Deck 36: Populations
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/76
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 36: Populations
1
Introduction of the brown tree snake on Guam coincided with the disappearance of birds and small reptiles on the island.Which of the following lead to this decline?
A)Competition for food with the snakes.
B)Predation by the snakes.
C)A side effect of poisons used to kill the snakes.
D)Competition for nesting sites with the snakes.
E)Habitat destruction that happened at the same time the snakes were introduced.
A)Competition for food with the snakes.
B)Predation by the snakes.
C)A side effect of poisons used to kill the snakes.
D)Competition for nesting sites with the snakes.
E)Habitat destruction that happened at the same time the snakes were introduced.
B
2
The number of individuals that are killed in a population per unit time is its:
A)Immigration rate
B)Emigration rate
C)Death rate
D)Birth rate
E)Expatriation rate
A)Immigration rate
B)Emigration rate
C)Death rate
D)Birth rate
E)Expatriation rate
C
3
In a survivorship curve,a type I species,like a human or elephant,is a species that:
A)Has an equal probability of dying at any age
B)Has the highest probability of dying as it reaches its maximum life span
C)Has a strong possibility of becoming extinct in a relatively short period of time
D)Has an extremely short life span
E)Has the highest probability of dying at a very young age
A)Has an equal probability of dying at any age
B)Has the highest probability of dying as it reaches its maximum life span
C)Has a strong possibility of becoming extinct in a relatively short period of time
D)Has an extremely short life span
E)Has the highest probability of dying at a very young age
B
4
The type of population distribution seen when individuals strongly repel one another is:
A)Clumped distribution
B)Random distribution
C)Non-selected distribution
D)Uniform distribution
E)Forced distribution
A)Clumped distribution
B)Random distribution
C)Non-selected distribution
D)Uniform distribution
E)Forced distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The brown tree snake in Guam had a ______of about 100 snakes per acre.
A)Population density
B)Population distribution
C)Population
D)Growth rate
E)Death rate
A)Population density
B)Population distribution
C)Population
D)Growth rate
E)Death rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The study of the factors that influence changes in a population's size is:
A)Population density
B)Population dynamics
C)Population geology
D)Population ethology
E)Population dispersion
A)Population density
B)Population dynamics
C)Population geology
D)Population ethology
E)Population dispersion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
All of the organisms in a given location or area is termed a:
A)Peer group
B)Flock
C)Community
D)Population
E)Herd
A)Peer group
B)Flock
C)Community
D)Population
E)Herd

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A method that could reduce the birth rate of the brown tree snake population on Guam is:
A)Use pheromones to attract the snakes to the traps
B)Use dead rats laced with acetaminophen
C)Capture and kill the snakes
D)Release sterilized males to compete with wild fertile males
E)All of the above
A)Use pheromones to attract the snakes to the traps
B)Use dead rats laced with acetaminophen
C)Capture and kill the snakes
D)Release sterilized males to compete with wild fertile males
E)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The type of population distribution seen when only portions of a habitat are the most favorable is:
A)Clumped distribution
B)Random distribution
C)Uniform distribution
D)Non-selected distribution
E)Forced distribution
A)Clumped distribution
B)Random distribution
C)Uniform distribution
D)Non-selected distribution
E)Forced distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the opening essay of chapter 36,the author discusses how the introduction of a new predator on the island of ___________________ decimated local populations of birds and small reptiles.
A)Cuba
B)Guam
C)Puerto Rico
D)Madagascar
E)Ceylon
A)Cuba
B)Guam
C)Puerto Rico
D)Madagascar
E)Ceylon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The type of population distribution seen when the habitat is relatively consistent and individuals do not strongly attract or repel one another is:
A)Clumped distribution
B)Uniform distribution
C)Non-selected distribution
D)Forced distribution
E)Random distribution
A)Clumped distribution
B)Uniform distribution
C)Non-selected distribution
D)Forced distribution
E)Random distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In a survivorship curve,a type II species,like a song bird,is a species that:
A)Has an equal probability of dying at any age
B)Has a strong possibility of becoming extinct in a relatively short period of time
C)Has the highest probability of dying as it reaches its maximum life span
D)Has an extremely short life span
E)Has the highest probability of dying at a very young age
A)Has an equal probability of dying at any age
B)Has a strong possibility of becoming extinct in a relatively short period of time
C)Has the highest probability of dying as it reaches its maximum life span
D)Has an extremely short life span
E)Has the highest probability of dying at a very young age

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The movement of individuals out of a population is termed:
A)Immigration
B)Extrapolation
C)Population dispersion
D)Clumping
E)Emigration
A)Immigration
B)Extrapolation
C)Population dispersion
D)Clumping
E)Emigration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The number of individuals of a species per unit area or volume of habitat is:
A)Carrying capacity
B)Population density
C)A community
D)Population distribution
E)Population dynamics
A)Carrying capacity
B)Population density
C)A community
D)Population distribution
E)Population dynamics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The physical location where an organism lives is termed its:
A)Home boundary
B)Range
C)Habitat
D)Community
E)Ecosystem
A)Home boundary
B)Range
C)Habitat
D)Community
E)Ecosystem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The number of new individuals produced per unit time in a population is its:
A)Immigration rate
B)Emigration rate
C)Death rate
D)Birth rate
E)Expatriation rate
A)Immigration rate
B)Emigration rate
C)Death rate
D)Birth rate
E)Expatriation rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A population age structure diagram showing roughly equal numbers in each age group depicts a:
A)Stable population
B)Growing population
C)Declining population
D)Population facing extinction
E)Very small population size
A)Stable population
B)Growing population
C)Declining population
D)Population facing extinction
E)Very small population size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The movement of individuals into a population is termed:
A)Emigration
B)Expatriation
C)Immigration
D)Population dispersion
E)Clumping
A)Emigration
B)Expatriation
C)Immigration
D)Population dispersion
E)Clumping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A group of organisms of one species occupying a geographical location at the same time is a:
A)Population
B)Community
C)Peer group
D)Flock
E)Herd
A)Population
B)Community
C)Peer group
D)Flock
E)Herd

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The study of the relationships among organisms and the environment is:
A)Ethology
B)Habitology
C)Ergonomics
D)Ecology
E)Geology
A)Ethology
B)Habitology
C)Ergonomics
D)Ecology
E)Geology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In regards to a species life history,K-selected species:
A)Have only a few offspring
B)Are short lived
C)Reproduce at an early age
D)Have a large number of offspring
E)Give very little care to their offspring
A)Have only a few offspring
B)Are short lived
C)Reproduce at an early age
D)Have a large number of offspring
E)Give very little care to their offspring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An example of a density-independent factors that affects a population's growth is:
A)Insects eating your tomato plants
B)Your tomato plants competing for water
C)A fungus infecting your tomato plants
D)Frost killing all of your tomato plants
E)All are correct
A)Insects eating your tomato plants
B)Your tomato plants competing for water
C)A fungus infecting your tomato plants
D)Frost killing all of your tomato plants
E)All are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If a deer herd has a population of 1000,a carrying capacity of 2000,and an intrinsic rate of growth of 10% (0.1),the growth curve for this deer population will be:
A)Exponential
B)Linear
C)Logistic
D)Negative
E)Impossible to say
A)Exponential
B)Linear
C)Logistic
D)Negative
E)Impossible to say

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the population growth curve equation G = rN(K-N)/K,when N is very small relative to K:
A)The population growth rate stabilizes
B)The population growth rate is high
C)The population growth rate is low
D)The population crashes
E)None of the above are correct
A)The population growth rate stabilizes
B)The population growth rate is high
C)The population growth rate is low
D)The population crashes
E)None of the above are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In 2010 India had a population of 1,170,000,000,a birth rate of 0.027,and a death rate of 0.013.What is the growth rate of India's population?
A)0.027
B)0.013
C)0.014
D)0.040
E)0.001
A)0.027
B)0.013
C)0.014
D)0.040
E)0.001

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If a deer herd has a population of 1000,a carrying capacity of 2000,and an intrinsic rate of growth of 10% (0.1),what must be true of this deer population?
A)Births = deaths
B)Births > deaths
C)Births < deaths
A)Births = deaths
B)Births > deaths
C)Births < deaths

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a deer herd has a population of 1000,a carrying capacity of 2000,and an intrinsic rate of growth of 10% (0.1),how much will the deer population grow in a year?
A)100
B)50
C)10
D)500
E)1000
A)100
B)50
C)10
D)500
E)1000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The maximum number of individuals that a habitat can support indefinitely is the habitat's:
A)Density dispersion
B)Carrying capacity
C)Growth capacity
D)Environmental load
E)Dispersion capacity
A)Density dispersion
B)Carrying capacity
C)Growth capacity
D)Environmental load
E)Dispersion capacity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the equation G = rN that is used to study populations,"r" represents:
A)The birth rate
B)The death rate
C)The number of individuals added per unit time
D)The number of individuals at the start of the time interval
E)The per capita rate of increase
A)The birth rate
B)The death rate
C)The number of individuals added per unit time
D)The number of individuals at the start of the time interval
E)The per capita rate of increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The combination of external factors that keep a population from reaching its maximum growth rate is:
A)Population aging
B)Environmental resistance
C)Environmental assuagement
D)Population clumping
E)Environmental augmentation
A)Population aging
B)Environmental resistance
C)Environmental assuagement
D)Population clumping
E)Environmental augmentation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Predation of deer by wolves is an example of a:
A)Density-independent limit
B)Density-codependent limit
C)Density-dependent limit
D)Death-dependent factor
E)Death-independent factor
A)Density-independent limit
B)Density-codependent limit
C)Density-dependent limit
D)Death-dependent factor
E)Death-independent factor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In the equation G = rN that is used to study populations "N" represents:
A)The per capita rate of increase
B)The birth rate
C)The death rate
D)The number of individuals at the start of the time interval
E)The number of individuals added per unit time
A)The per capita rate of increase
B)The birth rate
C)The death rate
D)The number of individuals at the start of the time interval
E)The number of individuals added per unit time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In a population the difference between the birth rate and the death rate is termed the:
A)Population density determining factor
B)Population dispersion factor
C)J-shaped population curve
D)S-shaped population curve
E)Per capita rate of increase
A)Population density determining factor
B)Population dispersion factor
C)J-shaped population curve
D)S-shaped population curve
E)Per capita rate of increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Two countries,_________________ and __________________,alone account for one third of the human population.
A)Russia, Brazil
B)China, Russia
C)China, India
D)India, Brazil
E)Russia, India
A)Russia, Brazil
B)China, Russia
C)China, India
D)India, Brazil
E)Russia, India

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In the equation G = rN that is used to study populations,"G" represents:
A)The number of individuals added per unit time
B)The per capita rate of increase
C)The birth rate
D)The death rate
E)The number of individuals at the start of the time interval
A)The number of individuals added per unit time
B)The per capita rate of increase
C)The birth rate
D)The death rate
E)The number of individuals at the start of the time interval

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A population with a large fraction of pre-reproductive individuals:
A)Is common in less-developed countries and will most likely increase in size
B)Is common in more-developed countries and will most likely increase in size
C)Is common in less-developed countries and will most likely decrease in size
D)Is common in more-developed countries and will most likely decrease in size
A)Is common in less-developed countries and will most likely increase in size
B)Is common in more-developed countries and will most likely increase in size
C)Is common in less-developed countries and will most likely decrease in size
D)Is common in more-developed countries and will most likely decrease in size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In a population growth curve that is affected by environmental resistance the formula G = rN(K-N)/K is used to calculate the number of new individuals added after each time interval.In this equation "K" represents the:
A)Environmental resistance
B)Per capita rate of increase
C)The number of individuals added per unit time
D)The carrying capacity for the organism being studied
E)The number of individuals at the start of a time interval
A)Environmental resistance
B)Per capita rate of increase
C)The number of individuals added per unit time
D)The carrying capacity for the organism being studied
E)The number of individuals at the start of a time interval

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In regards to a species life history,r-selected species:
A)Are long lived
B)Provide extensive care for their offspring
C)Are limited primarily by carrying capacity
D)Reproduce later in life
E)Produce many offspring
A)Are long lived
B)Provide extensive care for their offspring
C)Are limited primarily by carrying capacity
D)Reproduce later in life
E)Produce many offspring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In a survivorship curve,a type III species,like most insects and plants,is a species that:
A)Has an equal probability of dying at any age
B)Has a strong possibility of becoming extinct in a relatively short period of time
C)Has the highest probability of dying at a very young age
D)Has the highest probability of dying as it reaches its maximum life span
E)Has an extremely long life span
A)Has an equal probability of dying at any age
B)Has a strong possibility of becoming extinct in a relatively short period of time
C)Has the highest probability of dying at a very young age
D)Has the highest probability of dying as it reaches its maximum life span
E)Has an extremely long life span

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A population with a large fraction of post-reproductive individuals:
A)Is common in less-developed countries and will most likely increase in size
B)Is common in more-developed countries and will most likely increase in size
C)Is common in more-developed countries and will most likely decrease in size
D)Is common in less-developed countries and will most likely decrease in size
A)Is common in less-developed countries and will most likely increase in size
B)Is common in more-developed countries and will most likely increase in size
C)Is common in more-developed countries and will most likely decrease in size
D)Is common in less-developed countries and will most likely decrease in size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Why are the leading causes of death in high-income countries heart disease,stroke,and cancer,while in low-income countries infectious diseases are the leading causes of death?
A)Because life expectancy in high-income countries is longer
B)Because the ecological footprint in high-income countries is larger
C)Because the population density in high-income countries is larger
D)Because the population density in high-income countries is clustered
E)Because of genetic differences between populations
A)Because life expectancy in high-income countries is longer
B)Because the ecological footprint in high-income countries is larger
C)Because the population density in high-income countries is larger
D)Because the population density in high-income countries is clustered
E)Because of genetic differences between populations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What hypothesis did the scientists propose for females not preferring longer duration flashes?
A)The males would produce too large a spermatophore
B)They were similar to those from predatory fireflies
C)The males would produce too small a spermatophore
D)They may be from a different species of firefly
A)The males would produce too large a spermatophore
B)They were similar to those from predatory fireflies
C)The males would produce too small a spermatophore
D)They may be from a different species of firefly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When fireflies mate,a male places a protein-rich packet of sperm called a spermatophore into the female's reproductive tract,both fertilizing the female and providing food for the eggs.Which of the following would be a selective advantage for females?
A)Choosing a male who produces a lot of sperm
B)Choosing a larger male
C)Mating with multiple males
D)Choosing a male with a large spermatophore
E)Producing fewer eggs
A)Choosing a male who produces a lot of sperm
B)Choosing a larger male
C)Mating with multiple males
D)Choosing a male with a large spermatophore
E)Producing fewer eggs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A firefly flashing a light to attract a mate may also attract predators.The observation that animals take this risk to find a mate is consistent with which definition of natural selection?
A)Reproduction of the fittest
B)Survival of the fittest
C)Longevity of the fittest
D)Survival of the largest
E)Reproduction of the largest
A)Reproduction of the fittest
B)Survival of the fittest
C)Longevity of the fittest
D)Survival of the largest
E)Reproduction of the largest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What hypothesis did the scientists test?
A)That the frequency of a male's flashes indicated how healthy he was
B)That a male's flashes may correlate with the number of sperm he produces
C)That females reject males who present them small spermatophores
D)That females cannot determine the size of a male's spermatophore before mating
E)That a male's flashes may correlate with the size of his spermatophore
A)That the frequency of a male's flashes indicated how healthy he was
B)That a male's flashes may correlate with the number of sperm he produces
C)That females reject males who present them small spermatophores
D)That females cannot determine the size of a male's spermatophore before mating
E)That a male's flashes may correlate with the size of his spermatophore

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following best describes the link between survivorship curves and K-selected species?
A)K-selected species are limited by density-independent factors and have few offspring
B)K-selected species are limited by density-dependent factors and have many offspring
C)K-selected species are limited by density-dependent factors and have few offspring
D)K-selected species are limited by density-independent factors and have many offspring
A)K-selected species are limited by density-independent factors and have few offspring
B)K-selected species are limited by density-dependent factors and have many offspring
C)K-selected species are limited by density-dependent factors and have few offspring
D)K-selected species are limited by density-independent factors and have many offspring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Researchers studying guppies in Trinidad found that guppies in streams with high predation reproduced earlier and more frequently.Which of the following is most important in driving the guppies to change their life history in face of predation?
A)K-selection
B)r-selection
C)Density-independent factors
D)Density-dependent factors
E)Sexual selection
A)K-selection
B)r-selection
C)Density-independent factors
D)Density-dependent factors
E)Sexual selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
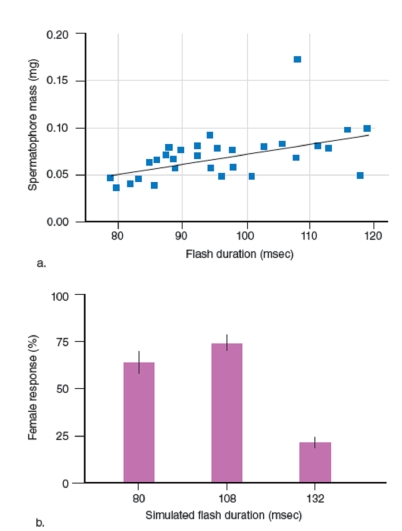
What correlation did the scientists observe in Figure 36.20a?
A)The longer the flash duration, the larger the size of the spermatophore
B)The shorter the flash duration, the larger the size of the spermatophore
C)The longer the flash duration, the smaller the size of the spermatophore
D)There was no correlation between the flash duration and the size of the spermatophore

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Conservation biologists are often trying to protect or create habitat for endangered species.How would this directly affect the equation G = rN(K-N)/K for this animal?
A)It would lower N
B)It would lower K
C)It would raise N
D)It would raise r
E)It would raise K
A)It would lower N
B)It would lower K
C)It would raise N
D)It would raise r
E)It would raise K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In 2010 India had a population of 1,170,000,000,a birth rate of 0.027,and a death rate of 0.013.Approximately how much will the Indian population grow in 2010?
A)170,000,000
B)1,700,000
C)170,000
D)17,000,000
E)17,000
A)170,000,000
B)1,700,000
C)170,000
D)17,000,000
E)17,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following best describes the link between survivorship curves and r-selected species?
A)r-selected species are limited by density-dependent factors and have few offspring
B)r-selected species are limited by density-independent factors and have few offspring
C)r-selected species are limited by density-independent factors and have many offspring
D)r-selected species are limited by density-dependent factors and have many offspring
A)r-selected species are limited by density-dependent factors and have few offspring
B)r-selected species are limited by density-independent factors and have few offspring
C)r-selected species are limited by density-independent factors and have many offspring
D)r-selected species are limited by density-dependent factors and have many offspring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
An ecologist catches 100 frogs from a pond,marks them and releases them back into the pond.After a few days,another 100 frogs are captured and 10 have the marks on them.How many frogs are in the pond?
A)1,000
B)10,000
C)100
D)900
E)90
A)1,000
B)10,000
C)100
D)900
E)90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
For a lady bug population at the end of summer the food supply decreases to where only 2000 lady bugs can be supported per acre.If there are 1000 lady bugs in a one-acre field,the rate of growth is 25%,and no immigration or emigration occur,what will the population growth be in the next generation? G = rN(K-N)/K,G=rN.
A)250
B)1250
C)125
D)0
E)1000
A)250
B)1250
C)125
D)0
E)1000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A male firefly uses flashes of light to attract mates.A female picking her mate based on these flashes leads to _________.
A)Natural selection
B)Artificial selection
C)Disruptive selection
D)Sexual selection
E)Random selection
A)Natural selection
B)Artificial selection
C)Disruptive selection
D)Sexual selection
E)Random selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A country's ecological footprint can be calculated by multiplying its population size by the footprint of each individual.Why are some ecologists concerned about the ecological footprint of a country like India?
A)Because its population is increasing
B)Because its standard of living is increasing
C)Because both its population and standard of living are increasing
D)Because its population and land area are increasing
E)Because its standard of living and land area are increasing
A)Because its population is increasing
B)Because its standard of living is increasing
C)Because both its population and standard of living are increasing
D)Because its population and land area are increasing
E)Because its standard of living and land area are increasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
How did the scientists obtain the different frequencies of flashes seen in figure 36.20b?
A)By training male fireflies to flash for a given duration
B)By electrically stimulating male fireflies to flash for a given duration
C)They made an artificial male firefly
D)By playing videotapes of fireflies flashing for a given duration
A)By training male fireflies to flash for a given duration
B)By electrically stimulating male fireflies to flash for a given duration
C)They made an artificial male firefly
D)By playing videotapes of fireflies flashing for a given duration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57

What correlation did the scientists observe in Figure 36.20b?
A)Females preferred males who flashed for 80 msec
B)Females preferred males who flashed for 132 msec
C)Females preferred males who flashed for 108 msec
D)Females did not show any preference based on flash duration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
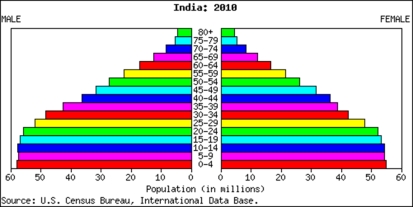
Based upon the population pyramid above you would expect the Indian population to:
A)Shrink
B)Stay constant
C)Grow and then stabilize
D)Grow exponentially

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Why have growth rates increased the most in developing countries in the past 50 years?
A)Death rates have fallen slower than birth rates
B)Death rates have gone up faster than birth rates
C)Death rates have fallen faster than birth rates
D)Death rates have gone up slower than birth rates
A)Death rates have fallen slower than birth rates
B)Death rates have gone up faster than birth rates
C)Death rates have fallen faster than birth rates
D)Death rates have gone up slower than birth rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
For a lady bug population at the beginning of summer the food supply and habitat are almost limitless.If there are 1000 lady bugs in a one acre field,the rate of growth is 25%,and no immigration or emigration occurs,what will the population growth be in the next generation? G = rN(K-N)/K,G=rN.
A)1250
B)250
C)0
D)1000
E)125
A)1250
B)250
C)0
D)1000
E)125

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Emigration is the migration out of a particular area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In the population growth equation G = rN,"N" is the number of individuals added per unit time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
On the island of Guam a single type of non-native organism,the black-footed ferret,is responsible for the disappearance of at least twelve species of birds and small reptiles from the island.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Immigration is the migration out of a particular area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The example of what happened to the reindeer population in 1964 that had been previously introduced to St.Matthew Island in the Bering Sea represents what is referred to as a population crash.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The United Nations has estimated (for the high estimate)that the world's human population may reach about 11 billion by the year 2050 and still be growing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
When exponential growth is plotted over time a J-shaped curve emerges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The world's human population now exceeds 6.5 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In the population growth equation G = rN,"r" is the per capita rate of growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Fireflies are _____.
A)Heterotrophic invertebrates
B)Heterotrophic vertebrates
C)Autotrophic invertebrates
D)Autotrophic vertebrates
A)Heterotrophic invertebrates
B)Heterotrophic vertebrates
C)Autotrophic invertebrates
D)Autotrophic vertebrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The example of what happened to the reindeer population in 1964 that had been previously introduced to St.Matthew Island in the Bering Sea represents what is referred to as a population boom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When exponential growth is plotted over time an S-shaped curve emerges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Governments of France,Canada,and China offer financial incentives to encourage citizens to have children.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The maximum number of individuals of a population that a habitat can support indefinitely is its carrying capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Conditions whose growth-limiting effects increase as a population grows are density independent factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Fireflies identifying members of the same species by the duration of their flashes would be most important in which of the following?
A)Allopatric speciation
B)Parapatric speciation
C)Autopatric speciation
D)Sympatric speciation
E)Gradualism
A)Allopatric speciation
B)Parapatric speciation
C)Autopatric speciation
D)Sympatric speciation
E)Gradualism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



