Deck 14: Competitive Market Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/18
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Competitive Market Equilibrium
1
The reason long run market supply curves are shallower than short run market supply curves is because individual firm supply curves are shallower in the long run than in the short run.
False
The reason long run market supply curves are shallower than short run market supply curves is because of entry and exit of firms.
The reason long run market supply curves are shallower than short run market supply curves is because of entry and exit of firms.
2
If a firm makes negative short run profits,it will exit the industry in the long run.
False
It may be that the firm simply has way too little capital -- and,when given a chance to hire more capital,it can lower its costs such that short run and long run profits will be non-negative.
It may be that the firm simply has way too little capital -- and,when given a chance to hire more capital,it can lower its costs such that short run and long run profits will be non-negative.
3
A decrease in the rental rate of capital can lead to a long run increase or decrease in the number of firms in the industry.
True
We know this will lead to a drop in output price -- which will cause the quantity demanded in the industry to increase.If all firms continue to produce the same quantity (or less),new firms must therefore have entered.But the lowest point of the AC curve could shift either to the left or the right -- and if it shifts to the right,firms end up producing more at the lower price.If they produce sufficiently more,then it could be the case that fewer firms provide more output in the long run equilibrium.
We know this will lead to a drop in output price -- which will cause the quantity demanded in the industry to increase.If all firms continue to produce the same quantity (or less),new firms must therefore have entered.But the lowest point of the AC curve could shift either to the left or the right -- and if it shifts to the right,firms end up producing more at the lower price.If they produce sufficiently more,then it could be the case that fewer firms provide more output in the long run equilibrium.
4
If all firms are identical,output prices will never change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suppose gasoline stations operate with identical costs in a perfectly competitive industry.In each of the following cases,explain what happens to an individual gasoline station and what happens to the overall quantity of gasoline sold in the short and long run.Assume that labor is the only variable input in the short run.
a.Last year's tax returns from gasoline station owners show unusually high income for these owners because of the upward trend in prices this past year.So Congress passes a one-time "profits tax" based on these unusually high incomes last year.
b.Continue with part (a).After the imposition of the "profits tax" from part (a),Congress has to decide what to do with the revenues.The Texas Congressional delegation persuades the government that running a gasoline station is patriotic but difficult work - and that the Congress should put all the revenues from the "profits tax" into a trust fund which will be used to finance annual Christmas gifts in the form of a $10,000 check for all gasoline station owners from now on.
c.Moved by a Hollywood movie on global warming,a teary-eyed senator persuades Congress to impose a $2 per gallon tax on all gasoline sold at the pump.
d.After the industry settles into its new long run equilibrium (following the tax increase from (c)),the Congress decides to help out the gas station owners once more by subsidizing their equipment purchases through a tax credit - thereby lowering the rental rate they have to pay on their equipment.(Assume equipment is fixed in the short run,variable in the long run.)
e.True or False: Since the short run marginal cost curve measures only costs associated with variable inputs (like labor)and not with fixed inputs (like capital),the short run marginal cost curve in the new long run equilibrium (following the policy in part (d))is the same as the short run marginal cost curve in the old equilibrium (before the policy in part (d)).Explain.
a.Last year's tax returns from gasoline station owners show unusually high income for these owners because of the upward trend in prices this past year.So Congress passes a one-time "profits tax" based on these unusually high incomes last year.
b.Continue with part (a).After the imposition of the "profits tax" from part (a),Congress has to decide what to do with the revenues.The Texas Congressional delegation persuades the government that running a gasoline station is patriotic but difficult work - and that the Congress should put all the revenues from the "profits tax" into a trust fund which will be used to finance annual Christmas gifts in the form of a $10,000 check for all gasoline station owners from now on.
c.Moved by a Hollywood movie on global warming,a teary-eyed senator persuades Congress to impose a $2 per gallon tax on all gasoline sold at the pump.
d.After the industry settles into its new long run equilibrium (following the tax increase from (c)),the Congress decides to help out the gas station owners once more by subsidizing their equipment purchases through a tax credit - thereby lowering the rental rate they have to pay on their equipment.(Assume equipment is fixed in the short run,variable in the long run.)
e.True or False: Since the short run marginal cost curve measures only costs associated with variable inputs (like labor)and not with fixed inputs (like capital),the short run marginal cost curve in the new long run equilibrium (following the policy in part (d))is the same as the short run marginal cost curve in the old equilibrium (before the policy in part (d)).Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Whenever a firm is making positive economic profit,there is nothing it can do to make more profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Short run market supply curves are formed by adding up individual firm supply curves in the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If all firms are identical,output demand shifts cannot cause changes in output price in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Suppose there are no recurring fixed costs and the daily production process for all identical firms in a perfectly competitive industry has decreasing returns to scale throughout.Then each firm will only produce a single good each day when the industry is in long run equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The long run market supply curve is formed by adding up individual firm supply curves in the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose you are Joe -- one of many souvenir shop owners in a town centered around tourism.All souvenir shop owners face the same decreasing returns to scale production technology as well as recurring annual fixed costs,and they all sell a single local novelty x that is identical across all shops.Assume at the outset of each part below that the souvenir shop market in this town is in long run equilibrium and treat each part separately - i.e.do not carry what you concluded in one part into the next - except for part (e)where you are explicitly asked to continue with the set-up in part (d).
a.The Disney Corporation has set up a new theme park in a town 20 miles away and,as a result,a fraction of tourists that used to stay in your town are now staying elsewhere on their vacation.What happens to your price and output in the market and in Joe's business in the short and long run (assuming that you remain open for business)? Can you tell whether the number of souvenir shops in your town increases or decreases?
b.A new mayor in your town lowers recurring annual business license fees.What happens to the price and output in the market and Joe's business in the short and long run? Will the number of souvenir shops in the town increase or decrease?
c.A local reporter discovers that the famous "Joe the Plummer" is a distant cousin of yours - and you convince your cousin Joe to join you in your business.The newly renamed souvenir shop,"Joe and Joe",is featured on national television after a visit by "Joe the Vice-President",and you decide to stamp "Greetings from Joe,Joe & Joe" on all of your merchandise.As a result,tourists are willing to pay $y more for your x than they would be willing to pay at any non-Joe store where x does not contain the coveted "Greetings from Joe,Joe & Joe" stamp.How does your output change in the short and long run (assuming capital is fixed in the short run but not in the long run and assuming it costs nothing to put the stamp on your products)?
d.Suppose this town is located on the beach in North Carolina where there is a "high season" during the 6 warm months of the year and a "low season" during the 6 cool months of the year.Demand is high during the high season and low during the low season.On two recent visits to this town - one in the summer and one in the winter -- I noticed that prices for x where considerably higher during the high season.Explain how two different prices in different seasons could exist in an industry that is in long run equilibrium.Use side-by-side graphs of the market and Joe's business in your explanation,illustrating both the high demand DH and the low demand DL in the market.How do these different prices relate to the lowest point of the long run AC curve at Joe's business?
e.Suppose that I noticed one other thing on my recent two visits to this town: only half the souvenir shops are open in the winter while all are open in the summer.Is this compatible with our assumption that souvenir shops face decreasing returns to scale throughout (and no short run fixed costs)? (Hint: Think about what must be true for half the shops to close for 6 months - and what this implies for short run cost curves and shut down prices.)
a.The Disney Corporation has set up a new theme park in a town 20 miles away and,as a result,a fraction of tourists that used to stay in your town are now staying elsewhere on their vacation.What happens to your price and output in the market and in Joe's business in the short and long run (assuming that you remain open for business)? Can you tell whether the number of souvenir shops in your town increases or decreases?
b.A new mayor in your town lowers recurring annual business license fees.What happens to the price and output in the market and Joe's business in the short and long run? Will the number of souvenir shops in the town increase or decrease?
c.A local reporter discovers that the famous "Joe the Plummer" is a distant cousin of yours - and you convince your cousin Joe to join you in your business.The newly renamed souvenir shop,"Joe and Joe",is featured on national television after a visit by "Joe the Vice-President",and you decide to stamp "Greetings from Joe,Joe & Joe" on all of your merchandise.As a result,tourists are willing to pay $y more for your x than they would be willing to pay at any non-Joe store where x does not contain the coveted "Greetings from Joe,Joe & Joe" stamp.How does your output change in the short and long run (assuming capital is fixed in the short run but not in the long run and assuming it costs nothing to put the stamp on your products)?
d.Suppose this town is located on the beach in North Carolina where there is a "high season" during the 6 warm months of the year and a "low season" during the 6 cool months of the year.Demand is high during the high season and low during the low season.On two recent visits to this town - one in the summer and one in the winter -- I noticed that prices for x where considerably higher during the high season.Explain how two different prices in different seasons could exist in an industry that is in long run equilibrium.Use side-by-side graphs of the market and Joe's business in your explanation,illustrating both the high demand DH and the low demand DL in the market.How do these different prices relate to the lowest point of the long run AC curve at Joe's business?
e.Suppose that I noticed one other thing on my recent two visits to this town: only half the souvenir shops are open in the winter while all are open in the summer.Is this compatible with our assumption that souvenir shops face decreasing returns to scale throughout (and no short run fixed costs)? (Hint: Think about what must be true for half the shops to close for 6 months - and what this implies for short run cost curves and shut down prices.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If firms differ in terms of their technologies,a drop in demand will cause a long run decrease in output price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An increase in labor demand accompanied by a decline in labor supply cannot result in a decline in wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose Congress passes a one-time tax refund of all taxes paid by firms in an industry last year.This will lead to a drop in output price in the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Suppose all firms in a perfectly competitive industry have production processes characterized by the production function 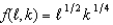 .Suppose the cost of labor is 20 and the cost of capital is 10.
.Suppose the cost of labor is 20 and the cost of capital is 10.
a.Suppose that the industry is in long run equilibrium and that firms are using 1 unit of capital.What is the short run cost function of each firm?
b.Suppose there are 5,000 firms in long run equilibrium.What is the short run market supply function?
c.Suppose market demand is
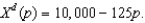 What is the equilibrium price?
What is the equilibrium price?
d.Firms in this industry face a recurring fixed cost FC.What must FC be in order for this industry to indeed be in long run equilibrium with its 100 firms?
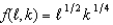 .Suppose the cost of labor is 20 and the cost of capital is 10.
.Suppose the cost of labor is 20 and the cost of capital is 10. a.Suppose that the industry is in long run equilibrium and that firms are using 1 unit of capital.What is the short run cost function of each firm?
b.Suppose there are 5,000 firms in long run equilibrium.What is the short run market supply function?
c.Suppose market demand is
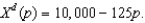 What is the equilibrium price?
What is the equilibrium price? d.Firms in this industry face a recurring fixed cost FC.What must FC be in order for this industry to indeed be in long run equilibrium with its 100 firms?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An increase in license fees -- a long run recurring fixed cost -- will lead to a drop in the number of firms competing in a competitive industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose a firm is making zero long run profit.Then it's short run profit cannot be negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A drop in output demand accompanied by a simultaneous drop in output supply will cause the output price to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



