Deck 34: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/68
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 34: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
1
During recessions investment
A)falls by a larger percentage than GDP.
B)falls by about the same percentage as GDP.
C)falls by a smaller percentage than GDP.
D)falls but the percentage change is sometimes much larger and sometimes much smaller.
A)falls by a larger percentage than GDP.
B)falls by about the same percentage as GDP.
C)falls by a smaller percentage than GDP.
D)falls but the percentage change is sometimes much larger and sometimes much smaller.
A
2
The classical model is appropriate for analysis of the economy in the
A)long run,since evidence indicates that money is not neutral in the long run.
B)long run,since real and nominal variables are essentially determined separately in the long run.
C)short run,provided money is not neutral.
D)short run,provided real and nominal variables are highly intertwined.
A)long run,since evidence indicates that money is not neutral in the long run.
B)long run,since real and nominal variables are essentially determined separately in the long run.
C)short run,provided money is not neutral.
D)short run,provided real and nominal variables are highly intertwined.
B
3
Which of the following explains why production rises in most years?
A)increases in the labor force
B)increases in the capital stock
C)advances in technological knowledge
D)All of the above are correct.
A)increases in the labor force
B)increases in the capital stock
C)advances in technological knowledge
D)All of the above are correct.
D
4
The aggregate quantity of goods and services demanded changes as the price level rises because
A)real wealth falls,interest rates rise,and the dollar appreciates.
B)real wealth falls,interest rates rise,and the dollar depreciates.
C)real wealth rises,interest rates fall,and the dollar appreciates.
D)real wealth rises,interest rates fall,and the dollar depreciates.
A)real wealth falls,interest rates rise,and the dollar appreciates.
B)real wealth falls,interest rates rise,and the dollar depreciates.
C)real wealth rises,interest rates fall,and the dollar appreciates.
D)real wealth rises,interest rates fall,and the dollar depreciates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The aggregate-demand curve
A)has a slope that is explained in the same way as the slope of the demand curve for a particular product.
B)is vertical in the long run.
C)shows an inverse relation between the price level and the quantity of all goods and services demanded.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)has a slope that is explained in the same way as the slope of the demand curve for a particular product.
B)is vertical in the long run.
C)shows an inverse relation between the price level and the quantity of all goods and services demanded.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following effects helps to explain the slope of the aggregate-demand curve?
A)the exchange-rate effect
B)the wealth effect
C)the interest-rate effect
D)All of the above are correct.
A)the exchange-rate effect
B)the wealth effect
C)the interest-rate effect
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Other things the same,if the price level falls,people
A)increase foreign bond purchases,so the currency appreciates.
B)increase foreign bond purchases,so the currency depreciates.
C)increase domestic bond purchases,so the currency appreciates.
D)increase domestic bond purchases,so the currency depreciates.
A)increase foreign bond purchases,so the currency appreciates.
B)increase foreign bond purchases,so the currency depreciates.
C)increase domestic bond purchases,so the currency appreciates.
D)increase domestic bond purchases,so the currency depreciates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Most economists use the aggregate demand and aggregate supply model primarily to analyze
A)short-run fluctuations in the economy.
B)the effects of macroeconomic policy on the prices of individual goods.
C)the long-run effects of international trade policies.
D)productivity and economic growth.
A)short-run fluctuations in the economy.
B)the effects of macroeconomic policy on the prices of individual goods.
C)the long-run effects of international trade policies.
D)productivity and economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Other things the same,a fall in an economy's overall level of prices tends to
A)raise both the quantity demanded and supplied of goods and services.
B)raise the quantity demanded of goods and services,but lower the quantity supplied.
C)lower the quantity demanded of goods and services,but raise the quantity supplied.
D)lower both the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of goods and services.
A)raise both the quantity demanded and supplied of goods and services.
B)raise the quantity demanded of goods and services,but lower the quantity supplied.
C)lower the quantity demanded of goods and services,but raise the quantity supplied.
D)lower both the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the price level falls,the real value of the currency
A)rises,so people will want to buy more.This response helps explain the slope of the aggregate demand curve.
B)rises,so people will want to buy more.This response shifts aggregate demand to the right.
C)falls,so people will want to buy less.This response helps explain the slope of the aggregate demand curve.
D)falls,so people will want to buy less.This response shifts aggregate demand to the left.
A)rises,so people will want to buy more.This response helps explain the slope of the aggregate demand curve.
B)rises,so people will want to buy more.This response shifts aggregate demand to the right.
C)falls,so people will want to buy less.This response helps explain the slope of the aggregate demand curve.
D)falls,so people will want to buy less.This response shifts aggregate demand to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The aggregate demand and aggregate supply graph has
A)quantity of output on the horizontal axis.Output can be measured by the GDP deflator.
B)quantity of output on the horizontal axis.Output can be measured by real GDP.
C)quantity of output on the vertical axis.Output can be measured by the GDP deflator.
D)quantity of output on the vertical axis.Output can be measured by real GDP.
A)quantity of output on the horizontal axis.Output can be measured by the GDP deflator.
B)quantity of output on the horizontal axis.Output can be measured by real GDP.
C)quantity of output on the vertical axis.Output can be measured by the GDP deflator.
D)quantity of output on the vertical axis.Output can be measured by real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the context of aggregate demand and aggregate supply,the wealth effect refers to the idea that,when the price level decreases,the real wealth of households
A)increases and as a result consumption spending increases.This effect contributes to the downward slope of the aggregate-demand curve.
B)decreases and as a result consumption spending increases.This effect contributes to the upward slope of the aggregate-supply curve.
C)increases and as a result households increase their money holdings; in turn,interest rates increase and investment spending decreases.This effect contributes to the downward slope of the aggregate-demand curve.
D)decreases and as a result households increase their money holdings; in turn,interest rates increase and investment spending decreases.This effect contributes to the upward slope of the aggregate-supply curve.
A)increases and as a result consumption spending increases.This effect contributes to the downward slope of the aggregate-demand curve.
B)decreases and as a result consumption spending increases.This effect contributes to the upward slope of the aggregate-supply curve.
C)increases and as a result households increase their money holdings; in turn,interest rates increase and investment spending decreases.This effect contributes to the downward slope of the aggregate-demand curve.
D)decreases and as a result households increase their money holdings; in turn,interest rates increase and investment spending decreases.This effect contributes to the upward slope of the aggregate-supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
According to classical macroeconomic theory,changes in the money supply affect
A)real GDP and the price level.
B)real GDP but not the price level.
C)the price level,but not real GDP.
D)neither the price level nor real GDP.
A)real GDP and the price level.
B)real GDP but not the price level.
C)the price level,but not real GDP.
D)neither the price level nor real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Other things the same,if the price level rises,then domestic interest rates
A)rise,so domestic residents will want to hold more foreign bonds.
B)rise,so domestic residents will want to hold fewer foreign bonds.
C)fall,so domestic residents will want to hold more foreign bonds.
D)fall,so domestic residents will want to hold fewer foreign bonds.
A)rise,so domestic residents will want to hold more foreign bonds.
B)rise,so domestic residents will want to hold fewer foreign bonds.
C)fall,so domestic residents will want to hold more foreign bonds.
D)fall,so domestic residents will want to hold fewer foreign bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is correct?
A)Real GDP is the variable most commonly used to measure short-run economic fluctuations.These fluctuations can be predicted with some accuracy.
B)Real GDP is the variable most commonly used to measure short-run economic fluctuations.It is almost impossible to predict these fluctuations with much accuracy.
C)Nominal GDP is the variable most commonly used to measure short-run economic fluctuations.These fluctuations can be predicted with some accuracy.
D)Nominal GDP is the variable most commonly used to measure short-run economic fluctuations.It is almost impossible to predict these fluctuations with much accuracy.
A)Real GDP is the variable most commonly used to measure short-run economic fluctuations.These fluctuations can be predicted with some accuracy.
B)Real GDP is the variable most commonly used to measure short-run economic fluctuations.It is almost impossible to predict these fluctuations with much accuracy.
C)Nominal GDP is the variable most commonly used to measure short-run economic fluctuations.These fluctuations can be predicted with some accuracy.
D)Nominal GDP is the variable most commonly used to measure short-run economic fluctuations.It is almost impossible to predict these fluctuations with much accuracy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following accounts for about two-thirds of the decline in output during a recession?
A)the decline in consumption expenditures on consumer durables alone
B)the decline in total consumption spending alone
C)the decline in investment spending alone
D)the combined decline in consumption and investment spending
A)the decline in consumption expenditures on consumer durables alone
B)the decline in total consumption spending alone
C)the decline in investment spending alone
D)the combined decline in consumption and investment spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply
A)is different from the model of supply and demand for a particular market,in that we cannot focus on the substitution of resources between markets to explain aggregate relationships.
B)is different from the model of supply and demand for a particular market,in that we have to separate real and nominal variables in the aggregate model.
C)is a straightforward extension of the model of supply and demand for a particular market,in which substitution of resources between markets is highlighted.
D)is a straightforward extension of the model of supply and demand for a particular market,in which the interaction between real and nominal variables is highlighted.
A)is different from the model of supply and demand for a particular market,in that we cannot focus on the substitution of resources between markets to explain aggregate relationships.
B)is different from the model of supply and demand for a particular market,in that we have to separate real and nominal variables in the aggregate model.
C)is a straightforward extension of the model of supply and demand for a particular market,in which substitution of resources between markets is highlighted.
D)is a straightforward extension of the model of supply and demand for a particular market,in which the interaction between real and nominal variables is highlighted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following decreases in response to the interest-rate effect from an increase in the price level?
A)both investment and consumption
B)consumption but not investment
C)investment but not consumption
D)neither investment nor consumption
A)both investment and consumption
B)consumption but not investment
C)investment but not consumption
D)neither investment nor consumption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
As the price level falls
A)people are more willing to lend,so interest rates rise.
B)people are more willing to lend,so interest rates fall.
C)people are less willing to lend,so interest rates fall.
D)people are less willing to lend,so interest rates rise.
A)people are more willing to lend,so interest rates rise.
B)people are more willing to lend,so interest rates fall.
C)people are less willing to lend,so interest rates fall.
D)people are less willing to lend,so interest rates rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The quantity of aggregate goods and service demanded rises when the
A)price level rises,because the interest rate rises.
B)price level rises,because the interest rate falls.
C)price level falls,because the interest rate rises.
D)price level falls,because the interest rate falls.
A)price level rises,because the interest rate rises.
B)price level rises,because the interest rate falls.
C)price level falls,because the interest rate rises.
D)price level falls,because the interest rate falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Other things the same,a decrease in the price level causes real wealth to
A)fall,interest rates to fall,and the dollar to appreciate.
B)fall,interest rates to rise,and the dollar to depreciate.
C)rise,interest rates to rise,and the dollar to appreciate.
D)rise,interest rates to fall,and the dollar to depreciate.
A)fall,interest rates to fall,and the dollar to appreciate.
B)fall,interest rates to rise,and the dollar to depreciate.
C)rise,interest rates to rise,and the dollar to appreciate.
D)rise,interest rates to fall,and the dollar to depreciate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following would cause prices and real GDP to rise in the short run?
A)short-run aggregate supply shifts right
B)short-run aggregate supply shifts left
C)aggregate demand shifts right
D)aggregate demand shifts left
A)short-run aggregate supply shifts right
B)short-run aggregate supply shifts left
C)aggregate demand shifts right
D)aggregate demand shifts left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
As the price level falls,
A)the exchange rate falls,so net exports fall.
B)the exchange rate falls,so net exports rise.
C)the exchange rate rises,so net exports fall.
D)the exchange rate rises,so net exports rise.
A)the exchange rate falls,so net exports fall.
B)the exchange rate falls,so net exports rise.
C)the exchange rate rises,so net exports fall.
D)the exchange rate rises,so net exports rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When taxes increase,consumption
A)decreases as shown by a movement to the left along a given aggregate-demand curve.
B)decreases as shown by a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the left.
C)increases as shown by a movement to the right along a given aggregate-demand curve.
D)increases as shown by a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the right.
A)decreases as shown by a movement to the left along a given aggregate-demand curve.
B)decreases as shown by a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the left.
C)increases as shown by a movement to the right along a given aggregate-demand curve.
D)increases as shown by a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Figure 34-1 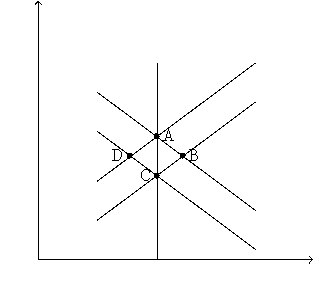
Refer to Figure 34-1.An increase in the money supply would move the economy from C to
A)B in the short run and the long run.
B)D in the short run and the long run.
C)B in the short run and A in the long run.
D)D in the short run and C in the long run.

Refer to Figure 34-1.An increase in the money supply would move the economy from C to
A)B in the short run and the long run.
B)D in the short run and the long run.
C)B in the short run and A in the long run.
D)D in the short run and C in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is correct?
A)The short-run,but not the long-run,aggregate supply curve is consistent with the idea that nominal variables do not affect real variables.
B)The long-run,but not the short-run,aggregate supply curve is consistent with the idea that nominal variables do not affect real variables.
C)The long-run and short-run supply curves are both consistent with the idea that nominal variables affect real variables.
D)Neither the long-run nor the short-run aggregate supply curve is consistent with the idea that nominal variables affect real variables.
A)The short-run,but not the long-run,aggregate supply curve is consistent with the idea that nominal variables do not affect real variables.
B)The long-run,but not the short-run,aggregate supply curve is consistent with the idea that nominal variables do not affect real variables.
C)The long-run and short-run supply curves are both consistent with the idea that nominal variables affect real variables.
D)Neither the long-run nor the short-run aggregate supply curve is consistent with the idea that nominal variables affect real variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When the currency depreciates,a country's
A)exports and imports increase.
B)exports increase,while imports decrease.
C)exports decrease,while imports increase.
D)exports and imports decrease.
A)exports and imports increase.
B)exports increase,while imports decrease.
C)exports decrease,while imports increase.
D)exports and imports decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
From 2001 to 2005 there was a dramatic rise in the price of houses.If this rise made people feel wealthier,then it would have shifted
A)aggregate demand right.
B)aggregate demand left.
C)aggregate supply right.
D)aggregate supply left.
A)aggregate demand right.
B)aggregate demand left.
C)aggregate supply right.
D)aggregate supply left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Suppose workers notice a fall in their nominal wage but are slow to notice that the price of things they consume have fallen by the same percentage.They may infer that the reward to working is
A)temporarily low and so supply a smaller quantity of labor.
B)temporarily low and so supply a larger quantity of labor.
C)temporarily high and so supply a smaller quantity of labor.
D)temporarily high and so supply a larger quantity of labor.
A)temporarily low and so supply a smaller quantity of labor.
B)temporarily low and so supply a larger quantity of labor.
C)temporarily high and so supply a smaller quantity of labor.
D)temporarily high and so supply a larger quantity of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The sticky-price theory implies that
A)the short-run aggregate-supply curve is upward-sloping.
B)an unexpected fall in the price level induces firms to reduce the quantity of goods and services they produce.
C)menu costs influence the speed of adjustment of prices.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)the short-run aggregate-supply curve is upward-sloping.
B)an unexpected fall in the price level induces firms to reduce the quantity of goods and services they produce.
C)menu costs influence the speed of adjustment of prices.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is not a determinant of the long-run level of real GDP?
A)the price level
B)the supply of labor
C)available natural resources
D)available technology
A)the price level
B)the supply of labor
C)available natural resources
D)available technology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Some countries have high minimum wages and require a lengthy and costly process to get permission to open a business
A)Reducing either the minimum wage or the time and cost to open a business would have no effect on the long-run aggregate supply curve.
B)Reducing the minimum wage and the time and cost to open a business would both shift the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
C)Reducing the minimum wage would shift long-run aggregate supply to the right.Reducing the time and cost to open a business would have no affect on the long-run aggregate supply curve.
D)Reducing the minimum wage would have no affect on the long-run aggregate supply curve.Reducing the time and cost to open a business would shift the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
A)Reducing either the minimum wage or the time and cost to open a business would have no effect on the long-run aggregate supply curve.
B)Reducing the minimum wage and the time and cost to open a business would both shift the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
C)Reducing the minimum wage would shift long-run aggregate supply to the right.Reducing the time and cost to open a business would have no affect on the long-run aggregate supply curve.
D)Reducing the minimum wage would have no affect on the long-run aggregate supply curve.Reducing the time and cost to open a business would shift the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An economic contraction caused by a shift in aggregate demand remedies itself over time as the expected price level
A)rises,shifting aggregate demand right.
B)rises,shifting aggregate demand left.
C)falls,shifting aggregate supply right.
D)falls,shifting aggregate supply left.
A)rises,shifting aggregate demand right.
B)rises,shifting aggregate demand left.
C)falls,shifting aggregate supply right.
D)falls,shifting aggregate supply left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The long-run aggregate supply curve shifts right if
A)technology improves.
B)the price level decreases.
C)the money supply increases.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)technology improves.
B)the price level decreases.
C)the money supply increases.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A decrease in the expected price level shifts
A)only the long-run aggregate supply curve right.
B)only the short-run aggregate supply curve right.
C)both the short-run and the long-run aggregate supply curve right.
D)Neither the short-run nor the long-run aggregate supply curve right.
A)only the long-run aggregate supply curve right.
B)only the short-run aggregate supply curve right.
C)both the short-run and the long-run aggregate supply curve right.
D)Neither the short-run nor the long-run aggregate supply curve right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Figure 34-1 
Refer to Figure 34-1.If the economy starts at C,an increase in the money supply moves the economy
A)to A in the long run.
B)to B in the long run.
C)back to C in the long run.
D)to D in the long run.

Refer to Figure 34-1.If the economy starts at C,an increase in the money supply moves the economy
A)to A in the long run.
B)to B in the long run.
C)back to C in the long run.
D)to D in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Wages tend to be sticky
A)because of contracts,social norms,and notions of fairness.
B)because of contracts,but not social norms or notions of fairness.
C)because of social norms and notions of fairness,but not contracts.
D)None of the above are correct.
A)because of contracts,social norms,and notions of fairness.
B)because of contracts,but not social norms or notions of fairness.
C)because of social norms and notions of fairness,but not contracts.
D)None of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Other things the same,if the money supply rises by 2% and people were expecting it to rise by 5%,then some firms have
A)higher than desired prices which increases their sales.
B)higher than desired prices which depresses their sales.
C)lower than desired prices which increases their sales.
D)lower than desired prices which depresses their sales.
A)higher than desired prices which increases their sales.
B)higher than desired prices which depresses their sales.
C)lower than desired prices which increases their sales.
D)lower than desired prices which depresses their sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When the money supply increases
A)interest rates fall and so aggregate demand shifts right.
B)interest rates fall and so aggregate demand shifts left.
C)interest rates rise and so aggregate demand shifts right.
D)interest rates rise and so aggregate demand shifts left.
A)interest rates fall and so aggregate demand shifts right.
B)interest rates fall and so aggregate demand shifts left.
C)interest rates rise and so aggregate demand shifts right.
D)interest rates rise and so aggregate demand shifts left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Sticky nominal wages can result in
A)lower profits for firms when the price level is lower than expected.
B)a decrease in real wages when the price level is lower than expected.
C)a short-run aggregate-supply curve that is vertical.
D)a long-run aggregate-supply curve that is upward-sloping.
A)lower profits for firms when the price level is lower than expected.
B)a decrease in real wages when the price level is lower than expected.
C)a short-run aggregate-supply curve that is vertical.
D)a long-run aggregate-supply curve that is upward-sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Like real GDP,investment fluctuates,but it fluctuates much less than real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Other things the same,as the price level falls,the exchange rate rises.A rise in the exchange rate leads to a decrease in net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
According to classical macroeconomic theory,changes in the money supply change nominal but not real variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Although wages,incomes,and interest rates are most often discussed in nominal terms,what matters most are their real values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Figure 34-2. 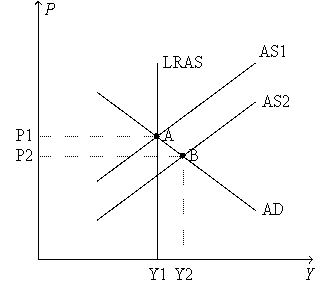
Refer to Figure 34-2.The appearance of the long-run aggregate-supply (LRAS)curve
A)is inconsistent with the concept of monetary neutrality.
B)is consistent with the idea that point A represents a long-run equilibrium but not a short-run equilibrium when the relevant short-run aggregate-supply curve is AS1.
C)indicates that Y1 is the natural rate of output.
D)All of the above are correct.

Refer to Figure 34-2.The appearance of the long-run aggregate-supply (LRAS)curve
A)is inconsistent with the concept of monetary neutrality.
B)is consistent with the idea that point A represents a long-run equilibrium but not a short-run equilibrium when the relevant short-run aggregate-supply curve is AS1.
C)indicates that Y1 is the natural rate of output.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Aggregate demand shifts to the left if the money supply increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Suppose that during the Great Depression long-run aggregate supply shifted left.To be consistent with what happened to the price level and output,what would have had to happen to aggregate demand?
A)It would have to have shifted left by less than aggregate supply.
B)It would have to have shifted left by more than aggregate supply.
C)It would have to have shifted right by less than aggregate supply.
D)It would have to have shifted right by more than aggregate supply.
A)It would have to have shifted left by less than aggregate supply.
B)It would have to have shifted left by more than aggregate supply.
C)It would have to have shifted right by less than aggregate supply.
D)It would have to have shifted right by more than aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An increase in the actual price level does not shift the short-run aggregate supply curve,but an expected increase in the price level shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Technological progress shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Stagflation exists when prices
A)and output rise.
B)rise and output falls.
C)fall and output rises.
D)and output fall.
A)and output rise.
B)rise and output falls.
C)fall and output rises.
D)and output fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Figure 34-2. 
Refer to Financial Crisis.What happens to the price level and real GDP in the short run?
A)both the price level and real GDP rise
B)the the price level level rises and real GDP falls
C)the the price level level falls and real GDP rises
D)both the price level and real GDP fall

Refer to Financial Crisis.What happens to the price level and real GDP in the short run?
A)both the price level and real GDP rise
B)the the price level level rises and real GDP falls
C)the the price level level falls and real GDP rises
D)both the price level and real GDP fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The long-run effect of an increase in government spending is to raise
A)both real output and the price level.
B)real output and lower the price level.
C)real output and leave the price level unchanged.
D)the price level and leave real output unchanged.
A)both real output and the price level.
B)real output and lower the price level.
C)real output and leave the price level unchanged.
D)the price level and leave real output unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If aggregate demand shifts right,then eventually price level expectations rise.This increase in price level expectations causes the aggregate demand curve to shift to the left back to its original position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose the economy is in long-run equilibrium.If there is a sharp decline in the stock market combined with a significant increase in immigration of skilled workers,then in the short run,
A)real GDP will rise and the price level might rise,fall,or stay the same.In the long-run,real GDP will rise and the price level might rise,fall,or stay the same.
B)the price level will fall,and real GDP might rise,fall,or stay the same.In the long-run,real GDP and the price level will be unaffected.
C)the price level will rise,and real GDP might rise,fall,or stay the same.In the long run,real GDP will rise and the price level will fall.
D)the price level will fall,and real GDP might rise,fall,or stay the same.In the long run,real GDP will rise and the price level will fall.
A)real GDP will rise and the price level might rise,fall,or stay the same.In the long-run,real GDP will rise and the price level might rise,fall,or stay the same.
B)the price level will fall,and real GDP might rise,fall,or stay the same.In the long-run,real GDP and the price level will be unaffected.
C)the price level will rise,and real GDP might rise,fall,or stay the same.In the long run,real GDP will rise and the price level will fall.
D)the price level will fall,and real GDP might rise,fall,or stay the same.In the long run,real GDP will rise and the price level will fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Recessions occur at irregular intervals and are almost impossible to predict with much accuracy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Policymakers who control monetary and fiscal policy and want to offset the effects on output of an economic contraction caused by a shift in aggregate supply could use policy to shift
A)aggregate supply to the right.
B)aggregate supply to the left.
C)aggregate demand to the right.
D)aggregate demand to the left.
A)aggregate supply to the right.
B)aggregate supply to the left.
C)aggregate demand to the right.
D)aggregate demand to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The effect of a change in the value of the currency in the foreign exchange market due to a change in the price level helps explain the slope of aggregate demand,but does not shift it.The effects of a change in the value of the currency in the foreign exchange market due to speculation is shown by shifting the aggregate demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Economists mostly agree that the Great Depression was principally caused by factors that shifted short-run aggregate supply left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Suppose the economy is in long-run equilibrium.If there is a sharp increase in the minimum wage as well as an increase in pessimism about future business conditions,then we would expect that in the short-run,
A)real GDP will rise and the price level might rise,fall,or stay the same.
B)real GDP will fall and the price level might rise,fall,or stay the same.
C)the price level will rise,and real GDP might rise,fall,or stay the same.
D)the price level will fall,and real GDP might rise,fall,or stay the same.
A)real GDP will rise and the price level might rise,fall,or stay the same.
B)real GDP will fall and the price level might rise,fall,or stay the same.
C)the price level will rise,and real GDP might rise,fall,or stay the same.
D)the price level will fall,and real GDP might rise,fall,or stay the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When the price level rises unexpectedly,some businesses may mistake part of the increase for an increase in the price of their product relative to others and so decrease their production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Explain how an increase in the price level changes interest rates.How does this change in interest rates lead to changes in investment and net exports?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
John Maynard Keynes advocated policies that would increase aggregate demand as a way to decrease unemployment caused by recessions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Illustrate the classical analysis of growth and inflation with aggregate demand and long-run aggregate supply curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Policymakers who influence aggregate demand can potentially mitigate the severity of economic fluctuations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What variables besides real GDP tend to decline during recessions?
Given the definition of real GDP,argue that declines in these variables are to be expected.
Given the definition of real GDP,argue that declines in these variables are to be expected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The primary purpose of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply model is to demonstrate the classical dichotomy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What do most economists believe concerning the relation between the price level and real output?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The long-run trend in real GDP is upward.How is this possible given business cycles?
What explains the upward trend?
What explains the upward trend?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



