Deck 22: Probability-Proportion-To-Size Sampling
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/24
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Probability-Proportion-To-Size Sampling
1
Assume the following relating to a PPS sample:
• Projected Misstatement = $20,000.
• Basic Precision = $16,000.
• Incremental Allowance = $4,500.
• Tolerable Misstatement = $34,000.
The most likely amount of misstatement in the population is equal to:
A)$20,000.
B)$20,500
C)$40,000.
D)$40,500.
E)$74,500.
• Projected Misstatement = $20,000.
• Basic Precision = $16,000.
• Incremental Allowance = $4,500.
• Tolerable Misstatement = $34,000.
The most likely amount of misstatement in the population is equal to:
A)$20,000.
B)$20,500
C)$40,000.
D)$40,500.
E)$74,500.
A
2
Assume the following relating to a PPS sample:
• Projected Misstatement = $20,000.
• Basic Precision = $16,000.
• Incremental Allowance = $4,500.
• Tolerable Misstatement = $34,000.
The upper limit on misstatement equals.
A)$20,000.
B)$20,500
C)$40,500.
D)$74,500.
• Projected Misstatement = $20,000.
• Basic Precision = $16,000.
• Incremental Allowance = $4,500.
• Tolerable Misstatement = $34,000.
The upper limit on misstatement equals.
A)$20,000.
B)$20,500
C)$40,500.
D)$74,500.
C
3
In a probability-proportional-to-size sample with a sampling interval of $10,000,an auditor discovered that a selected account receivable with a recorded amount of $5000 had an audited amount of $4,000.If this were the only misstatement discovered by the auditor,the projected misstatement of this sample would be:
A)$1,000.
B)$2,000.
C)$5,000.
D)$10,000.
A)$1,000.
B)$2,000.
C)$5,000.
D)$10,000.
B
4
Probability-proportional-to-size sampling is especially efficient for populations with high misstatement rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which statement is most proper for evaluating the results of this PPS sample?
A)Accept the population because the projected misstatement is less than the tolerable misstatement.
B)Accept the population because the sum of the projected misstatement and the basic precision exceeds the incremental allowance.
C)Reject the population because the sum of the projected misstatement, basic precision and incremental allowance exceeds the tolerable misstatement.
D)Reject the population because the tolerable misstatement exceeds the basic precision plus the incremental allowance.
A)Accept the population because the projected misstatement is less than the tolerable misstatement.
B)Accept the population because the sum of the projected misstatement and the basic precision exceeds the incremental allowance.
C)Reject the population because the sum of the projected misstatement, basic precision and incremental allowance exceeds the tolerable misstatement.
D)Reject the population because the tolerable misstatement exceeds the basic precision plus the incremental allowance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When using probability-proportional-to-size sampling,the allowance for sampling risk is the combination of basic precision and the:
A)Projected misstatement.
B)Incremental allowance.
C)Upper limit on misstatements.
D)Tainting.
A)Projected misstatement.
B)Incremental allowance.
C)Upper limit on misstatements.
D)Tainting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements is correct concerning probability-proportional-to-size sampling?
A)The sampling distribution should approximate the normal distribution.
B)The auditors control the risk of incorrect rejection by specifying that risk level for the sampling plan.
C)The sampling interval is calculated by dividing the population book value by the sample size.
D)The auditors control the risk of incorrect acceptance by incorporating an expected misstatement into the sample size formula.
A)The sampling distribution should approximate the normal distribution.
B)The auditors control the risk of incorrect rejection by specifying that risk level for the sampling plan.
C)The sampling interval is calculated by dividing the population book value by the sample size.
D)The auditors control the risk of incorrect acceptance by incorporating an expected misstatement into the sample size formula.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When no misstatements are identified in a PPS sample,the upper limit on misstatement equals.
A)An amount dependent upon the sample's standard deviation.
B)Basic precision.
C)½ of the allowance for sampling risk.
D)Zero.
A)An amount dependent upon the sample's standard deviation.
B)Basic precision.
C)½ of the allowance for sampling risk.
D)Zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The upper limit on misstatement in a probability-proportional-to-size sample plan consists of the total of the projected misstatement and the tolerable misstatement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A normally distributed sample is assumed when using probability-proportional-to-size sampling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Increasing the expected misstatement for a probability-proportional-to-size sample increases the required sample size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Assume the following relating to a PPS sample:
• Projected Misstatement = $20,000.
• Basic Precision = $16,000.
• Incremental Allowance = $4,500.
• Tolerable Misstatement = $34,000.
The allowance for sampling risk is equal to:
A)$20,000.
B)20,500.
C)$40,500.
D)$74,500.
• Projected Misstatement = $20,000.
• Basic Precision = $16,000.
• Incremental Allowance = $4,500.
• Tolerable Misstatement = $34,000.
The allowance for sampling risk is equal to:
A)$20,000.
B)20,500.
C)$40,500.
D)$74,500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An increase in the scope of analytical procedures may result in a lower allowable risk of incorrect acceptance for a substantive test of details.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When using probability-proportional-to-size sampling,the actual total misstatement in a population is most likely to be closest to the:
A)Projected misstatement.
B)Basic precision.
C)Allowance for sampling risk.
D)Upper limit on misstatement.
A)Projected misstatement.
B)Basic precision.
C)Allowance for sampling risk.
D)Upper limit on misstatement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
For which of the following populations would probability-proportional-to-size sampling be most likely to be the most efficient technique in confirming accounts receivable?
A)2,000 accounts with a standard deviation of $650, with few misstatements expected.
B)2,000 accounts with a standard deviation of $25, with few misstatements expected.
C)6,000 accounts with a standard deviation of $650, with many misstatements expected.
D)6,000 accounts with a standard deviation of $25 with many misstatements expected.
A)2,000 accounts with a standard deviation of $650, with few misstatements expected.
B)2,000 accounts with a standard deviation of $25, with few misstatements expected.
C)6,000 accounts with a standard deviation of $650, with many misstatements expected.
D)6,000 accounts with a standard deviation of $25 with many misstatements expected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In a probability-proportional-to-size sample with a sampling interval of $10,000,an auditor discovered that as selected account receivable with a recorded amount of $12,000 had an audited amount of $9,000.If this were the only misstatement discovered by the auditor,the projected misstatement of this sample would be:
A)$2,000.
B)$2,500.
C)$3,000.
D)$10,000.
A)$2,000.
B)$2,500.
C)$3,000.
D)$10,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In a probability-proportional-to-size sample with a sampling interval of $10,000,an auditor discovered that a selected account with a book value of $6,000 had an audited value of $4,000.The projected misstatement is:
A)$2,000.
B)$3,333.
C)$6,000.
D)$10,000.
A)$2,000.
B)$3,333.
C)$6,000.
D)$10,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In a probability-proportional-to-size sample,increasing the tolerable misstatement has what effect on sample size,when all other factors are held constant?
A)Increases.
B)Decreases.
C)No effect.
D)Indeterminate.
A)Increases.
B)Decreases.
C)No effect.
D)Indeterminate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In a PPS sample,the most likely misstatement in the population is equal to the:
A)Projected Misstatement.
B)Upper limit on misstatement.
C)Basic Precision.
D)Total misstatements identified in the sample.
A)Projected Misstatement.
B)Upper limit on misstatement.
C)Basic Precision.
D)Total misstatements identified in the sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The use of probability-proportional-to-size sampling would be least likely to be efficient if:
A)Commercial receivable accounts are being audited.
B)Statistical inferences are to be made.
C)Many accounts are known to be in error.
D)The population has a high total dollar value.
A)Commercial receivable accounts are being audited.
B)Statistical inferences are to be made.
C)Many accounts are known to be in error.
D)The population has a high total dollar value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The auditors of Smith Electronics wish to limit the audit risk of material misstatement in the test of accounts receivable to 5 percent.They believe that inherent risk is 100%,there is a 40 percent risk that material misstatement could have bypassed the client's system of internal control,and a 50 percent risk that any existing material misstatement would not have been brought to light by the auditors' analytical procedures.What is the maximum risk of incorrect acceptance the auditors should specify in their substantive tests of details of accounts receivable?
A)5 percent.
B)10 percent.
C)20 percent.
D)25 percent.
A)5 percent.
B)10 percent.
C)20 percent.
D)25 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Williams,CPA intends to use probability-proportional-to-size sampling.He has properly selected and audited a sample of 100 accounts receivable from his client's population of 3000 accounts.He calculated a sampling interval of $5,000 and the tolerable misstatement for the account is $40,000.He has the following table available: 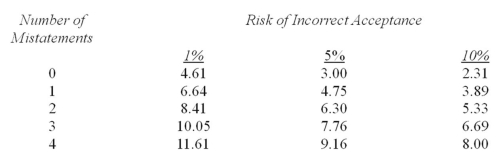 Williams also recalls that "basic precision" is equal to the appropriate reliability factor multiplied times the sampling interval.He wishes to accept a risk of incorrect acceptance of 10 percent.
Williams also recalls that "basic precision" is equal to the appropriate reliability factor multiplied times the sampling interval.He wishes to accept a risk of incorrect acceptance of 10 percent.
He found that 97 of the 100 accounts in the sample were properly calculated.However,the following three errors existed: a.Calculate the projected misstatement.
a.Calculate the projected misstatement.
b.Calculate the basic precision.
c.Calculate the incremental allowance.
d.Calculate the upper limit on misstatement.
e.Explain how the auditors would consider the results calculated above.
 Williams also recalls that "basic precision" is equal to the appropriate reliability factor multiplied times the sampling interval.He wishes to accept a risk of incorrect acceptance of 10 percent.
Williams also recalls that "basic precision" is equal to the appropriate reliability factor multiplied times the sampling interval.He wishes to accept a risk of incorrect acceptance of 10 percent.He found that 97 of the 100 accounts in the sample were properly calculated.However,the following three errors existed:
 a.Calculate the projected misstatement.
a.Calculate the projected misstatement.b.Calculate the basic precision.
c.Calculate the incremental allowance.
d.Calculate the upper limit on misstatement.
e.Explain how the auditors would consider the results calculated above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following factors would indicate that probability-proportional-to-size sampling should be used rather than other statistical sampling techniques?
A)There is a book value for every item in the population.
B)There is a low expected misstatement rate in the population.
C)The auditors wish to obtain an estimate of the amount of misstatement in the population.
D)The book value of the population is large.
A)There is a book value for every item in the population.
B)There is a low expected misstatement rate in the population.
C)The auditors wish to obtain an estimate of the amount of misstatement in the population.
D)The book value of the population is large.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which statement is correct with respect to the probability-proportional-to-size technique?
A)The technique insures that every account in the population has an equal chance of being selected.
B)The technique automatically stratifies the population.
C)The technique results in a representative sample every time.
D)The technique allows the auditors to measure more precisely the risk of incorrect acceptance.
A)The technique insures that every account in the population has an equal chance of being selected.
B)The technique automatically stratifies the population.
C)The technique results in a representative sample every time.
D)The technique allows the auditors to measure more precisely the risk of incorrect acceptance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



