Deck 33: A Macroeconomic Theory of the Open Economy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/67
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 33: A Macroeconomic Theory of the Open Economy
1
The value of net exports equals the value of
A)national saving.
B)public saving.
C)national saving - net capital outflow.
D)national saving - domestic investment.
A)national saving.
B)public saving.
C)national saving - net capital outflow.
D)national saving - domestic investment.
D
2
Which of the following would make both the equilibrium real interest rate and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds increase?
A)The demand for loanable funds shifts right.
B)The demand for loanable funds shifts left.
C)The supply of loanable funds shifts right.
D)The supply of loanable funds shifts left.
A)The demand for loanable funds shifts right.
B)The demand for loanable funds shifts left.
C)The supply of loanable funds shifts right.
D)The supply of loanable funds shifts left.
A
3
In an open economy,national saving equals
A)domestic investment plus net capital outflow.
B)domestic investment minus net capital outflow.
C)domestic investment.
D)net capital outflow.
A)domestic investment plus net capital outflow.
B)domestic investment minus net capital outflow.
C)domestic investment.
D)net capital outflow.
A
4
The explanation for the slope of
A)the supply of loanable funds curve is based on the logic that a higher real interest rate leads to higher saving.
B)the demand for loanable funds curve is based on the logic that a higher interest rate leads to higher saving.
C)the supply of loanable funds curve is based on the logic that a higher real interest rate leads to lower saving.
D)the demand for loanable funds curve is based on the logic that a higher interest rate leads to lower saving.
A)the supply of loanable funds curve is based on the logic that a higher real interest rate leads to higher saving.
B)the demand for loanable funds curve is based on the logic that a higher interest rate leads to higher saving.
C)the supply of loanable funds curve is based on the logic that a higher real interest rate leads to lower saving.
D)the demand for loanable funds curve is based on the logic that a higher interest rate leads to lower saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a country has a positive net capital outflow,then
A)on net it is purchasing assets from abroad.This adds to its demand for domestically generated loanable funds.
B)on net it is purchasing assets from abroad.This subtracts from its demand for domestically generated loanable funds.
C)on net other countries are purchasing assets from it.This adds to its demand for domestically generated loanable funds.
D)on net other countries are purchasing assets from it.This subtracts from its demand for domestically generated loanable funds.
A)on net it is purchasing assets from abroad.This adds to its demand for domestically generated loanable funds.
B)on net it is purchasing assets from abroad.This subtracts from its demand for domestically generated loanable funds.
C)on net other countries are purchasing assets from it.This adds to its demand for domestically generated loanable funds.
D)on net other countries are purchasing assets from it.This subtracts from its demand for domestically generated loanable funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the open-economy macroeconomic model,as the exchange rate rises,
A)desired net exports fall,so the quantity of dollars supplied rise.
B)desired net exports fall,so the quantity of dollars demanded falls.
C)desired net exports rise ,so the quantity of dollars supplied falls.
D)desired net exports rise,so the quantity of dollars demanded rises.
A)desired net exports fall,so the quantity of dollars supplied rise.
B)desired net exports fall,so the quantity of dollars demanded falls.
C)desired net exports rise ,so the quantity of dollars supplied falls.
D)desired net exports rise,so the quantity of dollars demanded rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The slope of the supply of loanable funds is based on an increase in
A)only national saving when the interest rate rises.
B)both national saving and net capital outflow when the interest rate rises.
C)only national saving when the interest rate falls.
D)both national saving and net capital outflow when the interest rate falls.
A)only national saving when the interest rate rises.
B)both national saving and net capital outflow when the interest rate rises.
C)only national saving when the interest rate falls.
D)both national saving and net capital outflow when the interest rate falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is correct in an open economy?
A)S = I
B)S = NX + NCO
C)S = NCO
D)S = I + NCO
A)S = I
B)S = NX + NCO
C)S = NCO
D)S = I + NCO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If net exports are negative,then
A)net capital outflow is positive,so foreign assets bought by Americans are greater than American assets bought by foreigners.
B)net capital outflow is positive,so American assets bought by foreigners are greater than foreign assets bought by Americans.
C)net capital outflow is negative,so foreign assets bought by Americans are greater than American assets bought by foreigners.
D)net capital outflow is negative,so American assets bought by foreigners are greater than foreign assets bought by Americans.
A)net capital outflow is positive,so foreign assets bought by Americans are greater than American assets bought by foreigners.
B)net capital outflow is positive,so American assets bought by foreigners are greater than foreign assets bought by Americans.
C)net capital outflow is negative,so foreign assets bought by Americans are greater than American assets bought by foreigners.
D)net capital outflow is negative,so American assets bought by foreigners are greater than foreign assets bought by Americans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the open-economy macroeconomic model,the supply of money in the market for foreign-currency exchange comes from
A)net exports
B)net capital outflow
C)net exports + net capital outflow
D)net exports - net capital outflow
A)net exports
B)net capital outflow
C)net exports + net capital outflow
D)net exports - net capital outflow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Other things the same,which of the following would shift the supply of money in the market for foreign exchange to the right?
A)foreigners want to buy more domestic bonds
B)foreigners want to buy fewer domestic bonds
C)foreigners want to buy more domestic goods and services.
D)foreigners want to buy fewer domestic goods and services.
A)foreigners want to buy more domestic bonds
B)foreigners want to buy fewer domestic bonds
C)foreigners want to buy more domestic goods and services.
D)foreigners want to buy fewer domestic goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The theory of purchasing-power parity implies that the demand curve for foreign-currency exchange is
A)downward sloping.
B)upward sloping.
C)horizontal.
D)vertical.
A)downward sloping.
B)upward sloping.
C)horizontal.
D)vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The real exchange rate measures the
A)price of domestic currency relative to foreign currency.
B)price of domestic goods relative to the price of foreign goods.
C)rate of domestic and foreign interest.
D)None of the above is correct.
A)price of domestic currency relative to foreign currency.
B)price of domestic goods relative to the price of foreign goods.
C)rate of domestic and foreign interest.
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The open-economy macroeconomic model examines the determination of
A)the output growth rate and the real interest rate.
B)unemployment and the exchange rate.
C)the output growth rate and the inflation rate.
D)the trade balance and the exchange rate.
A)the output growth rate and the real interest rate.
B)unemployment and the exchange rate.
C)the output growth rate and the inflation rate.
D)the trade balance and the exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Other things the same,as the real interest rate rises
A)domestic investment and net capital outflow both rise.
B)domestic investment and net capital outflow both fall.
C)domestic investment rises and net capital outflow falls.
D)domestic investment falls and net capital outflow rises.
A)domestic investment and net capital outflow both rise.
B)domestic investment and net capital outflow both fall.
C)domestic investment rises and net capital outflow falls.
D)domestic investment falls and net capital outflow rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the open economy macroeconomic model,the price that balances supply and demand in the market for foreign-currency exchange model is the
A)nominal exchange rate.
B)nominal interest rate.
C)real exchange rate.
D)real interest rate.
A)nominal exchange rate.
B)nominal interest rate.
C)real exchange rate.
D)real interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If there is a surplus in the market for loanable funds,the resulting change in the real interest rate
A)reduces both the quantity of loanable funds supplied and the quantity of loanable funds demanded.
B)reduces the quantity of loanable funds supplied and raises the quantity of loanable funds demanded
C)raises both the quantity of loanable funds supplied and the quantity of loanable funds demanded.
D)raises the quantity of loanable funds supplied and reduces the quantity of loanable funds demanded.
A)reduces both the quantity of loanable funds supplied and the quantity of loanable funds demanded.
B)reduces the quantity of loanable funds supplied and raises the quantity of loanable funds demanded
C)raises both the quantity of loanable funds supplied and the quantity of loanable funds demanded.
D)raises the quantity of loanable funds supplied and reduces the quantity of loanable funds demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the open-economy macroeconomic model,the market for loanable funds identity can be written as
A)S = I
B)S = NCO
C)S = I + NCO
D)S + I = NCO
A)S = I
B)S = NCO
C)S = I + NCO
D)S + I = NCO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the open-economy macroeconomic model,if net capital outflow increases then
A)the demand for dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange shifts right.
B)the demand for dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange shifts left.
C)the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange shifts right.
D)the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange shifts left.
A)the demand for dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange shifts right.
B)the demand for dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange shifts left.
C)the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange shifts right.
D)the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange shifts left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the open-economy macroeconomic model,the key determinant of net capital outflow is
A)the real exchange rate.When the real exchange rate rises,net capital outflow rises.
B)the real exchange rate.When the real exchange rate rises,net capital outflow falls.
C)the real interest rate.When the real interest rate rises,net capital outflow rises.
D)the real interest rate.When the real interest rate rises,net capital outflow falls.
A)the real exchange rate.When the real exchange rate rises,net capital outflow rises.
B)the real exchange rate.When the real exchange rate rises,net capital outflow falls.
C)the real interest rate.When the real interest rate rises,net capital outflow rises.
D)the real interest rate.When the real interest rate rises,net capital outflow falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If a country raises its budget deficit,then its
A)net capital outflow and net exports rise.
B)net capital outflow rises and net exports fall.
C)net capital outflow falls and net exports rise.
D)net capital outflow and net exports fall.
A)net capital outflow and net exports rise.
B)net capital outflow rises and net exports fall.
C)net capital outflow falls and net exports rise.
D)net capital outflow and net exports fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Figure 33-3
Refer to this diagram to answer the questions below.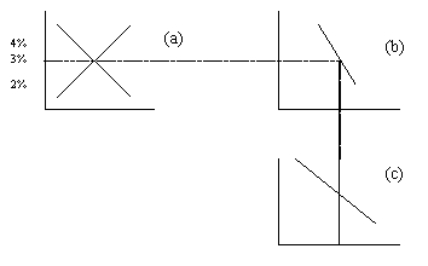
Refer to Figure 33-3.At an interest rate of 3 percent,the diagram indicates that
A)there is a surplus in the market for foreign-currency exchange.
B)national saving equals domestic investment.
C)net capital outflow + domestic investment = national saving.
D)in the market for foreign-currency exchange the quantity of dollars supplied equals the quantity of dollars demanded.
Refer to this diagram to answer the questions below.

Refer to Figure 33-3.At an interest rate of 3 percent,the diagram indicates that
A)there is a surplus in the market for foreign-currency exchange.
B)national saving equals domestic investment.
C)net capital outflow + domestic investment = national saving.
D)in the market for foreign-currency exchange the quantity of dollars supplied equals the quantity of dollars demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the open-economy macroeconomic model,if a country's interest rate rises,then its
A)net capital outflow and net exports rise.
B)net capital outflow rises and its net exports fall.
C)net capital outflow falls and its net exports rise.
D)net capital outflow and net exports fall.
A)net capital outflow and net exports rise.
B)net capital outflow rises and its net exports fall.
C)net capital outflow falls and its net exports rise.
D)net capital outflow and net exports fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A trade policy is a government policy
A)directed toward the goal of improving the tradeoff between equity and efficiency.
B)that directly influences the quantity of goods and services that a country imports or exports.
C)intended to exploit the tradeoff between inflation and unemployment by altering the budget deficit.
D)concerning employment laws.
A)directed toward the goal of improving the tradeoff between equity and efficiency.
B)that directly influences the quantity of goods and services that a country imports or exports.
C)intended to exploit the tradeoff between inflation and unemployment by altering the budget deficit.
D)concerning employment laws.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A rise in the government budget deficit
A)increases the interest rate so in the market for foreign-currency exchange,supply shifts right.
B)increases the interest rate so in the market for foreign-currency exchange,supply shifts left.
C)decreases the interest rate so in the market for foreign-currency exchange,supply shifts left.
D)decreases the interest rate so in the market for foreign-currency exchange supply shifts right.
A)increases the interest rate so in the market for foreign-currency exchange,supply shifts right.
B)increases the interest rate so in the market for foreign-currency exchange,supply shifts left.
C)decreases the interest rate so in the market for foreign-currency exchange,supply shifts left.
D)decreases the interest rate so in the market for foreign-currency exchange supply shifts right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Figure 33-4 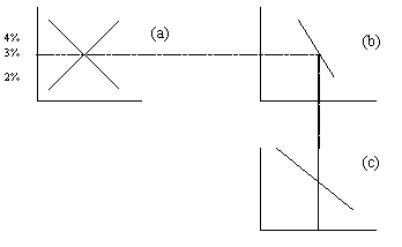
Refer to Figure 33-4.Suppose that the government goes from a budget surplus to a budget deficit.The effects of the change could be illustrated by
A)shifting the demand curve in panel a to the right and the demand curve in panel c to the left.
B)shifting the demand curve in panel a to the left and the supply curve in panel c to the left.
C)shifting the supply curve in panel a to the right and the demand curve in panel c to the right.
D)shifting the supply curve in panel a to the left and the supply curve in panel c to the left.

Refer to Figure 33-4.Suppose that the government goes from a budget surplus to a budget deficit.The effects of the change could be illustrated by
A)shifting the demand curve in panel a to the right and the demand curve in panel c to the left.
B)shifting the demand curve in panel a to the left and the supply curve in panel c to the left.
C)shifting the supply curve in panel a to the right and the demand curve in panel c to the right.
D)shifting the supply curve in panel a to the left and the supply curve in panel c to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a country raises its budget deficit then
A)both its supply of and demand for loanable funds shift.
B)its supply of but not its demand for loanable funds shifts.
C)its demand for but not its supply of loanable funds shifts.
D)neither its supply nor its demand for loanable funds shift.
A)both its supply of and demand for loanable funds shift.
B)its supply of but not its demand for loanable funds shifts.
C)its demand for but not its supply of loanable funds shifts.
D)neither its supply nor its demand for loanable funds shift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the budget deficit increases,then
A)an increase in the interest rate increases net capital outflow.
B)an increase in the interest rate decreases net capital outflow.
C)a decrease in the interest rate increases net capital outflow.
D)a decrease in the interest rate decreases net capital outflow.
A)an increase in the interest rate increases net capital outflow.
B)an increase in the interest rate decreases net capital outflow.
C)a decrease in the interest rate increases net capital outflow.
D)a decrease in the interest rate decreases net capital outflow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If the government of a country with a zero trade balance started with a budget deficit and moved to a budget surplus,domestic investment would
A)rise and there would be a trade surplus.
B)rise and there would be a trade deficit.
C)fall and there would be a trade surplus.
D)fall and there would be a trade deficit.
A)rise and there would be a trade surplus.
B)rise and there would be a trade deficit.
C)fall and there would be a trade surplus.
D)fall and there would be a trade deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In the open-economy macroeconomic model,a decrease in the domestic interest rate shifts
A)demand in the market for foreign-currency exchange to the right.
B)demand in the market for foreign-currency exchange to the left.
C)supply in the market for foreign-currency exchange to the right.
D)supply in the market for foreign-currency exchange to the left.
A)demand in the market for foreign-currency exchange to the right.
B)demand in the market for foreign-currency exchange to the left.
C)supply in the market for foreign-currency exchange to the right.
D)supply in the market for foreign-currency exchange to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Suppose that Chile has a government budget surplus,and then goes into deficit.This change would
A)increase national saving and shift Chile's supply of loanable funds left.
B)increase national saving and shift Chile's demand for loanable funds right.
C)decrease national saving and shift Chile's supply of loanable funds left.
D)decrease national saving and shift Chile's demand for loanable funds right.
A)increase national saving and shift Chile's supply of loanable funds left.
B)increase national saving and shift Chile's demand for loanable funds right.
C)decrease national saving and shift Chile's supply of loanable funds left.
D)decrease national saving and shift Chile's demand for loanable funds right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A tax on imported goods is called a(n)
A)excise tax.
B)tariff.
C)import quota.
D)None of the above is correct.
A)excise tax.
B)tariff.
C)import quota.
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If a country's budget deficit rises,then its exchange rate
A)rises,so its imports rise.
B)rises,so its imports fall.
C)falls,so its imports rise.
D)falls so its imports fall.
A)rises,so its imports rise.
B)rises,so its imports fall.
C)falls,so its imports rise.
D)falls so its imports fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the open-economy macroeconomic model,if the supply of loanable funds increases,then the interest rate
A)and the real exchange rate increase.
B)and the real exchange rate decrease.
C)increases and the real exchange rate decreases.
D)decreases and the real exchange rate increases.
A)and the real exchange rate increase.
B)and the real exchange rate decrease.
C)increases and the real exchange rate decreases.
D)decreases and the real exchange rate increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If a government increases its budget deficit,then domestic interest rates
A)and net exports rise.
B)rise and net exports fall.
C)fall and net exports rise.
D)and net exports fall.
A)and net exports rise.
B)rise and net exports fall.
C)fall and net exports rise.
D)and net exports fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In the open-economy macroeconomic model which of the following falls if there is an increase in the budget deficit?
A)the interest rate
B)net exports
C)the exchange rate
D)All of the above are correct.
A)the interest rate
B)net exports
C)the exchange rate
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If a country's budget deficit increases,then in the foreign exchange market,
A)the supply of its currency shifts right,so the exchange rate falls.
B)the demand for its currency shifts right,so the exchange rate rises.
C)the supply of its currency shifts left,so the exchange rate rises.
D)the demand for its currency shifts left.so the exchange rate falls.
A)the supply of its currency shifts right,so the exchange rate falls.
B)the demand for its currency shifts right,so the exchange rate rises.
C)the supply of its currency shifts left,so the exchange rate rises.
D)the demand for its currency shifts left.so the exchange rate falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A decrease in the budget deficit causes domestic interest rates
A)and investment to rise.
B)to rise and investment to fall.
C)to fall and investment to rise.
D)and investment to fall.
A)and investment to rise.
B)to rise and investment to fall.
C)to fall and investment to rise.
D)and investment to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is the most likely result from an increase in a country's government budget surplus?
A)higher interest rates
B)lower imports
C)lower net capital outflows
D)lower domestic investment
A)higher interest rates
B)lower imports
C)lower net capital outflows
D)lower domestic investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An increase in the budget surplus
A)raises net exports and domestic investment.
B)raises net exports and reduces domestic investment.
C)reduces net exports and raises domestic investment.
D)reduces net exports and domestic investment.
A)raises net exports and domestic investment.
B)raises net exports and reduces domestic investment.
C)reduces net exports and raises domestic investment.
D)reduces net exports and domestic investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A large and sudden movement of funds out of a country is called
A)arbitrage.
B)capital flight.
C)crowding out.
D)capital mobility.
A)arbitrage.
B)capital flight.
C)crowding out.
D)capital mobility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure 33-6 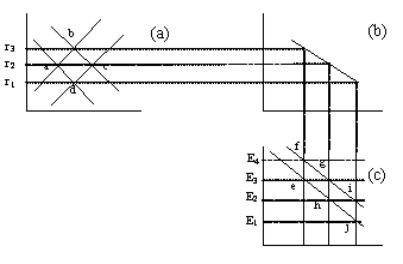
Refer to Figure 33-6.If the economy were initially in equilibrium at r2 and E3 and the government removed import quotas,the exchange rate would
A)appreciate to E4.
B)appreciate to E2.
C)depreciate to E1.
D)depreciate to E2.

Refer to Figure 33-6.If the economy were initially in equilibrium at r2 and E3 and the government removed import quotas,the exchange rate would
A)appreciate to E4.
B)appreciate to E2.
C)depreciate to E1.
D)depreciate to E2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Other things the same,a higher real exchange rate reduces net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In the open-economy macroeconomic model,if there is currently a surplus in the foreign exchange market,the quantity of desired net exports will increase as the market moves to equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When the government budget deficit increases,national saving increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is the correct way to show the effects of a newly imposed import quota?
A)Shift the demand for loanable funds right,the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange right,and the demand for dollars left.
B)Shift the demand for loanable funds right,and the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange left.
C)Shift the demand for dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange left.
D)None of the above is correct.
A)Shift the demand for loanable funds right,the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange right,and the demand for dollars left.
B)Shift the demand for loanable funds right,and the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange left.
C)Shift the demand for dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange left.
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If a country removed an import quota on cotton,then overall that country's
A)exports and imports would rise.
B)exports would rise and imports would fall.
C)exports would fall and imports would rise.
D)exports and imports would fall.
A)exports and imports would rise.
B)exports would rise and imports would fall.
C)exports would fall and imports would rise.
D)exports and imports would fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In an open economy,the demand for loanable funds comes from both domestic investment and net capital outflow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A firm produces manufacturing equipment,some of which it exports.Which of the following effects of capital flight in the country it produces in would likely reduce the quantity of equipment it sells?
A)both what happens to the interest rate and what happens to the exchange rate
B)what happens to the interest rate but not what happens to the exchange rate
C)what happens to the exchange rate but not what happens to the interest rate
D)neither what happens to the interest rate nor what happens to the interest rate.
A)both what happens to the interest rate and what happens to the exchange rate
B)what happens to the interest rate but not what happens to the exchange rate
C)what happens to the exchange rate but not what happens to the interest rate
D)neither what happens to the interest rate nor what happens to the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Figure 33-6 
Refer to Figure 33-6.If the interest rate were initially at r2 and an import quota were imposed,the interest rate would
A)stay at r2.
B)decrease because supply would shift right.
C)increase because supply would shift left.
D)decrease because demand would shift left.

Refer to Figure 33-6.If the interest rate were initially at r2 and an import quota were imposed,the interest rate would
A)stay at r2.
B)decrease because supply would shift right.
C)increase because supply would shift left.
D)decrease because demand would shift left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The primary focus of the open-economy macroeconomic model is the determination of GDP and the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A drop in a country's real interest rate reduces that country's net capital outflow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Other things the same,when a Canadian company imports bicycles from the U.S.,the open-economy macroeconomic model treats this transaction as an increase in the quantity of dollars demanded in the U.S.foreign-currency exchange market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When a country imposes a trade restriction,the real exchange rate of that country's currency appreciates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Capital flight raises a country's interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In the long run,import quotas increase net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
When Mexico suffered from capital flight in 1994,Mexico's net exports
A)decreased.
B)did not change.
C)increased.
D)decreased until the peso appreciated,then increased.
A)decreased.
B)did not change.
C)increased.
D)decreased until the peso appreciated,then increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
When a country imposes an import quota,its
A)net exports rise and its real exchange rate appreciates.
B)net exports rise and its real exchange rate depreciates.
C)net exports fall and its real exchange rate depreciates
D)None of the above is correct.
A)net exports rise and its real exchange rate appreciates.
B)net exports rise and its real exchange rate depreciates.
C)net exports fall and its real exchange rate depreciates
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Although trade policies do not affect a country's overall trade balance,they do affect specific firms and industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The key determinant of net capital outflow is the real interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
State what,if anything,each of the following does to the supply or demand of loanable funds.
a.net capital outflow increases at each interest rate
b.domestic investment increases at each interest rate
c.the government deficit increases
d.private saving increases
a.net capital outflow increases at each interest rate
b.domestic investment increases at each interest rate
c.the government deficit increases
d.private saving increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Suppose that the Turkish government budget deficit increases.What curves in the open-economy macroeconomic model shift?
Explain why each curve shifts the direction it does.
Explain why each curve shifts the direction it does.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Explain how the relation between the real exchange rate and net exports explains the downward slope of the demand for foreign-currency exchange curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What effect do protectionist policies have on the trade deficit?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
How are the identities S = NCO + I and NCO = NX related to the foreign currency exchange market and the loanable funds market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A tax credit for purchases of capital goods causes the interest rate to increase and the exchange rate to appreciate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Capital flight reduces a country's real exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



