism
C) commensalism
D) amensalism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The interacting populations of living plants and animals in a particular location are described as a(n)
A) metapopulation.
B) ecosystem.
C) community.
D) niche.
A) metapopulation.
B) ecosystem.
C) community.
D) niche.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In coral reefs, clownfish live unharmed among the poisonous tentacles of sea anemones. The sea anemones protect the clownfish from predation, while the clownfish scare off predators, such butterfly fish, which would otherwise eat the anemones. The clownfish may also provide important nutrients to the anemones. This is an example of which symbiotic relationship?
A) parasitism
B) mutualism
C) commensalism
D) amensalism
A) parasitism
B) mutualism
C) commensalism
D) amensalism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The proposition that no two species can occupy the same ecological niche is known as the
A) symbiosis.
B) competitive exclusion principle.
C) trophic pyramid theory.
D) ecological niche theory.
A) symbiosis.
B) competitive exclusion principle.
C) trophic pyramid theory.
D) ecological niche theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
As chemical pesticides move through the trophic pyramid, they may be amplified at each higher level in a process called
A) biomagnification.
B) trophic cascading.
C) competitive exclusion.
D) pyramidal decay.
A) biomagnification.
B) trophic cascading.
C) competitive exclusion.
D) pyramidal decay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Consider a simple food chain in which a grasshopper eats grass, the grasshopper is eaten by a frog, and the frog is eaten by a snake. Which of the following is not correctly matched
A) grass - autotroph
B) grasshopper - herbivore
C) frog - secondary consumer
D) snake - primary consumer
A) grass - autotroph
B) grasshopper - herbivore
C) frog - secondary consumer
D) snake - primary consumer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following would not be a limiting factor for a plant species?
A) soil phosphorus content
B) daily precipitation values
C) number of preadors
D) days below freezing
A) soil phosphorus content
B) daily precipitation values
C) number of preadors
D) days below freezing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The specific, unique role that a species performs within a given area is known as a(n)
A) ecotone.
B) habitat.
C) community.
D) niche.
A) ecotone.
B) habitat.
C) community.
D) niche.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
From the perspective of energy, which of the following is the most efficient trophic level?
A) primary producer
B) primary consumer
C) secondary consumer
D) tertiary consumer
A) primary producer
B) primary consumer
C) secondary consumer
D) tertiary consumer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The zonation of flora and fauna along an altitudinal transect similar to that found along latitudinal transects is known as the
A) altitude-latitude hypothesis.
B) vegetation similarity theory.
C) the life zone concept.
D) altitudinal zonation principle.
A) altitude-latitude hypothesis.
B) vegetation similarity theory.
C) the life zone concept.
D) altitudinal zonation principle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A black walnut (Juglans nigra) emits a chemical that may kill or inhibit the growth of other nearby shrubs or trees. However, the black walnut is unaffected by this interaction. This is an example of which symbiotic relationship?
A) parasitism
B) mutualism
C) commensalism
D) amensalism
A) parasitism
B) mutualism
C) commensalism
D) amensalism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Epiphytic plants, such as various species of orchids (Orchidaceae), grow upon another plant, using the plants for physical support, but bringing no harm to the host plant. This is an example of which symbiotic relationship?
A) parasitism
B) mutualism
C) commensalism
D) amensalism
A) parasitism
B) mutualism
C) commensalism
D) amensalism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If a lava flow completely denudes a mountain, leaving only bare rock, what type of succession will follow?
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When a random occurrence produces altered genetic material and inserts new traits into the inherited stream, ________ has occurred.
A) Lamarckian evolution
B) punctuated equilibrium
C) mutation
D) vicariance
A) Lamarckian evolution
B) punctuated equilibrium
C) mutation
D) vicariance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Since life arose on Earth, ________ major extinctions have occurred.
A) one
B) two
C) six
D) ten
A) one
B) two
C) six
D) ten

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following is not considered among the greatest anthopogenic threats to biodiversity?
A) habitat loss
B) introduction of non-native species
C) air, water, and soil pollution
D) climate change
E) habitat loss, non-native species, pollution, and climate change all represent threats to biodiversity
A) habitat loss
B) introduction of non-native species
C) air, water, and soil pollution
D) climate change
E) habitat loss, non-native species, pollution, and climate change all represent threats to biodiversity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A monocultural agriculture community is ________ vulnerable to disturbance than an area with high biodiversity.
A) less
B) more
C) equally
A) less
B) more
C) equally

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following has the highest number of known species?
A) plants
B) insects
C) chordates
D) bacteria
A) plants
B) insects
C) chordates
D) bacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Continental drift separating a once continuous population is an example of
A) Lamarckian evolution
B) punctuated equilibrium
C) mutation
D) vicariance
A) Lamarckian evolution
B) punctuated equilibrium
C) mutation
D) vicariance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following is the correct order of lake succession, from lowest to highest nutrient levels?
A) oligotrophic, mesotrophic, eutrophic
B) eutrophic, oligotrophic, mesotrophic
C) mesotrophic, eutrophic, oligotrophic
D) oligotrophic, eutrophic, mesotrophic
A) oligotrophic, mesotrophic, eutrophic
B) eutrophic, oligotrophic, mesotrophic
C) mesotrophic, eutrophic, oligotrophic
D) oligotrophic, eutrophic, mesotrophic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Increased foliage cover in parts of Australia has been attributed to which of the following climate change related phenomena.?
A) sea level rise
B) cloud albedo forcing
C) CO₂ fertilization effect
D) cloud greenhouse forcing
A) sea level rise
B) cloud albedo forcing
C) CO₂ fertilization effect
D) cloud greenhouse forcing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Human caused eutrophication is known as
A) oligotrophication.
B) mesotrophication.
C) cultural eutrophication.
D) anthropotrophication.
A) oligotrophication.
B) mesotrophication.
C) cultural eutrophication.
D) anthropotrophication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In which portion of a lake would oligotrophic conditions most likely occur?
A) along the shore
B) in shallow bays
C) in deep water
D) in areas where high nutrient inputs occur.
A) along the shore
B) in shallow bays
C) in deep water
D) in areas where high nutrient inputs occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Studies have shown that ________ biodiversity in an ecosystem leads to ________ long-term stability and productivity.
A) greater; greater
B) greater; less
C) less; greater
D) less; slightly more
A) greater; greater
B) greater; less
C) less; greater
D) less; slightly more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The first species to colonize previously disturbed or damaged ecosystems are called a(n)
A) sere.
B) pioneer community.
C) successor.
D) establishment.
A) sere.
B) pioneer community.
C) successor.
D) establishment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When a community is disturbed to the point that most or all of its species are eliminated, a process called ________ occurs in which the area undergoes a series of changes in species composition as newer communities replace older ones.
A) rejuvenation
B) mass extinction
C) ecological succession
D) patch dynamics
A) rejuvenation
B) mass extinction
C) ecological succession
D) patch dynamics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The ability of an ecosystem to recover quickly from a disturbance and return to its original state is known as
A) resilience.
B) vicariance.
C) punctuated equilibrium.
D) succession.
A) resilience.
B) vicariance.
C) punctuated equilibrium.
D) succession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The notion that the traits that help a species survive and reproduce are passed along more frequently than those that do not (i.e. differential reproduction and adaptation) is known as
A) Lamarckianism.
B) punctuated equilibrium.
C) natural selection.
D) gradualism.
A) Lamarckianism.
B) punctuated equilibrium.
C) natural selection.
D) gradualism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Approximately what percentage of plant and animal species have been classified overall.
A) 1%
B) 13%
C) 67%
D) 92%
A) 1%
B) 13%
C) 67%
D) 92%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The origin of the Earth's biological diversity is embodied in
A) the life zone concept.
B) the theory of evolution.
C) ecological succession principle.
D) competitive exclusion principle.
A) the life zone concept.
B) the theory of evolution.
C) ecological succession principle.
D) competitive exclusion principle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If a forest fire destroyed the vegetation in an area, but left some vestiges of the previously functioning community and the soil intact, what type of succession would follow?
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following is not a measure of biological diversity?
A) species diversity
B) genetic diversity
C) ecosystem diversity
D) species diversity, genetic diversity, and ecosystem diversity are all measures of biodiversity.
A) species diversity
B) genetic diversity
C) ecosystem diversity
D) species diversity, genetic diversity, and ecosystem diversity are all measures of biodiversity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



