Deck 29: Unemployment
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/64
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 29: Unemployment
1
Table 29-3
2010 Labor Data for Adults (age 16 and older) in Meditor
-Refer to Table 29-3.What is the adult female labor-force participation rate in Meditor?
A)38.1 percent
B)61.9 percent
C)66.7 percent
D)95.2 percent
2010 Labor Data for Adults (age 16 and older) in Meditor
-Refer to Table 29-3.What is the adult female labor-force participation rate in Meditor?
A)38.1 percent
B)61.9 percent
C)66.7 percent
D)95.2 percent
66.7 percent
2
The labor-force participation rate measures the percentage of the
A)total adult population that is in the labor force.
B)total adult population that is employed.
C)labor force that is employed.
D)labor force that is either employed or unemployed.
A)total adult population that is in the labor force.
B)total adult population that is employed.
C)labor force that is employed.
D)labor force that is either employed or unemployed.
A
3
Table 29-3
2010 Labor Data for Adults (age 16 and older) in Meditor
-Refer to Table 29-3.What is the adult male population in Meditor?
A)50 million
B)90 million
C)130 million
D)135 million
2010 Labor Data for Adults (age 16 and older) in Meditor
-Refer to Table 29-3.What is the adult male population in Meditor?
A)50 million
B)90 million
C)130 million
D)135 million
135 million
4
The labor-force participation rate is computed as
A)(Employed Adult Population) 100.
B)(Employed Labor Force) 100.
C)(Labor Force Adult Population) 100.
D)(Adult Population Labor Force) 100.
A)(Employed Adult Population) 100.
B)(Employed Labor Force) 100.
C)(Labor Force Adult Population) 100.
D)(Adult Population Labor Force) 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Table 29-2
2009 Labor Data for Baltivia
-Refer to Table 29-2.What was Baltivia's labor-force participation rate in 2009?
A)55 percent
B)63 percent
C)66.9 percent
D)87.3 percent
2009 Labor Data for Baltivia
-Refer to Table 29-2.What was Baltivia's labor-force participation rate in 2009?
A)55 percent
B)63 percent
C)66.9 percent
D)87.3 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
-Refer to Sample Population.How many in the sample are unemployed?
A)5
B)4
C)3
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
-Refer to Sample Population.How many in the sample are in the labor force?
A)10
B)9
C)8
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Table 29-3
2010 Labor Data for Adults (age 16 and older) in Meditor
-Refer to Table 29-3.What is the adult labor force in Meditor?
A)90 million
B)150 million
C)160 million
D)230 million
2010 Labor Data for Adults (age 16 and older) in Meditor
-Refer to Table 29-3.What is the adult labor force in Meditor?
A)90 million
B)150 million
C)160 million
D)230 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The labor-force participation rate tells us the fraction of the population that
A)is able to participate in the labor market.
B)has ever been employed.
C)has chosen to participate in the labor market.
D)has chosen not to participate in the labor market.
A)is able to participate in the labor market.
B)has ever been employed.
C)has chosen to participate in the labor market.
D)has chosen not to participate in the labor market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A person who is not employed and claims to be trying hard to find a job but really is not trying hard to find a job
A)is counted as out of the labor force but should be counted as unemployed.
B)is counted as unemployed but should be counted as out of the labor force.
C)is correctly counted as out of the labor force.
D)is correctly counted as unemployed.
A)is counted as out of the labor force but should be counted as unemployed.
B)is counted as unemployed but should be counted as out of the labor force.
C)is correctly counted as out of the labor force.
D)is correctly counted as unemployed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose people in the adult population in a small country are classified based on their age.
-Refer to Labor Force Statistics by Age.Suppose that the natural rate of unemployment is 5% for those under 55 and 3% for those 55 and older.The cyclical unemployment rate for those under 55 is
A).88% which is greater than the cyclical unemployment rate for those 55 and older.
B).88% which is less than the cyclical unemployment rate for those 55 and older.
C)-.83% which is greater than the cyclical unemployment rate for those 55 and older.
D)-.83% which is less than the cyclical unemployment rate for those 55 and older.
-Refer to Labor Force Statistics by Age.Suppose that the natural rate of unemployment is 5% for those under 55 and 3% for those 55 and older.The cyclical unemployment rate for those under 55 is
A).88% which is greater than the cyclical unemployment rate for those 55 and older.
B).88% which is less than the cyclical unemployment rate for those 55 and older.
C)-.83% which is greater than the cyclical unemployment rate for those 55 and older.
D)-.83% which is less than the cyclical unemployment rate for those 55 and older.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Suppose people in the adult population in a small country are classified based on their age.
-Refer to Labor Force Statistics by Age.In the proper order,which age group has the highest unemployment rate and which has the highest participation rate?
A)under 55,under 55
B)under 55,55 and older
C)55 and older,under 55
D)55 and older,55 and older
-Refer to Labor Force Statistics by Age.In the proper order,which age group has the highest unemployment rate and which has the highest participation rate?
A)under 55,under 55
B)under 55,55 and older
C)55 and older,under 55
D)55 and older,55 and older

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Suppose some country had an adult population of about 46 million,a labor-force participation rate of 75 percent,and an unemployment rate of 8 percent.How many people were unemployed?
A)2.54 million
B)2.76 million
C)3.68 million
D)8 million
A)2.54 million
B)2.76 million
C)3.68 million
D)8 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Table 29-2
2009 Labor Data for Baltivia
-Refer to Table 29-2.How many people were unemployed in Baltivia in 2009?
A)1,400
B)1,600
C)2,000
D)2,780
2009 Labor Data for Baltivia
-Refer to Table 29-2.How many people were unemployed in Baltivia in 2009?
A)1,400
B)1,600
C)2,000
D)2,780

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The unemployment rate is computed as the number of unemployed
A)divided by the labor force,all times 100.
B)divided by the number of employed,all times 100.
C)divided by the adult population,all times 100.
D)times the labor-force participation rate,all times 100.
A)divided by the labor force,all times 100.
B)divided by the number of employed,all times 100.
C)divided by the adult population,all times 100.
D)times the labor-force participation rate,all times 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose that some people are counted as unemployed when,to maintain unemployment compensation,they search for work only at places where they are unlikely to be hired.If these individuals were counted as out of the labor force instead of as unemployed,then
A)both the unemployment rate and labor-force participation rate would be higher.
B)both the unemployment rate and labor-force participation rate would be lower.
C)the unemployment rate would be lower and the labor-force participation rate would be higher.
D)the unemployment rate would be higher and the participation rate would be lower.
A)both the unemployment rate and labor-force participation rate would be higher.
B)both the unemployment rate and labor-force participation rate would be lower.
C)the unemployment rate would be lower and the labor-force participation rate would be higher.
D)the unemployment rate would be higher and the participation rate would be lower.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Table 29-3
2010 Labor Data for Adults (age 16 and older) in Meditor
-Refer to Table 29-3.What is the adult population in Meditor?
A)90 million
B)160 million
C)230 million
D)240 million
2010 Labor Data for Adults (age 16 and older) in Meditor
-Refer to Table 29-3.What is the adult population in Meditor?
A)90 million
B)160 million
C)230 million
D)240 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Table 29-3
2010 Labor Data for Adults (age 16 and older) in Meditor
-Refer to Table 29-3.What is the adult male labor force in Meditor?
A)50 million
B)85 million
C)90 million
D)130 million
2010 Labor Data for Adults (age 16 and older) in Meditor
-Refer to Table 29-3.What is the adult male labor force in Meditor?
A)50 million
B)85 million
C)90 million
D)130 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Table 29-2
2009 Labor Data for Baltivia
-Refer to Table 29-2.How many people were employed in Baltivia in 2009?
A)9,600
B)10,600
C)11,000
D)11,200
2009 Labor Data for Baltivia
-Refer to Table 29-2.How many people were employed in Baltivia in 2009?
A)9,600
B)10,600
C)11,000
D)11,200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose that the adult population is 4 million,the number of unemployed is 0.25 million,and the labor-force participation rate is 75%.What is the unemployment rate?
A)6.25%
B)8.3%
C)9.1%
D)18.75%
A)6.25%
B)8.3%
C)9.1%
D)18.75%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When a union bargains successfully with employers,in that industry,
A)both the quantity of labor supplied and the quantity of labor demanded increase.
B)both the quantity of labor supplied and the quantity of labor demanded decrease.
C)the quantity of labor supplied increases and the quantity of labor demanded decreases.
D)the quantity of labor demanded increases and the quantity of labor supplied decreases.
A)both the quantity of labor supplied and the quantity of labor demanded increase.
B)both the quantity of labor supplied and the quantity of labor demanded decrease.
C)the quantity of labor supplied increases and the quantity of labor demanded decreases.
D)the quantity of labor demanded increases and the quantity of labor supplied decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Frictional unemployment is inevitable because
A)sectoral shifts are always happening.
B)there is a minimum-wage law
C)some people do not want to be employed.
D)unions are very popular
A)sectoral shifts are always happening.
B)there is a minimum-wage law
C)some people do not want to be employed.
D)unions are very popular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If unions were formed in more industries,the supply of labor in other industries would
A)increase,causing employment in other industries to rise.
B)increase,causing employment in other industries to fall.
C)decrease,causing employment in other industries to rise.
D)decrease,causing employment in other industries to fall.
A)increase,causing employment in other industries to rise.
B)increase,causing employment in other industries to fall.
C)decrease,causing employment in other industries to rise.
D)decrease,causing employment in other industries to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Economists would predict that,other things the same,the more generous unemployment compensation a country has,
A)the shorter the duration of each spell of unemployment,and the higher the unemployment rate.
B)the shorter the duration of each spell of unemployment,and the lower the unemployment rate.
C)the longer the duration of each spell of unemployment,and the higher the unemployment rate.
D)the longer the duration of each spell of unemployment,and the lower the unemployment rate.
A)the shorter the duration of each spell of unemployment,and the higher the unemployment rate.
B)the shorter the duration of each spell of unemployment,and the lower the unemployment rate.
C)the longer the duration of each spell of unemployment,and the higher the unemployment rate.
D)the longer the duration of each spell of unemployment,and the lower the unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Most spells of unemployment are
A)long,and most unemployment observed at any given time is long term.
B)long,but most unemployment observed at any given time is short term.
C)short,but most unemployment observed at any given time is long term.
D)short,and most unemployment observed at any given time is short term.
A)long,and most unemployment observed at any given time is long term.
B)long,but most unemployment observed at any given time is short term.
C)short,but most unemployment observed at any given time is long term.
D)short,and most unemployment observed at any given time is short term.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose that telemarketers are not unionized.If they unionize,then the supply of labor in other sectors of the economy will
A)decrease,raising wages in industries that are not unionized.
B)decrease,reducing wages in industries that are not unionized.
C)increase,raising wages in industries that are not unionized.
D)increase,reducing wages in industries that are not unionized.
A)decrease,raising wages in industries that are not unionized.
B)decrease,reducing wages in industries that are not unionized.
C)increase,raising wages in industries that are not unionized.
D)increase,reducing wages in industries that are not unionized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Government-run employment agencies and public training programs are operated by the government to try to facilitate job search and reduce unemployment.
A)Almost all economists agree that such programs are of no use.
B)Almost all economists agree that such programs work very well.
C)Some economists claim that the government can do these things no better than firms and individuals could do them for themselves.
D)Some economists claim that these programs increase frictional unemployment.
A)Almost all economists agree that such programs are of no use.
B)Almost all economists agree that such programs work very well.
C)Some economists claim that the government can do these things no better than firms and individuals could do them for themselves.
D)Some economists claim that these programs increase frictional unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Other things the same,an increase in wages above their equilibrium level
A)increases frictional unemployment but leaves the natural rate of unemployment unchanged.
B)increases frictional unemployment and increases the natural rate of unemployment.
C)increases structural unemployment but leaves the natural rate of unemployment unchanged.
D)increases structural unemployment and increases the natural rate of unemployment.
A)increases frictional unemployment but leaves the natural rate of unemployment unchanged.
B)increases frictional unemployment and increases the natural rate of unemployment.
C)increases structural unemployment but leaves the natural rate of unemployment unchanged.
D)increases structural unemployment and increases the natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Cyclical unemployment is caused by
A)frictional and structural unemployment
B)frictional but not structural unemployment
C)structural but not frictional unemployment
D)neither frictional nor structural unemployment
A)frictional and structural unemployment
B)frictional but not structural unemployment
C)structural but not frictional unemployment
D)neither frictional nor structural unemployment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An increase in the minimum wage
A)increases both the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of labor.
B)decreases both the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of labor.
C)increases the quantity of labor demanded but decreases the quantity of labor supplied.
D)decreases the quantity of labor demanded but increases the quantity of labor supplied.
A)increases both the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of labor.
B)decreases both the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of labor.
C)increases the quantity of labor demanded but decreases the quantity of labor supplied.
D)decreases the quantity of labor demanded but increases the quantity of labor supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If outsiders had more say in union contracts then it is likely that union wages would be
A)higher so unemployment would be higher.
B)higher so unemployment would be lower.
C)lower so unemployment would be higher.
D)lower so unemployment would be lower.
A)higher so unemployment would be higher.
B)higher so unemployment would be lower.
C)lower so unemployment would be higher.
D)lower so unemployment would be lower.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Public policy
A)can reduce both frictional unemployment and the natural rate of unemployment.
B)can reduce frictional unemployment,but it cannot reduce the natural rate of unemployment.
C)cannot reduce frictional unemployment,but it can reduce the natural rate of unemployment.
D)cannot reduce either frictional unemployment or the natural rate of unemployment.
A)can reduce both frictional unemployment and the natural rate of unemployment.
B)can reduce frictional unemployment,but it cannot reduce the natural rate of unemployment.
C)cannot reduce frictional unemployment,but it can reduce the natural rate of unemployment.
D)cannot reduce either frictional unemployment or the natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Sam has no job but keeps applying to get a job with a business that is unionized.He is qualified and he finds the pay attractive,but the firm is not hiring.Sam is
A)structurally unemployed.Structural unemployment exists even in the long run.
B)structurally unemployed.Structural unemployment does not exist in the long run.
C)frictionally unemployed.Frictional unemployment exists even in the long run.
D)frictionally unemployed.Frictional unemployment does not exist in the long run.
A)structurally unemployed.Structural unemployment exists even in the long run.
B)structurally unemployed.Structural unemployment does not exist in the long run.
C)frictionally unemployed.Frictional unemployment exists even in the long run.
D)frictionally unemployed.Frictional unemployment does not exist in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the absence of right-to-work laws,workers
A)that went on strike could be permanently replaced.
B)might be required to join the union if they worked for a unionized firm.
C)would not be able to unionize.
D)would not be able to strike.
A)that went on strike could be permanently replaced.
B)might be required to join the union if they worked for a unionized firm.
C)would not be able to unionize.
D)would not be able to strike.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Figure 29-1 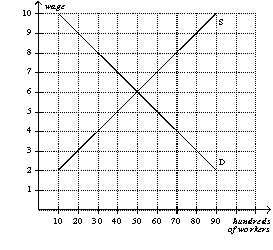
Refer to Figure 29-1.If the government imposes a minimum wage of 4 pounds,then unemployment will increase by
A)0 workers.
B)2000 workers.
C)4000 workers.
D)5000 workers.

Refer to Figure 29-1.If the government imposes a minimum wage of 4 pounds,then unemployment will increase by
A)0 workers.
B)2000 workers.
C)4000 workers.
D)5000 workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Evidence indicates that the typical person who becomes unemployed will
A)soon find a job.
B)find a job,but not before a year or more has gone by.
C)leave the labor force and never return.
D)retire soon after
A)soon find a job.
B)find a job,but not before a year or more has gone by.
C)leave the labor force and never return.
D)retire soon after

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Consumers decide to ride bikes more and drive cars less.Bicycle companies expand production while automobile companies fire workers.This is an example of
A)frictional unemployment created by sectoral shifts.
B)frictional unemployment created by efficiency wages.
C)structural unemployment created by efficiency wages.
D)structural unemployment created by sectoral shifts.
A)frictional unemployment created by sectoral shifts.
B)frictional unemployment created by efficiency wages.
C)structural unemployment created by efficiency wages.
D)structural unemployment created by sectoral shifts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Figure 29-1 
Refer to Figure 29-1.At the equilibrium wage,how many workers are unemployed?
A)0
B)4000
C)5000
D)8000

Refer to Figure 29-1.At the equilibrium wage,how many workers are unemployed?
A)0
B)4000
C)5000
D)8000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Minimum wages create unemployment in markets where they create a
A)shortage of labor.Unemployment of this type is called frictional.
B)shortage of labor.Unemployment of this type is called structural.
C)surplus of labor.Unemployment of this type is called frictional.
D)surplus of labor.Unemployment of this type is called structural.
A)shortage of labor.Unemployment of this type is called frictional.
B)shortage of labor.Unemployment of this type is called structural.
C)surplus of labor.Unemployment of this type is called frictional.
D)surplus of labor.Unemployment of this type is called structural.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Consider two labor markets in which jobs are equally attractive in all respects other than the wage rate.All workers are equally able to do either job.Initially,both labor markets are perfectly competitive.If a union organizes workers in one of the markets,then the wage rates will tend to
A)rise in both markets.
B)fall in both markets
C)rise for the union jobs,but remain unchanged for the nonunion jobs.
D)rise for the union jobs and fall for the nonunion jobs.
A)rise in both markets.
B)fall in both markets
C)rise for the union jobs,but remain unchanged for the nonunion jobs.
D)rise for the union jobs and fall for the nonunion jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Most spells of unemployment are short,and most unemployment observed at any given time is long-term.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
There are always some workers without jobs,even when the overall economy is doing well.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Efficiency wages
A)create a shortage of labor,and so reduce unemployment.
B)create a shortage of labor,and so raise unemployment.
C)create a surplus of labor,and so reduce unemployment.
D)create a surplus of labor,and so raise unemployment.
A)create a shortage of labor,and so reduce unemployment.
B)create a shortage of labor,and so raise unemployment.
C)create a surplus of labor,and so reduce unemployment.
D)create a surplus of labor,and so raise unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Minimum-wage laws and unions are similar to each other but different from efficiency wages in that minimum-wage law and unions
A)cause unemployment,but efficiency wages do not.
B)cause the quantity of labor supplied to exceed the quantity of labor demanded,but efficiency wages do not.
C)cause wages to be above the equilibrium level.
D)prevent firms from lowering wages in the presence of a surplus of workers.
A)cause unemployment,but efficiency wages do not.
B)cause the quantity of labor supplied to exceed the quantity of labor demanded,but efficiency wages do not.
C)cause wages to be above the equilibrium level.
D)prevent firms from lowering wages in the presence of a surplus of workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The natural rate of unemployment is the desirable rate of unemployment for an economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Measuring the amount of unemployment in the economy is a straightforward task.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Unemployment insurance causes workers to be less likely to seek guarantees of job security when they negotiate with employers over the terms of employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
More than one-third of the unemployed are recent entrants into the labor force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Structural unemployment results when wages are,for some reason,set above the level that brings supply and demand into equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The normal rate of unemployment around which the unemployment rate fluctuates is called cyclical unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If the number of people unemployed rose but the number of people employed and the adult population stayed the same,then the labor force participation rate would rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Paying efficiency wages means that wages are
A)above equilibrium and profits are higher than otherwise.
B)above equilibrium and profits are lower than otherwise.
C)below equilibrium and profits are higher than otherwise.
D)below equilibrium and profits are lower than otherwise.
A)above equilibrium and profits are higher than otherwise.
B)above equilibrium and profits are lower than otherwise.
C)below equilibrium and profits are higher than otherwise.
D)below equilibrium and profits are lower than otherwise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If there were no factors keeping wages from reaching equilibrium then there would be no
A)cyclical unemployment.
B)frictional unemployment.
C)structural unemployment.
D)natural rate of unemployment.
A)cyclical unemployment.
B)frictional unemployment.
C)structural unemployment.
D)natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The adult population must equal the sum of the employed and the unemployed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Public policy can reduce the economy's natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If all workers and all jobs were the same such that all workers were equally well suited for all jobs,then there would be no frictional unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The labor-force participation rate equals the percentage of the labor force that is employed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Changes in the composition of demand among industries or regions are called sectoral shifts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Monique is the newly appointed CEO of a company that manufactures external hard drives on an assembly line.Her staff has told her that the output the firm produces,given the number of workers employed,indicates that some workers may be shirking.According to efficiency wage theory,what should she do?
A)pay all workers more than the equilibrium wage rate
B)pay all workers below the equilibrium wage rate to make up for the loss from shirking
C)make sure that workers are getting paid exactly the equilibrium wage rate
D)pay bonuses to workers who report the shirking of other workers
A)pay all workers more than the equilibrium wage rate
B)pay all workers below the equilibrium wage rate to make up for the loss from shirking
C)make sure that workers are getting paid exactly the equilibrium wage rate
D)pay bonuses to workers who report the shirking of other workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If people who report being unemployed are not,in fact,trying hard to find a job,then the reported unemployment rate will be baised upward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Teenage unemployment is higher than unemployment of people ages 20 and over.Explain why economists would attribute at least part of this difference to minimum-wage laws.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Most spells of unemployment are short,and most unemployment observed at any given time is long term.How can this be?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What is the theory of efficiency wages?
Provide four reasons that employers might pay efficiency wages.
Provide four reasons that employers might pay efficiency wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Why might a favorable change in the economy,such as technological improvement or a decrease in the price of imported oil,be associated with an increase in frictional unemployment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



