Deck 12: Acids and Bases
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Acids and Bases
1
Identify the major ions present in an aqueous LiOH solution.
A)Li2+, O−, H−
B)Li+, OH−
C)LiO−, H+
D)Li+, O2−, H+
E)Li−, OH+
A)Li2+, O−, H−
B)Li+, OH−
C)LiO−, H+
D)Li+, O2−, H+
E)Li−, OH+
Li+, OH−
2
What is the name of a proton donor in an acid-base reaction?
A)Arrhenius acid
B)Arrhenius base
C)Brønsted acid
D)Brønsted base
E)Lewis base
A)Arrhenius acid
B)Arrhenius base
C)Brønsted acid
D)Brønsted base
E)Lewis base
Brønsted acid
3
The substance (CH3CH2)2NH is considered to be
A)a weak acid.
B)a weak base.
C)a strong acid.
D)a strong base.
E)neither acidic nor basic.
A)a weak acid.
B)a weak base.
C)a strong acid.
D)a strong base.
E)neither acidic nor basic.
a weak base.
4
Which is the strongest acid?
A)HBrO4
B)HBr
C)HBrO2
D)HBrO
E)HBrO3
A)HBrO4
B)HBr
C)HBrO2
D)HBrO
E)HBrO3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which is a strong base?
A)LiOH
B)CH3COOH
C)NH3
D)H3PO4
E)HClO2
A)LiOH
B)CH3COOH
C)NH3
D)H3PO4
E)HClO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which is a strong acid?
A)Ba(OH)2
B)H3PO4
C)HC2H3O2
D)NaCl
E)HClO4
A)Ba(OH)2
B)H3PO4
C)HC2H3O2
D)NaCl
E)HClO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The substance HClO4 is considered to be
A)a weak acid.
B)a weak base.
C)a strong acid.
D)a strong base.
E)neither acidic nor basic.
A)a weak acid.
B)a weak base.
C)a strong acid.
D)a strong base.
E)neither acidic nor basic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which is present in all aqueous Brønsted acid solutions?
A)H2
B)H+
C)OH-
D)H2SO4
E)Cl-
A)H2
B)H+
C)OH-
D)H2SO4
E)Cl-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which is a weak base?
A)NH3
B)Ca(OH)2
C)Ba(OH)2
D)NaOH
E)CH3COOH
A)NH3
B)Ca(OH)2
C)Ba(OH)2
D)NaOH
E)CH3COOH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which one of the following is a strong acid?
A)H2CO3
B)H2SO3
C)H2SO4
D)H3PO4
E)CH3COOH
A)H2CO3
B)H2SO3
C)H2SO4
D)H3PO4
E)CH3COOH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is a strong base?
A)NH3
B)Ca(OH)2
C)Al(OH)3
D)B(OH)3
E)CH3OH
A)NH3
B)Ca(OH)2
C)Al(OH)3
D)B(OH)3
E)CH3OH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which is the strongest acid?
A)SO42−
B)H2SO3
C)H2SO4
D)HSO4−
E)HSO3−
A)SO42−
B)H2SO3
C)H2SO4
D)HSO4−
E)HSO3−

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is a weak acid?
A)H2SO4
B)HNO3
C)HF
D)HBr
E)HCl
A)H2SO4
B)HNO3
C)HF
D)HBr
E)HCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Identify the major ions present in an aqueous HNO3 solution.
A)HN2+, O2−
B)OH−, NO3−
C)OH−, NO+
D)H+, N3−, O2−
E)H+, NO3−
A)HN2+, O2−
B)OH−, NO3−
C)OH−, NO+
D)H+, N3−, O2−
E)H+, NO3−

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The substance NH3 is considered to be
A)a weak acid.
B)a weak base.
C)a strong acid.
D)a strong base.
E)neither acidic nor basic.
A)a weak acid.
B)a weak base.
C)a strong acid.
D)a strong base.
E)neither acidic nor basic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is a strong acid?
A)H3PO4
B)HNO3
C)HF
D)CH3COOH
E)H2O
A)H3PO4
B)HNO3
C)HF
D)CH3COOH
E)H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which is the strongest acid?
A)HBrO3
B)HClO
C)HBrO2
D)HBrO
E)HClO3
A)HBrO3
B)HClO
C)HBrO2
D)HBrO
E)HClO3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which one of the following is a strong acid?
A)CH3COOH
B)H2SO3
C)NH3
D)H3PO4
E)HClO3
A)CH3COOH
B)H2SO3
C)NH3
D)H3PO4
E)HClO3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Complete the following reaction and identify the Brønsted acid.NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) →
A)NaH(aq) + HOCl(aq); NaOH is the acid.
B)NaH(aq) + HOCl(aq); HCl is the acid.
C)NaCl(aq) + H2O(l); NaOH is the acid.
D)NaCl(aq) + H2O(l); HCl is the acid.
E)NaCl(aq) + H2O(l); NaCl is the acid.
A)NaH(aq) + HOCl(aq); NaOH is the acid.
B)NaH(aq) + HOCl(aq); HCl is the acid.
C)NaCl(aq) + H2O(l); NaOH is the acid.
D)NaCl(aq) + H2O(l); HCl is the acid.
E)NaCl(aq) + H2O(l); NaCl is the acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the name of a proton acceptor in an acid-base reaction?
A)Arrhenius acid
B)Arrhenius base
C)Brønsted acid
D)Brønsted base
E)Lewis base
A)Arrhenius acid
B)Arrhenius base
C)Brønsted acid
D)Brønsted base
E)Lewis base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which is the net ionic equation for the reaction between aqueous solutions of lithium hydroxide and hydrobromic acid? LiOH(aq) + HBr(aq) → H2O(l) + LiBr(aq)
A)LiOH(aq) → Li+(aq) + OH−(aq)
B)HBr(aq) → H+(aq) + Br−(aq)
C)H+(aq) + OH−(aq) → H2O(l)
D)Li+(aq) + Br−(aq) → LiBr(aq)
E)Li+(aq) + OH−(aq)+ H+(aq) + Br−(aq) → H2O(l) + LiBr(aq)
A)LiOH(aq) → Li+(aq) + OH−(aq)
B)HBr(aq) → H+(aq) + Br−(aq)
C)H+(aq) + OH−(aq) → H2O(l)
D)Li+(aq) + Br−(aq) → LiBr(aq)
E)Li+(aq) + OH−(aq)+ H+(aq) + Br−(aq) → H2O(l) + LiBr(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which solution is the most acidic?
A)3 × 10−4 M H+
B)5 × 10−5 M H+
C)6 × 10−3 M H+
D)1 × 10−6 M H+
E)5 × 10−2 M H+
A)3 × 10−4 M H+
B)5 × 10−5 M H+
C)6 × 10−3 M H+
D)1 × 10−6 M H+
E)5 × 10−2 M H+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the conjugate base of sulfuric acid?
A)HSO4−
B)H3O+
C)OH−
D)SO42−
E)H3SO4+
A)HSO4−
B)H3O+
C)OH−
D)SO42−
E)H3SO4+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which solution is the most acidic?
A)pH = 1.00
B)pH = 10.00
C)pH = 5.00
D)pH = 3.00
E)pH = 4.00
A)pH = 1.00
B)pH = 10.00
C)pH = 5.00
D)pH = 3.00
E)pH = 4.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is [OH−] for a solution at 25°C that has [H3O+] = 2.35 × 10−3 M?
A)4.26 × 10−5 M
B)2.35 ×10−11 M
C)4.26 × 10−12 M
D)2.35 × 10−17 M
E)2.35 ×10−3 M
A)4.26 × 10−5 M
B)2.35 ×10−11 M
C)4.26 × 10−12 M
D)2.35 × 10−17 M
E)2.35 ×10−3 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the concentration of H+ in a 0.025 M HCl solution?
A)0
B)0.013 M
C)0.025 M
D)0.050 M
E)0.010 M
A)0
B)0.013 M
C)0.025 M
D)0.050 M
E)0.010 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is the conjugate base of NH3?
A)NH2
B)NH2+
C)NH2−
D)NH4
E)NH4+
A)NH2
B)NH2+
C)NH2−
D)NH4
E)NH4+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the concentration of OH− in a 0.083 M NaOH solution?
A)0.083 M
B)1.21 × 10−13 M
C)8.30 × 10−16 M
D)7 M
E)8.30 × 1012 M
A)0.083 M
B)1.21 × 10−13 M
C)8.30 × 10−16 M
D)7 M
E)8.30 × 1012 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which solution is the most acidic?
A)1 × 10−4 M H+
B)1 × 10−9 M H+
C)1 × 10−3 M H+
D)1 × 10−7 M H+
E)1 × 10−10 M H+
A)1 × 10−4 M H+
B)1 × 10−9 M H+
C)1 × 10−3 M H+
D)1 × 10−7 M H+
E)1 × 10−10 M H+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the name given to a substance that can act as a Brønsted acid or as a Brønsted base according to what it is reacting with?
A)hydrophilic
B)hydrophobic
C)amphoteric
D)isoprotic
E)isoelectronic
A)hydrophilic
B)hydrophobic
C)amphoteric
D)isoprotic
E)isoelectronic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A solution with a pH of 8.15 is
A)slightly acidic.
B)very basic.
C)neutral.
D)very acidic.
E)slightly basic.
A)slightly acidic.
B)very basic.
C)neutral.
D)very acidic.
E)slightly basic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Complete the following reaction and identify the Brønsted base: NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) →
A)Na(aq) + HOCl(aq); NaOH is the base.
B)NaCl(aq) + OH−(aq); HCl is the base.
C)NaCl(aq) + OH−(aq); NaOH is the base.
D)H2O(l) + NaCl(aq); HCl is the base.
E)NaCl(aq)+ H2O(l); NaOH is the base.
A)Na(aq) + HOCl(aq); NaOH is the base.
B)NaCl(aq) + OH−(aq); HCl is the base.
C)NaCl(aq) + OH−(aq); NaOH is the base.
D)H2O(l) + NaCl(aq); HCl is the base.
E)NaCl(aq)+ H2O(l); NaOH is the base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the conjugate base of water?
A)H3O+
B)OH−
C)H3O
D)OH
E)H2O2
A)H3O+
B)OH−
C)H3O
D)OH
E)H2O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the pH of a 0.056 M HNO3 solution?
A)0.056
B)1.25
C)12.75
D)2.88
E)11.11
A)0.056
B)1.25
C)12.75
D)2.88
E)11.11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which one of these responses is with regard to a 0.1 M solution of a weak acid HA?
A)[H+] > 0.1 M.
B)pH = 1.0
C)[H+] < [A-]
D)pH > 1.0
E)[OH-] > [H+]
A)[H+] > 0.1 M.
B)pH = 1.0
C)[H+] < [A-]
D)pH > 1.0
E)[OH-] > [H+]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is [OH−] for a solution at 25°C that has [H3O+] = 8.23 × 10−2 M?
A)8.23 × 10−2 M
B)1.22 × 10−6 M
C)8.23 × 10−12 M
D)1.22 × 10−13 M
E)8.23 × 10−16 M
A)8.23 × 10−2 M
B)1.22 × 10−6 M
C)8.23 × 10−12 M
D)1.22 × 10−13 M
E)8.23 × 10−16 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the H+ ion concentration in a 2.1 × 10−4 M Ca(OH)2 solution?
A)7.3 × 10−4 M
B)4.2 × 10−4 M
C)2.1 × 10−4 M
D)2.4 × 10−11 M
E)4.8 × 10−11 M
A)7.3 × 10−4 M
B)4.2 × 10−4 M
C)2.1 × 10−4 M
D)2.4 × 10−11 M
E)4.8 × 10−11 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the conjugate acid of the acetate ion?
A)CH3O2−
B)COOH
C)HC2H3O2
D)H2O
E)CH4
A)CH3O2−
B)COOH
C)HC2H3O2
D)H2O
E)CH4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which solution is basic?
A)pH = 1.00
B)pH = 10.00
C)pH = 5.00
D)pH = 3.00
E)pH = 4.00
A)pH = 1.00
B)pH = 10.00
C)pH = 5.00
D)pH = 3.00
E)pH = 4.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the concentration of OH− in a 1.0 × 10−3 M Ba(OH)2 solution?
A)0.50 × 10−3 M
B)1.0 × 10−3 M
C)2.0 × 10−3 M
D)1.0 × 10−2 M
E)3.3 × 10−4 M
A)0.50 × 10−3 M
B)1.0 × 10−3 M
C)2.0 × 10−3 M
D)1.0 × 10−2 M
E)3.3 × 10−4 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is the conjugate acid of CO32− in the reaction below? CO32− + HSO4−  HCO3− + SO42−
HCO3− + SO42−
A)HCO3−
B)HSO4−
C)OH−
D)H3O+
E)SO42−
 HCO3− + SO42−
HCO3− + SO42−A)HCO3−
B)HSO4−
C)OH−
D)H3O+
E)SO42−

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the pH of a solution in which [H+] is 1.22 × 10−4 M?
A)−3.914
B)1.220
C)3.914
D)4.000
E)4.086
A)−3.914
B)1.220
C)3.914
D)4.000
E)4.086

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The pH of a Ba(OH)2 solution is 10.00.What is the H+ ion concentration of this solution?
A)4.0 × 10−11 M
B)1.6 × 10−10 M
C)1.3 × 10−5 M
D)1.0 × 10−10 M
E)10.00 M
A)4.0 × 10−11 M
B)1.6 × 10−10 M
C)1.3 × 10−5 M
D)1.0 × 10−10 M
E)10.00 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Automobile batteries use 3.0 M H2SO4 as an electrolyte.How much 1.20 M NaOH will be needed to neutralize 225 mL of battery acid? H2SO4(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) → 2H2O(l) + Na2SO4(aq)
A)0.045 L
B)0.28 L
C)0.56 L
D)0.90 L
E)1.1 L
A)0.045 L
B)0.28 L
C)0.56 L
D)0.90 L
E)1.1 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What volume of a 0.442 M NaOH solution is needed to neutralize 65.0 mL of a 0.296 M solution of HNO3?
A)8.71 mL
B)21.8 mL
C)43.5 mL
D)87.1 mL
E)174 mL
A)8.71 mL
B)21.8 mL
C)43.5 mL
D)87.1 mL
E)174 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What volume of a 0.452 M NaOH solution is needed to neutralize 85.0 mL of a 0.176 M solution of H2SO4?
A)218.3 mL
B)66.2 mL
C)38.4 mL
D)436.6 mL
E)33.1 mL
A)218.3 mL
B)66.2 mL
C)38.4 mL
D)436.6 mL
E)33.1 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the reaction, HSO4
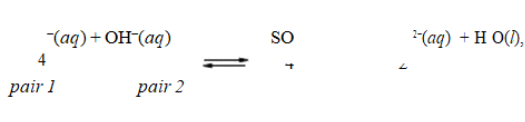 , the conjugate acid-base pairs are
, the conjugate acid-base pairs are
A)HSO − and SO 2−; H O and OH−.4 4
2
B)HSO4− and H3O+; SO42 − and OH−.
C)HSO4− and OH−; SO42 − and H2O.
D)HSO4− and H2O; OH − and SO42−.
E)HSO4− and OH−; SO42 − and H3O+.
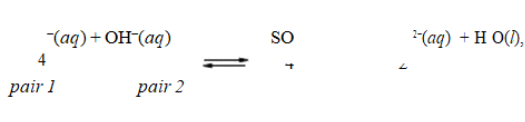 , the conjugate acid-base pairs are
, the conjugate acid-base pairs areA)HSO − and SO 2−; H O and OH−.4 4
2

B)HSO4− and H3O+; SO42 − and OH−.
C)HSO4− and OH−; SO42 − and H2O.
D)HSO4− and H2O; OH − and SO42−.
E)HSO4− and OH−; SO42 − and H3O+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the pH of a 0.050 M LiOH solution?
A)1.30
B)3.00
C)11.00
D)12.39
E)12.70
A)1.30
B)3.00
C)11.00
D)12.39
E)12.70

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is the conjugate base of HSO4− in the reaction below? CO32− + HSO4−  HCO3− + SO42−
HCO3− + SO42−
A)HSO4−
B)CO32−
C)OH−
D)H O+
3
E)SO42−
 HCO3− + SO42−
HCO3− + SO42−A)HSO4−
B)CO32−
C)OH−
D)H O+
3
E)SO42−

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the [H3O+] for a solution at 25°C that has pOH = 5.640?
A)2.34 × 10−4 M
B)2.29 × 10−6 M
C)4.37 × 10−9 M
D)4.27 × 10−11 M
E)8.360 M
A)2.34 × 10−4 M
B)2.29 × 10−6 M
C)4.37 × 10−9 M
D)4.27 × 10−11 M
E)8.360 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Identify the conjugate base of HPO42− in the reaction HCO3− + HPO42−  H2CO3 + PO43−
H2CO3 + PO43−
A)H2O
B)HCO3−
C)H2CO3
D)PO43−
E)None of these
 H2CO3 + PO43−
H2CO3 + PO43−A)H2O
B)HCO3−
C)H2CO3
D)PO43−
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
During a titration, it is found that 53.5 mL of a solution of NaOH is needed to neutralize a solution that contains 1.86 g of HCl.What is the concentration of the NaOH solution?
A)0.051 M
B)0.686 M
C)1.05 M
D)0.035 M
E)0.953 M
A)0.051 M
B)0.686 M
C)1.05 M
D)0.035 M
E)0.953 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is the pH of a 0.056 M HNO3 solution?
A)0.056
B)1.25
C)12.75
D)2.88
E)11.11
A)0.056
B)1.25
C)12.75
D)2.88
E)11.11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the [H+] in a solution with a pH of 5.63?
A)2.344 × 10−6 M H+
B)2.344 × 10−5 M H+
C)5.63 M H+
D)2.3 × 10−6 M H+
E)2.3 × 10−5 M H+
A)2.344 × 10−6 M H+
B)2.344 × 10−5 M H+
C)5.63 M H+
D)2.3 × 10−6 M H+
E)2.3 × 10−5 M H+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A standard solution of 0.243 M NaOH was used to determine the concentration of a hydrochloric acid solution.If 46.33 mL of NaOH is needed to neutralize 10.00 mL of the acid, what is the molar concentration of the acid in the original solution?
A)0.243 M
B)0.200 M
C)1.13 M
D)0.563 M
E)0.0313 M
A)0.243 M
B)0.200 M
C)1.13 M
D)0.563 M
E)0.0313 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A 34.62-mL of 0.1510 M NaOH was needed to neutralize 50.0 mL of an H2SO4 solution.What is the concentration of the original sulfuric acid solution?
A)0.0229 M
B)0.218 M
C)0.0523 M
D)0.209 M
E)0.105 M
A)0.0229 M
B)0.218 M
C)0.0523 M
D)0.209 M
E)0.105 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Vinegar is a solution of acetic acid, HC2H3O2 , dissolved in water.A 5.54-g sample of vinegar was neutralized by 30.10 mL of 0.100 M NaOH.What is the percent by weight of acetic acid in the vinegar?
A)0.0543%
B)1.08%
C)3.26%
D)5.43%
E)9.23%
A)0.0543%
B)1.08%
C)3.26%
D)5.43%
E)9.23%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What is the pOH of a 0.0085 M KOH solution?
A)2.07
B)4.85
C)9.15
D)11.93
E)0.0085
A)2.07
B)4.85
C)9.15
D)11.93
E)0.0085

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is the pH of a 0.014 M Ca(OH)2 solution?
A)1.85
B)1.55
C)12.15
D)12.45
E)15.85
A)1.85
B)1.55
C)12.15
D)12.45
E)15.85

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the pOH of a 0.025 M HI solution?
A)0.025
B)0.94
C)1.60
D)12.40
E)10.31
A)0.025
B)0.94
C)1.60
D)12.40
E)10.31

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which one of these salts will form an acidic solution upon dissolving in water?
A)LiBr
B)NaF
C)NH4Br
D)KOH
E)NaCN
A)LiBr
B)NaF
C)NH4Br
D)KOH
E)NaCN

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which one of these salts will form a basic solution upon dissolving in water?
A)NaCl
B)NaNO2
C)NH4NO3
D)KBr
E)AlCl3
A)NaCl
B)NaNO2
C)NH4NO3
D)KBr
E)AlCl3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which pair of substances could form a buffered aqueous solution?
A)HCl, NaCl
B)HNO3, NaNO3
C)H3PO4, NaH2PO4
D)H2SO4, CH3COOH
E)NH3, NaOH
A)HCl, NaCl
B)HNO3, NaNO3
C)H3PO4, NaH2PO4
D)H2SO4, CH3COOH
E)NH3, NaOH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which pair of substances is capable of forming a buffer in aqueous solution?
A)H3PO4, Na3PO3
B)HNO3, NaNO3
C)HCl, NaCl
D)H2CO3, NaNO2
E)CH3COOH, CH3COONa
A)H3PO4, Na3PO3
B)HNO3, NaNO3
C)HCl, NaCl
D)H2CO3, NaNO2
E)CH3COOH, CH3COONa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which pair of substances cannot form a buffered aqueous solution?
A)HCN and KCN
B)NH3 and (NH4)2SO4
C)HNO3 and NaNO3
D)HF and NaF
E)HNO2 and NaNO2
A)HCN and KCN
B)NH3 and (NH4)2SO4
C)HNO3 and NaNO3
D)HF and NaF
E)HNO2 and NaNO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



