Deck 11: One Input and One Output: a Short-Run Producer Model
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/29
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: One Input and One Output: a Short-Run Producer Model
1
In the one-input model,the marginal cost curve is U-shaped.
False
If the production frontier has diminishing slope throughout,then the marginal cost curve is upward sloping throughout.
If the production frontier has diminishing slope throughout,then the marginal cost curve is upward sloping throughout.
2
In the one-input model,a convex producer choice set implies an upward sloping marginal cost curve.
True
A convex producer choice set implies diminishing marginal product throughout -- which means it is getting harder and harder to produce.Thus,marginal costs are increasing.
A convex producer choice set implies diminishing marginal product throughout -- which means it is getting harder and harder to produce.Thus,marginal costs are increasing.
3
If the single-input producer choice set is fully convex,the first order conditions of the profit maximization problem are necessary but not sufficient for identifying the profit maximizing production plan.
False
In this case,the first order conditions are both necessary and sufficient.
In this case,the first order conditions are both necessary and sufficient.
4
In the one-input model,a decrease in output price will always cause labor demand to shift in.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Price-taking producers have horizontal marginal revenue curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The law of diminishing marginal product holds so long as the input is not a Giffen good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If income effects are sufficiently strong,it may be the case that labor demand curves slope up.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the one-input model,profit is always maximized where marginal revenue product is equal to the input price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Whenever average cost is increasing,marginal cost must also be increasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Output supply curves always slope up in the one-input model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An increase in the wage will cause the output supply curve in the one-input model to shift in unless labor is an inferior input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
For price-taking producers,isoprofit curves are always parallel to one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The output level is constant along any isoprofit line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When single-input producer choice sets are non-convex,the first order condition of the profit maximization problem is neither necessary nor sufficient for identifying the profit maximizing production plan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the one-input model,the marginal product of labor curve falls below the horizontal axis only if the production frontier slopes down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If the single-input producer choice set is convex,the marginal product of labor curve must have a negative slope that is getting steeper with increases in labor input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A competitive (price-taking)firm will produce so long as its economic profit is sufficiently above zero to enable the firm to pay the owners of the firm for their time and effort.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the one-input model of production,increasing marginal product implies non-convexity of the producer choice set.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the one-input model,the cost curve is the inverse of the production frontier if and only if the input price is 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Labor demand curves always slope down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Suppose a single-input production function has initially increasing but eventually decreasing marginal product.In this case,the first order condition for the profit maximization problem
a.
is necessary for identifying the profit maximizing production plan.
b.
is sufficient for identifying the profit maximizing production plan.
c.
is both necessary and sufficient for identifying the profit maximizing production plan.
d.
is neither necessary nor sufficient for identifying the profit maximizing production plan.
a.
is necessary for identifying the profit maximizing production plan.
b.
is sufficient for identifying the profit maximizing production plan.
c.
is both necessary and sufficient for identifying the profit maximizing production plan.
d.
is neither necessary nor sufficient for identifying the profit maximizing production plan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Every cost-minimizing producer is profit-maximizing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Since the marginal product of labor can increase initially as I hire more workers,demand for labor is also upward sloping for the initial workers I hire.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Calvin buys newspapers and delivers them (by bike)to his customers' houses while Hobbes sells lemonade at his lemonade stand.One day they compare notes and find that Calvin,after paying for the newspapers and the maintenance on his bike,clears $5 per hour while Hobbes,after paying for the lemonade ingredients and upkeep of his lemonade stand,clears $4.50 per hour.The newspaper and lemonade businesses are the only possible trades for Calvin and Hobbes.
a.If Calvin and Hobbes are identical,how much economic profit (per hour)is each making?
b.Suppose Hobbes is slower on his bike than Calvin -- and he could only deliver half as many newspapers per hour.What's his economic profit in the lemonade business?
a.If Calvin and Hobbes are identical,how much economic profit (per hour)is each making?
b.Suppose Hobbes is slower on his bike than Calvin -- and he could only deliver half as many newspapers per hour.What's his economic profit in the lemonade business?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Suppose a single-input production function has initially increasing but eventually decreasing marginal product -- and suppose we know that an interior solution is profit maximizing.In this case,the first order condition for the profit maximization problem
a.
is necessary for identifying the profit maximizing production plan.
b.
is sufficient for identifying the profit maximizing production plan.
c.
is both necessary and sufficient for identifying the profit maximizing production plan.
d.
is neither necessary nor sufficient for identifying the profit maximizing production plan.
a.
is necessary for identifying the profit maximizing production plan.
b.
is sufficient for identifying the profit maximizing production plan.
c.
is both necessary and sufficient for identifying the profit maximizing production plan.
d.
is neither necessary nor sufficient for identifying the profit maximizing production plan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose you solve the profit maximization problem for a single-input,price-taking producer whose technology is given by 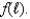 The labor demand function is
The labor demand function is 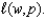
a.Suppose
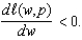 Might
Might
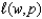 in fact be the correct labor demand function? Explain.
in fact be the correct labor demand function? Explain.
b.Suppose
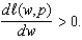 Might
Might
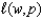 in fact be the correct labor demand function? Explain.
in fact be the correct labor demand function? Explain.
c.Intuitively explain how (b)might arise from the profit maximization problem.
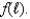 The labor demand function is
The labor demand function is 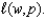
a.Suppose
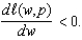 Might
Might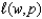 in fact be the correct labor demand function? Explain.
in fact be the correct labor demand function? Explain. b.Suppose
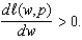 Might
Might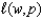 in fact be the correct labor demand function? Explain.
in fact be the correct labor demand function? Explain. c.Intuitively explain how (b)might arise from the profit maximization problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Suppose a technology is described by the production function 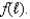
a.For a price taking producer who faces output price p and wage w,derive the first order condition and interpret it.
b.Without knowing more about the function f,is the condition you derived in (a)either necessary or sufficient for deriving the profit maximizing production plan? Explain.
c.Suppose
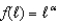 .Derive the first order condition you illustrated in (a)and solve for
.Derive the first order condition you illustrated in (a)and solve for
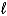 .
.
d.For what values of
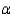 is this first order condition necessary and sufficient for deriving a profit maximizing production plan? Explain.
is this first order condition necessary and sufficient for deriving a profit maximizing production plan? Explain.
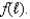
a.For a price taking producer who faces output price p and wage w,derive the first order condition and interpret it.
b.Without knowing more about the function f,is the condition you derived in (a)either necessary or sufficient for deriving the profit maximizing production plan? Explain.
c.Suppose
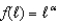 .Derive the first order condition you illustrated in (a)and solve for
.Derive the first order condition you illustrated in (a)and solve for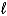 .
. d.For what values of
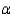 is this first order condition necessary and sufficient for deriving a profit maximizing production plan? Explain.
is this first order condition necessary and sufficient for deriving a profit maximizing production plan? Explain.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Labor demand curves are homogeneous of degree zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Every profit-maximizing producer is cost minimizing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



