Deck 8: The Lower Extremity: The Knee, Ankle, and Foot
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/20
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: The Lower Extremity: The Knee, Ankle, and Foot
1
Analyze the muscular involvement in the motion of the knee joint in a kicking motion. Be sure to include both the preparation phase and the propulsion phase.
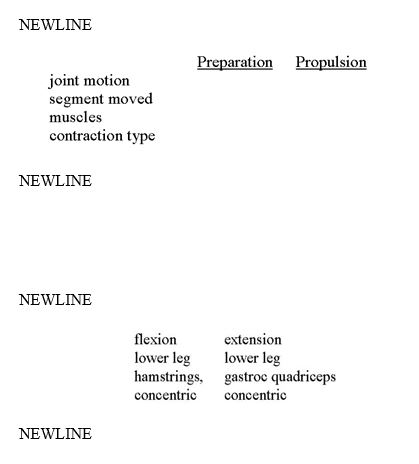
2
Why is the knee classified as a modified hinge joint?
A) because of the action of the femur on the tibia
B) because of the structure of the menisci
C) because of the action of the gliding motion of the patella on the femur
D) because of the action of the rotation of the fibula
A) because of the action of the femur on the tibia
B) because of the structure of the menisci
C) because of the action of the gliding motion of the patella on the femur
D) because of the action of the rotation of the fibula
because of the action of the femur on the tibia
3
Extreme pronation of the feet is likely to place stress on the knee joints. Explain the nature of that stress and discuss the structures which will be affected.
tension on medial side of knee-stretch collateral ligaments, pull on medial meniscus
4
Why are deep knee bends considered to be a potentially dangerous exercise?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the primary factor in ankle stability?
A) ligamentous support
B) strong joint capsule
C) deep bony articulation
D) muscular support
A) ligamentous support
B) strong joint capsule
C) deep bony articulation
D) muscular support

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which three bones make up the ankle joint?
A) calcaneus, talus, tibia
B) tibia, fibula, talus
C) fibula, tibia, calcaneus
D) tibia, talus, femu
A) calcaneus, talus, tibia
B) tibia, fibula, talus
C) fibula, tibia, calcaneus
D) tibia, talus, femu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What muscle action is involved in the movement of the knee joints in the power phase of the standing long jump?
A) concentric contraction of the hamstrings
B) concentric contraction of the quadriceps femoris
C) eccentric contraction of the hamstrings
D) eccentric contraction of the quadriceps femoris
A) concentric contraction of the hamstrings
B) concentric contraction of the quadriceps femoris
C) eccentric contraction of the hamstrings
D) eccentric contraction of the quadriceps femoris

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following muscles contracts in pronation to counteract the supination action of the tibialis anterior and the extensor hallicus longus?
A) tibialis posterior
B) flexor hallicus longus
C) extensor digitorum longus
D) flexor digitorum longus
Short Answer Questions
A) tibialis posterior
B) flexor hallicus longus
C) extensor digitorum longus
D) flexor digitorum longus
Short Answer Questions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which type of joint is the tibiofemoral joint?
A) gliding
B) condyloid
C) hinge
D) pivot
A) gliding
B) condyloid
C) hinge
D) pivot

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which muscles are most responsible for lifting the body weight through ankle plantar flexion?
A) gastrocnemius, soleus
B) gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris
C) gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris, peroneus
D) gastrocnemius, soleus, peroneus
A) gastrocnemius, soleus
B) gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris
C) gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris, peroneus
D) gastrocnemius, soleus, peroneus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which structures provide rotatory stability in the knee?
A) the cruciate ligaments
B) the collateral ligaments
C) the menisci
D) the joint capsule
A) the cruciate ligaments
B) the collateral ligaments
C) the menisci
D) the joint capsule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In performing a deep squat the prime movers at the knee are: 1) rectus femoris
2) biceps femoris
3) vastus lateralis
4) vastus medialis
5) semimembranosus
A) 1, 2, 3
B) 2, 5
C) 1, 4, 5
D) 1, 3, 4
2) biceps femoris
3) vastus lateralis
4) vastus medialis
5) semimembranosus
A) 1, 2, 3
B) 2, 5
C) 1, 4, 5
D) 1, 3, 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Many people find it more difficult to grasp the ankles in a long sit position if the ankle joint is dorsiflexed. Explain this phenomenon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following produces pronation of the foot?
A) tibialis anterior
B) extensor digitorum longus
C) extensor hallicus longus
D) soleus
A) tibialis anterior
B) extensor digitorum longus
C) extensor hallicus longus
D) soleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following does not attach to the patella?
A) rectus femoris
B) vastus medialis
C) vastus lateralis
D) semimembranosus
A) rectus femoris
B) vastus medialis
C) vastus lateralis
D) semimembranosus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Give an anatomical explanation for the preponderance of lateral sprains in the `ankle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which side of the ankle receives primary support from the deltoid ligament?
A) anterior
B) posterior
C) medial
D) lateral
A) anterior
B) posterior
C) medial
D) lateral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following motions are produced by the tibialis anterior?
A) ankle plantar flexion, inversion of foot
B) ankle dorsiflexion, inversion of foot
C) ankle plantar flexion, eversion of foot
D) ankle dorsiflexion, eversion of foot
A) ankle plantar flexion, inversion of foot
B) ankle dorsiflexion, inversion of foot
C) ankle plantar flexion, eversion of foot
D) ankle dorsiflexion, eversion of foot

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Prime movers in ankle dorsiflexion are the: 1) gastrocnemius
2) tibialis anterior
3) extensor hallicus longus
4) flexor digitorum longus
5) extensor digitorum longus
A) 1, 2, 3
B) 1, 2, 4
C) 2, 3, 4
D) 2, 3, 5
2) tibialis anterior
3) extensor hallicus longus
4) flexor digitorum longus
5) extensor digitorum longus
A) 1, 2, 3
B) 1, 2, 4
C) 2, 3, 4
D) 2, 3, 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Where is there increased tensile stress when one is knock-kneed?
A) anteriorly
B) laterally
C) medially
D) posteriorly
A) anteriorly
B) laterally
C) medially
D) posteriorly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



