Deck 9: Sexual Reproduction
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Sexual Reproduction
1
The formation of sperm is termed
A)oogenesis.
B)homologous formation.
C)spermatogenesis.
D)synapsis.
E)mitosis.
A)oogenesis.
B)homologous formation.
C)spermatogenesis.
D)synapsis.
E)mitosis.
C
Explanation: Spermatogenesis is the process of forming sperm.
Explanation: Spermatogenesis is the process of forming sperm.
2
Figure: 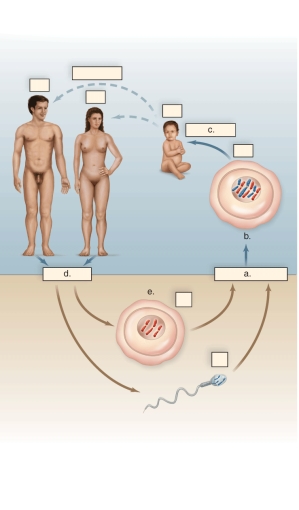
In the figure of the life cycle of humans,what does "e" represent?
A)meiosis
B)mitosis
C)haploid egg
D)diploid egg
E)zygote or embryo

In the figure of the life cycle of humans,what does "e" represent?
A)meiosis
B)mitosis
C)haploid egg
D)diploid egg
E)zygote or embryo
C
Explanation: The egg is the human female's gamete and is haploid.
Explanation: The egg is the human female's gamete and is haploid.
3
During which stage do homologous chromosomes move away from each other?
A)anaphase I
B)prophase
C)anaphase II
D)metaphase I
E)metaphase II
A)anaphase I
B)prophase
C)anaphase II
D)metaphase I
E)metaphase II
A
Explanation: Homologs separate during anaphase I.
Explanation: Homologs separate during anaphase I.
4
A geneticist is studying the failure of chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis.Which of the following would he be studying?
A)crossing-over
B)synapsis
C)translocation
D)inversion
E)nondisjunction
A)crossing-over
B)synapsis
C)translocation
D)inversion
E)nondisjunction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A person with Klinefelter syndrome has long arms,long legs and some breast development due to which chromosomal anomaly?
A)XYY
B)Trisomy 18
C)Trisomy 13
D)XXY
E)Monosomy X
A)XYY
B)Trisomy 18
C)Trisomy 13
D)XXY
E)Monosomy X

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Gametes and spores
A)are both produced by animals.
B)are autosomal.
C)are haploid.
D)are diploiD.
E)join in fertilization.
A)are both produced by animals.
B)are autosomal.
C)are haploid.
D)are diploiD.
E)join in fertilization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Meiosis results in a change in chromosome number which can be written as
A)"3n to 2n."
B)"2n to n."
C)"3n to n."
D)"4n to 3n."
E)"4n to 2n."
A)"3n to 2n."
B)"2n to n."
C)"3n to n."
D)"4n to 3n."
E)"4n to 2n."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Figure: 
In the figure of the life cycle of humans,what does "a" represent?
A)diploid egg
B)meiosis II
C)zygote or embryo
D)fertilization
E)mitosis

In the figure of the life cycle of humans,what does "a" represent?
A)diploid egg
B)meiosis II
C)zygote or embryo
D)fertilization
E)mitosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A geneticist found that the gene order is ABCDEFG on one chromosome and the gene order is ABCDEDEFG on the other homologous chromosome.That means that there was a change in the chromosome structure called a(n)
A)duplication.
B)inversion.
C)translocation.
D)trisomy.
E)deletion.
A)duplication.
B)inversion.
C)translocation.
D)trisomy.
E)deletion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Genetic variation in organisms is produced by
A)mitosis.
B)crossing-over,independent assortment,and fertilization.
C)random fertilization.
D)mutations.
E)meiosis.
A)mitosis.
B)crossing-over,independent assortment,and fertilization.
C)random fertilization.
D)mutations.
E)meiosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Figure: 
In the figure of the life cycle of humans,what does "d" represent?
A)fertilization
B)zygote or embryo
C)gamete production
D)mitosis
E)meiosis II

In the figure of the life cycle of humans,what does "d" represent?
A)fertilization
B)zygote or embryo
C)gamete production
D)mitosis
E)meiosis II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following chromosomal anomalies does not usually cause any symptoms in humans?
A)Trisomy 13
B)Trisomy X
C)Trisomy 18
D)Trisomy 21
E)Trisomy Y
A)Trisomy 13
B)Trisomy X
C)Trisomy 18
D)Trisomy 21
E)Trisomy Y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A geneticist is studying the movement of a chromosome segment from one chromosome to another.This scientist would be studying a(n)
A)duplication.
B)trisomy.
C)inversion.
D)deletion.
E)translocation.
A)duplication.
B)trisomy.
C)inversion.
D)deletion.
E)translocation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An organism that has more or less than the normal number of chromosomes is called:
A)haploid.
B)tetraploid.
C)aneuploid.
D)triploiD.
E)karyoploid.
A)haploid.
B)tetraploid.
C)aneuploid.
D)triploiD.
E)karyoploid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A basic difference between spermatogenesis and oogenesis is that in oogenesis
A)four functional eggs are produced.
B)only one cell eventually completes meiosis II.
C)both sperm and egg are produced.
D)four cells are produced and fertilization is required for completion.
E)one cell is produced and fertilization is required for completion.
A)four functional eggs are produced.
B)only one cell eventually completes meiosis II.
C)both sperm and egg are produced.
D)four cells are produced and fertilization is required for completion.
E)one cell is produced and fertilization is required for completion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A geneticist finds three copies of chromosome 21 in the karyotype of a patient,leading to the conclusion that the patient has what anomaly?
A)Turner syndrome
B)Patau syndrome
C)Klinefelter syndrome
D)Down syndrome
E)Edwards syndrome
A)Turner syndrome
B)Patau syndrome
C)Klinefelter syndrome
D)Down syndrome
E)Edwards syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The fusion of sperm and egg is called synapsis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Crossing-over occurs during which of the following phases?
A)prophase II
B)metaphase II
C)anaphase I
D)metaphase I
E)prophase I
A)prophase II
B)metaphase II
C)anaphase I
D)metaphase I
E)prophase I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The second meiotic division is essentially a mitotic division except for the fact that the cells produced are
A)diploid.
B)somatic.
C)haploid.
D)polyploidy.
E)autosomal.
A)diploid.
B)somatic.
C)haploid.
D)polyploidy.
E)autosomal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which chromosome configuration designates a person with Turner syndrome?
A)XO
B)XY
C)XYY
D)XX
E)XXY
A)XO
B)XY
C)XYY
D)XX
E)XXY

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Autosomes are the majority of human chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The nuclear envelope does not reform during telophase I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The nuclear envelope does not reform during telophase II.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What phase of meiosis precedes prophase II?
A)telophase I
B)anaphase I
C)metaphase II
D)anaphase II
E)telophase II
A)telophase I
B)anaphase I
C)metaphase II
D)anaphase II
E)telophase II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Females with Turner Syndrome have sex chromosomes which can be represented as
A)XO
B)XX
C)XY
D)XXY
E)OY
A)XO
B)XX
C)XY
D)XXY
E)OY

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
X chromosomes are examples of autosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Chromosomes condense during prophase I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The plant lifecycle is one of alternation of generations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A geneticist is studying the genetic makeup of a baby and discovers that part of chromosome five has a piece missing.The baby is suffering from:
A)Down syndrome
B)Turner syndrome
C)Edward syndrome
D)Klinefelter syndrome
E)Cri du Chat syndrome
A)Down syndrome
B)Turner syndrome
C)Edward syndrome
D)Klinefelter syndrome
E)Cri du Chat syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of these events happens during anaphase I?
A)Sister chromatids separate.
B)Chromosomes condense.
C)Homologous chromosomes separate.
D)The nuclear membrane disappears.
E)Recombination occurs.
A)Sister chromatids separate.
B)Chromosomes condense.
C)Homologous chromosomes separate.
D)The nuclear membrane disappears.
E)Recombination occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Chromosomes do not need to condense during prophase I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of these events happens during anaphase II?
A)Sister chromatids separate.
B)Chromosomes condense.
C)Homologous chromosomes separate.
D)The nuclear membrane disappears.
E)Recombination occurs.
A)Sister chromatids separate.
B)Chromosomes condense.
C)Homologous chromosomes separate.
D)The nuclear membrane disappears.
E)Recombination occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Nondisjunction can lead to aneuploid organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Mitosis and meiosis differ in that
A)meiosis does not change the number of chromosomes per cell.
B)mitosis doubles the number of chromosomes per cell.
C)meiosis doubles the number of chromosomes per cell.
D)mitosis does not change the number of chromosomes per cell.
E)mitosis triples the number of chromosomes per cell.
A)meiosis does not change the number of chromosomes per cell.
B)mitosis doubles the number of chromosomes per cell.
C)meiosis doubles the number of chromosomes per cell.
D)mitosis does not change the number of chromosomes per cell.
E)mitosis triples the number of chromosomes per cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If a new kind of slug were found which had a system of sex determination just like that of humans,it would have
A)both sex chromosomes and autosomes.
B)both sex chromosomes and plasmids.
C)both sex chromosomes and asexual chromosomes..
D)both X and Z chromosomes.
E)both autosomes and Y chromosomes.
A)both sex chromosomes and autosomes.
B)both sex chromosomes and plasmids.
C)both sex chromosomes and asexual chromosomes..
D)both X and Z chromosomes.
E)both autosomes and Y chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Mitosis produces half as many daughter cells as meiosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Persons affected by Kleinfelter Syndrome can be helped by supplemental estrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
It is possible for a person with Down's Syndrome to live an active,successful life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Common lifecycles include haploid and diploid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Males with Kleinfelter syndrome have sex chromosomes which can be represented as
A)XO
B)XX
C)XY
D)XXY
E)OY
A)XO
B)XX
C)XY
D)XXY
E)OY

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Mitosis and meiosis result in cells containing the same total number of chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The process which leads to more genetic diversity in meiosis is called
A)nondisjunction.
B)disjunction.
C)inheritance.
D)crossing over.
E)syngamy.
A)nondisjunction.
B)disjunction.
C)inheritance.
D)crossing over.
E)syngamy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The long parts of chromosomes are called legs of the chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When genetic variation is created in meiosis I,this explains independent assortment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Homologues are corresponding chromosomes with genes in the same order,though alleles may differ between them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Chromosomes cannot be homoloques if they have the same genes but different alleles of those genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Mitosis and meiosis both require two nuclear divisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Animals and flowering plants generally have pairs of chromosomes in their nuclei.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When a scientist observes a cell undergoing meiosis,microscopic examination shows too much DNA in one gamete and too little in another.The most likely explanation is that there was an occurrence of
A)nondisjunction.
B)misinheritance.
C)synapsis.
D)telophase I.
E)mitosis.
A)nondisjunction.
B)misinheritance.
C)synapsis.
D)telophase I.
E)mitosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Mitosis and meiosis both produce genetically identical daughter cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



