Deck 7: The Electronic Structure of Atoms
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/115
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: The Electronic Structure of Atoms
1
What is the binding energy (in J/mol or kJ/mol)of an electron in a metal whose threshold frequency for photoelectrons is 2.50 * 1014 /s?
A)99.7 kJ/mol
B)1.66 * 10-19 J/mol
C)2.75 * 10-43 J/mol
D)7.22 * 1017 kJ/mol
E)1.20 * 10-6 J/mol
A)99.7 kJ/mol
B)1.66 * 10-19 J/mol
C)2.75 * 10-43 J/mol
D)7.22 * 1017 kJ/mol
E)1.20 * 10-6 J/mol
99.7 kJ/mol
2
What is the energy in joules of a mole of photons associated with red light of wavelength 7.00 * 102 nm?
A)256 kJ
B)1.71 * 105 J
C)4.72 * 10-43 J
D)12.4 kJ
E)2.12 * 1042 J
A)256 kJ
B)1.71 * 105 J
C)4.72 * 10-43 J
D)12.4 kJ
E)2.12 * 1042 J
1.71 * 105 J
3
Calculate the frequency of the light emitted by a hydrogen atom during a transition of its electron from the n = 6 to the n = 3 principal energy level. Recall that for hydrogen En = -2.18 * 10-18 J(1/n2).
A)1.64 * 1015 /s
B)9.13 * 1013 /s
C)3.65 * 1014 /s
D)1.82 * 10-19 /s
E)2.74 * 1014/s
A)1.64 * 1015 /s
B)9.13 * 1013 /s
C)3.65 * 1014 /s
D)1.82 * 10-19 /s
E)2.74 * 1014/s
2.74 * 1014/s
4
Calculate the wavelength, in nanometers, of the light emitted by a hydrogen atom when its electron falls from the n = 7 to the n = 4 principal energy level. Recall that the energy levels of the H atom are given by En = -2.18 * 10-18 J(1/n2)
A)4.45 * 10-20 nm
B)2.16 * 10-6 nm
C)9.18 * 10-20 nm
D)1.38 * 1014 nm
E)2.16 * 103 nm
A)4.45 * 10-20 nm
B)2.16 * 10-6 nm
C)9.18 * 10-20 nm
D)1.38 * 1014 nm
E)2.16 * 103 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Calculate the frequency of visible light having a wavelength of 686 nm.
A)4.37 * 1014 /s
B)4.37 * 105 /s
C)6.17 * 1014 /s
D)2.29 * 10-15 /s
E)2.29 * 10-6 /s
A)4.37 * 1014 /s
B)4.37 * 105 /s
C)6.17 * 1014 /s
D)2.29 * 10-15 /s
E)2.29 * 10-6 /s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the energy in joules of a mole of photons associated with visible light of wavelength 486 nm?
A)6.46 * 10-16 J
B)6.46 * 10-25 J
C)2.46 * 10-4 J
D)12.4 kJ
E)246 kJ
A)6.46 * 10-16 J
B)6.46 * 10-25 J
C)2.46 * 10-4 J
D)12.4 kJ
E)246 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the following diagram of a wave 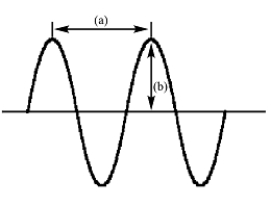
A)(a)is amplitude and (b)is wavelength
B)(a)is frequency and (b)is amplitude
C)(a)is wavelength and (b)is frequency
D)(a)is amplitude and (b)is frequency
E)(a)is wavelength and (b)is amplitude

A)(a)is amplitude and (b)is wavelength
B)(a)is frequency and (b)is amplitude
C)(a)is wavelength and (b)is frequency
D)(a)is amplitude and (b)is frequency
E)(a)is wavelength and (b)is amplitude

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The second line of the Balmer series occurs at a wavelength of 486.1 nm. What is the energy difference between the initial and final levels of the hydrogen atom in this emission process?
A)2.44 * 1018 J
B)4.09 * 10-19 J
C)4.09 * 10-22 J
D)4.09 * 10-28 J
E)1.07 * 10-48 J
A)2.44 * 1018 J
B)4.09 * 10-19 J
C)4.09 * 10-22 J
D)4.09 * 10-28 J
E)1.07 * 10-48 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A proton is roughly 1800 times more massive than an electron. If a proton and an electron are traveling at the same speed,
A)the wavelength of the photon will be about 1800 times longer than the wavelength of the electron.
B)the wavelength of the photon will be about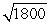 times longer than the wavelength of the electron.
times longer than the wavelength of the electron.
C)the wavelength of the photon will be roughly equal to the wavelength of the electron.
D)the wavelength of the electron will be about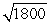 times longer than the wavelength of the photon.
times longer than the wavelength of the photon.
E)the wavelength of the electron will be about 1800 times longer than the wavelength of the photon.
A)the wavelength of the photon will be about 1800 times longer than the wavelength of the electron.
B)the wavelength of the photon will be about
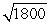 times longer than the wavelength of the electron.
times longer than the wavelength of the electron.C)the wavelength of the photon will be roughly equal to the wavelength of the electron.
D)the wavelength of the electron will be about
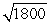 times longer than the wavelength of the photon.
times longer than the wavelength of the photon.E)the wavelength of the electron will be about 1800 times longer than the wavelength of the photon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If a hydrogen atom and a helium atom are traveling at the same speed,
A)the wavelength of the hydrogen atom will be about 4 times longer than the wavelength of the helium atom.
B)the wavelength of the hydrogen atom will be about 2 times longer than the wavelength of the helium.
C)the wavelength of the hydrogen atom will be roughly equal to the wavelength of the helium atom.
D)the wavelength of the helium atom will be about 2 times longer than the wavelength of the hydrogen atom.
E)the wavelength of the helium atom will be about 4 times longer than the wavelength of the hydrogen atom.
A)the wavelength of the hydrogen atom will be about 4 times longer than the wavelength of the helium atom.
B)the wavelength of the hydrogen atom will be about 2 times longer than the wavelength of the helium.
C)the wavelength of the hydrogen atom will be roughly equal to the wavelength of the helium atom.
D)the wavelength of the helium atom will be about 2 times longer than the wavelength of the hydrogen atom.
E)the wavelength of the helium atom will be about 4 times longer than the wavelength of the hydrogen atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the wavelength of radiation that has a frequency of 2.10 * 1014 s -1?
A)6.30 * 1022 m
B)7.00 * 102 nm
C)7.00 * 105 m
D)1.43 * 10-6 m
E)3.00 * 108 m
A)6.30 * 1022 m
B)7.00 * 102 nm
C)7.00 * 105 m
D)1.43 * 10-6 m
E)3.00 * 108 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Calculate the energy, in joules, required to excite a hydrogen atom by causing an electronic transition from the n = 1 to the n = 4 principal energy level. Recall that the energy levels of the H atom are given by En = -2.18 * 10-18 J(1/n2)
A)2.07 * 10-29 J
B)2.19 * 105 J
C)2.04 * 10-18 J
D)3.27 * 10-17 J
E)2.25 * 10-18 J
A)2.07 * 10-29 J
B)2.19 * 105 J
C)2.04 * 10-18 J
D)3.27 * 10-17 J
E)2.25 * 10-18 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Complete this sentence: Atoms emit visible and ultraviolet light
A)as electrons jump from lower energy levels to higher levels.
B)as the atoms condense from a gas to a liquid.
C)as electrons jump from higher energy levels to lower levels.
D)as they are heated and the solid melts to form a liquid.
E)as the electrons move about the atom within an orbit.
A)as electrons jump from lower energy levels to higher levels.
B)as the atoms condense from a gas to a liquid.
C)as electrons jump from higher energy levels to lower levels.
D)as they are heated and the solid melts to form a liquid.
E)as the electrons move about the atom within an orbit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Calculate the frequency of visible light having a wavelength of 486 nm.
A)2.06 * 1014 /s
B)2.06 * 106 /s
C)6.17 * 1014 /s
D)1.20 * 10-15 /s
E)4.86 * 10-7 /s
A)2.06 * 1014 /s
B)2.06 * 106 /s
C)6.17 * 1014 /s
D)1.20 * 10-15 /s
E)4.86 * 10-7 /s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Calculate the wavelength of the light emitted by a hydrogen atom during a transition of its electron from the n = 4 to the n = 1 principal energy level. Recall that for hydrogen En = -2.18 * 10-18 J(1/n2)
A)97.2 nm
B)82.6 nm
C)365 nm
D)0.612 nm
E)6.8 * 10-18 nm
A)97.2 nm
B)82.6 nm
C)365 nm
D)0.612 nm
E)6.8 * 10-18 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Calculate the frequency of the light emitted by a hydrogen atom during a transition of its electron from the n = 4 to the n = 1 principal energy level. Recall that for hydrogen En = -2.18 * 10 -18 J(1/n2)
A)3.08 * 1015 /s
B)1.03 * 108 /s
C)2.06 * 1014 /s
D)1.35 * 10-51 /s
E)8.22 * 1014 /s
A)3.08 * 1015 /s
B)1.03 * 108 /s
C)2.06 * 1014 /s
D)1.35 * 10-51 /s
E)8.22 * 1014 /s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the energy in joules of one photon of microwave radiation with a wavelength 0.122 m? (c = 2.9979 * 108 m/s; h = 6.626 * 10-34 J.s)
A)2.70 * 10-43 J
B)5.43 * 10-33 J
C)1.63 * 10-24 J
D)4.07 * 10-10 J
E)2.46 * 109 J
A)2.70 * 10-43 J
B)5.43 * 10-33 J
C)1.63 * 10-24 J
D)4.07 * 10-10 J
E)2.46 * 109 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the wavelength of radiation that has a frequency of 5.39 * 1014 s-1? (c = 2.9979 * 108 m/s)
A)1.80 * 10-3 nm
B)556 nm
C)618 nm
D)6180 nm
E)1.61 * 1023 nm
A)1.80 * 10-3 nm
B)556 nm
C)618 nm
D)6180 nm
E)1.61 * 1023 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A photon is roughly 1800 times more massive than an electron. If a proton and an electron have the same kinetic energy,
A)the wavelength of the photon will be about 1800 times longer than the wavelength of the electron.
B)the wavelength of the photon will be about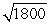 times longer than the wavelength of the electron.
times longer than the wavelength of the electron.
C)the wavelength of the photon will be roughly equal to the wavelength of the electron.
D)the wavelength of the electron will be about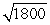 times longer than the wavelength of the photon.
times longer than the wavelength of the photon.
E)the wavelength of the electron will be about 1800 times longer than the wavelength of the photon.
A)the wavelength of the photon will be about 1800 times longer than the wavelength of the electron.
B)the wavelength of the photon will be about
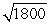 times longer than the wavelength of the electron.
times longer than the wavelength of the electron.C)the wavelength of the photon will be roughly equal to the wavelength of the electron.
D)the wavelength of the electron will be about
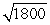 times longer than the wavelength of the photon.
times longer than the wavelength of the photon.E)the wavelength of the electron will be about 1800 times longer than the wavelength of the photon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
As the frequency of an electromagnetic wave increases
A)its speed must increase.
B)its wavelength must increase.
C)its amplitude must increase.
D)its energy must increase.
A)its speed must increase.
B)its wavelength must increase.
C)its amplitude must increase.
D)its energy must increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In an electron microscope, electrons are accelerated to great velocities. Calculate the wavelength of an electron traveling with a velocity of 7.0 * 103 kilometers per second. The mass of an electron is 9.1 * 10-28 g.
A)1.0 * 10-13 m
B)1.0 * 10-7 m
C)1.0 m
D)1.0 * 10-10 m
A)1.0 * 10-13 m
B)1.0 * 10-7 m
C)1.0 m
D)1.0 * 10-10 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
"No two electrons in an atom can have the same four quantum numbers" is a statement of
A)the Pauli exclusion principle.
B)Bohr's equation.
C)Hund's rule.
D)de Broglie's relation.
E)Dalton's atomic theory.
A)the Pauli exclusion principle.
B)Bohr's equation.
C)Hund's rule.
D)de Broglie's relation.
E)Dalton's atomic theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Electrons can be used to probe the arrangement of atoms on a solid surface if the wavelength of the electrons is comparable with the spacing between the atoms. Which of the following electron velocities would be appropriate for use in this application if the atoms are separated by 0.320 nm?
A)2.27 * 106 m/s
B)1.24 * 103 m/s
C)3.00 * 108 m/s
D)4.41 * 106 m/s
E)8.06 * 103 m/s
A)2.27 * 106 m/s
B)1.24 * 103 m/s
C)3.00 * 108 m/s
D)4.41 * 106 m/s
E)8.06 * 103 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A single pulse of a laser yields an average of 5.00 * 1018 photons with = 633 nm. If melting ice to water at 0°C requires 6.01 kJ/mol, what is the fewest number of laser pulses need to melt 10.0 g of ice?
A)3830
B)3340
C)38300
D)2120
E)212
A)3830
B)3340
C)38300
D)2120
E)212

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A possible set of quantum numbers for the last electron added to complete an atom of germanium (Ge)in its ground state is 
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The maximum number of electrons that can occupy an energy level described by the principal quantum number, n, is
A)n
B)n + 1
C)2n
D)2n2
E)n2
A)n
B)n + 1
C)2n
D)2n2
E)n2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Electrons in an orbital with l = 3 are in a/an
A)d orbital.
B)f orbital.
C)g orbital.
D)p orbital.
E)s orbital.
A)d orbital.
B)f orbital.
C)g orbital.
D)p orbital.
E)s orbital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When photons with a wavelength of 310. nm strike a magnesium plate, the maximum velocity of the ejected electrons is 3.45 *105 m/s. Calculate the binding energy of electrons to the magnesium surface.
A)386 kJ/mol
B)419 kJ/mol
C)32.7 kJ/mol
D)321 kJ/mol
E)353 kJ/mol
A)386 kJ/mol
B)419 kJ/mol
C)32.7 kJ/mol
D)321 kJ/mol
E)353 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Calculate the wavelength of a neutron that has a velocity of 250 cm/s. (The mass of a neutron = 1.675 * 10-24 g; h = 6.626 * 10-34 J.s)
A)16 pm
B)0.016 nm
C)0.16 nm
D)160 nm
E)1.6 * 10-4 m
A)16 pm
B)0.016 nm
C)0.16 nm
D)160 nm
E)1.6 * 10-4 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which one of the following sets of quantum numbers is not possible? 
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which one of the following sets of quantum numbers is not possible? 
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A common way of initiating certain chemical reactions with light involves the generation of free halogen atoms in solution. If H for the reaction Cl2(g) 2Cl(g)is 242.8 kJ/mol, what is the longest wavelength of light that will produce free chlorine atoms in solution?
A)246.3 nm
B)465.2 nm
C)349.3 nm
D)698.6 nm
E)492.6 nm
A)246.3 nm
B)465.2 nm
C)349.3 nm
D)698.6 nm
E)492.6 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A possible set of quantum numbers for the last electron added to complete an atom of gallium (Ga)in its ground state is 
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The longest wavelength of light that causes electrons to be ejected from the surface of a copper plate is 243 nm. What is the maximum velocity of the electrons ejected when light of wavelength 200. nm shines on a copper plate?
A)1.48 * 106 m/s
B)6.22 * 105 m/s
C)4.67 * 104 m/s
D)1.97 * 104 m/s
E)1.34 * 106 m/s
A)1.48 * 106 m/s
B)6.22 * 105 m/s
C)4.67 * 104 m/s
D)1.97 * 104 m/s
E)1.34 * 106 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If a hydrogen atom and a helium atom have the same kinetic energy,
A)the wavelength of the hydrogen atom will be about 4 times longer than the wavelength of the helium atom.
B)the wavelength of the hydrogen atom will be about 2 times longer than the wavelength of the helium.
C)the wavelength of the hydrogen atom will be roughly equal to the wavelength of the helium atom.
D)the wavelength of the helium atom will be about 2 times longer than the wavelength of the hydrogen atom.
E)the wavelength of the helium atom will be about 4 times longer than the wavelength of the hydrogen atom.
A)the wavelength of the hydrogen atom will be about 4 times longer than the wavelength of the helium atom.
B)the wavelength of the hydrogen atom will be about 2 times longer than the wavelength of the helium.
C)the wavelength of the hydrogen atom will be roughly equal to the wavelength of the helium atom.
D)the wavelength of the helium atom will be about 2 times longer than the wavelength of the hydrogen atom.
E)the wavelength of the helium atom will be about 4 times longer than the wavelength of the hydrogen atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Calculate the wavelength associated with a 20Ne+ ion moving at a velocity of 2.0 * 105 m/s. The atomic mass of Ne-20 is 19.992 amu.
A)1.0 * 10-13 m
B)1.0 * 10-16 m
C)1.0 * 10-18 m
D)9.7 * 1012 m
E)2.0 * 10-13 cm
A)1.0 * 10-13 m
B)1.0 * 10-16 m
C)1.0 * 10-18 m
D)9.7 * 1012 m
E)2.0 * 10-13 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
How many orbitals are allowed in a subshell if the angular momentum quantum number for electrons in that subshell is 3?
A)1
B)3
C)5
D)7
E)9
A)1
B)3
C)5
D)7
E)9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The orbital diagram for a ground-state nitrogen atom is 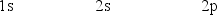
A)
B)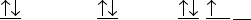
C)
D)
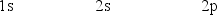
A)

B)
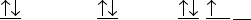
C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is the maximum number of electrons in an atom that can have the following set of quantum numbers? n = 4 l = 3 ml = -2 ms = +1/2
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)6
E)10
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)6
E)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The number of orbitals in a d subshell is
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)5
E)7
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)5
E)7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which element has the following ground-state electron configuration? 1s22s22p63s2
A)Na
B)Mg
C)Al
D)Si
E)Ne
A)Na
B)Mg
C)Al
D)Si
E)Ne

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The electron configuration of a ground-state copper atom is
A)[Ar]4s24d4.
B)[Ar]4s24p63d3.
C)[Ar]4s23d9.
D)[Ar]3d9.
E)[Ar]4s13d10.
A)[Ar]4s24d4.
B)[Ar]4s24p63d3.
C)[Ar]4s23d9.
D)[Ar]3d9.
E)[Ar]4s13d10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which element has the following ground-state electron configuration? [Kr]5s14d5
A)Mn
B)Mo
C)Nb
D)Re
E)Tc
A)Mn
B)Mo
C)Nb
D)Re
E)Tc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which element has the following ground-state electron configuration? [Kr]5s24d105p2
A)Sn
B)Sb
C)Pb
D)Ge
E)Te
A)Sn
B)Sb
C)Pb
D)Ge
E)Te

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A ground-state atom of arsenic has
A)no unpaired electrons.
B)one unpaired electron.
C)two unpaired electrons.
D)three unpaired electrons.
E)four unpaired electrons.
A)no unpaired electrons.
B)one unpaired electron.
C)two unpaired electrons.
D)three unpaired electrons.
E)four unpaired electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
How many unpaired electrons does a ground-state atom of sulfur have?
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)4
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
How many electrons are there in the 2nd principal energy level (n = 2)of a phosphorus atom?
A)3
B)5
C)6
D)8
E)10
A)3
B)5
C)6
D)8
E)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The ground-state electron configuration for an atom of indium is
A)[Kr]5s24p64d5.
B)[Ar]4s23d104p1.
C)[Ar]4s24p63d5.
D)[Kr]5s25p64d5.
E)[Kr]5s24d105p1.
A)[Kr]5s24p64d5.
B)[Ar]4s23d104p1.
C)[Ar]4s24p63d5.
D)[Kr]5s25p64d5.
E)[Kr]5s24d105p1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which ground-state atom has an electron configuration described by the following orbital diagram? 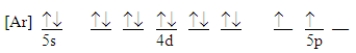
A)antimony
B)germanium
C)indium
D)lead
E)tin
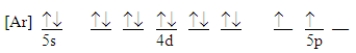
A)antimony
B)germanium
C)indium
D)lead
E)tin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which element has the following ground-state electron configuration? [Ar]4s23d104p5
A)aresnic
B)bromine
C)iodine
D)selenium
E)tellerium
A)aresnic
B)bromine
C)iodine
D)selenium
E)tellerium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The orbital diagram for a ground-state oxygen atom is 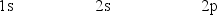
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)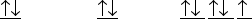
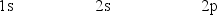
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)
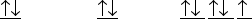

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The electron configuration of a ground-state Co atom is
A)[Ar]4s23d7.
B)1s22s22p63s23d9.
C)[Ne]3s23d7.
D)[Ar]4s13d5.
E)[Ar]4s24d7.
A)[Ar]4s23d7.
B)1s22s22p63s23d9.
C)[Ne]3s23d7.
D)[Ar]4s13d5.
E)[Ar]4s24d7.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
How many electrons are there in the 3rd principal energy level (n = 3)of a phosphorus atom?
A)3
B)5
C)6
D)8
E)10
A)3
B)5
C)6
D)8
E)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The electron configuration of a ground-state vanadium atom is
A)[Ar]4s24d3.
B)[Ar]4s24p3.
C)[Ar]4s23d3.
D)[Ar]3d5.
A)[Ar]4s24d3.
B)[Ar]4s24p3.
C)[Ar]4s23d3.
D)[Ar]3d5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which element has the following ground-state electron configuration? [Kr]5s24d105p3
A)Sn
B)Sb
C)Pb
D)Bi
E)Te
A)Sn
B)Sb
C)Pb
D)Bi
E)Te

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which ground-state atom has an electron configuration described by the following orbital diagram? 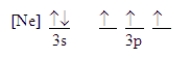
A)phosphorus
B)nitrogen
C)arsenic
D)vanadium
E)none of these
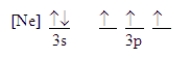
A)phosphorus
B)nitrogen
C)arsenic
D)vanadium
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which ground-state atom has an electron configuration described by the following orbital diagram? 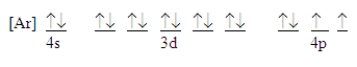
A)phosphorus
B)germanium
C)selenium
D)tellurium
E)none of these
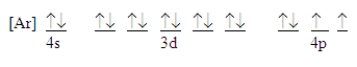
A)phosphorus
B)germanium
C)selenium
D)tellurium
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is the ground-state electron configuration of a calcium atom?
A)[Ne]3s2
B)[Ne]3s23p6
C)[Ar]4s13d1
D)[Ar]4s2
E)[Ar]3d2
A)[Ne]3s2
B)[Ne]3s23p6
C)[Ar]4s13d1
D)[Ar]4s2
E)[Ar]3d2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The orbital diagram for a ground state carbon atom is 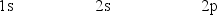
A)
B)
C)
D)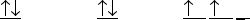
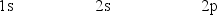
A)

B)

C)

D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A ground-state atom of manganese has ___ unpaired electrons and is _____.
A)0, diamagnetic
B)2, diamagnetic
C)3, paramagnetic
D)5, paramagnetic
E)7, paramagnetic
A)0, diamagnetic
B)2, diamagnetic
C)3, paramagnetic
D)5, paramagnetic
E)7, paramagnetic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The ground-state electron configuration of Cr, Mo, and Ag are exceptions to the Aufbau principle. Which of the following is the electron configuration for Mo?
A)[Kr]5s14d5
B)[Kr]5s24d4
C)[Xe]6s25d4
D)[Ar]4s24d4
E)[Kr]5s24d6
A)[Kr]5s14d5
B)[Kr]5s24d4
C)[Xe]6s25d4
D)[Ar]4s24d4
E)[Kr]5s24d6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which choice lists two elements with ground-state electron configurations that are well known exceptions to the Aufbau principle?
A)Cu and C
B)Cr and Cu
C)Cs and Cl
D)Rb and Co
E)Fe and Co
A)Cu and C
B)Cr and Cu
C)Cs and Cl
D)Rb and Co
E)Fe and Co

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Transition metal elements have atoms or ions with partially filled
A)s subshells.
B)p subshells.
C)d subshells.
D)f subshells.
E)g subshells.
A)s subshells.
B)p subshells.
C)d subshells.
D)f subshells.
E)g subshells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A ground-state chromium atom has how many unpaired electrons?
A)1
B)2
C)4
D)5
E)6
A)1
B)2
C)4
D)5
E)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Lanthanide (or rare earth elements)have atoms or ions with partially filled
A)s subshells.
B)p subshells.
C)d subshells.
D)f subshells.
E)g subshells.
A)s subshells.
B)p subshells.
C)d subshells.
D)f subshells.
E)g subshells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When the electron in a hydrogen atom falls from its first excited energy level to the ground state energy level, a photon with wavelength is emitted. A proton having this same wavelength would have a velocity of
A)3.87 m/s.
B)5990 m/s.
C)1.21 * 10-7 m/s.
D)3.26 m/s.
E)5.99 m/s.
A)3.87 m/s.
B)5990 m/s.
C)1.21 * 10-7 m/s.
D)3.26 m/s.
E)5.99 m/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following is the electron configuration of an excited state of a copper atom?
A)[Ar]4s23d9
B)[Ar]4s13d10
C)[Ar]4s13d8
D)[Ar]4s23d8
E)[Ar]4s03d10
A)[Ar]4s23d9
B)[Ar]4s13d10
C)[Ar]4s13d8
D)[Ar]4s23d8
E)[Ar]4s03d10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
How many electrons in a ground-state cadmium atom are in orbitals labeled by ml = -1?
A)2
B)10
C)12
D)18
E)36
A)2
B)10
C)12
D)18
E)36

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The electron in a hydrogen atom falls from an excited energy level to the ground state in two steps, causing the emission of photons with wavelengths of 1870 and 102.5 nm. What is the quantum number of the initial excited energy level from which the electron falls?
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)6
E)8
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)6
E)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following is the electron configuration of an excited state of an iron atom?
A)[Ar]4s23d7
B)[Ar]4s23d6
C)[Ar]4s23d8
D)[Ar]4s13d7
E)[Ar]4s13d5
A)[Ar]4s23d7
B)[Ar]4s23d6
C)[Ar]4s23d8
D)[Ar]4s13d7
E)[Ar]4s13d5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following ground-state atoms is diamagnetic?
A)Ca
B)As
C)Cu
D)Fe
E)none of these
A)Ca
B)As
C)Cu
D)Fe
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following is diamagnetic both in its ground state and in all of its excited states?
A)Mg
B)Ne
C)Cu
D)Zn
E)none of these
A)Mg
B)Ne
C)Cu
D)Zn
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A ground-state atom of iron has ___ unpaired electrons and is _____.
A)0, diamagnetic
B)6, diamagnetic
C)3, paramagnetic
D)5, paramagnetic
E)4, paramagnetic
A)0, diamagnetic
B)6, diamagnetic
C)3, paramagnetic
D)5, paramagnetic
E)4, paramagnetic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When the electron in a hydrogen atom falls from the n = 3 excited energy level to the ground state energy level, a photon with wavelength is emitted. An electron having this same wavelength would have a velocity of
A)7.10 * 103 m/s.
B)2.93* 106 m/s.
C)2.93 * 103 m/s.
D)7.10 m/s.
E)3.00 * 108 m/s.
A)7.10 * 103 m/s.
B)2.93* 106 m/s.
C)2.93 * 103 m/s.
D)7.10 m/s.
E)3.00 * 108 m/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
How many electrons in a ground-state tellurium atom are in orbitals labeled by l = 1?
A)4
B)10
C)12
D)16
E)22
A)4
B)10
C)12
D)16
E)22

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is the electron configuration of an excited state of an oxygen atom?
A)1s22s22p4
B)1s22s22p5
C)1s22s22p33s1
D)1s22s22p6
E)1s22s22p3
A)1s22s22p4
B)1s22s22p5
C)1s22s22p33s1
D)1s22s22p6
E)1s22s22p3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following atoms is paramagnetic both in its ground state and in all of its excited states?
A)C
B)N
C)O
D)Ti
E)Cr
A)C
B)N
C)O
D)Ti
E)Cr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A ground-state atom of vanadium has ___ unpaired electrons and is _____.
A)0, diamagnetic
B)2, diamagnetic
C)3, paramagnetic
D)5, paramagnetic
E)4, diamagnetic
A)0, diamagnetic
B)2, diamagnetic
C)3, paramagnetic
D)5, paramagnetic
E)4, diamagnetic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The electron in a hydrogen atom falls from an excited energy level to the ground state in two steps, causing the emission of photons with wavelengths of 2624 and 97.2 nm. What is the quantum number of the initial excited energy level from which the electron falls?
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)6
E)8
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)6
E)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Breaking the oxygen-oxygen bond in hydrogen peroxide requires 210 kJ/mol. What is the longest wavelength of light that can cause this bond to be broken?
A)5.7 * 10-4 m
B)9.5 * 10-31 m
C)2.8 * 10-7 m
D)9.5 * 10-28 m
E)5.7 * 10-7 m
A)5.7 * 10-4 m
B)9.5 * 10-31 m
C)2.8 * 10-7 m
D)9.5 * 10-28 m
E)5.7 * 10-7 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



