Deck 26: Saving,investment,and the Financial System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/61
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Saving,investment,and the Financial System
1
People who buy stock in a corporation such as General Electric become
A)creditors of General Electric,so the benefits of holding the stock depend on General Electric's profits.
B)creditors of General Electric,but the benefits of holding the stock do not depend on General Electric's profits.
C)part owners of General Electric,so the benefits of holding the stock depend on General Electric's profits.
D)part owners of General Electric,but the benefits of holding the stock do not depend on General Electric's profits.
A)creditors of General Electric,so the benefits of holding the stock depend on General Electric's profits.
B)creditors of General Electric,but the benefits of holding the stock do not depend on General Electric's profits.
C)part owners of General Electric,so the benefits of holding the stock depend on General Electric's profits.
D)part owners of General Electric,but the benefits of holding the stock do not depend on General Electric's profits.
C
2
A mutual fund
A)is a financial institution that stands between savers and borrowers.
B)is a financial intermediary.
C)allows people with small amounts of money to diversify their holdings.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)is a financial institution that stands between savers and borrowers.
B)is a financial intermediary.
C)allows people with small amounts of money to diversify their holdings.
D)All of the above are correct.
D
3
We associate the term debt finance with
A)the bond market,and we associate the term equity finance with the stock market.
B)the stock market,and we associate the term equity finance with the bond market.
C)financial intermediaries,and we associate the term equity finance with financial markets.
D)financial markets,and we associate the term equity finance with financial intermediaries.
A)the bond market,and we associate the term equity finance with the stock market.
B)the stock market,and we associate the term equity finance with the bond market.
C)financial intermediaries,and we associate the term equity finance with financial markets.
D)financial markets,and we associate the term equity finance with financial intermediaries.
A
4
The fact that borrowers sometimes default on their loans by declaring bankruptcy is directly related to the characteristic of a bond called
A)credit risk.
B)interest risk.
C)term risk.
D)private risk.
A)credit risk.
B)interest risk.
C)term risk.
D)private risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following would both make the interest rate on a bond higher than otherwise?
A)the interest it pays is taxed and it is long term
B)the interest it pays is taxed and it is short term
C)the interest it pays is tax exempt and it is long term
D)the interest it pays is tax exempt and it is short term
A)the interest it pays is taxed and it is long term
B)the interest it pays is taxed and it is short term
C)the interest it pays is tax exempt and it is long term
D)the interest it pays is tax exempt and it is short term

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is correct?
A)Lenders sell bonds and borrowers buy them.
B)Long-term bonds usually pay a lower interest rate than do short-term bonds because long-term bonds are riskier.
C)The term junk bonds refers to bonds that have been resold many times.
D)None of the above is correct.
A)Lenders sell bonds and borrowers buy them.
B)Long-term bonds usually pay a lower interest rate than do short-term bonds because long-term bonds are riskier.
C)The term junk bonds refers to bonds that have been resold many times.
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The sale of stocks
A)and bonds to raise money is called debt finance.
B)and bonds to raise money is called equity finance.
C)to raise money is called debt finance,while the sale of bonds to raise funds is called equity finance.
D)to raise money is called equity finance,while the sale of bonds to raise funds is called debt finance.
A)and bonds to raise money is called debt finance.
B)and bonds to raise money is called equity finance.
C)to raise money is called debt finance,while the sale of bonds to raise funds is called equity finance.
D)to raise money is called equity finance,while the sale of bonds to raise funds is called debt finance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Two bonds have the same term to maturity.The first was issued by a government and the probability of default is believed to be low.The other was issued by a corporation and the probability of default is believed to be high.Which of the following is correct?
A)Because they have the same term to maturity the interest rates should be the same.
B)Because of the differences in tax treatment and credit risk,the state bond should have the higher interest rate.
C)Because of the differences in tax treatment and credit risk,the corporate bond should have the higher interest rate.
D)It is not possible to say if one bond has a higher interest rate than the other.
A)Because they have the same term to maturity the interest rates should be the same.
B)Because of the differences in tax treatment and credit risk,the state bond should have the higher interest rate.
C)Because of the differences in tax treatment and credit risk,the corporate bond should have the higher interest rate.
D)It is not possible to say if one bond has a higher interest rate than the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following statements about the term of a bond is correct?
A)Term refers to the various characteristics of a bond,including its interest rate and tax treatment.
B)The term of a bond is determined entirely by its credit risk.
C)The term of a bond is determined entirely by how much sales charge the buyer of the bond pays when he or she purchases the bond.
D)Interest rates on long-term bonds are usually higher than interest rates on short-term bonds.
A)Term refers to the various characteristics of a bond,including its interest rate and tax treatment.
B)The term of a bond is determined entirely by its credit risk.
C)The term of a bond is determined entirely by how much sales charge the buyer of the bond pays when he or she purchases the bond.
D)Interest rates on long-term bonds are usually higher than interest rates on short-term bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A stock index is
A)an average of a group of stock prices.
B)an average of a group of stock yields.
C)a measure of the risk relative to the profitability of corporations.
D)a report in a newspaper or other media outlet on the price of the stock and earnings of the corporation that issued the stock.
A)an average of a group of stock prices.
B)an average of a group of stock yields.
C)a measure of the risk relative to the profitability of corporations.
D)a report in a newspaper or other media outlet on the price of the stock and earnings of the corporation that issued the stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
You observe a closed economy that has a government deficit and positive investment.Which of the following is correct?
A)Private and public saving are both positive.
B)Private saving is positive; public saving is negative.
C)Private saving is negative; public saving is positive.
D)Both private saving and public saving are negative.
A)Private and public saving are both positive.
B)Private saving is positive; public saving is negative.
C)Private saving is negative; public saving is positive.
D)Both private saving and public saving are negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Compared to stocks,bonds offer the holder
A)lower risk and lower potential return.
B)lower risk and higher potential return.
C)higher risk and lower potential return.
D)higher risk and higher potential return.
A)lower risk and lower potential return.
B)lower risk and higher potential return.
C)higher risk and lower potential return.
D)higher risk and higher potential return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The primary economic function of the financial system is to
A)keep interest rates low.
B)provide expert advice to savers and investors.
C)match one person's consumption expenditures with another person's capital expenditures.
D)match one person's saving with another person's investment.
A)keep interest rates low.
B)provide expert advice to savers and investors.
C)match one person's consumption expenditures with another person's capital expenditures.
D)match one person's saving with another person's investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
As an alternative to selling shares of stock as a means of raising funds,a large company could,instead,
A)invest in physical capital.
B)use equity finance.
C)sell bonds.
D)purchase bonds.
A)invest in physical capital.
B)use equity finance.
C)sell bonds.
D)purchase bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Retained earnings are
A)earnings of a company that are not paid out to stockholders.
B)the amount of revenue a corporation receives for the sale of its products minus its costs of production as measured by its accountants.
C)the single most important piece of information about a stock.
D)computed by multiplying the dividend yield by the price of the stock.
A)earnings of a company that are not paid out to stockholders.
B)the amount of revenue a corporation receives for the sale of its products minus its costs of production as measured by its accountants.
C)the single most important piece of information about a stock.
D)computed by multiplying the dividend yield by the price of the stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Long-term bonds are
A)riskier than short-term bonds,and so interest rates on long-term bonds are usually lower than interest rates on short-term bonds.
B)riskier than short-term bonds,and so interest rates on long-term bonds are usually higher than interest rates on short-term bonds.
C)less risky than short-term bonds,and so interest rates on long-term bonds are usually lower than interest rates on short-term bonds.
D)less risky than short-term bonds,and so interest rates on long-term bonds are usually higher than interest rates on short-term bonds.
A)riskier than short-term bonds,and so interest rates on long-term bonds are usually lower than interest rates on short-term bonds.
B)riskier than short-term bonds,and so interest rates on long-term bonds are usually higher than interest rates on short-term bonds.
C)less risky than short-term bonds,and so interest rates on long-term bonds are usually lower than interest rates on short-term bonds.
D)less risky than short-term bonds,and so interest rates on long-term bonds are usually higher than interest rates on short-term bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose the government finds a major defect in one of a company's products and demands that the product be taken off the market.We would expect that the
A)supply of existing shares of the stock and the price will both rise.
B)supply of existing shares of the stock and the price will both fall.
C)demand for existing shares of the stock and the price will both rise.
D)demand for existing shares of the stock and the price will both fall.
A)supply of existing shares of the stock and the price will both rise.
B)supply of existing shares of the stock and the price will both fall.
C)demand for existing shares of the stock and the price will both rise.
D)demand for existing shares of the stock and the price will both fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Over-the-Rhine Cheese Corporation had a P/E ratio of 20,retained earnings of 1.70 dinars per share and a dividend of 0.80 dinars.What was its dividend yield?
A)1.25%
B)1.60%
C)3.33%
D)7.50%
A)1.25%
B)1.60%
C)3.33%
D)7.50%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A low P/E for a stock indicates that
A)people may expect earnings to fall in the future,perhaps because the firm will be faced with increased competition.
B)its dividends have been low so that no one is willing to pay very much for it.
C)the corporation is possibly overvalued.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)people may expect earnings to fall in the future,perhaps because the firm will be faced with increased competition.
B)its dividends have been low so that no one is willing to pay very much for it.
C)the corporation is possibly overvalued.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A corporation's earnings are the amount of revenue it receives for the sale of its products
A)minus its cost of production as measured by its accountants.Earnings must be paid out as dividends.
B)minus its cost of production as measured by its accountants.Earnings may be paid out as dividends or retained by the corporation.
C)minus its direct and indirect costs as measured by its economists.Earnings must be paid out as dividends.
D)minus its direct and indirect cost as measure by its economists.Earnings may be paid out as dividends or retained by the corporation.
A)minus its cost of production as measured by its accountants.Earnings must be paid out as dividends.
B)minus its cost of production as measured by its accountants.Earnings may be paid out as dividends or retained by the corporation.
C)minus its direct and indirect costs as measured by its economists.Earnings must be paid out as dividends.
D)minus its direct and indirect cost as measure by its economists.Earnings may be paid out as dividends or retained by the corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following events could explain a decrease in interest rates together with an increase in investment?
A)The government went from surplus to deficit.
B)The government instituted an investment tax credit.
C)The government reduced the tax rate on savings.
D)None of the above is correct.
A)The government went from surplus to deficit.
B)The government instituted an investment tax credit.
C)The government reduced the tax rate on savings.
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In a closed economy,national saving equals
A)investment.
B)income minus the sum of consumption and government purchases.
C)private saving plus public saving.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)investment.
B)income minus the sum of consumption and government purchases.
C)private saving plus public saving.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Figure 26-1. 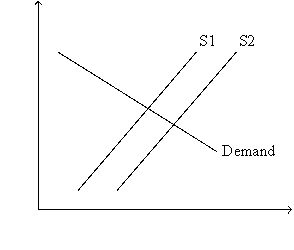
Refer to Figure 26-1.Which of the following events would shift the supply curve from S1 to S2?
A)In response to tax reform,firms are encouraged to invest more than they previously invested.
B)In response to tax reform,households are encouraged to save more than they previously saved.
C)Government goes from running a balanced budget to running a budget deficit.
D)Any of the above events would shift the supply curve from S1 to S2.

Refer to Figure 26-1.Which of the following events would shift the supply curve from S1 to S2?
A)In response to tax reform,firms are encouraged to invest more than they previously invested.
B)In response to tax reform,households are encouraged to save more than they previously saved.
C)Government goes from running a balanced budget to running a budget deficit.
D)Any of the above events would shift the supply curve from S1 to S2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A budget surplus is created if
A)the government sells more bonds than it buys back.
B)the government spends more than it receives in tax revenue.
C)private saving is greater than zero.
D)None of the above is correct.
A)the government sells more bonds than it buys back.
B)the government spends more than it receives in tax revenue.
C)private saving is greater than zero.
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the government currently has a budget deficit,then
A)it does not necessarily have a debt.
B)its debt is increasing.
C)government expenditures are greater than taxes.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)it does not necessarily have a debt.
B)its debt is increasing.
C)government expenditures are greater than taxes.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The slope of the demand for loanable funds curve represents the
A)positive relation between the real interest rate and investment.
B)negative relation between the real interest rate and investment.
C)positive relation between the real interest rate and saving.
D)negative relation between the real interest rate and saving.
A)positive relation between the real interest rate and investment.
B)negative relation between the real interest rate and investment.
C)positive relation between the real interest rate and saving.
D)negative relation between the real interest rate and saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If national saving in a closed economy is greater than zero,which of the following must be true?
A)Either public saving or private saving must be greater than zero.
B)Investment is positive.
C)
D)All of the above are correct.
A)Either public saving or private saving must be greater than zero.
B)Investment is positive.
C)
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If Japan goes from a small budget deficit to a large budget deficit,it will reduce
A)private saving and so shift the supply of loanable funds left.
B)investment and so shift the demand for loanable funds left.
C)public saving and so shift the supply of loanable funds left.
D)None of the above is correct.
A)private saving and so shift the supply of loanable funds left.
B)investment and so shift the demand for loanable funds left.
C)public saving and so shift the supply of loanable funds left.
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
According to the definitions of national saving and private saving,if Y,C,and G remained the same,an increase in taxes would
A)raise both national saving and private saving.
B)raise national saving and reduce private saving.
C)leave national saving and private saving unchanged.
D)leave national saving unchanged and reduce private saving.
A)raise both national saving and private saving.
B)raise national saving and reduce private saving.
C)leave national saving and private saving unchanged.
D)leave national saving unchanged and reduce private saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If the quantity of loanable funds demanded exceeds the quantity of loanable funds supplied,
A)there is a surplus and the interest rate is above the equilibrium level.
B)there is a surplus and the interest rate is below the equilibrium level.
C)there is a shortage and the interest rate is above the equilibrium level.
D)there is a shortage and the interest rate is below the equilibrium level.
A)there is a surplus and the interest rate is above the equilibrium level.
B)there is a surplus and the interest rate is below the equilibrium level.
C)there is a shortage and the interest rate is above the equilibrium level.
D)there is a shortage and the interest rate is below the equilibrium level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Suppose that in a closed economy GDP is 11,000,consumption is 7,500,and taxes are 2,000.What value of government purchases would make national savings equal to 1,000 and at that value would the government have a deficit or surplus?
A)2,500,deficit
B)2,500,surplus
C)1,000,deficit
D)1,000,surplus
A)2,500,deficit
B)2,500,surplus
C)1,000,deficit
D)1,000,surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In 2002 mortgage rates fell and mortgage lending increased.Which of the following could explain both of these changes?
A)The demand for loanable funds shifted rightward.
B)The demand for loanable funds shifted leftward.
C)The supply of loanable funds shifted rightward.
D)The supply of loanable funds shifted leftward.
A)The demand for loanable funds shifted rightward.
B)The demand for loanable funds shifted leftward.
C)The supply of loanable funds shifted rightward.
D)The supply of loanable funds shifted leftward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Other things the same,when the interest rate rises,
A)people would want to lend more,making the supply of loanable funds increase.
B)people would want to lend less,making the supply of loanable funds decrease.
C)people would want to lend more,making the quantity of loanable funds supplied increase.
D)people would want to lend less,making the quantity of loanable funds supplied decrease.
A)people would want to lend more,making the supply of loanable funds increase.
B)people would want to lend less,making the supply of loanable funds decrease.
C)people would want to lend more,making the quantity of loanable funds supplied increase.
D)people would want to lend less,making the quantity of loanable funds supplied decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What would happen in the market for loanable funds if the government were to increase the tax on interest income?
A)Interest rates would rise.
B)Interest rates would be unaffected.
C)Interest rates would fall.
D)The effect on the interest rate is uncertain.
A)Interest rates would rise.
B)Interest rates would be unaffected.
C)Interest rates would fall.
D)The effect on the interest rate is uncertain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following equations represents GDP for an open economy?
A)Y = C + I + G + NX
B)NX = I - G
C)I = Y - C + G + NX
D)Y = C + I + G
A)Y = C + I + G + NX
B)NX = I - G
C)I = Y - C + G + NX
D)Y = C + I + G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the demand for loanable funds shifts to the left,then the equilibrium interest rate
A)and quantity of loanable funds rise.
B)and quantity of loanable funds fall.
C)rises and the quantity of loanable funds falls.
D)falls and the quantity of loanable funds rises.
A)and quantity of loanable funds rise.
B)and quantity of loanable funds fall.
C)rises and the quantity of loanable funds falls.
D)falls and the quantity of loanable funds rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For an imaginary closed economy,T = 5,000; S =11,000; C = 50,000; and the government is running a budget deficit of 1,000.Then
A)private saving = 10,000 and GDP = 54,000.
B)private saving = 10,000 and GDP = 58,000.
C)private saving = 12,000 and GDP = 67,000.
D)private saving = 12,000 and GDP = 72,000.
A)private saving = 10,000 and GDP = 54,000.
B)private saving = 10,000 and GDP = 58,000.
C)private saving = 12,000 and GDP = 67,000.
D)private saving = 12,000 and GDP = 72,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If an economy is closed and if it has no government,then
A)national saving = private saving.
B)total income = consumption + investment.
C)saving = total income - consumption.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)national saving = private saving.
B)total income = consumption + investment.
C)saving = total income - consumption.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
For an economy that engages in international trade,GDP is divided into four components.Which of the following items is not one of those components?
A)consumption
B)taxes
C)government purchases
D)net exports
A)consumption
B)taxes
C)government purchases
D)net exports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The identity that shows that total income and total expenditure are equal is
A)GDP = Y.
B)Y = DI + T + NX.
C)GDP = GNP - NX.
D)Y = C + I + G + NX.
A)GDP = Y.
B)Y = DI + T + NX.
C)GDP = GNP - NX.
D)Y = C + I + G + NX.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Banks and mutual funds are examples of financial markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The term crowding out refers to decreases in the interest rate caused by government budget surpluses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What are the basic differences between bonds and stocks?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An increase in the demand for loanable funds increases the equilibrium interest rate and increases the equilibrium level of saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A decrease in taxes on interest income would increase the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Anything other than a change in the interest rate that decreases national saving shifts the supply of loanable funds to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
All financial intermediaries are financial institutions,but not all financial institutions are financial intermediaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Financial crises seldom involve economic downturns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Public saving is equal to national saving minus private saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A government may use deficit financing to smooth tax rates over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The financial system coordinates investment and saving,which are important determinants of long-run real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When economists refer to investment,they mean the purchasing of stocks and bonds and other types of saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
On a graph that depicts the market for loanable funds,the nominal interest rate is measured along the vertical axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose that you are a broker and people tell you the following about themselves.What sort of bond would you recommend to each?
Defend your choices.
a."I am in a high federal income tax bracket and I don't want to take very much risk."
b."I want a high return and I am willing to take a lot of risk to get it."
c."I want a decent return and I have enough deductions that I don't value tax breaks highly."
Defend your choices.
a."I am in a high federal income tax bracket and I don't want to take very much risk."
b."I want a high return and I am willing to take a lot of risk to get it."
c."I want a decent return and I have enough deductions that I don't value tax breaks highly."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In the national income accounting identity showing the equality between national saving and investment,what are the algebraic expressions for private saving and public saving?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When a firm wants to borrow directly from the public to finance the purchase of new equipment,it does so by selling shares of stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Most entrepreneurs finance their purchases of real capital using their past saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A government reduces its budget deficit,but at the same time people become concerned that the outlook for future government expenditures and revenues increase the chance it will default.Which of the following is correct.
A)The reduced budget deficit will raise interest rates in general.The increased risk of default will raise interest rates on government bonds.
B)The reduced budget deficit will raise interest rates in general.The increased risk of default will reduce interest rates on government bonds.
C)The reduced budget deficit will reduce interest rates in general.The increased risk of default will raise interest rates on government bonds.
D)The reduced budget deficit will reduce interest rates in general.The increased risk of default will reduce interest rates on government bonds.
A)The reduced budget deficit will raise interest rates in general.The increased risk of default will raise interest rates on government bonds.
B)The reduced budget deficit will raise interest rates in general.The increased risk of default will reduce interest rates on government bonds.
C)The reduced budget deficit will reduce interest rates in general.The increased risk of default will raise interest rates on government bonds.
D)The reduced budget deficit will reduce interest rates in general.The increased risk of default will reduce interest rates on government bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When an economy's government goes from running a budget deficit to running a budget surplus,the economy's long-run growth prospects are improved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Your brother-in-law wants to buy either stock or bonds in Cedar Valley Furniture,which manufactures wooden furniture.He wants your advice on whether to buy stock or bonds.Explain how each of his quotes below should affect his choice between the stock and the bond.
a."I have reason to believe that people are soon going to find rocking chairs have health benefits."
b."I would like to tell people I am part owner of Cedar Valley Furniture."
c."I do not want to take on much risk."
a."I have reason to believe that people are soon going to find rocking chairs have health benefits."
b."I would like to tell people I am part owner of Cedar Valley Furniture."
c."I do not want to take on much risk."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Draw and label a graph showing equilibrium in the market for loanable funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



