Deck 14: Firms in Competitive Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Firms in Competitive Markets
1
If a firm in a competitive market doubles its number of units sold,total revenue for the firm will
A)more than double.
B)double.
C)increase but by less than double.
D)may increase or decrease depending on the price elasticity of demand.
A)more than double.
B)double.
C)increase but by less than double.
D)may increase or decrease depending on the price elasticity of demand.
B
2
Which of the following statements is correct?
A)For all firms,marginal revenue equals the price of the good.
B)Only for competitive firms does average revenue equal the price of the good.
C)Marginal revenue can be calculated as total revenue divided by the quantity sold.
D)Only for competitive firms does average revenue equal marginal revenue.
A)For all firms,marginal revenue equals the price of the good.
B)Only for competitive firms does average revenue equal the price of the good.
C)Marginal revenue can be calculated as total revenue divided by the quantity sold.
D)Only for competitive firms does average revenue equal marginal revenue.
D
3
Table 14-11
Suppose that a firm in a competitive market faces the following prices and costs:
-Refer to Table 14-11.If the firm is producing 2 units of output,it should
A)produce more units of output because its marginal revenue is greater than its marginal cost.
B)fewer units of output because its marginal revenue is less than its marginal cost.
C)produce more units of output because its marginal revenue is less than its marginal cost.
D)produce fewer units of output because its marginal revenue is greater than its marginal cost.
Suppose that a firm in a competitive market faces the following prices and costs:
-Refer to Table 14-11.If the firm is producing 2 units of output,it should
A)produce more units of output because its marginal revenue is greater than its marginal cost.
B)fewer units of output because its marginal revenue is less than its marginal cost.
C)produce more units of output because its marginal revenue is less than its marginal cost.
D)produce fewer units of output because its marginal revenue is greater than its marginal cost.
produce more units of output because its marginal revenue is greater than its marginal cost.
4
When profit-maximizing firms in competitive markets are earning profits,
A)market demand must exceed market supply at the market equilibrium price.
B)market supply must exceed market demand at the market equilibrium price.
C)new firms will enter the market.
D)the most inefficient firms will be encouraged to leave the market.
A)market demand must exceed market supply at the market equilibrium price.
B)market supply must exceed market demand at the market equilibrium price.
C)new firms will enter the market.
D)the most inefficient firms will be encouraged to leave the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Changes in the output of a perfectly competitive firm,without any change in the price of the product,will change the firm's
A)total revenue.
B)marginal revenue.
C)average revenue.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)total revenue.
B)marginal revenue.
C)average revenue.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following characteristics of competitive markets is necessary for firms to be price takers?
(i)There are many sellers.
(ii)Firms can freely enter or exit the market.
(iii)Goods offered for sale are largely the same.
A)(i)and (ii)only
B)(i)and (iii)only
C)(ii)only
D)(i),(ii),and (iii)
(i)There are many sellers.
(ii)Firms can freely enter or exit the market.
(iii)Goods offered for sale are largely the same.
A)(i)and (ii)only
B)(i)and (iii)only
C)(ii)only
D)(i),(ii),and (iii)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Table 14-11
Suppose that a firm in a competitive market faces the following prices and costs:
-Refer to Table 14-11.The marginal revenue from producing the 3rd unit equals
(i)5.
(ii)the price.
(iii)the marginal cost.
A)(i)only
B)(i)and (ii)only
C)(ii)only
D)(i),(ii),and (iii)
Suppose that a firm in a competitive market faces the following prices and costs:
-Refer to Table 14-11.The marginal revenue from producing the 3rd unit equals
(i)5.
(ii)the price.
(iii)the marginal cost.
A)(i)only
B)(i)and (ii)only
C)(ii)only
D)(i),(ii),and (iii)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements best expresses a firm's profit-maximizing decision rule?
A)If marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost,the firm should increase its output.
B)If marginal revenue is less than marginal cost,the firm should decrease its output.
C)If marginal revenue equals marginal cost,the firm should continue producing its current level of output.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)If marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost,the firm should increase its output.
B)If marginal revenue is less than marginal cost,the firm should decrease its output.
C)If marginal revenue equals marginal cost,the firm should continue producing its current level of output.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following industries is most likely to exhibit the characteristic of free entry?
A)nuclear power
B)municipal water and sewer
C)dairy farming
D)airport security
A)nuclear power
B)municipal water and sewer
C)dairy farming
D)airport security

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Comparing marginal revenue to marginal cost
(i)reveals the contribution of the last unit of production to total profit.
(ii)is helpful in making profit-maximizing production decisions.
(iii)tells a firm whether its fixed costs are too high.
A)(i)only
B)(i)and (ii)only
C)(ii)and (iii)only
D)(i)and (iii)only
(i)reveals the contribution of the last unit of production to total profit.
(ii)is helpful in making profit-maximizing production decisions.
(iii)tells a firm whether its fixed costs are too high.
A)(i)only
B)(i)and (ii)only
C)(ii)and (iii)only
D)(i)and (iii)only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Table 14-11
Suppose that a firm in a competitive market faces the following prices and costs:
-Refer to Table 14-11.Marginal revenue equals marginal cost when the firm produces
A)2 units.
B)3 units.
C)4 units.
D)5 units.
Suppose that a firm in a competitive market faces the following prices and costs:
-Refer to Table 14-11.Marginal revenue equals marginal cost when the firm produces
A)2 units.
B)3 units.
C)4 units.
D)5 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
One of the defining characteristics of a perfectly competitive market is
A)a small number of sellers.
B)a large number of buyers and a small number of sellers.
C)a similar product.
D)significant advertising by firms to promote their products.
A)a small number of sellers.
B)a large number of buyers and a small number of sellers.
C)a similar product.
D)significant advertising by firms to promote their products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A market is competitive if
(i)firms have the flexibility to price their own product.
(ii)each buyer is small compared to the market.
(iii)each seller is small compared to the market.
A)(i)and (ii)only
B)(i)and (iii)only
C)(ii)and (iii)only
D)(i),(ii),and (iii)
(i)firms have the flexibility to price their own product.
(ii)each buyer is small compared to the market.
(iii)each seller is small compared to the market.
A)(i)and (ii)only
B)(i)and (iii)only
C)(ii)and (iii)only
D)(i),(ii),and (iii)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Firms operating in competitive markets produce output levels where marginal revenue equals
A)price.
B)average revenue.
C)total revenue divided by output.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)price.
B)average revenue.
C)total revenue divided by output.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements regarding a competitive firm is correct?
A)Because demand is downward sloping,if a firm increases its level of output,the firm will have to charge a lower price to sell the additional output.
B)If a firm raises its price,the firm may be able to increase its total revenue even though it will sell fewer units.
C)By lowering its price below the market price,the firm will benefit from selling more units at the lower price than it could have sold by charging the market price.
D)For all firms,average revenue equals the price of the good.
A)Because demand is downward sloping,if a firm increases its level of output,the firm will have to charge a lower price to sell the additional output.
B)If a firm raises its price,the firm may be able to increase its total revenue even though it will sell fewer units.
C)By lowering its price below the market price,the firm will benefit from selling more units at the lower price than it could have sold by charging the market price.
D)For all firms,average revenue equals the price of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Table 14-11
Suppose that a firm in a competitive market faces the following prices and costs:
-Refer to Table 14-11.In order to maximize profits,the firm should stop producing after it makes the
A)first unit.
B)second unit.
C)fourth unit.
D)fifth unit.
Suppose that a firm in a competitive market faces the following prices and costs:
-Refer to Table 14-11.In order to maximize profits,the firm should stop producing after it makes the
A)first unit.
B)second unit.
C)fourth unit.
D)fifth unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If a competitive firm is currently producing a level of output at which marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost,then
A)a one-unit increase in output will increase the firm's profit.
B)a one-unit decrease in output will increase the firm's profit.
C)total revenue exceeds total cost.
D)total cost exceeds total revenue.
A)a one-unit increase in output will increase the firm's profit.
B)a one-unit decrease in output will increase the firm's profit.
C)total revenue exceeds total cost.
D)total cost exceeds total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A firm has market power if it can
A)maximize profits.
B)minimize costs.
C)influence the market price of the good it sells.
D)hire as many workers as it needs at the prevailing wage rate.
A)maximize profits.
B)minimize costs.
C)influence the market price of the good it sells.
D)hire as many workers as it needs at the prevailing wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Max sells maps.The map industry is competitive.Max hires a business consultant to analyze his company's financial records.The consultant recommends that Max increase his production.The consultant must have concluded that Max's
A)total revenues exceed his total accounting costs.
B)marginal revenue exceeds his total cost.
C)marginal revenue exceeds his marginal cost.
D)marginal cost exceeds his marginal revenue.
A)total revenues exceed his total accounting costs.
B)marginal revenue exceeds his total cost.
C)marginal revenue exceeds his marginal cost.
D)marginal cost exceeds his marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A seller in a competitive market can
A)sell all he wants at the going price,so he has little reason to charge less.
B)influence the market price by adjusting his output.
C)influence the profits earned by competing firms by adjusting his output.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)sell all he wants at the going price,so he has little reason to charge less.
B)influence the market price by adjusting his output.
C)influence the profits earned by competing firms by adjusting his output.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Figure 14-12 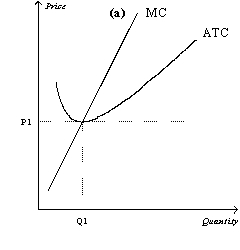
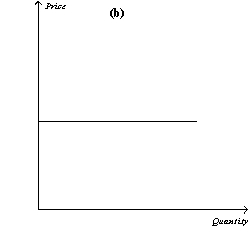
Refer to Figure 14-12.If the figure in panel (a)reflects the long-run equilibrium of a profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market,the figure in panel (b)most likely reflects
A)perfectly inelastic long-run market supply.
B)perfectly elastic long-run market supply.
C)the entry of firms into the industry when some resources used in production are available only in limited quantities.
D)the fact that zero profits cannot be sustained in the long run.


Refer to Figure 14-12.If the figure in panel (a)reflects the long-run equilibrium of a profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market,the figure in panel (b)most likely reflects
A)perfectly inelastic long-run market supply.
B)perfectly elastic long-run market supply.
C)the entry of firms into the industry when some resources used in production are available only in limited quantities.
D)the fact that zero profits cannot be sustained in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Assume a firm in a competitive industry is producing 800 units of output,and it sells each unit for $6.Its average total cost is $4.Its profit is
A)$-1,600.
B)$1,600.
C)$3,200.
D)$8,000.
A)$-1,600.
B)$1,600.
C)$3,200.
D)$8,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following statements is correct regarding a firm's decision-making?
A)The decision to shut down and the decision to exit are both short-run decisions.
B)The decision to shut down and the decision to exit are both long-run decisions.
C)The decision to shut down is a short-run decision,whereas the decision to exit is a long-run decision.
D)The decision to exit is a short-run decision,whereas the decision to shut down is a long-run decision.
A)The decision to shut down and the decision to exit are both short-run decisions.
B)The decision to shut down and the decision to exit are both long-run decisions.
C)The decision to shut down is a short-run decision,whereas the decision to exit is a long-run decision.
D)The decision to exit is a short-run decision,whereas the decision to shut down is a long-run decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The short-run market supply curve in a perfectly competitive industry
A)shows the total quantity supplied by all firms at each possible price.
B)is perfectly inelastic at the market price.
C)is perfectly elastic at the market price.
D)shows the variety of prices that different firms will charge for a given quantity.
A)shows the total quantity supplied by all firms at each possible price.
B)is perfectly inelastic at the market price.
C)is perfectly elastic at the market price.
D)shows the variety of prices that different firms will charge for a given quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Figure 14-2
Suppose a firm operating in a competitive market has the following cost curves: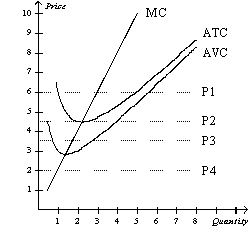
Refer to Figure 14-2.Which of the four prices corresponds to a firm earning positive economic profits in the short run?
A)P1
B)P2
C)P3
D)P4
Suppose a firm operating in a competitive market has the following cost curves:

Refer to Figure 14-2.Which of the four prices corresponds to a firm earning positive economic profits in the short run?
A)P1
B)P2
C)P3
D)P4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Figure 14-2
Suppose a firm operating in a competitive market has the following cost curves:
Refer to Figure 14-2.If the market price is P1,in the short run the firm will earn
A)positive economic profits.
B)negative economic profits but will try to remain open.
C)negative economic profits and will shut down.
D)zero economic profits.
Suppose a firm operating in a competitive market has the following cost curves:

Refer to Figure 14-2.If the market price is P1,in the short run the firm will earn
A)positive economic profits.
B)negative economic profits but will try to remain open.
C)negative economic profits and will shut down.
D)zero economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market will always make marginal adjustments to production as long as
A)average revenue is greater than average total cost.
B)average revenue is equal to marginal cost.
C)marginal cost is greater than average total cost.
D)price is above or below marginal cost.
A)average revenue is greater than average total cost.
B)average revenue is equal to marginal cost.
C)marginal cost is greater than average total cost.
D)price is above or below marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Competitive firms that earn a loss in the short run should
A)shut down if P < AVC.
B)raise their price.
C)lower their output.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)shut down if P < AVC.
B)raise their price.
C)lower their output.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Profit-maximizing firms in a competitive market produce an output level where
A)marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
B)marginal cost equals average total cost.
C)marginal revenue is increasing.
D)price is less than marginal revenue.
A)marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
B)marginal cost equals average total cost.
C)marginal revenue is increasing.
D)price is less than marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In a competitive market with identical firms,
A)an increase in demand in the short run will result in a new price above the minimum of average total cost,allowing firms to earn a positive economic profit in both the short run and the long run.
B)firms cannot earn positive economic profit in either the short run or long run.
C)firms can earn positive economic profit in the long run if the long-run market supply curve is upward sloping.
D)free entry and exit into the market requires that firms earn zero economic profit in the long run even though they may be able to earn positive economic profit in the short run.
A)an increase in demand in the short run will result in a new price above the minimum of average total cost,allowing firms to earn a positive economic profit in both the short run and the long run.
B)firms cannot earn positive economic profit in either the short run or long run.
C)firms can earn positive economic profit in the long run if the long-run market supply curve is upward sloping.
D)free entry and exit into the market requires that firms earn zero economic profit in the long run even though they may be able to earn positive economic profit in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Figure 14-5
Suppose a firm operating in a competitive market has the following cost curves: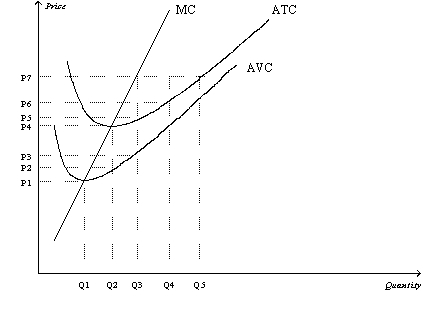
-Refer to Figure 14-5.When market price is P7,a profit-maximizing firm's short-run profits can be represented by the area
A)P7 * Q5.
B)P7 * Q3.
C)(P7 - P5) * Q3.
D)We are unable to determine the firm's profits because the quantity that the firm would produce is not labeled on the graph.
Suppose a firm operating in a competitive market has the following cost curves:

-Refer to Figure 14-5.When market price is P7,a profit-maximizing firm's short-run profits can be represented by the area
A)P7 * Q5.
B)P7 * Q3.
C)(P7 - P5) * Q3.
D)We are unable to determine the firm's profits because the quantity that the firm would produce is not labeled on the graph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When a profit-maximizing firm is earning profits,those profits can be identified by
A)P * Q.
B)(MC - AVC) * Q.
C)(P - ATC) * Q.
D)(P - AVC) * Q.
A)P * Q.
B)(MC - AVC) * Q.
C)(P - ATC) * Q.
D)(P - AVC) * Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Suppose a firm operates in the short run at a price above its average total cost of production.In the long run the firm should expect
A)new firms to enter the market.
B)the market price to fall.
C)its profits to fall.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)new firms to enter the market.
B)the market price to fall.
C)its profits to fall.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the short run,a firm operating in a competitive industry will produce the quantity of output where price equals marginal cost as long as the
A)price is less than average total cost.
B)marginal revenue exceeds the marginal cost.
C)price is greater than average variable cost.
D)price is greater than average fixed cost but less than average variable cost.
A)price is less than average total cost.
B)marginal revenue exceeds the marginal cost.
C)price is greater than average variable cost.
D)price is greater than average fixed cost but less than average variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Figure 14-5
Suppose a firm operating in a competitive market has the following cost curves:
-Refer to Figure 14-5.When market price is P2,a profit-maximizing firm's losses can be represented by the area
A)(P4 - P2) * Q2.
B)(P2 - P1) * (Q2-Q1).
C)At a market price of P2,the firm earns profits,not losses.
D)At a market price of P2 the firm has losses,but the reference points in the figure don't identify the losses.
Suppose a firm operating in a competitive market has the following cost curves:

-Refer to Figure 14-5.When market price is P2,a profit-maximizing firm's losses can be represented by the area
A)(P4 - P2) * Q2.
B)(P2 - P1) * (Q2-Q1).
C)At a market price of P2,the firm earns profits,not losses.
D)At a market price of P2 the firm has losses,but the reference points in the figure don't identify the losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Suppose a profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market produces rubber bands.When the market price for rubber bands rises above the minimum of its average variable cost,but still lies below the minimum of average total cost,in the short run the firm will
A)experience losses but will continue to produce rubber bands.
B)shut down.
C)earn both economic and accounting profits.
D)raise the price of its product.
A)experience losses but will continue to produce rubber bands.
B)shut down.
C)earn both economic and accounting profits.
D)raise the price of its product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Consider a competitive market with 50 identical firms.Suppose the market demand is given by the equation QD = 200 - 10P and the market supply is given by the equation QS = 10P.In addition,suppose the following table shows the marginal cost of production for various levels of output for firms in this market. How many units should a firm in this market produce to maximize profit?
A)1 unit
B)2 units
C)3 units
D)4 units
A)1 unit
B)2 units
C)3 units
D)4 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When a profit-maximizing competitive firm finds itself minimizing losses because it is unable to earn a positive profit,this task is accomplished by producing the quantity at which price is equal to
A)sunk cost.
B)average fixed cost.
C)average variable cost.
D)marginal cost.
A)sunk cost.
B)average fixed cost.
C)average variable cost.
D)marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If a competitive firm is currently producing a level of output at which profit is not maximized,then it must be true that
A)marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost.
B)marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue.
C)total cost exceeds total revenue.
D)None of the above is correct.
A)marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost.
B)marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue.
C)total cost exceeds total revenue.
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Suppose a competitive market is comprised of firms that face identical cost curves.The firms experience an increase in demand that results in positive profits for the firms.Which of the following events are then most likely to occur?
(i)New firms will enter the market.
(ii)In the short run,price will rise; in the long run,price will rise further.
(iii)In the long run,all firms will be producing at their efficient scale.
A)(i)and (ii)only
B)(i)and (iii)only
C)(ii)and (iii)only
D)(i),(ii)and (iii)
(i)New firms will enter the market.
(ii)In the short run,price will rise; in the long run,price will rise further.
(iii)In the long run,all firms will be producing at their efficient scale.
A)(i)and (ii)only
B)(i)and (iii)only
C)(ii)and (iii)only
D)(i),(ii)and (iii)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The production decisions of perfectly competitive firms follow one of the Ten Principles of Economics,which states that rational people
A)consider sunk costs.
B)equate prices to the average costs of production.
C)prefer to purchase products from smaller rather than larger firms.
D)think at the margin.
A)consider sunk costs.
B)equate prices to the average costs of production.
C)prefer to purchase products from smaller rather than larger firms.
D)think at the margin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Because nothing can be done about sunk costs,they are irrelevant to decisions about business strategy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If all existing firms and all potential firms have the same cost curves,there are no inputs in limited quantities,and the market is characterized by free entry and exit,then the long-run market supply curve
A)is horizontal and equal to the minimum of long-run marginal cost for each firm.
B)must slope downward.
C)must slope upward.
D)is horizontal and equal to the minimum of long-run average cost for each firm.
A)is horizontal and equal to the minimum of long-run marginal cost for each firm.
B)must slope downward.
C)must slope upward.
D)is horizontal and equal to the minimum of long-run average cost for each firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A firm is currently producing 100 units of output per day.The manager reports to the owner that producing the 100th unit costs the firm 5 dollars.The firm can sell the 100th unit for 5 dollars.The firm should continue to produce 100 units in order to maximize its profits (or minimize its losses).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A firm operating in a competitive market will stay in business in the short run so long as the market price exceeds the firm's average total cost; otherwise,the firm will shut down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A firm operating in a perfectly competitive industry will shut down in the short run but earn losses if the market price is less than that firm's average variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Figure 14-13
Suppose a firm in a competitive industry has the following cost curves: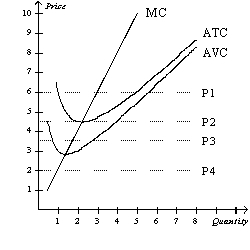
Refer to Figure 14-13.If the price is P1 in the short run,what will happen in the long run?
A)Nothing.The price is consistent with zero economic profits,so there is no incentive for firms to enter or exit the industry.
B)Individual firms will earn positive economic profits in the short run,which will entice other firms to enter the industry.
C)Individual firms will earn negative economic profits in the short run,which will cause some firms to exit the industry.
D)Because the price is below the firm's average variable costs,the firms will shut down.
Suppose a firm in a competitive industry has the following cost curves:

Refer to Figure 14-13.If the price is P1 in the short run,what will happen in the long run?
A)Nothing.The price is consistent with zero economic profits,so there is no incentive for firms to enter or exit the industry.
B)Individual firms will earn positive economic profits in the short run,which will entice other firms to enter the industry.
C)Individual firms will earn negative economic profits in the short run,which will cause some firms to exit the industry.
D)Because the price is below the firm's average variable costs,the firms will shut down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If there is an increase in market demand in a perfectly competitive market,then in the short run prices will
A)rise.
B)remain unchanged at the minimum of average total cost.
C)fall.
D)remain unchanged at the minimum of marginal cost.
A)rise.
B)remain unchanged at the minimum of average total cost.
C)fall.
D)remain unchanged at the minimum of marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When a profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market experiences rising prices,it will respond with an increase in production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
For a firm operating in a perfectly competitive industry,total revenue,marginal revenue,and average revenue are all equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Because there are many sellers in a competitive market,individual firms are unable to maximize profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If occupational safety laws were changed so that firms no longer had to take expensive steps to meet regulatory requirements,we would expect that
A)the demand for products in this industry would increase.
B)the market price of products in this industry would decrease in the short run but not in the long run.
C)the firms in the industry would make a long-run economic profit.
D)competition would force producers to pass the lower production costs on to consumers in the long run.
A)the demand for products in this industry would increase.
B)the market price of products in this industry would decrease in the short run but not in the long run.
C)the firms in the industry would make a long-run economic profit.
D)competition would force producers to pass the lower production costs on to consumers in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In a perfectly competitive market,the process of entry and exit will end when
(i)accounting profits are zero.
(ii)economic profits are zero.
(iii)price equals minimum marginal cost.
(iv)price equals minimum average total cost.
A)(i)and (ii)only
B)(ii)and (iii)only
C)(ii)and (iv)only
D)(i),(ii),(iii),and (iv)
(i)accounting profits are zero.
(ii)economic profits are zero.
(iii)price equals minimum marginal cost.
(iv)price equals minimum average total cost.
A)(i)and (ii)only
B)(ii)and (iii)only
C)(ii)and (iv)only
D)(i),(ii),(iii),and (iv)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market will decrease production when marginal cost exceeds average revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Figure 14-14 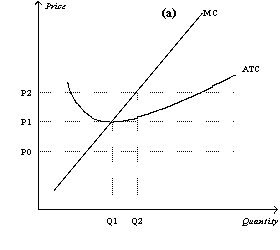
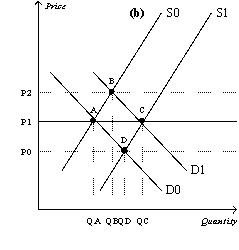
Refer to Figure 14-14.Assume that the market starts in equilibrium at point A in panel (b)and that panel (a)illustrates the cost curves facing individual firms.Suppose that demand increases from D0 to D1.Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Points A,B,and C represent both short-run and long-run equilibria.
B)Points A,B,C,and D represent short-run equilibria.
C)Points A and B represent long-run equilibria.
D)Points A and C represent long-run equilibria.


Refer to Figure 14-14.Assume that the market starts in equilibrium at point A in panel (b)and that panel (a)illustrates the cost curves facing individual firms.Suppose that demand increases from D0 to D1.Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Points A,B,and C represent both short-run and long-run equilibria.
B)Points A,B,C,and D represent short-run equilibria.
C)Points A and B represent long-run equilibria.
D)Points A and C represent long-run equilibria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In calculating accounting profit,accountants typically don't include
A)long-run costs.
B)sunk costs.
C)explicit costs of production.
D)opportunity costs that do not involve an outflow of money.
A)long-run costs.
B)sunk costs.
C)explicit costs of production.
D)opportunity costs that do not involve an outflow of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Figure 14-13
Suppose a firm in a competitive industry has the following cost curves:
Refer to Figure 14-13.If the price is P2 in the short run,what will happen in the long run?
A)Nothing.The price is consistent with zero economic profits,so there is no incentive for firms to enter or exit the industry.
B)Individual firms will earn positive economic profits in the short run,which will entice other firms to enter the industry.
C)Individual firms will earn negative economic profits in the short run,which will cause some firms to exit the industry.
D)Because the price is below the firm's average variable costs,the firms will shut down.
Suppose a firm in a competitive industry has the following cost curves:

Refer to Figure 14-13.If the price is P2 in the short run,what will happen in the long run?
A)Nothing.The price is consistent with zero economic profits,so there is no incentive for firms to enter or exit the industry.
B)Individual firms will earn positive economic profits in the short run,which will entice other firms to enter the industry.
C)Individual firms will earn negative economic profits in the short run,which will cause some firms to exit the industry.
D)Because the price is below the firm's average variable costs,the firms will shut down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Firms in a competitive market are said to be price takers because there are many sellers in the market,and the goods offered by the firms are very similar if not identical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Suppose a firm is considering producing zero units of output.We call this shutting down in the short run and exiting an industry in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When a profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market has zero economic profit,accounting profit
A)is negative.
B)is at least zero.
C)is also zero.
D)could be positive,negative or zero.
A)is negative.
B)is at least zero.
C)is also zero.
D)could be positive,negative or zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
All competitive firms earn zero economic profit in both the short run and the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In making a short-run profit-maximizing production decision,the firm must consider both fixed and variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Describe the difference between average revenue and marginal revenue.Why are both of these revenue measures important to a profit-maximizing firm?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Why would a firm in a perfectly competitive market always choose to set its price equal to the current market price?
If a firm set its price below the current market price,what effect would this have on the market?
If a firm set its price below the current market price,what effect would this have on the market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
When economic profits are zero in equilibrium,the firm's revenue must be sufficient to cover all opportunity costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Use a graph to demonstrate the circumstances that would prevail in a competitive market where firms are earning economic profits.Can this scenario be maintained in the long run?
Explain your answer.
Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The long-run supply curve in a competitive market is more elastic than the short-run supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If identical firms that remain in a competitive market over the long run make zero economic profit,why do these firms choose to remain in the market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Explain how a firm in a competitive market identifies the profit-maximizing level of production.When should the firm raise production,and when should the firm lower production?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A competitive market will typically experience entry and exit until accounting profits are zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



