Deck 36: The Short-Run Trade-Off Between Inflation and Unemployment
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/67
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 36: The Short-Run Trade-Off Between Inflation and Unemployment
1
If inflation expectations decline,then the short-run Phillips curve shifts
A)left,so that at any inflation rate unemployment is lower in the short run than before.
B)right,so that at any inflation rate unemployment is lower in the short run than before.
C)right,so that at any inflation rate unemployment is higher in the short run than before.
D)left,so that at any inflation rate unemployment is higher in the short run than before.
A)left,so that at any inflation rate unemployment is lower in the short run than before.
B)right,so that at any inflation rate unemployment is lower in the short run than before.
C)right,so that at any inflation rate unemployment is higher in the short run than before.
D)left,so that at any inflation rate unemployment is higher in the short run than before.
A
2
Figure 36-4 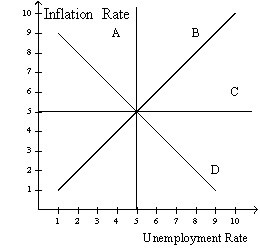
Refer to figure 36-4.In this order,which curve is a long-run Phillips curve and which is a short-run Phillips curve?
A)A,B
B)A,D
C)C,B
D)None of the above is correct.

Refer to figure 36-4.In this order,which curve is a long-run Phillips curve and which is a short-run Phillips curve?
A)A,B
B)A,D
C)C,B
D)None of the above is correct.
B
3
Figure 36-5
Use the graph below to answer the following questions.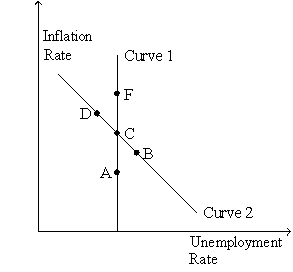
Refer to Figure 36-5.The money supply growth rate is greatest at
A)A.
B)B.
C)C.
D)F.
Use the graph below to answer the following questions.

Refer to Figure 36-5.The money supply growth rate is greatest at
A)A.
B)B.
C)C.
D)F.
D
4
For a number of years Canada and many European countries have had higher average unemployment rates than the United States.The Phillips curve suggests that these countries
A)have higher average inflation rates than the United States.
B)have long-run Phillips curves to the right of the United States'.
C)may have less generous unemployment compensation or lower minimum wages.
D)All of the above are consistent with the evidence on unemployment rates.
A)have higher average inflation rates than the United States.
B)have long-run Phillips curves to the right of the United States'.
C)may have less generous unemployment compensation or lower minimum wages.
D)All of the above are consistent with the evidence on unemployment rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Figure 36-7
Use this graph to answer the questions below.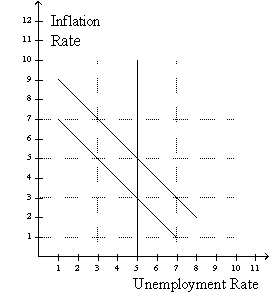
Refer to figure 36-7.Suppose the economy starts at 5% unemployment and 3% inflation and expected inflation remains at 3%.Which one of the following points could the economy move to in the short run if the Federal Reserve pursues a more expansionary monetary policy?
A)7% unemployment and 1% inflation
B)7% unemployment and 3% inflation
C)3% unemployment and 5% inflation
D)3% unemployment and 7% inflation
Use this graph to answer the questions below.

Refer to figure 36-7.Suppose the economy starts at 5% unemployment and 3% inflation and expected inflation remains at 3%.Which one of the following points could the economy move to in the short run if the Federal Reserve pursues a more expansionary monetary policy?
A)7% unemployment and 1% inflation
B)7% unemployment and 3% inflation
C)3% unemployment and 5% inflation
D)3% unemployment and 7% inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If the natural rate of unemployment falls,
A)both the short-run Phillips curve and the long-run Phillips curve shift.
B)only the short-run Phillips curve shifts.
C)only the long-run Phillips curve shifts.
D)neither the short-run nor the long-run Phillips curves shift.
A)both the short-run Phillips curve and the long-run Phillips curve shift.
B)only the short-run Phillips curve shifts.
C)only the long-run Phillips curve shifts.
D)neither the short-run nor the long-run Phillips curves shift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In his famous article published in an economics journal in 1958,a.W.Phillips
A)used data for the United States to show a negative relationship between the rate of change of the U.S.consumer price index and the U.S.unemployment rate.
B)used data for the United States to show a negative relationship between the rate of change of wages in the U.S.and the U.S.unemployment rate.
C)used data for the United Kingdom to show a negative relationship between the rate of change of the U.K.consumer price index and the U.K.unemployment rate.
D)used data for the United Kingdom to show a negative relationship between the rate of change of wages in the U.K.and the U.K.unemployment rate.
A)used data for the United States to show a negative relationship between the rate of change of the U.S.consumer price index and the U.S.unemployment rate.
B)used data for the United States to show a negative relationship between the rate of change of wages in the U.S.and the U.S.unemployment rate.
C)used data for the United Kingdom to show a negative relationship between the rate of change of the U.K.consumer price index and the U.K.unemployment rate.
D)used data for the United Kingdom to show a negative relationship between the rate of change of wages in the U.K.and the U.K.unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Figure 36-1.The left-hand graph shows a short-run aggregate-supply (SRAS)curve and two aggregate-demand (AD)curves.On the right-hand diagram,U represents the unemployment rate. 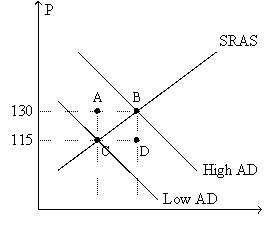
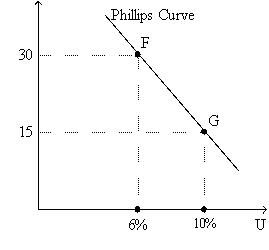
Refer to Figure 36-1.Suppose points F and G on the right-hand graph represent two possible outcomes for an imaginary economy in the year 2012,and those two points correspond to points B and C,respectively,on the left-hand graph.Also suppose we know that the price index equaled 120 in 2011.Then the numbers 115 and 130 on the vertical axis of the left-hand graph would have to be replaced by
A)155 and 175,respectively.
B)138 and 156,respectively.
C)137.5 and 154.75,respectively.
D)135 and 150,respectively.


Refer to Figure 36-1.Suppose points F and G on the right-hand graph represent two possible outcomes for an imaginary economy in the year 2012,and those two points correspond to points B and C,respectively,on the left-hand graph.Also suppose we know that the price index equaled 120 in 2011.Then the numbers 115 and 130 on the vertical axis of the left-hand graph would have to be replaced by
A)155 and 175,respectively.
B)138 and 156,respectively.
C)137.5 and 154.75,respectively.
D)135 and 150,respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following leads to a lower level of unemployment in the long run?
A)both an increase in the size of the money supply and an increase in the money supply growth rate
B)an increase in the size of the money supply but not an increase in the money supply growth rate
C)an increase in the money supply growth rate,but not an increase in the size of the money supply
D)neither an increase in the size of the money supply nor an increase in the money supply growth rate
A)both an increase in the size of the money supply and an increase in the money supply growth rate
B)an increase in the size of the money supply but not an increase in the money supply growth rate
C)an increase in the money supply growth rate,but not an increase in the size of the money supply
D)neither an increase in the size of the money supply nor an increase in the money supply growth rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A basis for the slope of the short-run Phillips curve is that when unemployment is high there are
A)downward pressures on prices and wages.
B)downward pressures on prices and upward pressures on wages.
C)upward pressures on prices and downward pressures on wages.
D)upward pressures on prices and wages.
A)downward pressures on prices and wages.
B)downward pressures on prices and upward pressures on wages.
C)upward pressures on prices and downward pressures on wages.
D)upward pressures on prices and wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Figure 36-3.The left-hand graph shows a short-run aggregate-supply (SRAS)curve and two aggregate-demand (AD)curves.On the left-hand diagram,Y represents output and on the right-hand diagram,U represents the unemployment rate. 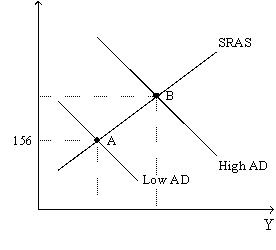
Refer to Figure 36-3.Assume the figure charts possible outcomes for the year 2018.In 2018,the economy is at point B on the left-hand graph,which corresponds to point B on the right-hand graph.Also,point A on the left-hand graph corresponds to A on the right-hand graph.The price level in the year 2018 is
A)155.56.
B)159.00.
C)163.50.
D)170.04.


Refer to Figure 36-3.Assume the figure charts possible outcomes for the year 2018.In 2018,the economy is at point B on the left-hand graph,which corresponds to point B on the right-hand graph.Also,point A on the left-hand graph corresponds to A on the right-hand graph.The price level in the year 2018 is
A)155.56.
B)159.00.
C)163.50.
D)170.04.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Samuelson and Solow argued that a combination of low unemployment and low inflation
A)was impossible given the historical data as summarized by the Phillips curve.
B)could be achieved with an "appropriate" fiscal policy.
C)could be achieved with an "appropriate" monetary policy.
D)could be achieved with an "appropriate" mix of monetary and fiscal policies.
A)was impossible given the historical data as summarized by the Phillips curve.
B)could be achieved with an "appropriate" fiscal policy.
C)could be achieved with an "appropriate" monetary policy.
D)could be achieved with an "appropriate" mix of monetary and fiscal policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the late 1960s,Milton Friedman and Edmund Phelps argued that
A)the trade-off between inflation and unemployment did not apply in the long run This claim is consistent with monetary neutrality in the long run.
B)the trade-off between inflation and unemployment did not apply in the long run.This claim is inconsistent with monetary neutrality in the long run.
C)the trade-off between inflation and unemployment applied in both the short run and the long run.This claim is consistent with monetary neutrality in the long run.
D)the trade-off between inflation and unemployment applied in both the short run and the long run.This claim is inconsistent with monetary neutrality in the long run.
A)the trade-off between inflation and unemployment did not apply in the long run This claim is consistent with monetary neutrality in the long run.
B)the trade-off between inflation and unemployment did not apply in the long run.This claim is inconsistent with monetary neutrality in the long run.
C)the trade-off between inflation and unemployment applied in both the short run and the long run.This claim is consistent with monetary neutrality in the long run.
D)the trade-off between inflation and unemployment applied in both the short run and the long run.This claim is inconsistent with monetary neutrality in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A policy that raised the natural rate of unemployment would shift
A)both the short-run and the long-run Phillips curves to the right.
B)the short-run Phillips curve right but leave the long-run Phillips curve unchanged.
C)the long-run Phillips curve right but leave the short-run Phillips curve unchanged.
D)neither the long-run Phillips curve nor the short-run Phillips curve right.
A)both the short-run and the long-run Phillips curves to the right.
B)the short-run Phillips curve right but leave the long-run Phillips curve unchanged.
C)the long-run Phillips curve right but leave the short-run Phillips curve unchanged.
D)neither the long-run Phillips curve nor the short-run Phillips curve right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the long run,
A)the natural rate of unemployment depends primarily on the level of aggregate demand.
B)inflation depends primarily upon the money supply growth rate.
C)there is a tradeoff between the inflation rate and the natural rate of unemployment.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)the natural rate of unemployment depends primarily on the level of aggregate demand.
B)inflation depends primarily upon the money supply growth rate.
C)there is a tradeoff between the inflation rate and the natural rate of unemployment.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Figure 36-1.The left-hand graph shows a short-run aggregate-supply (SRAS)curve and two aggregate-demand (AD)curves.On the right-hand diagram,U represents the unemployment rate. 

Refer to Figure 36-1.The curve that is depicted on the right-hand graph offers policymakers a "menu" of combinations
A)that applies both in the short run and in the long run.
B)that is relevant to choices involving fiscal policy,but not to choices involving monetary policy.
C)of inflation and unemployment.
D)All of the above are correct.


Refer to Figure 36-1.The curve that is depicted on the right-hand graph offers policymakers a "menu" of combinations
A)that applies both in the short run and in the long run.
B)that is relevant to choices involving fiscal policy,but not to choices involving monetary policy.
C)of inflation and unemployment.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If the short-run Phillips curve were stable,which of the following would be unusual?
A)an increase in government spending and a fall in unemployment
B)an increase in inflation and a decrease in output
C)a decrease in the inflation rate and a rise in the unemployment rate
D)a decrease in the money supply and a rise in the unemployment rate.
A)an increase in government spending and a fall in unemployment
B)an increase in inflation and a decrease in output
C)a decrease in the inflation rate and a rise in the unemployment rate
D)a decrease in the money supply and a rise in the unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The equation,
Unemployment rate = Natural rate of unemployment - a * ctual inflation - Expected inflation),
A)Is the equation of the short-run Phillips curve.
B)implies there can be no stable short-run Phillips curve.
C)reflects the reasoning of Friedman and Phelps.
D)All of the above are correct.
Unemployment rate = Natural rate of unemployment - a * ctual inflation - Expected inflation),
A)Is the equation of the short-run Phillips curve.
B)implies there can be no stable short-run Phillips curve.
C)reflects the reasoning of Friedman and Phelps.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If policymakers decrease aggregate demand,then in the long run
A)prices will be lower and unemployment will be higher.
B)prices will be lower and unemployment will be unchanged.
C)prices and unemployment will be unchanged.
D)None of the above is correct.
A)prices will be lower and unemployment will be higher.
B)prices will be lower and unemployment will be unchanged.
C)prices and unemployment will be unchanged.
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If the central bank decreases the money supply,then in the short run prices
A)rise and unemployment falls.
B)fall and unemployment rises.
C)and unemployment rise.
D)and unemployment fall.
A)rise and unemployment falls.
B)fall and unemployment rises.
C)and unemployment rise.
D)and unemployment fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
According to Friedman and Phelps,the unemployment rate
A)is never below its natural rate.
B)is below its natural rate when actual inflation is greater than expected inflation.
C)is below its natural rate when actual inflation is less than expected inflation.
D)is below its natural rate when actual inflation equals expected inflation.
A)is never below its natural rate.
B)is below its natural rate when actual inflation is greater than expected inflation.
C)is below its natural rate when actual inflation is less than expected inflation.
D)is below its natural rate when actual inflation equals expected inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Disinflation would eventually cause
A)the short-run and the long run Phillips curve to shift right.
B)the short-run and the long run Phillips curve to shift left.
C)the short-run Phillips curve but not the long run Phillips curve to shift right.
D)the short-run Phillips curve but not the long run Phillips curve to shift left.
A)the short-run and the long run Phillips curve to shift right.
B)the short-run and the long run Phillips curve to shift left.
C)the short-run Phillips curve but not the long run Phillips curve to shift right.
D)the short-run Phillips curve but not the long run Phillips curve to shift left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The idea that the long-run Phillips curve is
A)vertical stems from the analysis of Samuelson and Solow.
B)vertical stems from the analysis of Friedman and Phelps.
C)vertical was disproved by the experiment that monetary and fiscal policymakers inadvertently created in the 1970s.
D)downward-sloping can be correct if unemployment responds very quickly to unexpected inflation.
A)vertical stems from the analysis of Samuelson and Solow.
B)vertical stems from the analysis of Friedman and Phelps.
C)vertical was disproved by the experiment that monetary and fiscal policymakers inadvertently created in the 1970s.
D)downward-sloping can be correct if unemployment responds very quickly to unexpected inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If people anticipate higher inflation,but inflation remains the same then
A)the short-run Phillips curve would shift right and unemployment would rise.
B)the short-run Phillips curve would shift right and unemployment would fall.
C)the short-run Phillips curve would shift left and unemployment would rise.
D)the short-run Phillips curve would shift left and unemployment would fall.
A)the short-run Phillips curve would shift right and unemployment would rise.
B)the short-run Phillips curve would shift right and unemployment would fall.
C)the short-run Phillips curve would shift left and unemployment would rise.
D)the short-run Phillips curve would shift left and unemployment would fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
For many years country A has had a lower unemployment rate than country B.According to the long-run Phillips curve which of the following could explain this?
Country A has
A)maintained a higher money supply growth rate.
B)maintained a lower money supply growth rate.
C)a higher minimum wage than country B.
D)a lower minimum wage than country B.
Country A has
A)maintained a higher money supply growth rate.
B)maintained a lower money supply growth rate.
C)a higher minimum wage than country B.
D)a lower minimum wage than country B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the long run a reduction in the money supply growth rate affects
A)the inflation rate and the natural rate of unemployment.
B)the inflation rate but not the natural rate of unemployment.
C)neither the inflation rate nor the natural rate of unemployment.
D)the natural rate of unemployment,but not the inflation rate.
A)the inflation rate and the natural rate of unemployment.
B)the inflation rate but not the natural rate of unemployment.
C)neither the inflation rate nor the natural rate of unemployment.
D)the natural rate of unemployment,but not the inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the long run,a decrease in the money supply growth rate
A)increases inflation and shifts the short-run Phillips curve right.
B)increases inflation and shifts the short-run Phillips curve left.
C)decreases inflation and shifts the short-run Philips curve right.
D)decreases inflation and shifts the short-run Phillips curve left.
A)increases inflation and shifts the short-run Phillips curve right.
B)increases inflation and shifts the short-run Phillips curve left.
C)decreases inflation and shifts the short-run Philips curve right.
D)decreases inflation and shifts the short-run Phillips curve left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An event that directly affects firms' costs of production and thus the prices they charge is called
A)a Phillips contraction.
B)an inflationary spiral.
C)a demand shock.
D)a supply shock.
A)a Phillips contraction.
B)an inflationary spiral.
C)a demand shock.
D)a supply shock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If a government redesigned its unemployment insurance programs so that the unemployed had greater incentives to quickly find appropriate jobs,then which of the following curves would shift right?
A)the long-run Phillips curve and the long-run aggregate supply curve
B)the long-run Phillips curve but not the long-run aggregate supply curve
C)the long-run aggregate supply curve but not the long-run Phillips curve
D)neither the long-run Phillips curve nor the long-run aggregate supply curve
A)the long-run Phillips curve and the long-run aggregate supply curve
B)the long-run Phillips curve but not the long-run aggregate supply curve
C)the long-run aggregate supply curve but not the long-run Phillips curve
D)neither the long-run Phillips curve nor the long-run aggregate supply curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If people eventually adjust their inflation expectations so that in the long run actual and expected inflation are the same,then policymakers
A)Can not exploit a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment in either the short or long run.
B)Can exploit a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment in the short run but not in the long run.
C)Can exploit a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment in both the short run and the long run.
D)Can exploit a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment in the long run,but not the short run.
A)Can not exploit a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment in either the short or long run.
B)Can exploit a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment in the short run but not in the long run.
C)Can exploit a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment in both the short run and the long run.
D)Can exploit a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment in the long run,but not the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Figure 36-8.The left-hand graph shows a short-run aggregate-supply (SRAS)curve and two aggregate-demand (AD)curves.On the right-hand diagram,"Inf Rate" means "Inflation Rate." 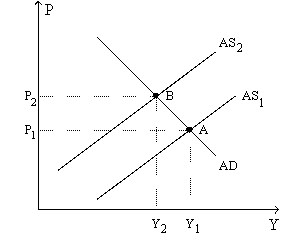
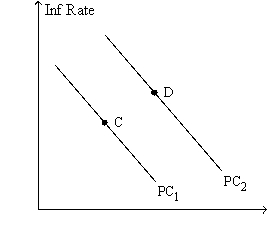
Refer to Figure 36-8.Subsequent to the shift of the Phillips curve from PC1 to PC2,the curve will soon shift back to PC1 if people perceive the
A)increase in the inflation rate as a temporary aberration.
B)economic boom as a temporary aberration.
C)increase in the inflation rate as a sign of a new era of higher inflation.
D)economic boom as a sign of a new era of higher economic growth.


Refer to Figure 36-8.Subsequent to the shift of the Phillips curve from PC1 to PC2,the curve will soon shift back to PC1 if people perceive the
A)increase in the inflation rate as a temporary aberration.
B)economic boom as a temporary aberration.
C)increase in the inflation rate as a sign of a new era of higher inflation.
D)economic boom as a sign of a new era of higher economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Figure 36-8.The left-hand graph shows a short-run aggregate-supply (SRAS)curve and two aggregate-demand (AD)curves.On the right-hand diagram,"Inf Rate" means "Inflation Rate." 

Refer to Figure 36-8.The shift of the aggregate-supply curve from AS1 to AS2
A)results in a more favorable trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
B)results in a more favorable trade-off between inflation and the growth rate of real GDP.
C)represents an adverse shock to aggregate supply.
D)represents a favorable shock to aggregate supply.


Refer to Figure 36-8.The shift of the aggregate-supply curve from AS1 to AS2
A)results in a more favorable trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
B)results in a more favorable trade-off between inflation and the growth rate of real GDP.
C)represents an adverse shock to aggregate supply.
D)represents a favorable shock to aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is correct if there is a favorable supply shock?
A)the short-run aggregate supply curve and the short-run Phillips curve both shift right.
B)the short-run aggregate supply curve and the short-run Phillips curve both shift left.
C)the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts right and the short-run Phillips curve shifts left.
D)the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts left and the short-run Phillips curve shifts right.
A)the short-run aggregate supply curve and the short-run Phillips curve both shift right.
B)the short-run aggregate supply curve and the short-run Phillips curve both shift left.
C)the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts right and the short-run Phillips curve shifts left.
D)the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts left and the short-run Phillips curve shifts right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the long run,an increase in the money supply
A)leaves prices and unemployment unchanged.
B)raises prices and unemployment.
C)raises prices and leaves unemployment unchanged.
D)leaves prices unchanged and reduces unemployment.
A)leaves prices and unemployment unchanged.
B)raises prices and unemployment.
C)raises prices and leaves unemployment unchanged.
D)leaves prices unchanged and reduces unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Disinflation is defined as a
A)zero rate of inflation.
B)constant rate of inflation.
C)reduction in the rate of inflation.
D)negative rate of inflation.
A)zero rate of inflation.
B)constant rate of inflation.
C)reduction in the rate of inflation.
D)negative rate of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following would cause the price level to fall and output to rise in the short run?
A)an increase in the money supply
B)a decrease in the money supply
C)an adverse supply shock
D)a favorable supply shock
A)an increase in the money supply
B)a decrease in the money supply
C)an adverse supply shock
D)a favorable supply shock

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In the nineteenth century,some countries were on a gold standard so that on average the money supply growth rate was close to zero and expected inflation was more or less constant.For these countries during this time period,we find that increases in actual inflation were generally associated with falling unemployment.These findings
A)are consistent with Friedman and Phelps's theories,because they argued that when inflation was higher than expected,unemployment would fall.
B)are consistent with Friedman and Phelps's theories,because they argued that when prices rose unemployment would fall whether actual inflation was higher than expected or not.
C)are inconsistent with Friedman and Phelps's theories,because they argued that higher inflation would increase unemployment.
D)are inconsistent with Friedman and Phelps's theories,because they argued that inflation and unemployment are unrelated.
A)are consistent with Friedman and Phelps's theories,because they argued that when inflation was higher than expected,unemployment would fall.
B)are consistent with Friedman and Phelps's theories,because they argued that when prices rose unemployment would fall whether actual inflation was higher than expected or not.
C)are inconsistent with Friedman and Phelps's theories,because they argued that higher inflation would increase unemployment.
D)are inconsistent with Friedman and Phelps's theories,because they argued that inflation and unemployment are unrelated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If unemployment is above its natural rate,what happens to move the economy to long-run equilibrium?
A)Inflation expectations rise which shifts the short-run Phillips curve to the right.
B)Inflation expectations rise which shifts the short-run Phillips curve to the left.
C)Inflation expectations fall which shifts the short-run Phillips curve to the right.
D)Inflation expectations fall which shifts the short-run Phillips curve to the left.
A)Inflation expectations rise which shifts the short-run Phillips curve to the right.
B)Inflation expectations rise which shifts the short-run Phillips curve to the left.
C)Inflation expectations fall which shifts the short-run Phillips curve to the right.
D)Inflation expectations fall which shifts the short-run Phillips curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A shock increases the costs of production.Given the effects of this shock,if the central bank wants to return the unemployment rate towards its previous level it would
A)increase the rate at which the money supply increases.This will also move inflation closer to its previous rate..
B)increase the rate at which the money supply increases.However,this will make inflation higher than its previous rate
C)decrease the rate at which the money supply increases.This will also move inflation closer to its original rate
D)decrease the rate at which the money supply increases.However,this will make higher than its previous rate.
A)increase the rate at which the money supply increases.This will also move inflation closer to its previous rate..
B)increase the rate at which the money supply increases.However,this will make inflation higher than its previous rate
C)decrease the rate at which the money supply increases.This will also move inflation closer to its original rate
D)decrease the rate at which the money supply increases.However,this will make higher than its previous rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If policymakers accommodate an adverse supply shock,then in the short run the unemployment rate
A)and the inflation rate rise.
B)and the inflation rate fall.
C)rises and the inflation rate falls.
D)falls and the inflation rate rises.
A)and the inflation rate rise.
B)and the inflation rate fall.
C)rises and the inflation rate falls.
D)falls and the inflation rate rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the Friedman-Phelps analysis,when inflation is less than expected,the unemployment rate is less than the natural rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A rightward shift of the short-run aggregate-supply curve results in a more favorable trade-off between inflation and unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
An increase in the inflation rate permanently reduces the natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If a central bank reduces inflation 2 percentage points and this makes output fall 3 percentage points and unemployment rise 5 percentage points for one year,the sacrifice ratio is
A)5/2.
B)3/2.
C)2/3.
D)2/5.
A)5/2.
B)3/2.
C)2/3.
D)2/5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The sacrifice ratio is the
A)sum of the inflation and unemployment rates.
B)inflation rate divided by the unemployment rate.
C)number of percentage points annual output falls for each percentage point reduction in inflation.
D)number of percentage points unemployment rises for each percentage point reduction in inflation.
A)sum of the inflation and unemployment rates.
B)inflation rate divided by the unemployment rate.
C)number of percentage points annual output falls for each percentage point reduction in inflation.
D)number of percentage points unemployment rises for each percentage point reduction in inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A central bank announces it will decrease the inflation rate by 10 percentage points.People are skeptical of the announcement,but do expect the central bank will reduce inflation by 5 percentage points and so expected inflation falls by 5 percentage points.If the central bank decreases inflation by only 3 percentage points then the unemployment rate will fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Other things the same,an increase in aggregate demand reduces unemployment and raises inflation in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In response to the financial crisis of 2007-2008,policymakers used
A)expansionary monetary policy and expansionary fiscal policy.
B)expansionary monetary policy and contractionary fiscal policy.
C)contractionary monetary policy and expansionary fiscal policy.
D)contractionary monetary policy and contractionary fiscal policy.
A)expansionary monetary policy and expansionary fiscal policy.
B)expansionary monetary policy and contractionary fiscal policy.
C)contractionary monetary policy and expansionary fiscal policy.
D)contractionary monetary policy and contractionary fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If monetary policy moves unemployment below its natural rate,both expected and actual inflation will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A country is likely to have a higher sacrifice ratio if
A)Contracts are shorter,and people believe the central bank will reduce inflation.
B)Contracts are longer,and people believe the central bank will not reduce inflation
C)Contracts are longer,and people believe the central bank will reduce inflation.
D)Contracts are shorter,and people believe the central bank will not reduce inflation.
A)Contracts are shorter,and people believe the central bank will reduce inflation.
B)Contracts are longer,and people believe the central bank will not reduce inflation
C)Contracts are longer,and people believe the central bank will reduce inflation.
D)Contracts are shorter,and people believe the central bank will not reduce inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Proponents of rational expectations argued that the sacrifice ratio
A)could be high because it was rational for people not to immediately change their expectations.
B)could be high because people might adjust their expectations quickly if they found anti-inflation policy credible.
C)could be low because it was rational for people not to immediately change their expectations.
D)could be low because people might adjust their expectations quickly if they found anti-inflation policy credible.
A)could be high because it was rational for people not to immediately change their expectations.
B)could be high because people might adjust their expectations quickly if they found anti-inflation policy credible.
C)could be low because it was rational for people not to immediately change their expectations.
D)could be low because people might adjust their expectations quickly if they found anti-inflation policy credible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Just as the aggregate-supply curve slopes upward only in the short run,the trade-off between inflation and unemployment holds only in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The logic behind the tradeoff between inflation and unemployment is that high aggregate demand puts upward pressure on wages and prices while raising output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Contractionary monetary policy
A)leads to disinflation and makes the short-run Phillips curve shift right.
B)leads to disinflation and makes the short-run Phillips curve shift left.
C)does not lead to disinflation but makes the short-run Phillips curve shift right.
D)does not lead to disinflation but makes the short-run Phillips curve shift left.
A)leads to disinflation and makes the short-run Phillips curve shift right.
B)leads to disinflation and makes the short-run Phillips curve shift left.
C)does not lead to disinflation but makes the short-run Phillips curve shift right.
D)does not lead to disinflation but makes the short-run Phillips curve shift left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The short-run Phillips curve indicates that expansionary monetary policy will temporarily raise the unemployment rate above its natural rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The classical notion of monetary neutrality is consistent both with a vertical long-run aggregate-supply curve and with a vertical long-run Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A decrease in government expenditures serves as an example of an adverse supply shock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the long run,the natural rate of unemployment depends primarily on the growth rate of the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The theory by which people optimally use all available information when forecasting the future is known as
A)rational expectations.
B)perfect expectations.
C)credible expectations.
D)Predictive expectations.
A)rational expectations.
B)perfect expectations.
C)credible expectations.
D)Predictive expectations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Other things the same,a decrease in aggregate demand decreases both inflation and unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In the long run what primarily determines the natural rate of unemployment?
In the long run what primarily determines the inflation rate?
How does this relate to the classical dichotomy?
In the long run what primarily determines the inflation rate?
How does this relate to the classical dichotomy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Suppose that the Prime Minister and Parliament of Veridian are disappointed with the high inflation rates under the current system where the Veridian Ministry of Finance is in charge of the money supply.They make reforms to lower inflation from its current rate of 8%.Suppose further that the public is confident that with the reforms in place that inflation will fall to 2%.Also suppose that those in control of the money supply actually conduct monetary policy so that the actual inflation rate is 4%.Using long-run and short-run Phillips curves and assuming the natural rate of unemployment is 6%,show the initial long run equilibrium of Veridian and label it "A".Assuming that the government had actually set inflation at 2% and that the public believed this,label the long-run equilibrium "B".Now,suppose that inflation expectations fell to 2% and that the government unexpectedly created inflation of 4%.Show the short-run equilibrium and label it "C".If the money supply continues to grow at a rate consistent with 4% inflation,show where the economy ends up and label that point "D".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Are the effects of an increase in aggregate demand in the aggregate demand and aggregate supply model consistent with the Phillips curve?
Explain.
Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A low sacrifice ratio would make a central bank less willing to reduce the inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Suppose that the economy is at an inflation rate such that unemployment is above the natural rate.How does the economy return to the natural rate of unemployment if this lower inflation rate persists?
Use sticky-wage theory to explain your answer.
Use sticky-wage theory to explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A decrease in the growth rate of the money supply eventually causes the short-run Phillips curve to shift right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Some countries have inflation around or in excess of 8 percent.Suppose that the sacrifice ratio is 2.5.What is the cost of reducing inflation from 8 percent to 2 percent?
In your answer,define the sacrifice ratio and explain how you found the cost of inflation reduction.
In your answer,define the sacrifice ratio and explain how you found the cost of inflation reduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



