Deck 15: Monopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Monopoly
1
Figure 15-1 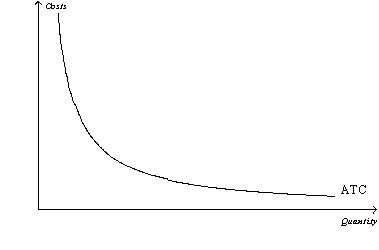
Refer to Figure 15-1.The shape of the average total cost curve reveals information about the nature of the barrier to entry that might exist in a monopoly market.Which of the following monopoly types best coincides with the figure?
A)ownership of a key resource by a single firm
B)natural monopoly
C)government-created monopoly
D)a patent or copyright monopoly

Refer to Figure 15-1.The shape of the average total cost curve reveals information about the nature of the barrier to entry that might exist in a monopoly market.Which of the following monopoly types best coincides with the figure?
A)ownership of a key resource by a single firm
B)natural monopoly
C)government-created monopoly
D)a patent or copyright monopoly
B
2
Figure 15-3 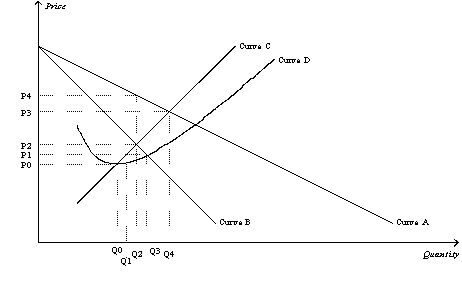
Refer to Figure 15-3.The demand curve for a monopoly firm is depicted by curve
A)A.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Refer to Figure 15-3.The demand curve for a monopoly firm is depicted by curve
A)A.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.
A
3
Which of the following are necessary characteristics of a monopoly?
(i)The firm is the sole seller of its product.
(ii)The firm's product does not have close substitutes.
(iii)The firm generates a large economic profit.
(iv)The firm is located in a small geographic market.
A)(i)and (ii)only
B)(i)and (iii)only
C)(i),(ii),and (iii)only
D)(i),(ii),(iii),and (iv)
(i)The firm is the sole seller of its product.
(ii)The firm's product does not have close substitutes.
(iii)The firm generates a large economic profit.
(iv)The firm is located in a small geographic market.
A)(i)and (ii)only
B)(i)and (iii)only
C)(i),(ii),and (iii)only
D)(i),(ii),(iii),and (iv)
A
4
Because many good substitutes exist for a competitive firm's product,the demand curve that it faces is
A)unit-elastic.
B)perfectly inelastic.
C)perfectly elastic.
D)inelastic only over a certain region.
A)unit-elastic.
B)perfectly inelastic.
C)perfectly elastic.
D)inelastic only over a certain region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is an example of a barrier to entry?
A)Tom charges a higher price than his competitors for his house-painting services.
B)Dick obtains a copyright for the new computer game that he invented.
C)Harry offers free concerts on Sunday afternoons as a form of advertising.
D)Larry charges a lower price than his competitors for his lawn-mowing services.
A)Tom charges a higher price than his competitors for his house-painting services.
B)Dick obtains a copyright for the new computer game that he invented.
C)Harry offers free concerts on Sunday afternoons as a form of advertising.
D)Larry charges a lower price than his competitors for his lawn-mowing services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
For a monopolist,when does marginal revenue exceed average revenue?
A)never
B)when output is less than the profit-maximizing level of output
C)when output is greater than the profit-maximizing level of output
D)for all levels of output greater than zero
A)never
B)when output is less than the profit-maximizing level of output
C)when output is greater than the profit-maximizing level of output
D)for all levels of output greater than zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Figure 15-3 
Refer to Figure 15-3.The average total cost curve for a monopoly firm is depicted by curve
A)A.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Refer to Figure 15-3.The average total cost curve for a monopoly firm is depicted by curve
A)A.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
One difference between a perfectly competitive firm and a monopoly is that a perfectly competitive firm produces where
A)marginal cost equals price,while a monopolist produces where price exceeds marginal cost.
B)marginal cost equals price,while a monopolist produces where marginal cost exceeds price.
C)price exceeds marginal cost,while a monopolist produces where marginal cost equals price.
D)marginal cost exceeds price,while a monopolist produces where marginal cost equals price.
A)marginal cost equals price,while a monopolist produces where price exceeds marginal cost.
B)marginal cost equals price,while a monopolist produces where marginal cost exceeds price.
C)price exceeds marginal cost,while a monopolist produces where marginal cost equals price.
D)marginal cost exceeds price,while a monopolist produces where marginal cost equals price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The fundamental source of monopoly power is
A)barriers to entry.
B)profit.
C)decreasing average total cost.
D)a product without close substitutes.
A)barriers to entry.
B)profit.
C)decreasing average total cost.
D)a product without close substitutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Suppose a firm has a monopoly on the sale of a computer game and faces a downward-sloping demand curve.When selling the 50th game,the firm will always receive
A)less marginal revenue on the 50th game than it received on the 49th game.
B)more average revenue on the 50th game than it received on the 49th game.
C)more total revenue on the 50 game than it received on the first 49 game.
D)Both b)and c)are correct.
A)less marginal revenue on the 50th game than it received on the 49th game.
B)more average revenue on the 50th game than it received on the 49th game.
C)more total revenue on the 50 game than it received on the first 49 game.
D)Both b)and c)are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Most markets are not monopolies in the real world because
A)firms usually face downward-sloping demand curves.
B)supply curves slope upward.
C)firms usually equate price with marginal cost.
D)there are reasonable substitutes for most goods.
A)firms usually face downward-sloping demand curves.
B)supply curves slope upward.
C)firms usually equate price with marginal cost.
D)there are reasonable substitutes for most goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Patent and copyright laws encourage
A)creative activity.
B)lower prices due to decreasing average total costs.
C)competition among firms.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)creative activity.
B)lower prices due to decreasing average total costs.
C)competition among firms.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements is correct for a monopolist?
I)The firm maximizes profits by equating marginal revenue with marginal cost.
Ii)The firm maximizes profits by equating price with marginal cost.
Iii)Demand equals marginal revenue.
Iv)Average revenue equals price.
A)i),iii),and iv)only
B)i)and iv)only
C)i),ii),and iv)only
D)i),ii),iii),and iv)
I)The firm maximizes profits by equating marginal revenue with marginal cost.
Ii)The firm maximizes profits by equating price with marginal cost.
Iii)Demand equals marginal revenue.
Iv)Average revenue equals price.
A)i),iii),and iv)only
B)i)and iv)only
C)i),ii),and iv)only
D)i),ii),iii),and iv)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Figure 15-1 
Refer to Figure 15-1.Considering the relationship between average total cost and marginal cost,the marginal cost curve for this firm
A)must lie entirely above the average total cost curve.
B)must lie entirely below the average total cost curve.
C)must be upward sloping.
D)does not exist.

Refer to Figure 15-1.Considering the relationship between average total cost and marginal cost,the marginal cost curve for this firm
A)must lie entirely above the average total cost curve.
B)must lie entirely below the average total cost curve.
C)must be upward sloping.
D)does not exist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If the monopolist's linear demand curve intersects the quantity axis at Q = 30,then the monopolist's marginal revenue will be equal to zero at
A)Q = 10.
B)Q = 15.
C)Q = 20.
D)Q = 30.
A)Q = 10.
B)Q = 15.
C)Q = 20.
D)Q = 30.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
For a monopolist,when the output effect is greater than the price effect,marginal revenue is
A)positive.
B)negative.
C)zero.
D)maximized.
A)positive.
B)negative.
C)zero.
D)maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Economists assume that monopolists behave as
A)cost minimizers.
B)profit maximizers.
C)price maximizers.
D)maximizers of social welfare.
A)cost minimizers.
B)profit maximizers.
C)price maximizers.
D)maximizers of social welfare.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements is (are)true of a monopoly?
(i)A monopoly has the ability to set the price of its product at whatever level it desires.
(ii)A monopoly's total revenue will always increase when it increases the price of its product.
(iii)A monopoly can earn unlimited profits.
A)(i)only
B)(ii)only
C)(i)and (ii)only
D)(ii)and (iii)only
(i)A monopoly has the ability to set the price of its product at whatever level it desires.
(ii)A monopoly's total revenue will always increase when it increases the price of its product.
(iii)A monopoly can earn unlimited profits.
A)(i)only
B)(ii)only
C)(i)and (ii)only
D)(ii)and (iii)only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Patent and copyright laws are major sources of
A)natural monopolies.
B)government-created monopolies.
C)resource monopolies.
D)antitrust regulation.
A)natural monopolies.
B)government-created monopolies.
C)resource monopolies.
D)antitrust regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following statements is correct?
A)The demand curve facing a competitive firm is horizontal,as is the demand curve facing a monopolist.
B)The demand curve facing a competitive firm is downward sloping,whereas the demand curve facing a monopolist is horizontal.
C)The demand curve facing a competitive firm is horizontal,whereas the demand curve facing a monopolist is downward sloping.
D)The demand curve facing a competitive firm is downward sloping,as is the demand curve facing a monopolist.
A)The demand curve facing a competitive firm is horizontal,as is the demand curve facing a monopolist.
B)The demand curve facing a competitive firm is downward sloping,whereas the demand curve facing a monopolist is horizontal.
C)The demand curve facing a competitive firm is horizontal,whereas the demand curve facing a monopolist is downward sloping.
D)The demand curve facing a competitive firm is downward sloping,as is the demand curve facing a monopolist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following statements is correct?
Monopolies are socially inefficient because they
(i)charge a price above marginal cost.
(ii)produce too little output.
(iii)earn profits at the expense of consumers.
(iv)maximize the market's total surplus.
A)(iii)only
B)(iii)and (iv)only
C)(i)and (ii)only
D)(i),(ii),(iii),and (iv)
Monopolies are socially inefficient because they
(i)charge a price above marginal cost.
(ii)produce too little output.
(iii)earn profits at the expense of consumers.
(iv)maximize the market's total surplus.
A)(iii)only
B)(iii)and (iv)only
C)(i)and (ii)only
D)(i),(ii),(iii),and (iv)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Monopoly pricing prevents some mutually beneficial trades from taking place.These unrealized,mutually beneficial trades are
A)less of a concern for a monopoly than competitive market.
B)offset by the higher profits earned by a monopolist.
C)a function of the reduction in the quantity produced by a monopolist in comparison to a competitive market.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)less of a concern for a monopoly than competitive market.
B)offset by the higher profits earned by a monopolist.
C)a function of the reduction in the quantity produced by a monopolist in comparison to a competitive market.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The economic inefficiency of a monopolist can be measured by the
A)number of consumers who are unable to purchase the product because of its high price.
B)excess profit generated by monopoly firms.
C)poor quality of service offered by monopoly firms.
D)deadweight loss.
A)number of consumers who are unable to purchase the product because of its high price.
B)excess profit generated by monopoly firms.
C)poor quality of service offered by monopoly firms.
D)deadweight loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Figure 15-7 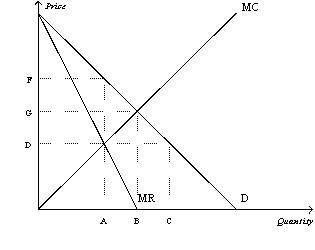
Refer to Figure 15-7.What is the socially efficient price and quantity?
A)price = F; quantity = A
B)price = G; quantity = B
C)price = G; quantity = A
D)price = D; quantity = A

Refer to Figure 15-7.What is the socially efficient price and quantity?
A)price = F; quantity = A
B)price = G; quantity = B
C)price = G; quantity = A
D)price = D; quantity = A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A firm cannot price discriminate if it
A)has perfect information about consumer demand.
B)operates in a competitive market.
C)faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
D)is regulated by the government.
A)has perfect information about consumer demand.
B)operates in a competitive market.
C)faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
D)is regulated by the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Figure 15-3 
Refer to Figure 15-3.If the monopoly firm wants to maximize its profit,it should operate at a level of output equal to
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.
D)Q4.

Refer to Figure 15-3.If the monopoly firm wants to maximize its profit,it should operate at a level of output equal to
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.
D)Q4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Figure 15-7 ![<strong>Figure 15-7 Refer to Figure 15-7.What area represents the total surplus lost due to monopoly pricing?</strong> A)the rectangle (F-D)xA B)the triangle 1/2[(F-D)x(B-A)] C)the triangle 1/2[(F-G)x(B-A)] D)the rectangle (F-D)xA plus the triangle 1/2[(F-D)x(B-A)]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4793/11ea7a3f_c0ba_b08c_81a2_71eb3968ce04_TB4793_00_TB4793_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 15-7.What area represents the total surplus lost due to monopoly pricing?
A)the rectangle (F-D)xA
B)the triangle 1/2[(F-D)x(B-A)]
C)the triangle 1/2[(F-G)x(B-A)]
D)the rectangle (F-D)xA plus the triangle 1/2[(F-D)x(B-A)]
![<strong>Figure 15-7 Refer to Figure 15-7.What area represents the total surplus lost due to monopoly pricing?</strong> A)the rectangle (F-D)xA B)the triangle 1/2[(F-D)x(B-A)] C)the triangle 1/2[(F-G)x(B-A)] D)the rectangle (F-D)xA plus the triangle 1/2[(F-D)x(B-A)]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4793/11ea7a3f_c0ba_b08c_81a2_71eb3968ce04_TB4793_00_TB4793_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 15-7.What area represents the total surplus lost due to monopoly pricing?
A)the rectangle (F-D)xA
B)the triangle 1/2[(F-D)x(B-A)]
C)the triangle 1/2[(F-G)x(B-A)]
D)the rectangle (F-D)xA plus the triangle 1/2[(F-D)x(B-A)]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Table 15-1
-Refer to Table 15-1.If the monopolist sells 8 units of its product,how much total revenue will it receive from the sale?
A)14
B)40
C)112
D)164
-Refer to Table 15-1.If the monopolist sells 8 units of its product,how much total revenue will it receive from the sale?
A)14
B)40
C)112
D)164

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Table 15-1
-Refer to Table 15-1.If the monopolist wants to maximize its revenue,how many units of its product should it sell?
A)4
B)5
C)6
D)8
-Refer to Table 15-1.If the monopolist wants to maximize its revenue,how many units of its product should it sell?
A)4
B)5
C)6
D)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Figure 15-5 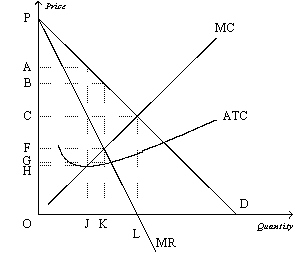
Refer to Figure 15-5.How much output will the monopolist produce?
A)O
B)J
C)K
D)L

Refer to Figure 15-5.How much output will the monopolist produce?
A)O
B)J
C)K
D)L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Financial aid to college students,quantity discounts,and senior citizen discounts are all examples of
A)consumer surplus.
B)deadweight loss.
C)price discrimination.
D)nonprofit pricing strategies.
A)consumer surplus.
B)deadweight loss.
C)price discrimination.
D)nonprofit pricing strategies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Figure 15-3 
Refer to Figure 15-3.A profit-maximizing monopoly's total revenue is equal to
A)P4 x Q2.
B)P3 x Q4.
C)(P4-P2) x Q2.
D)(P4-P3)x Q2.

Refer to Figure 15-3.A profit-maximizing monopoly's total revenue is equal to
A)P4 x Q2.
B)P3 x Q4.
C)(P4-P2) x Q2.
D)(P4-P3)x Q2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
For a profit-maximizing monopolist,
A)P > MR = MC.
B)P = MR = MC.
C)P > MR > MC.
D)MR < MC < P.
A)P > MR = MC.
B)P = MR = MC.
C)P > MR > MC.
D)MR < MC < P.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Figure 15-5 ![<strong>Figure 15-5 Refer to Figure 15-5.What area measures the monopolist's profit?</strong> A)(B-F)*K B)(A-H)*J C)(B-G)*K D)0.5[(B-F)*(L-K)]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4793/11ea7a3f_c0b9_50fa_81a2_077ca14d9b9f_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 15-5.What area measures the monopolist's profit?
A)(B-F)*K
B)(A-H)*J
C)(B-G)*K
D)0.5[(B-F)*(L-K)]
![<strong>Figure 15-5 Refer to Figure 15-5.What area measures the monopolist's profit?</strong> A)(B-F)*K B)(A-H)*J C)(B-G)*K D)0.5[(B-F)*(L-K)]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4793/11ea7a3f_c0b9_50fa_81a2_077ca14d9b9f_TB4793_00_TB4793_00_TB4793_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 15-5.What area measures the monopolist's profit?
A)(B-F)*K
B)(A-H)*J
C)(B-G)*K
D)0.5[(B-F)*(L-K)]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Figure 15-5 
Refer to Figure 15-5.What price will the monopolist charge?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)F

Refer to Figure 15-5.What price will the monopolist charge?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Table 15-1
-Refer to Table 15-1.Assume this monopolist's marginal cost is constant at 12 dinar.What quantity of output (Q)will it produce and what price (P)will it charge?
A)Q = 4,P = 29
B)Q = 4,P = 26
C)Q = 5,P = 23
D)Q = 7,P = 17
-Refer to Table 15-1.Assume this monopolist's marginal cost is constant at 12 dinar.What quantity of output (Q)will it produce and what price (P)will it charge?
A)Q = 4,P = 29
B)Q = 4,P = 26
C)Q = 5,P = 23
D)Q = 7,P = 17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Price discrimination
A)forces monopolies to charge a lower price as a result of government regulation.
B)is an attempt by a monopoly to prevent some customers from purchasing its product by charging a high price.
C)is an attempt by a monopoly to increases its profit by selling the same good to different customers at different prices.
D)increases the consumer surplus associated with a monopolistic market.
A)forces monopolies to charge a lower price as a result of government regulation.
B)is an attempt by a monopoly to prevent some customers from purchasing its product by charging a high price.
C)is an attempt by a monopoly to increases its profit by selling the same good to different customers at different prices.
D)increases the consumer surplus associated with a monopolistic market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The practice of selling the same goods to different customers at different prices,but with the same marginal cost,is known as
A)price segregation.
B)price discrimination.
C)arbitrage.
D)monopoly pricing.
A)price segregation.
B)price discrimination.
C)arbitrage.
D)monopoly pricing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
During the holiday season,high-end retailers frequently place a high price on merchandise on weekends and discount the price during the week.They do this because they believe that two groups of customers exist: shoppers with little free time and bargain hunters.Bargain hunters have time to shop around and frequently shop during the week.What do economists call this price strategy used by high-end retailers?
A)oligopoly
B)price discrimination
C)compensating differential
D)in-kind transfers
A)oligopoly
B)price discrimination
C)compensating differential
D)in-kind transfers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
For a monopoly,the socially efficient level of output occurs where
A)marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B)average revenue equals marginal cost.
C)marginal revenue equals average total cost.
D)average revenue equals average total cost.
A)marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B)average revenue equals marginal cost.
C)marginal revenue equals average total cost.
D)average revenue equals average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following can defeat the profit-maximizing strategy of price discrimination?
A)consumer surplus
B)deadweight loss
C)market power
D)arbitrage
A)consumer surplus
B)deadweight loss
C)market power
D)arbitrage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A monopolist does not have a supply curve because the firm's decision about how much to supply is impossible to separate from the demand curve it faces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Two examples of early antitrust laws are the Clinton and Stigler Antitrust Acts.
B)Antitrust laws automatically prevent mergers between companies that produce similar products.
C)Antitrust laws reduce the government's power to regulate private companies.
D)Antitrust laws can reduce social welfare if they prevent mergers that would lower costs through more efficient joint production.
A)Two examples of early antitrust laws are the Clinton and Stigler Antitrust Acts.
B)Antitrust laws automatically prevent mergers between companies that produce similar products.
C)Antitrust laws reduce the government's power to regulate private companies.
D)Antitrust laws can reduce social welfare if they prevent mergers that would lower costs through more efficient joint production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The fundamental cause of monopolies is barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Average revenue for a monopoly is the total revenue divided by the quantity produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
With perfect price discrimination the monopoly
A)eliminates all price discrimination by charging each customer the same price.
B)charges each customer an amount equal to the monopolist's marginal cost of production.
C)eliminates deadweight loss.
D)eliminates profits and increases consumer surplus.
A)eliminates all price discrimination by charging each customer the same price.
B)charges each customer an amount equal to the monopolist's marginal cost of production.
C)eliminates deadweight loss.
D)eliminates profits and increases consumer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A patent gives a single person or firm the exclusive right to sell some good or service forever.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Firms with some degree of monopoly power are common,but firms with substantial monopoly power are rare.
B)Firms with some degree of monopoly power are rare,as are firms with substantial monopoly power.
C)Firms with some degree of monopoly power are common,as are firms with substantial monopoly power.
D)Firms with some degree of monopoly power are rare,but firms with substantial monopoly power are common.
A)Firms with some degree of monopoly power are common,but firms with substantial monopoly power are rare.
B)Firms with some degree of monopoly power are rare,as are firms with substantial monopoly power.
C)Firms with some degree of monopoly power are common,as are firms with substantial monopoly power.
D)Firms with some degree of monopoly power are rare,but firms with substantial monopoly power are common.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A monopolist's supply curve is horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
How does a competitive market compare to a monopoly that engages in perfect price discrimination?
A)In both cases,total social welfare is the same.
B)Total social welfare is higher in the competitive market than with the perfectly price discriminating monopoly.
C)In both cases,some potentially mutually beneficial trades do not occur.
D)Consumer surplus is the same in both cases.
A)In both cases,total social welfare is the same.
B)Total social welfare is higher in the competitive market than with the perfectly price discriminating monopoly.
C)In both cases,some potentially mutually beneficial trades do not occur.
D)Consumer surplus is the same in both cases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A monopolist produces where P = MC = MR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A monopolist maximizes profit by producing an output level where marginal cost equals price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following statements comparing monopoly with competition is correct?
A)A monopolist produces a higher level of output and charges a lower price than a competitive firm would.
B)With perfect price discrimination,the total surplus under monopoly can be the same as under competition.
C)With or without price discrimination,the consumer surplus under monopoly is at least as large as it would be under competition.
D)The deadweight loss associated with monopoly is caused by the positive economic profits of the monopolist; competitive firms do not earn a positive economic profit so there is no deadweight loss under competition.
A)A monopolist produces a higher level of output and charges a lower price than a competitive firm would.
B)With perfect price discrimination,the total surplus under monopoly can be the same as under competition.
C)With or without price discrimination,the consumer surplus under monopoly is at least as large as it would be under competition.
D)The deadweight loss associated with monopoly is caused by the positive economic profits of the monopolist; competitive firms do not earn a positive economic profit so there is no deadweight loss under competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is the preferred strategy for the government to follow to remedy the inefficient allocation of resources associated with monopolies?
A)preventing mergers through antitrust laws
B)regulating the prices that monopolies can charge
C)doing nothing
D)None of the above strategies is preferred.Each is a viable strategy.
A)preventing mergers through antitrust laws
B)regulating the prices that monopolies can charge
C)doing nothing
D)None of the above strategies is preferred.Each is a viable strategy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In a monopoly market,the socially efficient quantity of output is typically higher than the profit-maximizing quantity of output for the monopolist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Even with market power,monopolists cannot achieve any level of profit they desire because they will sell lower quantities at higher prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In order for antitrust laws to raise social welfare,the government must
A)disallow synergy benefits from accruing to monopolists.
B)disallow any mergers from taking place.
C)be able to determine which mergers are desirable and which are not.
D)always attempt to keep markets in their most competitive form.
A)disallow synergy benefits from accruing to monopolists.
B)disallow any mergers from taking place.
C)be able to determine which mergers are desirable and which are not.
D)always attempt to keep markets in their most competitive form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
For a long while,electricity producers were thought to be a classic example of a natural monopoly.People held this view because
A)the average cost of producing units of electricity by one producer in a specific region was lower than if the same quantity were produced by two or more producers in the same region.
B)the average cost of producing units of electricity by one producer in a specific region was higher than if the same quantity were produced by two or more produced in the same region.
C)the marginal cost of producing units of electricity by one producer in a specific region was higher than if the same quantity were produced by two or more producers in the same region.
D)electricity is a special non-excludable good that could never be sold in a competitive market.
A)the average cost of producing units of electricity by one producer in a specific region was lower than if the same quantity were produced by two or more producers in the same region.
B)the average cost of producing units of electricity by one producer in a specific region was higher than if the same quantity were produced by two or more produced in the same region.
C)the marginal cost of producing units of electricity by one producer in a specific region was higher than if the same quantity were produced by two or more producers in the same region.
D)electricity is a special non-excludable good that could never be sold in a competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Suppose a profit-maximizing monopolist faces a constant marginal cost of 20 dollars produces an output level of 100 units,and charges a price of 50 dollars.The socially efficient level of output is 200 units.Assume that the demand curve and marginal revenue curve are the typical downward-sloping straight lines.The monopoly deadweight loss equals 1,500 dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
One problem with regulating a monopolist on the basis of cost is that
A)by focusing on costs,the regulators ignore profits.
B)it does not provide an incentive for the monopolist to reduce its cost.
C)a monopolist's costs,by definition,are higher than costs of perfectly competitive firms.
D)a monopolist is still able to generate excessive economic profits.
A)by focusing on costs,the regulators ignore profits.
B)it does not provide an incentive for the monopolist to reduce its cost.
C)a monopolist's costs,by definition,are higher than costs of perfectly competitive firms.
D)a monopolist is still able to generate excessive economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Graphically depict the deadweight loss caused by a monopoly.How is this similar to the deadweight loss from taxation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Movie theatres charge different prices to different groups of people based on the differing marginal costs that exist from group to group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In order for a firm to maximize profits through price discrimination,the firm must have some market power and be able to prevent arbitrage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The best solution to the problem of welfare loss from monopoly is public ownership.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Some companies merge in order to lower costs through efficient joint production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Explain how a profit-maximizing monopolist chooses its level of output and the price of its goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Assume that a monopolist decides to maximize revenue rather than profit.How does this operating objective change the size of the deadweight loss?
If you are a "benevolent" manager of a monopoly firm and are interested in reducing the deadweight loss of monopoly,should you maximize profits or maximize revenue?
Explain your answer.
If you are a "benevolent" manager of a monopoly firm and are interested in reducing the deadweight loss of monopoly,should you maximize profits or maximize revenue?
Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Give some examples of the benefits and costs of antitrust laws.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Describe how government is involved in creating a monopoly.Why might the government create one?
Give an example.
Give an example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A monopolist that can practice perfect price discrimination will not impose a deadweight loss on society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



