Deck 7: Consumers, producers, and the Efficiency of Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/64
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Consumers, producers, and the Efficiency of Markets
1
Motor oil and gasoline are complements.If the price of motor oil increases,consumer surplus in the gasoline market
A)decreases.
B)is unchanged.
C)increases.
D)may increase,decrease,or remain unchanged.
A)decreases.
B)is unchanged.
C)increases.
D)may increase,decrease,or remain unchanged.
D
2
A drought destroys many red grapes.As a result of the drought,the consumer surplus in the market for red grapes
A)increases,and the consumer surplus in the market for red wine increases.
B)increases,and the consumer surplus in the market for red wine decreases.
C)decreases,and the consumer surplus in the market for red wine increases.
D)decreases,and the consumer surplus in the market for red wine decreases.
A)increases,and the consumer surplus in the market for red wine increases.
B)increases,and the consumer surplus in the market for red wine decreases.
C)decreases,and the consumer surplus in the market for red wine increases.
D)decreases,and the consumer surplus in the market for red wine decreases.
D
3
Which of the following will cause an increase in consumer surplus?
A)an increase in the production cost of the good
B)a technological improvement in the production of the good
C)a decrease in the number of sellers of the good
D)the imposition of a binding price floor in the market
A)an increase in the production cost of the good
B)a technological improvement in the production of the good
C)a decrease in the number of sellers of the good
D)the imposition of a binding price floor in the market
B
4
Economists normally assume people's preferences should be
A)respected.
B)adjusted.
C)overruled.
D)ignored.
A)respected.
B)adjusted.
C)overruled.
D)ignored.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
On a graph,consumer surplus is represented by the area
A)between the demand and supply curves.
B)below the demand curve and above price.
C)below the price and above the supply curve.
D)below the demand curve and to the right of equilibrium price.
A)between the demand and supply curves.
B)below the demand curve and above price.
C)below the price and above the supply curve.
D)below the demand curve and to the right of equilibrium price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In a market,the marginal buyer is the buyer
A)whose willingness to pay is higher than that of all other buyers and potential buyers.
B)whose willingness to pay is lower than that of all other buyers and potential buyers.
C)who is willing to buy exactly one unit of the good.
D)who would be the first to leave the market if the price were any higher.
A)whose willingness to pay is higher than that of all other buyers and potential buyers.
B)whose willingness to pay is lower than that of all other buyers and potential buyers.
C)who is willing to buy exactly one unit of the good.
D)who would be the first to leave the market if the price were any higher.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A result of welfare economics is that the equilibrium price of a product is considered to be the best price because it
A)maximizes both the total revenue for firms and the quantity supplied of the product.
B)maximizes the combined welfare of buyers and sellers.
C)minimizes costs and maximizes output.
D)minimizes the level of welfare payments.
A)maximizes both the total revenue for firms and the quantity supplied of the product.
B)maximizes the combined welfare of buyers and sellers.
C)minimizes costs and maximizes output.
D)minimizes the level of welfare payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Figure 7-8 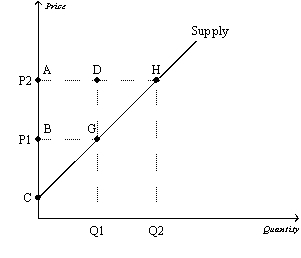
Refer to Figure 7-8.Which area represents producer surplus when the price is P2?
A)BCG
B)ACH
C)ABGD
D)AHGB

Refer to Figure 7-8.Which area represents producer surplus when the price is P2?
A)BCG
B)ACH
C)ABGD
D)AHGB

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Producer surplus is
A)measured using the demand curve for a good.
B)always a negative number for sellers in a competitive market.
C)the amount a seller is paid minus the cost of production.
D)the opportunity cost of production minus the cost of producing goods that go unsold.
A)measured using the demand curve for a good.
B)always a negative number for sellers in a competitive market.
C)the amount a seller is paid minus the cost of production.
D)the opportunity cost of production minus the cost of producing goods that go unsold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Figure 7-2 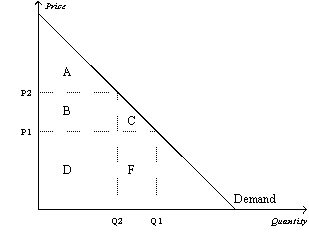
Refer to Figure 7-2.When the price is P1,consumer surplus is
A)A.
B)A+B.
C)A+B+C.
D)A+B+D.

Refer to Figure 7-2.When the price is P1,consumer surplus is
A)A.
B)A+B.
C)A+B+C.
D)A+B+D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The maximum price that a buyer will pay for a good is called the
A)cost.
B)willingness to pay.
C)Equity.
D)efficiency.
A)cost.
B)willingness to pay.
C)Equity.
D)efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A demand curve reflects each of the following except the
A)willingness to pay of all buyers in the market.
B)value each buyer in the market places on the good.
C)highest price buyers are willing to pay for each quantity.
D)ability of buyers to obtain the quantity they desire.
A)willingness to pay of all buyers in the market.
B)value each buyer in the market places on the good.
C)highest price buyers are willing to pay for each quantity.
D)ability of buyers to obtain the quantity they desire.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Figure 7-7 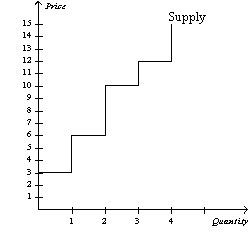
Refer to Figure 7-7.If the price of the good is 9.50,then producer surplus is
A)2.50.
B)6.50.
C)8.00.
D)10.00.

Refer to Figure 7-7.If the price of the good is 9.50,then producer surplus is
A)2.50.
B)6.50.
C)8.00.
D)10.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Figure 7-6 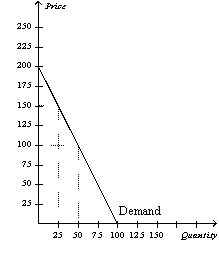
Refer to Figure 7-6.What happens to the consumer surplus if the price rises from 100 to 150?
A)The new consumer surplus is half of the original consumer surplus.
B)The new consumer surplus is 25 percent of the original consumer surplus.
C)The new consumer surplus is double the original consumer surplus.
D)The new consumer surplus is triple the original consumer surplus.

Refer to Figure 7-6.What happens to the consumer surplus if the price rises from 100 to 150?
A)The new consumer surplus is half of the original consumer surplus.
B)The new consumer surplus is 25 percent of the original consumer surplus.
C)The new consumer surplus is double the original consumer surplus.
D)The new consumer surplus is triple the original consumer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Figure 7-8 
Refer to Figure 7-8.Which area represents producer surplus when the price is P1?
A)BCG
B)ACH
C)ABGD
D)DGH

Refer to Figure 7-8.Which area represents producer surplus when the price is P1?
A)BCG
B)ACH
C)ABGD
D)DGH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When a buyer's willingness to pay for a good is equal to the price of the good,the
A)buyer's consumer surplus for that good is maximized.
B)buyer will buy as much of the good as the buyer's budget allows.
C)price of the good exceeds the value that the buyer places on the good.
D)buyer is indifferent between buying the good and not buying it.
A)buyer's consumer surplus for that good is maximized.
B)buyer will buy as much of the good as the buyer's budget allows.
C)price of the good exceeds the value that the buyer places on the good.
D)buyer is indifferent between buying the good and not buying it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If the cost of producing sofas decreases,then consumer surplus in the sofa market will
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain constant.
D)increase for some buyers and decrease for other buyers.
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain constant.
D)increase for some buyers and decrease for other buyers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Figure 7-2 
Refer to Figure 7-2.When the price rises from P1 to P2,consumer surplus
A)increases by an amount equal to A.
B)decreases by an amount equal to B+C.
C)increases by an amount equal to B+C.
D)decreases by an amount equal to C.

Refer to Figure 7-2.When the price rises from P1 to P2,consumer surplus
A)increases by an amount equal to A.
B)decreases by an amount equal to B+C.
C)increases by an amount equal to B+C.
D)decreases by an amount equal to C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Welfare economics is the study of how
A)the allocation of resources affects economic well-being.
B)a price ceiling compares to a price floor.
C)the government helps poor people.
D)a consumer's optimal choice affects her demand curve.
A)the allocation of resources affects economic well-being.
B)a price ceiling compares to a price floor.
C)the government helps poor people.
D)a consumer's optimal choice affects her demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A seller's opportunity cost measures the
A)value of everything he must give up to produce a good.
B)amount he is paid for a good minus his cost of providing it.
C)consumer surplus.
D)out of pocket expenses to produce a good but not the value of his time.
A)value of everything he must give up to produce a good.
B)amount he is paid for a good minus his cost of providing it.
C)consumer surplus.
D)out of pocket expenses to produce a good but not the value of his time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Figure 7-12 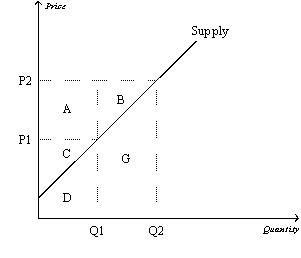
Refer to Figure 7-12.Area A represents
A)producer surplus to new producers entering the market as the result of an increase in price from P1 to P2.
B)the increase in consumer surplus that results from an upward-sloping supply curve.
C)the increase in total surplus when sellers are willing and able to increase supply from Q1 to Q2.
D)the increase in producer surplus to those producers already in the market when the price increases from P1 to P2.

Refer to Figure 7-12.Area A represents
A)producer surplus to new producers entering the market as the result of an increase in price from P1 to P2.
B)the increase in consumer surplus that results from an upward-sloping supply curve.
C)the increase in total surplus when sellers are willing and able to increase supply from Q1 to Q2.
D)the increase in producer surplus to those producers already in the market when the price increases from P1 to P2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Figure 7-12 
Refer to Figure 7-12.Suppose producer surplus is larger than C but smaller than A+B+C.The price of the good must be
A)lower than P1.
B)P1.
C)between P1 and P2.
D)higher than P2.

Refer to Figure 7-12.Suppose producer surplus is larger than C but smaller than A+B+C.The price of the good must be
A)lower than P1.
B)P1.
C)between P1 and P2.
D)higher than P2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Figure 7-17 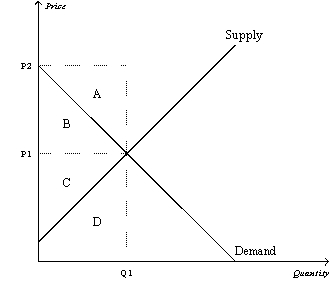
Refer to Figure 7-17.Which area represents producer surplus when the price is P1?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Refer to Figure 7-17.Which area represents producer surplus when the price is P1?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Figure 7-16 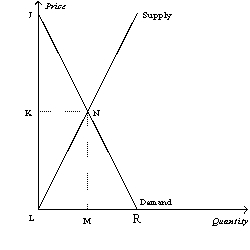
Refer to Figure 7-16.Total surplus can be measured as the area
A)JNK.
B)JNML.
C)JRL.
D)JNL.

Refer to Figure 7-16.Total surplus can be measured as the area
A)JNK.
B)JNML.
C)JRL.
D)JNL.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Figure 7-12 
Refer to Figure 7-12.When the price is P2,producer surplus is
A)A.
B)A+C.
C)A+B+C.
D)D+G.

Refer to Figure 7-12.When the price is P2,producer surplus is
A)A.
B)A+C.
C)A+B+C.
D)D+G.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose the demand for peaches decreases.What will happen to producer surplus in the market for peaches?
A)It increases.
B)It decreases.
C)It remains unchanged.
D)It may increase,decrease,or remain unchanged.
A)It increases.
B)It decreases.
C)It remains unchanged.
D)It may increase,decrease,or remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Total surplus is equal to
A)value to buyers - profit to sellers.
B)value to buyers - cost to sellers.
C)consumer surplus x producer surplus.
D)(consumer surplus + producer surplus)x equilibrium quantity.
A)value to buyers - profit to sellers.
B)value to buyers - cost to sellers.
C)consumer surplus x producer surplus.
D)(consumer surplus + producer surplus)x equilibrium quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Total surplus is represented by the area
A)under the demand curve and above the price.
B)above the supply curve and up to the price.
C)under the supply curve and up to the price.
D)between the demand and supply curves up to the point of equilibrium.
A)under the demand curve and above the price.
B)above the supply curve and up to the price.
C)under the supply curve and up to the price.
D)between the demand and supply curves up to the point of equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Figure 7-17 
Refer to Figure 7-17.Which area represents consumer surplus when the price is P1?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Refer to Figure 7-17.Which area represents consumer surplus when the price is P1?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Figure 7-14 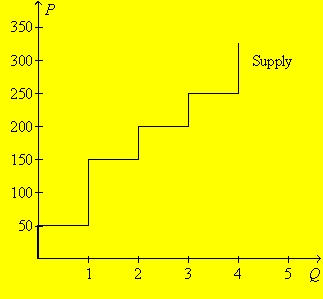
Refer to Figure 7-14.Suppose the willingness to pay of the marginal buyer of the 3rd unit is $225.Then total surplus is maximized if
A)1 unit of the good is produced and sold.
B)2 units of the good are produced and sold.
C)3 units of the good are produced and sold.
D)4 units of the good are produced and sold.

Refer to Figure 7-14.Suppose the willingness to pay of the marginal buyer of the 3rd unit is $225.Then total surplus is maximized if
A)1 unit of the good is produced and sold.
B)2 units of the good are produced and sold.
C)3 units of the good are produced and sold.
D)4 units of the good are produced and sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Total surplus
A)can be used to measure a market's efficiency.
B)is the sum of consumer and producer surplus.
C)is the to value to buyers minus the cost to sellers.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)can be used to measure a market's efficiency.
B)is the sum of consumer and producer surplus.
C)is the to value to buyers minus the cost to sellers.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Producer surplus equals
A)Value to buyers - Amount paid by buyers.
B)Amount received by sellers - Costs of sellers.
C)Value to buyers - Costs of sellers.
D)Value to buyers - Amount paid by buyers + Amount received by sellers - Costs of sellers.
A)Value to buyers - Amount paid by buyers.
B)Amount received by sellers - Costs of sellers.
C)Value to buyers - Costs of sellers.
D)Value to buyers - Amount paid by buyers + Amount received by sellers - Costs of sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following equations is valid?
A)Consumer surplus = Total surplus - Cost to sellers
B)Producer surplus = Total surplus - Consumer surplus
C)Total surplus = Value to buyers - Amount paid by buyers
D)Total surplus = Amount received by sellers - Cost to sellers
A)Consumer surplus = Total surplus - Cost to sellers
B)Producer surplus = Total surplus - Consumer surplus
C)Total surplus = Value to buyers - Amount paid by buyers
D)Total surplus = Amount received by sellers - Cost to sellers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If an allocation of resources is efficient,then
A)consumer surplus is maximized.
B)producer surplus is maximized.
C)all potential gains from trade among buyers are sellers are being realized.
D)the allocation achieves equality as well.
A)consumer surplus is maximized.
B)producer surplus is maximized.
C)all potential gains from trade among buyers are sellers are being realized.
D)the allocation achieves equality as well.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Figure 7-16 
Refer to Figure 7-16.For quantities greater than M,the value to the marginal buyer is
A)greater than the cost to the marginal seller,so increasing the quantity increases total surplus.
B)less than the cost to the marginal seller,so increasing the quantity increases total surplus.
C)greater than the cost to the marginal seller,so decreasing the quantity increases total surplus.
D)less than the cost to the marginal seller,so decreasing the quantity increases total surplus.

Refer to Figure 7-16.For quantities greater than M,the value to the marginal buyer is
A)greater than the cost to the marginal seller,so increasing the quantity increases total surplus.
B)less than the cost to the marginal seller,so increasing the quantity increases total surplus.
C)greater than the cost to the marginal seller,so decreasing the quantity increases total surplus.
D)less than the cost to the marginal seller,so decreasing the quantity increases total surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Figure 7-20 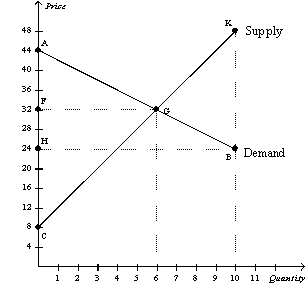
Refer to Figure 7-20.At equilibrium,total surplus is measured by the area
A)ACG.
B)AFG.
C)KBG.
D)CFG.

Refer to Figure 7-20.At equilibrium,total surplus is measured by the area
A)ACG.
B)AFG.
C)KBG.
D)CFG.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Figure 7-12 
Refer to Figure 7-12.Area B represents
A)the combined profits of all producers when the price is P2.
B)the increase in producer surplus to all producers as the result of an increase in the price from P1 to P2.
C)producer surplus to new producers entering the market as the result of an increase in the price from P1 to P2.
D)that portion of the increase in producer surplus that is offset by a loss in consumer surplus when the price increases from P1 to P2.

Refer to Figure 7-12.Area B represents
A)the combined profits of all producers when the price is P2.
B)the increase in producer surplus to all producers as the result of an increase in the price from P1 to P2.
C)producer surplus to new producers entering the market as the result of an increase in the price from P1 to P2.
D)that portion of the increase in producer surplus that is offset by a loss in consumer surplus when the price increases from P1 to P2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Efficiency in a market is achieved when
A)a social planner intervenes and sets the quantity of output after evaluating buyers' willingness to pay and sellers' costs.
B)the sum of producer surplus and consumer surplus is maximized.
C)all firms are producing the good at the same low cost per unit.
D)no buyer is willing to pay more than the equilibrium price for any unit of the good.
A)a social planner intervenes and sets the quantity of output after evaluating buyers' willingness to pay and sellers' costs.
B)the sum of producer surplus and consumer surplus is maximized.
C)all firms are producing the good at the same low cost per unit.
D)no buyer is willing to pay more than the equilibrium price for any unit of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the demand for light bulbs increases,producer surplus in the market for light bulbs
A)increases.
B)decreases.
C)remains the same.
D)may increase,decrease,or remain the same.
A)increases.
B)decreases.
C)remains the same.
D)may increase,decrease,or remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The marginal seller is the seller who
A)cannot compete with the other sellers in the market.
B)would leave the market first if the price were any lower.
C)can produce at the lowest cost.
D)has the largest producer surplus.
A)cannot compete with the other sellers in the market.
B)would leave the market first if the price were any lower.
C)can produce at the lowest cost.
D)has the largest producer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Figure 7-22 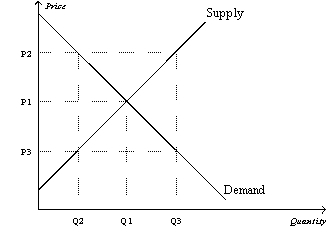
Refer to Figure 7-22.At the quantity Q2,the marginal value to buyers
A)and the marginal cost to sellers are both P2.
B)is P2,and the marginal cost to sellers is P3.
C)and the marginal cost to sellers are both P3.
D)is P3,and the marginal cost to sellers is P2.

Refer to Figure 7-22.At the quantity Q2,the marginal value to buyers
A)and the marginal cost to sellers are both P2.
B)is P2,and the marginal cost to sellers is P3.
C)and the marginal cost to sellers are both P3.
D)is P3,and the marginal cost to sellers is P2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The area below the demand curve and above the supply curve measures the producer surplus in a market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Figure 7-22 
Refer to Figure 7-22.At the quantity Q3,
A)the market is in equilibrium.
B)consumer surplus is maximized.
C)the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is maximized.
D)the marginal value to buyers is less than the marginal cost to sellers.

Refer to Figure 7-22.At the quantity Q3,
A)the market is in equilibrium.
B)consumer surplus is maximized.
C)the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is maximized.
D)the marginal value to buyers is less than the marginal cost to sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Suppose there is an increase in supply that reduces market price.Consumer surplus increases because (1)consumer surplus received by existing buyers increases and (2)new buyers enter the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Free markets allocate (a)the supply of goods to the buyers who value them most highly and (b)the demand for goods to the sellers who can produce them at least cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Even though participants in the economy are motivated by self-interest,the "invisible hand" of the marketplace guides this self-interest into promoting general economic well-being.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The lower the price,the lower the producer surplus,all else equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A buyer is willing to buy a product at a price greater than or equal to his willingness to pay,but would refuse to buy a product at a price less than his willingness to pay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Figure 7-20 
Refer to Figure 7-20.The equilibrium allocation of resources is
A)efficient because total surplus is maximized at the equilibrium.
B)efficient because consumer surplus is maximized at the equilibrium.
C)inefficient because consumer surplus is larger than producer surplus at the equilibrium.
D)inefficient because total surplus is maximized when 10 units of output are produced and sold.

Refer to Figure 7-20.The equilibrium allocation of resources is
A)efficient because total surplus is maximized at the equilibrium.
B)efficient because consumer surplus is maximized at the equilibrium.
C)inefficient because consumer surplus is larger than producer surplus at the equilibrium.
D)inefficient because total surplus is maximized when 10 units of output are produced and sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Total surplus in a market will increase when the government
A)imposes a binding price floor or a binding price ceiling on that market.
B)imposes a tax on that market.
C)Both a and b are correct.
D)Neither a nor b is correct.
A)imposes a binding price floor or a binding price ceiling on that market.
B)imposes a tax on that market.
C)Both a and b are correct.
D)Neither a nor b is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Consumer surplus can be measured as the area between the demand curve and the equilibrium price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If a market is in equilibrium,then it is impossible for a social planner to raise economic welfare by increasing or decreasing the quantity of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Efficiency refers to whether a market outcome is fair,while equality refers to whether the maximum amount of output was produced from a given number of inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A)An invisible hand leads buyers and sellers to an equilibrium that maximizes total surplus.
B)Market power can cause markets to be inefficient.
C)Externalities can cause markets to be inefficient.
D)The invisible hand can remedy most if not all types of market failures.
A)An invisible hand leads buyers and sellers to an equilibrium that maximizes total surplus.
B)Market power can cause markets to be inefficient.
C)Externalities can cause markets to be inefficient.
D)The invisible hand can remedy most if not all types of market failures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In order to conclude that markets are efficient,we assume that they are perfectly competitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
At any quantity,the price given by the supply curve shows the cost of the lowest-cost seller.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Market power and externalities are examples of market failures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Let P represent price; let QS represent quantity supplied; and assume the equation of the supply curve is
.If 80 units of the good are produced and sold,then producer surplus amounts to $1,200.
.If 80 units of the good are produced and sold,then producer surplus amounts to $1,200.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Welfare economics is the study of the welfare system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Total surplus = Value to buyers - Costs to sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Answer each of the following questions about supply and producer surplus.
a.What is producer surplus,and how is it measured?
b.What is the relationship between the cost to sellers and the supply curve?
c.Other things equal,what happens to producer surplus when the price of a good rises? Illustrate your answer on a supply curve.
a.What is producer surplus,and how is it measured?
b.What is the relationship between the cost to sellers and the supply curve?
c.Other things equal,what happens to producer surplus when the price of a good rises? Illustrate your answer on a supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Given the following two equations:
1)Total Surplus = Consumer Surplus + Producer Surplus
2)Total Surplus = Value to Buyers - Cost to Sellers
Show how equation (1)can be used to derive equation (2).
1)Total Surplus = Consumer Surplus + Producer Surplus
2)Total Surplus = Value to Buyers - Cost to Sellers
Show how equation (1)can be used to derive equation (2).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Tammy loves sweets.The table shown reflects the value Tammy places on each sweet she eats:
Value of first sweet
0.60
Value of second sweet
0.50
Value of third sweet
0.40
Value of fourth sweet
0.30
Value of fifth sweet
0.20
Value of sixth sweet
0.10
a.Use this information to construct Tammy's demand curve for sweets.
b.If the price of sweets is 0.20,how many donuts will Tammy buy?
c.Show Tammy's consumer surplus on your graph.How much consumer surplus would she have at a price of 0.20?
d.If the price of sweets rose to 0.40,how many sweets would she purchase now? What would happen to Tammy's consumer surplus? Show this change on your graph.
Value of first sweet
0.60
Value of second sweet
0.50
Value of third sweet
0.40
Value of fourth sweet
0.30
Value of fifth sweet
0.20
Value of sixth sweet
0.10
a.Use this information to construct Tammy's demand curve for sweets.
b.If the price of sweets is 0.20,how many donuts will Tammy buy?
c.Show Tammy's consumer surplus on your graph.How much consumer surplus would she have at a price of 0.20?
d.If the price of sweets rose to 0.40,how many sweets would she purchase now? What would happen to Tammy's consumer surplus? Show this change on your graph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Answer each of the following questions about demand and consumer surplus.
a.What is consumer surplus,and how is it measured?
b.What is the relationship between the demand curve and the willingness to pay?
c.Other things equal,what happens to consumer surplus if the price of a good falls? Why? Illustrate using a demand curve.
d.In what way does the demand curve represent the benefit consumers receive from participating in a market? In addition to the demand curve,what else must be considered to determine consumer surplus?
a.What is consumer surplus,and how is it measured?
b.What is the relationship between the demand curve and the willingness to pay?
c.Other things equal,what happens to consumer surplus if the price of a good falls? Why? Illustrate using a demand curve.
d.In what way does the demand curve represent the benefit consumers receive from participating in a market? In addition to the demand curve,what else must be considered to determine consumer surplus?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



