Deck 20: International Finance
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/151
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: International Finance
1
The U.S.desire for foreign currency represents
A)A demand for U.S.dollars.
B)A supply of U.S.dollars.
C)The foreign demand for U.S.exports.
D)A point of disequilibrium in the foreign exchange market.
A)A demand for U.S.dollars.
B)A supply of U.S.dollars.
C)The foreign demand for U.S.exports.
D)A point of disequilibrium in the foreign exchange market.
B
2
The exchange rate is the
A)Opportunity cost at which goods are produced domestically.
B)Balance-of-trade ratio of one country to another.
C)Price of one country's currency expressed in terms of another country's currency.
D)Amount of currency that can be purchased with one ounce of golD.The price of one currency in terms of another is the exchange rate; for example,$2 = £1 indicates that a British pound costs two dollars.
A)Opportunity cost at which goods are produced domestically.
B)Balance-of-trade ratio of one country to another.
C)Price of one country's currency expressed in terms of another country's currency.
D)Amount of currency that can be purchased with one ounce of golD.The price of one currency in terms of another is the exchange rate; for example,$2 = £1 indicates that a British pound costs two dollars.
C
3
When foreign countries buy wheat grown in the United States,they are generating a
A)Demand for U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
B)Demand for U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
C)Supply of U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
D)Supply of U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
A)Demand for U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
B)Demand for U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
C)Supply of U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
D)Supply of U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
B
4
When foreigners buy U.S.dollars because they are a more stable currency than the currencies in their countries,they are generating a
A)Demand for U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
B)Supply of U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
C)Demand for U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
D)Supply of U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
A)Demand for U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
B)Supply of U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
C)Demand for U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
D)Supply of U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The supply of U.S.dollars is determined by all of the following except
A)Foreign demand for American exports.
B)American demand for imports.
C)American investments in foreign nations.
D)Speculation.
A)Foreign demand for American exports.
B)American demand for imports.
C)American investments in foreign nations.
D)Speculation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following generates a supply of U.S.dollars?
A)The demand for U.S.exports to foreign countries.
B)Foreign tourists visiting the United States.
C)The construction of a plant abroad by a U.S.corporation.
D)Chinese buyers of American aircraft.
A)The demand for U.S.exports to foreign countries.
B)Foreign tourists visiting the United States.
C)The construction of a plant abroad by a U.S.corporation.
D)Chinese buyers of American aircraft.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When a Japanese businesswoman traveling in the United States asks,"How many U.S.dollars can I get for these yen?" she wants to know the
A)Gold standard rate.
B)Exchange rate.
C)Terms of trade.
D)Currency trade rate.
A)Gold standard rate.
B)Exchange rate.
C)Terms of trade.
D)Currency trade rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The demand for dollars in the foreign exchange market
A)Is represented by a point in a diagram of foreign exchange supply and demand.
B)Depends in part on the foreign demand for U.S.goods.
C)Depends on U.S.demand for foreign goods and services.
D)Is the ratio of the dollars demanded to the amount of foreign currency supplieD.Whenever foreigners purchase goods or services from U.S.firms,or U.S.assets,they create a demand for the dollar.
A)Is represented by a point in a diagram of foreign exchange supply and demand.
B)Depends in part on the foreign demand for U.S.goods.
C)Depends on U.S.demand for foreign goods and services.
D)Is the ratio of the dollars demanded to the amount of foreign currency supplieD.Whenever foreigners purchase goods or services from U.S.firms,or U.S.assets,they create a demand for the dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following generates demand for foreign currencies?
A)Expenditures by Americans traveling abroad.
B)Exports from the United States to foreign countries.
C)The purchase by foreigners of bonds issued by the U.S.government.
D)Transfers of money from foreigners to relatives in the United States.
A)Expenditures by Americans traveling abroad.
B)Exports from the United States to foreign countries.
C)The purchase by foreigners of bonds issued by the U.S.government.
D)Transfers of money from foreigners to relatives in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When American companies buy office buildings in Australia,they are generating a
A)Supply of U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
B)Supply of U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
C)Demand for U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
D)Demand for U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
A)Supply of U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
B)Supply of U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
C)Demand for U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
D)Demand for U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The U.S.demand for foreign currency arises from speculation and the
A)U.S.demand for foreign goods,services,and financial assets.
B)Foreign demand for U.S.goods,services,and financial assets.
C)Foreign demand for U.S.holdings of gold.
D)Supply of goods and services from the United States.
A)U.S.demand for foreign goods,services,and financial assets.
B)Foreign demand for U.S.goods,services,and financial assets.
C)Foreign demand for U.S.holdings of gold.
D)Supply of goods and services from the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The exchange rate is the price of
A)One good in terms of another.
B)An import purchased at the local electronics store.
C)One currency in terms of another.
D)An export purchased in a foreign nation.
A)One good in terms of another.
B)An import purchased at the local electronics store.
C)One currency in terms of another.
D)An export purchased in a foreign nation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The demand for U.S.dollars originates from all of the following except
A)Foreign demand for U.S.exports.
B)Speculation in U.S.dollars.
C)Foreign demand for U.S.investments.
D)U.S.demand for imported goods.
A)Foreign demand for U.S.exports.
B)Speculation in U.S.dollars.
C)Foreign demand for U.S.investments.
D)U.S.demand for imported goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The demand for U.S.dollars in the foreign exchange market is determined by all of the following except
A)Foreign demand for American exports.
B)Foreign demand for American investments.
C)Europeans who would rather hold U.S.dollars than euros.
D)American demand for American products.
A)Foreign demand for American exports.
B)Foreign demand for American investments.
C)Europeans who would rather hold U.S.dollars than euros.
D)American demand for American products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When Americans buy Mercedes-Benz automobiles made in Germany,they are generating a
A)Supply of U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
B)Supply of U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
C)Demand for U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
D)Demand for U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
A)Supply of U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
B)Supply of U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
C)Demand for U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
D)Demand for U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following generates demand for foreign currencies?
A)Exports from the United States to foreign countries.
B)Imports of foreign goods by firms located in the United States.
C)The building of plants by foreign corporations in the United States.
D)Foreign tourists traveling to the United States.
A)Exports from the United States to foreign countries.
B)Imports of foreign goods by firms located in the United States.
C)The building of plants by foreign corporations in the United States.
D)Foreign tourists traveling to the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following generates a demand for dollars in the foreign exchange market?
A)Transfers of money by foreign workers in the United States to relatives abroad.
B)U.S.military installations abroad.
C)Foreign aid given by the United States.
D)Travel by foreign visitors in the United States.
A)Transfers of money by foreign workers in the United States to relatives abroad.
B)U.S.military installations abroad.
C)Foreign aid given by the United States.
D)Travel by foreign visitors in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The supply of U.S.dollars originates from
A)Demand by foreigners for U.S.-produced goods.
B)Demand for U.S.dollars for speculative purposes.
C)Foreign investments in America.
D)American demand for imported goods.
A)Demand by foreigners for U.S.-produced goods.
B)Demand for U.S.dollars for speculative purposes.
C)Foreign investments in America.
D)American demand for imported goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When foreigners come to the United States as tourists,they are generating a
A)Demand for U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
B)Supply of U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
C)Supply of U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
D)Demand for U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
A)Demand for U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
B)Supply of U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
C)Supply of U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
D)Demand for U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When reality show participants travel through foreign countries,they are generating a
A)Demand for U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
B)Supply of U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
C)Demand for U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
D)Supply of U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
A)Demand for U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
B)Supply of U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
C)Demand for U.S.dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
D)Supply of U.S.dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The current account balance is equal to
A)Trade balance + services balance - capital account balance.
B)Trade balance + services balance + capital account balance.
C)Trade balance + unilateral transfers.
D)Total payments made by residents of the United States to foreigners plus total payments made by foreigners to residents of the United States.
A)Trade balance + services balance - capital account balance.
B)Trade balance + services balance + capital account balance.
C)Trade balance + unilateral transfers.
D)Total payments made by residents of the United States to foreigners plus total payments made by foreigners to residents of the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The net balance of payments is
A)The difference between exports and imports.
B)The difference between the current account balance and the capital account balance.
C)The sum of the current account balance and the trade account balance.
D)The sum of the current account balance and the capital account balance.
A)The difference between exports and imports.
B)The difference between the current account balance and the capital account balance.
C)The sum of the current account balance and the trade account balance.
D)The sum of the current account balance and the capital account balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If one euro is equal to 0.60 U.S.dollars,what would be the euro price of a car that costs $10,000?
A)5,000 euros.
B)16,667 euros.
C)60,000 euros.
D)10,000 euros.
A)5,000 euros.
B)16,667 euros.
C)60,000 euros.
D)10,000 euros.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The capital account balance is equal to the
A)Current account balance plus foreign purchases of U.S.assets.
B)Current account balance plus U.S.purchases of foreign assets.
C)U.S.purchases of foreign assets minus foreign purchases of U.S.assets.
D)Foreign purchases of U.S.assets minus U.S.purchases of foreign assets.
A)Current account balance plus foreign purchases of U.S.assets.
B)Current account balance plus U.S.purchases of foreign assets.
C)U.S.purchases of foreign assets minus foreign purchases of U.S.assets.
D)Foreign purchases of U.S.assets minus U.S.purchases of foreign assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An increase in the price of the U.S.dollar in terms of euros will cause,ceteris paribus,
A)A lower European inflation rate.
B)Higher interest rates in the United States.
C)European goods to be cheaper to residents of the United States.
D)European goods to be more expensive to residents of the United States.
A)A lower European inflation rate.
B)Higher interest rates in the United States.
C)European goods to be cheaper to residents of the United States.
D)European goods to be more expensive to residents of the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The trade balance for the United States equals
A)The difference between service exports and service imports.
B)The difference between the dollar value of exports and the dollar value of imports.
C)Exports plus imports.
D)The current account balance minus the capital account balance.
A)The difference between service exports and service imports.
B)The difference between the dollar value of exports and the dollar value of imports.
C)Exports plus imports.
D)The current account balance minus the capital account balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The capital account includes
A)Trade in goods.
B)Trade in services.
C)Unilateral transfers.
D)Foreign purchases of U.S.assets.
A)Trade in goods.
B)Trade in services.
C)Unilateral transfers.
D)Foreign purchases of U.S.assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In a floating exchange rate system,the capital account balance equals
A)The current account balance minus imports.
B)Foreign purchases of U.S.assets plus U.S.purchases of foreign assets.
C)The balance of payments plus the sum of the merchandise balance,the services balance,and unilateral transfers.
D)The negative of the current account balance.
A)The current account balance minus imports.
B)Foreign purchases of U.S.assets plus U.S.purchases of foreign assets.
C)The balance of payments plus the sum of the merchandise balance,the services balance,and unilateral transfers.
D)The negative of the current account balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Theoretically,the net balance of payments is
A)Foreign demand for a country's currency minus foreign supply.
B)The current account plus the capital account.
C)A country's capital inflow minus its capital outflow.
D)Exports minus imports.
A)Foreign demand for a country's currency minus foreign supply.
B)The current account plus the capital account.
C)A country's capital inflow minus its capital outflow.
D)Exports minus imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A change in the exchange rate for a country's currency alters the prices of
A)Exports only.
B)Imports only.
C)Both exports and imports.
D)Only domestic goods and services.
A)Exports only.
B)Imports only.
C)Both exports and imports.
D)Only domestic goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When the exchange rate between the U.S.dollar and the Japanese yen is $1 = 100 yen,this is an indication that
A)It would take 100 yen to purchase $1.
B)The yen is stronger than the U.S.dollar.
C)The dollar is depreciating compared to the yen.
D)American companies are investing heavily in Japan.
A)It would take 100 yen to purchase $1.
B)The yen is stronger than the U.S.dollar.
C)The dollar is depreciating compared to the yen.
D)American companies are investing heavily in Japan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Suppose a men's suit produced in Moldavia sells for 250 euros.If the exchange rate between euros and dollars is €1 = $1.38,how much will an American pay for the suit?
A)$345.00.
B)$181.16.
C)$250.00.
D)$138.00.
A)$345.00.
B)$181.16.
C)$250.00.
D)$138.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Changes in the value of the euro affect the economies of
A)Only those countries using the euro as currency.
B)All European countries,but there would be no significant impact on countries outside Europe.
C)Potentially the entire world.
D)No countries as long as exchange rates are flexible.
A)Only those countries using the euro as currency.
B)All European countries,but there would be no significant impact on countries outside Europe.
C)Potentially the entire world.
D)No countries as long as exchange rates are flexible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Under floating exchange rates,the capital account balance is equal to the negative of
A)Trade balance + unilateral transfers.
B)Trade balance + current account balance + services balance.
C)Current account balance + exports + unilateral transfers.
D)Unilateral transfers + exports + imports.
A)Trade balance + unilateral transfers.
B)Trade balance + current account balance + services balance.
C)Current account balance + exports + unilateral transfers.
D)Unilateral transfers + exports + imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The current account balance is equal to
A)Imports minus exports.
B)Exports minus imports.
C)The trade balance plus unilateral transfers.
D)The trade balance times unilateral transfers.
A)Imports minus exports.
B)Exports minus imports.
C)The trade balance plus unilateral transfers.
D)The trade balance times unilateral transfers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A summary record of a country's international economic transactions in a given time period is the
A)Balance of payments.
B)Current account.
C)Capital account.
D)Exchange rate balance.
A)Balance of payments.
B)Current account.
C)Capital account.
D)Exchange rate balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the exchange rate between the U.S.dollar and Japanese yen changes from $1 = 100 yen to $1 = 90 yen,then
A)All Japanese producers and consumers will lose.
B)U.S.auto producers and autoworkers will lose.
C)U.S.consumers of Japanese TV sets will benefit.
D)Japanese tourists to the United States will benefit.
A)All Japanese producers and consumers will lose.
B)U.S.auto producers and autoworkers will lose.
C)U.S.consumers of Japanese TV sets will benefit.
D)Japanese tourists to the United States will benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Suppose a bottle of wine produced in France sells for 35 euros.If the exchange rate between euros and dollars is €1 = $1.30,how much will an American pay for the bottle of wine in America?
A)$130.00.
B)$35.00.
C)$45.50.
D)$26.92.
A)$130.00.
B)$35.00.
C)$45.50.
D)$26.92.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Suppose a U.S.firm purchases some English china.The china costs 1,000 British pounds.At the exchange rate of $1.45 = 1 pound,the dollar price of the china is
A)$250.
B)$690.
C)$1,450.
D)$2,000.
A)$250.
B)$690.
C)$1,450.
D)$2,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Exports minus imports define a country's
A)Current account balance.
B)Capital account balance.
C)Balance of payments.
D)Trade balance.
A)Current account balance.
B)Capital account balance.
C)Balance of payments.
D)Trade balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following does not involve exports and imports?
A)Net exports.
B)Current account.
C)Balance of trade.
D)Capital account.
A)Net exports.
B)Current account.
C)Balance of trade.
D)Capital account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following might cause a depreciation of the U.S.dollar versus the Japanese yen?
A)A recession in Japan.
B)A recession in the United States.
C)More Japanese visitors to Hawaii.
D)A greater demand for U.S.coal by Japan.
A)A recession in Japan.
B)A recession in the United States.
C)More Japanese visitors to Hawaii.
D)A greater demand for U.S.coal by Japan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Suppose that today 1 British pound exchanges for $1.60.If next week 1 pound exchanges for $1.70,it is clear that
A)The pound has depreciated relative to the dollar.
B)The dollar has appreciated relative to the pound.
C)Both currencies have appreciated.
D)The dollar has depreciated relative to the pounD.The dollar has depreciated relative to the pound because with the new exchange rate,it takes more dollars to get the same amount of British pounds.
A)The pound has depreciated relative to the dollar.
B)The dollar has appreciated relative to the pound.
C)Both currencies have appreciated.
D)The dollar has depreciated relative to the pounD.The dollar has depreciated relative to the pound because with the new exchange rate,it takes more dollars to get the same amount of British pounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Except for a statistical error under flexible exchange rates,any current account deficit
A)Can be only partially offset by capital account surpluses and unilateral transfers.
B)Must be completely offset by unilateral transfers.
C)Must be completely offset by a capital account surplus.
D)Must be completely offset by a trade surplus.
A)Can be only partially offset by capital account surpluses and unilateral transfers.
B)Must be completely offset by unilateral transfers.
C)Must be completely offset by a capital account surplus.
D)Must be completely offset by a trade surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following could be responsible for the depreciation of a country's currency?
A)The country expands its tourist industry.
B)Speculators anticipate economic growth in that nation.
C)The country experiences a sudden drop in the rate of inflation while other nations do not.
D)The country defaults on bonds held by foreigners.
A)The country expands its tourist industry.
B)Speculators anticipate economic growth in that nation.
C)The country experiences a sudden drop in the rate of inflation while other nations do not.
D)The country defaults on bonds held by foreigners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The depreciation of a country's currency causes the price of imports to
A)Rise and the prices of exports to rise.
B)Rise and the prices of exports to fall.
C)Fall and the prices of exports to rise.
D)Fall and the prices of exports to fall.
A)Rise and the prices of exports to rise.
B)Rise and the prices of exports to fall.
C)Fall and the prices of exports to rise.
D)Fall and the prices of exports to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An increase in the U.S.trade deficit could be caused by
A)An increase in the rate of inflation in other countries.
B)An appreciation of the dollar in terms of other currencies.
C)The imposition of a tariff on imported goods.
D)A depreciation of the dollar in terms of other currencies.
A)An increase in the rate of inflation in other countries.
B)An appreciation of the dollar in terms of other currencies.
C)The imposition of a tariff on imported goods.
D)A depreciation of the dollar in terms of other currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A good time for an American to hold German stocks,ceteris paribus,is when the
A)Euro is stable compared to the U.S.dollar.
B)U.S.dollar depreciates in value compared to the euro.
C)U.S.dollar appreciates in value compared to the euro.
D)The return in the German stock market has no relationship to the value of the dollar compared to the euro.
A)Euro is stable compared to the U.S.dollar.
B)U.S.dollar depreciates in value compared to the euro.
C)U.S.dollar appreciates in value compared to the euro.
D)The return in the German stock market has no relationship to the value of the dollar compared to the euro.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Generally speaking,a country whose currency appreciates will experience,as a result,
A)Reduced aggregate demand because of a decrease in exports.
B)Inflationary pressure from higher import prices.
C)Increasing interest rates from capital inflow.
D)Increased exports.
A)Reduced aggregate demand because of a decrease in exports.
B)Inflationary pressure from higher import prices.
C)Increasing interest rates from capital inflow.
D)Increased exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
American citizens planning a vacation abroad would welcome: =
A)Appreciation of the dollar.
B)Depreciation of the dollar.
C)Devaluation of the dollar.
D)Appreciation of the foreign currency.
A)Appreciation of the dollar.
B)Depreciation of the dollar.
C)Devaluation of the dollar.
D)Appreciation of the foreign currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following groups would be aided by a depreciation of the American dollar?
A)Foreign producers of goods imported by the United States.
B)American producers of goods for export.
C)U.S.importers of goods from abroad.
D)Foreign workers.
A)Foreign producers of goods imported by the United States.
B)American producers of goods for export.
C)U.S.importers of goods from abroad.
D)Foreign workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Appreciation of the U.S.dollar can be caused by
A)A decrease in the demand for dollars.
B)An increase in the demand for dollars.
C)An increase in the supply of dollars.
D)A decrease in the U.S.interest rate.
A)A decrease in the demand for dollars.
B)An increase in the demand for dollars.
C)An increase in the supply of dollars.
D)A decrease in the U.S.interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If the U.S.dollar depreciates,in the long run the United States should experience a
A)Lower inflation rate.
B)Smaller deficit in the U.S.trade balance.
C)Larger deficit in the U.S.current account.
D)Larger deficit in the U.S.capital account.
A)Lower inflation rate.
B)Smaller deficit in the U.S.trade balance.
C)Larger deficit in the U.S.current account.
D)Larger deficit in the U.S.capital account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Import-competing industries in the United States are likely to resist
A)Evaluation of the dollar.
B)Depreciation of the dollar.
C)Devaluation of the dollar.
D)Appreciation of the dollar.
A)Evaluation of the dollar.
B)Depreciation of the dollar.
C)Devaluation of the dollar.
D)Appreciation of the dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A depreciation of the Korean won against the U.S.dollar will
A)Raise the dollar price of Korean goods.
B)Lower the dollar price of U.S.goods.
C)Raise the won price of U.S.goods.
D)Lower the won price of Korean goods.
A)Raise the dollar price of Korean goods.
B)Lower the dollar price of U.S.goods.
C)Raise the won price of U.S.goods.
D)Lower the won price of Korean goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When foreign residents increase their demand for U.S.dollars,ceteris paribus,
A)The dollar price of foreign currency will rise.
B)Foreign residents,at the same time,reduce their supply of foreign currency to the foreign exchange market.
C)The dollar will appreciate in value.
D)The dollar will depreciate in value.
A)The dollar price of foreign currency will rise.
B)Foreign residents,at the same time,reduce their supply of foreign currency to the foreign exchange market.
C)The dollar will appreciate in value.
D)The dollar will depreciate in value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Appreciation of the dollar refers to
A)A loss of foreign exchange reserves.
B)An increase in the dollar price of foreign currency.
C)Intervention in international money markets.
D)A fall in the dollar price of a foreign currency.
A)A loss of foreign exchange reserves.
B)An increase in the dollar price of foreign currency.
C)Intervention in international money markets.
D)A fall in the dollar price of a foreign currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If speculators with Swiss francs believed the yen was going to depreciate against the dollar,they would most likely: =
A)Purchase euros.
B)Purchase dollars.
C)Purchase yen.
D)Not participate in foreign exchange markets because of the volatility.
A)Purchase euros.
B)Purchase dollars.
C)Purchase yen.
D)Not participate in foreign exchange markets because of the volatility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Generally speaking,a country whose currency depreciates will experience,as a result,
A)Increasing unemployment in export sectors.
B)Reduced aggregate demand.
C)Inflationary pressure because the prices of imports rise.
D)Falling interest rates from a capital outflow.
A)Increasing unemployment in export sectors.
B)Reduced aggregate demand.
C)Inflationary pressure because the prices of imports rise.
D)Falling interest rates from a capital outflow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Depreciation of the dollar refers to
A)A loss of foreign exchange reserves.
B)An increase in the dollar price of foreign currency.
C)Intervention in international money markets.
D)A fall in the dollar price of a foreign currency.
A)A loss of foreign exchange reserves.
B)An increase in the dollar price of foreign currency.
C)Intervention in international money markets.
D)A fall in the dollar price of a foreign currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
During the Asian Crisis of 1997-1998,U.S.hog farmers experienced decreased demand and lower prices for their products because of
A)A decrease in the value of Southeast Asian currencies relative to the U.S.dollar.
B)Protectionist trade policies in Southeast Asia that set quotas on U.S.farm imports.
C)A general Asia-wide depreciation of the U.S.dollar.
D)An increase in Southeast Asian incomes.
A)A decrease in the value of Southeast Asian currencies relative to the U.S.dollar.
B)Protectionist trade policies in Southeast Asia that set quotas on U.S.farm imports.
C)A general Asia-wide depreciation of the U.S.dollar.
D)An increase in Southeast Asian incomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
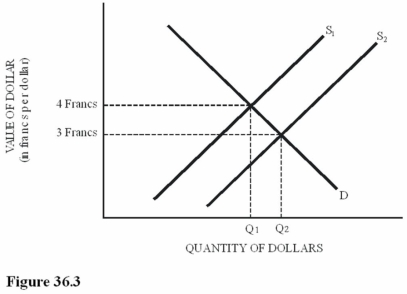 Suppose the supply of dollars decreased from S2 to S1 in Figure 36.3.As a result of this change,
Suppose the supply of dollars decreased from S2 to S1 in Figure 36.3.As a result of this change,A)Swiss chocolate imports to the United States will be lower-priced.
B)U.S.computer exports to Switzerland will be lower-priced.
C)A trade deficit will be created in Switzerland.
D)The Swiss franc will gain value worldwide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
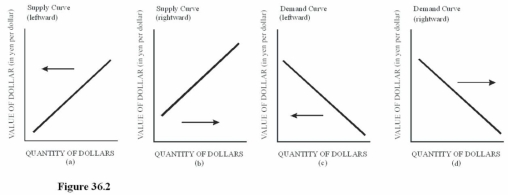 Choose the letter of the diagram in Figure 36.2 that represents the shift in the foreign exchange market for dollars given the following situation,ceteris paribus: The Japanese remove some tariffs on American goods.
Choose the letter of the diagram in Figure 36.2 that represents the shift in the foreign exchange market for dollars given the following situation,ceteris paribus: The Japanese remove some tariffs on American goods.A)a.
B)b.
C)c.
D)D.The demand for the dollar in the foreign exchange market increases because Japanese buyers will be more inclined to purchase U.S.goods when Japan removes tariffs on American goods,leading to a rightward shift in the demand for dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
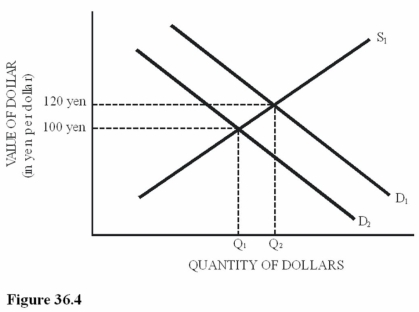 Refer to Figure 36.4 for the dollar-yen foreign exchange market.A decrease in demand from D1 to D2 could have been caused by
Refer to Figure 36.4 for the dollar-yen foreign exchange market.A decrease in demand from D1 to D2 could have been caused byA)A decrease in the demand for U.S.computers.
B)An increase in the number of Japanese visitors to the United States.
C)A quota placed on Japanese television imports to the United States.
D)A poor performance by the Japanese stock market compared to the U.S.stock market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The quantity of foreign currency demanded or supplied by residents of any country depends mainly on
A)The exchange rate.
B)The balance of payments.
C)The terms of trade.
D)Domestic economic conditions.
A)The exchange rate.
B)The balance of payments.
C)The terms of trade.
D)Domestic economic conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Ceteris paribus,if incomes increase faster in the United States than in less developed countries,then the currencies of less developed countries should
A)Appreciate,and the dollar should appreciate.
B)Appreciate,and the dollar should depreciate.
C)Depreciate,and the dollar should appreciate.
D)Depreciate,and the dollar should depreciate.
A)Appreciate,and the dollar should appreciate.
B)Appreciate,and the dollar should depreciate.
C)Depreciate,and the dollar should appreciate.
D)Depreciate,and the dollar should depreciate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Ceteris paribus,if interest rates in the United States rise relative to those abroad,then the surplus in the U.S.capital account would
A)Become smaller and the dollar would appreciate.
B)Become smaller and the dollar would depreciate.
C)Grow larger and the dollar would appreciate.
D)Grow larger and the dollar would depreciate.
A)Become smaller and the dollar would appreciate.
B)Become smaller and the dollar would depreciate.
C)Grow larger and the dollar would appreciate.
D)Grow larger and the dollar would depreciate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
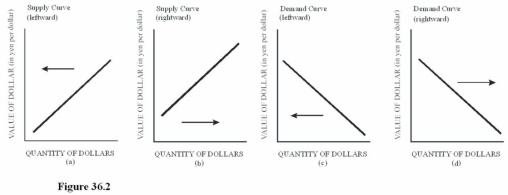 Choose the letter of the diagram in Figure 36.2 that represents the shift in the foreign exchange market for dollars given the following situation,ceteris paribus: A sudden,unexpected surge in inflation in the United States causes reduced purchases of U.S.goods by foreigners.
Choose the letter of the diagram in Figure 36.2 that represents the shift in the foreign exchange market for dollars given the following situation,ceteris paribus: A sudden,unexpected surge in inflation in the United States causes reduced purchases of U.S.goods by foreigners.A)a.
B)b.
C)c.
D)D.As foreigners cut back on U.S.purchases,the demand for the dollar will decrease,causing a leftward shift of the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Ceteris paribus,if African countries experience a drought and purchase food from the United States,the currencies of the African countries should
A)Appreciate,and the dollar should appreciate.
B)Appreciate,and the dollar should depreciate.
C)Depreciate,and the dollar should appreciate.
D)Depreciate,and the dollar should depreciate.
A)Appreciate,and the dollar should appreciate.
B)Appreciate,and the dollar should depreciate.
C)Depreciate,and the dollar should appreciate.
D)Depreciate,and the dollar should depreciate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A result of the Asian Crisis of 1997-1998 was
A)An increase in the value of the U.S.dollar relative to Southeast Asian currencies.
B)A major increase in the level of U.S.exports to Southeast Asia.
C)Political stability in many Southeast Asian countries.
D)An increase in the value of Southeast Asian currencies relative to the U.S.dollar.
A)An increase in the value of the U.S.dollar relative to Southeast Asian currencies.
B)A major increase in the level of U.S.exports to Southeast Asia.
C)Political stability in many Southeast Asian countries.
D)An increase in the value of Southeast Asian currencies relative to the U.S.dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Places where foreign currencies are bought and sold are
A)Capital account markets.
B)Foreign exchange reserves.
C)Foreign exchange markets.
D)Currency appreciation markets.
A)Capital account markets.
B)Foreign exchange reserves.
C)Foreign exchange markets.
D)Currency appreciation markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
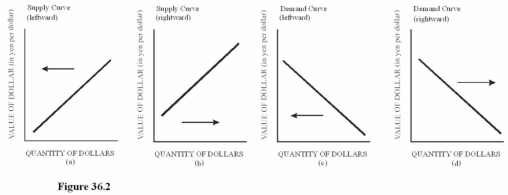 Choose the letter of the diagram in Figure 36.2 that represents the shift in the foreign exchange market for dollars given the following situation,ceteris paribus: The U.S.economy suddenly experiences a recession.
Choose the letter of the diagram in Figure 36.2 that represents the shift in the foreign exchange market for dollars given the following situation,ceteris paribus: The U.S.economy suddenly experiences a recession.A)a.
B)b.
C)c.
D)D.A recession will cause a leftward shift in the supply of dollars since U.S.consumers,feeling the pinch of the recession,will cut back on purchases of imports,reducing the supply of dollars on the foreign exchange market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Exchange rates change because of relative
A)Income changes but not relative price changes.
B)Price changes but not relative interest rate changes.
C)Interest rate changes but not relative income changes.
D)Income,relative price,and relative interest rates of countries.
A)Income changes but not relative price changes.
B)Price changes but not relative interest rate changes.
C)Interest rate changes but not relative income changes.
D)Income,relative price,and relative interest rates of countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
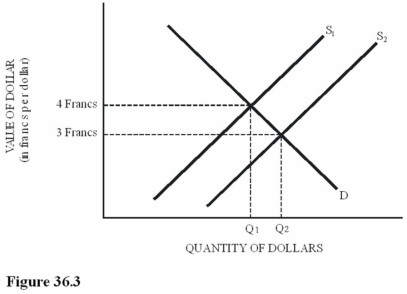 Suppose the supply of dollars increased from S1 to S2 in Figure 36.3.As a result of this change,
Suppose the supply of dollars increased from S1 to S2 in Figure 36.3.As a result of this change,A)Swiss chocolate imports to the United States will be lower-priced.
B)U.S.computer exports to Switzerland will be lower-priced.
C)A trade surplus will be created in Switzerland.
D)The Swiss franc will lose value worldwide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
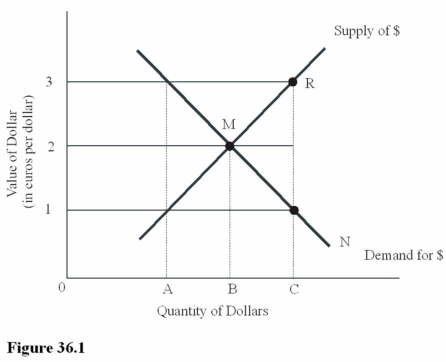 Ceteris paribus,an increase in the U.S.demand for Greek goods in Figure 36.1 will
Ceteris paribus,an increase in the U.S.demand for Greek goods in Figure 36.1 willA)Result in a movement from M to R on the supply curve for dollars.
B)Result in a movement from M to N on the demand curve for dollars.
C)Increase the dollar price of euros above $2 = 1 euro.
D)Make U.S.goods more expensive to Greek residents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
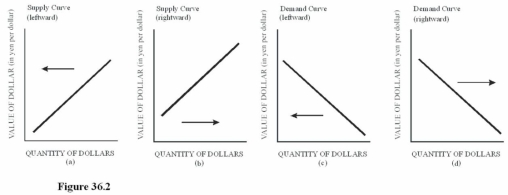 Choose the letter of the diagram in Figure 36.2 that represents the shift in the foreign exchange market for dollars given the following situation,ceteris paribus: The president of the United States decides to support the dollar by purchasing dollars with U.S.holdings of foreign currencies.
Choose the letter of the diagram in Figure 36.2 that represents the shift in the foreign exchange market for dollars given the following situation,ceteris paribus: The president of the United States decides to support the dollar by purchasing dollars with U.S.holdings of foreign currencies.A)a.
B)b.
C)c.
D)D.When the United States buys dollars with foreign currency holdings,the demand for the dollar in the foreign exchange market leads to a rightward shift in the demand for dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following events would result in a greater demand for U.S.dollars in the foreign exchange market,ceteris paribus?
A)An increase in interest rates in the United States.
B)An increase in interest rates in Japan.
C)Higher tariffs imposed by the United States on imports.
D)Higher quotas imposed by the United States on imports.
A)An increase in interest rates in the United States.
B)An increase in interest rates in Japan.
C)Higher tariffs imposed by the United States on imports.
D)Higher quotas imposed by the United States on imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
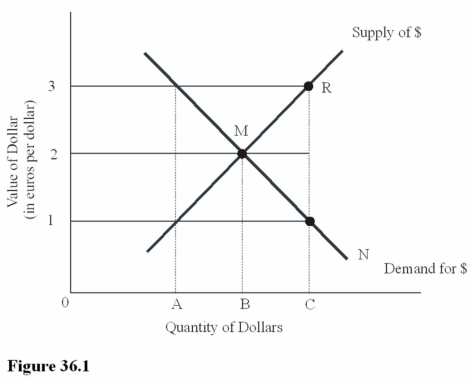 At an exchange rate of $1 = €1 in Figure 36.1,there is
At an exchange rate of $1 = €1 in Figure 36.1,there isA)Equilibrium in the foreign exchange market.
B)A surplus of dollars.
C)A shortage of euros.
D)An excess demand for dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
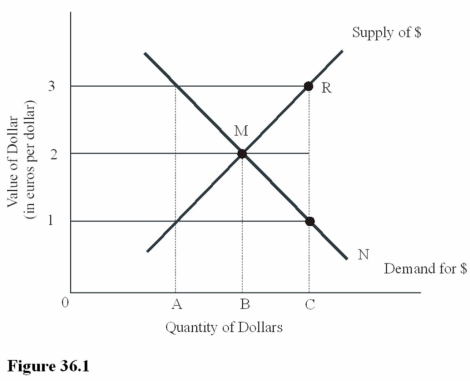 You have decided to purchase,directly from the French manufacturer,a helicopter that costs 800,000 euros.At the equilibrium exchange rate between dollars and euros in Figure 36.1,this purchase will cost you
You have decided to purchase,directly from the French manufacturer,a helicopter that costs 800,000 euros.At the equilibrium exchange rate between dollars and euros in Figure 36.1,this purchase will cost youA)$1,600,000.
B)$800,000.
C)$400,000.
D)$200,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
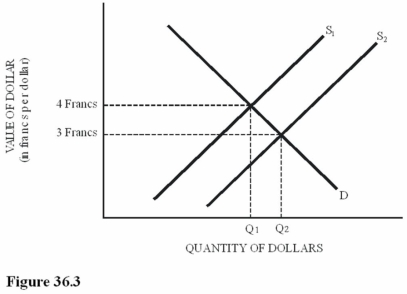 Refer to Figure 36.3 for the dollar-Swiss franc foreign exchange market.Which of the following is true?
Refer to Figure 36.3 for the dollar-Swiss franc foreign exchange market.Which of the following is true?A)The U.S.dollar appreciates in value compared to the franc when supply increases from S1 to S2.
B)The Swiss franc appreciates in value compared to the U.S.dollar when supply decreases from S2 to S1.
C)An increase in supply from S1 to S2 could be caused by an increase in the U.S.demand for Swiss chocolate.
D)An increase in supply from S1 to S2 could be caused by an increase in Swiss demand for U.S.corn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



