Deck 7: Pricing Decisions, customer Profitability, and Cost Management
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/94
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Pricing Decisions, customer Profitability, and Cost Management
1
The cost of goods sold equals total manufacturing costs when there is not beginning or ending inventory of a product.
True
2
What is a key factor affecting pricing decisions when there is a decrease in competition?
The key factor is the customer's willingness to pay based on the value that consumers place on products or services.It is not the costs or the competitors.
3
Companies operating in competitive markets must not accept the prices set by the market.
False
Explanation: Companies operating in competitive markets must always accept the prices set by the market.They use the market-based approach to costing products and services.
Explanation: Companies operating in competitive markets must always accept the prices set by the market.They use the market-based approach to costing products and services.
4
Which of the following is not true about pricing decisions?
A)Customers are an influence on demand and supply.
B)Competitors are an influence on demand and supply.
C)Costs are an influence on demand and supply.
D)Managers price products based on supply and demand.
E)Customers never have an influence on demand and supply.
A)Customers are an influence on demand and supply.
B)Competitors are an influence on demand and supply.
C)Costs are an influence on demand and supply.
D)Managers price products based on supply and demand.
E)Customers never have an influence on demand and supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
How can costs impact the supply and demand of products?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
To set long-run prices,managers calculate the ________ -cost of producing and selling a product.
A)full
B)small
C)partial
D)initial
E)strategic
A)full
B)small
C)partial
D)initial
E)strategic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The lower the cost of producing a product,the lower the quantity of product the company is willing to supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Companies operating in competitive markets use the:
A)cost-based approach.
B)direct-based approach.
C)market-based approach.
D)strategic-based approach.
E)consumer-based approach.
A)cost-based approach.
B)direct-based approach.
C)market-based approach.
D)strategic-based approach.
E)consumer-based approach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The managerial accountant at the Wright Company reported the following information:
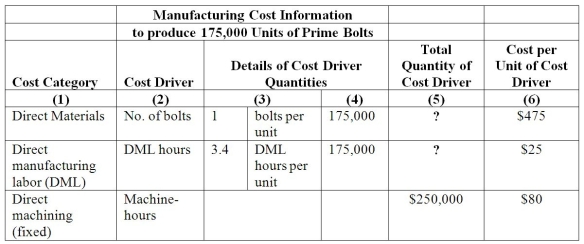
Required:
Compute the Total quantity of cost driver of direct materials and direct manufacturing labor (DML).
A)175,000;595,000
B)180,000;600,000
C)185,000;605,000
D)190,000;610,000
E)195,000;615,000

Required:
Compute the Total quantity of cost driver of direct materials and direct manufacturing labor (DML).
A)175,000;595,000
B)180,000;600,000
C)185,000;605,000
D)190,000;610,000
E)195,000;615,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is not true about competitors?
A)Businesses do not operate in a vacuum.
B)Managers must be aware of the actions of their competitors.
C)Some companies have distinctive products and limited competition.
D)When there are competitors,managers try to learn about competitors' plant capacities.
E)It is not necessary for managers to learn about their competitors' technologies.
A)Businesses do not operate in a vacuum.
B)Managers must be aware of the actions of their competitors.
C)Some companies have distinctive products and limited competition.
D)When there are competitors,managers try to learn about competitors' plant capacities.
E)It is not necessary for managers to learn about their competitors' technologies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Accounting managers that start pricing decisions by asking "Given what our customers want and how our competitors will react to what we do,what price should we charge" is most likely to use:
A)cost-plus approach.
B)cost-based approach.
C)market-based approach.
D)strategic-based approach.
E)consumer-based approach.
A)cost-plus approach.
B)cost-based approach.
C)market-based approach.
D)strategic-based approach.
E)consumer-based approach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The higher the price a monopolist sets,the higher the demand for the monopolist's product as customers seek substitute products or forgo buying the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
How can the competitor influence demand and supply of products and services?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is true about costs?
A)Costs never influence prices because they do not affect supply.
B)The higher the cost of producing the product,the greater the quantity supplied.
C)As companies increase supply,the cost of producing the product initially declines but eventually increases.
D)Managers set prices to maximize profits and they do not set prices that make the products attractive to consumers.
E)Companies supply products as long as selling additional units is lower than the cost to produce those products.
A)Costs never influence prices because they do not affect supply.
B)The higher the cost of producing the product,the greater the quantity supplied.
C)As companies increase supply,the cost of producing the product initially declines but eventually increases.
D)Managers set prices to maximize profits and they do not set prices that make the products attractive to consumers.
E)Companies supply products as long as selling additional units is lower than the cost to produce those products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The cost-based approach is also called:
A)cost-plus.
B)direct-plus.
C)market-plus.
D)strategic-plus.
E)consumer-plus.
A)cost-plus.
B)direct-plus.
C)market-plus.
D)strategic-plus.
E)consumer-plus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Fluctuations in exchange rates between different countries' currencies never affect costs and pricing decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The strategic decision designed to build long-run relationships with customers based on stable and predictable prices is ________.
A)mid-run pricing
B)cost-run pricing
C)some-run pricing
D)short-run pricing
E)long-run pricing
A)mid-run pricing
B)cost-run pricing
C)some-run pricing
D)short-run pricing
E)long-run pricing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is not true about international competition?
A)Competition spans international borders.
B)Fluctuations in exchange rates between different countries.
C)Different countries' currencies affect costs.
D)Fluctuations in exchange rates between different countries' currencies affect costs and pricing decisions.
E)Different countries' currencies have no impact on pricing decisions.
A)Competition spans international borders.
B)Fluctuations in exchange rates between different countries.
C)Different countries' currencies affect costs.
D)Fluctuations in exchange rates between different countries' currencies affect costs and pricing decisions.
E)Different countries' currencies have no impact on pricing decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The Trust Manufacturing Company reported $50,000,000 in direct manufacturing costs for 140,000 units of product.Compute the manufacturing cost per unit.
A)$357.14
B)$700,000
C)$985,000
D)$7,000,000
E)$49,860,000
A)$357.14
B)$700,000
C)$985,000
D)$7,000,000
E)$49,860,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The Wright Company reported a 7% defect rate of bolts and there are 140,000 units of bolts.Compute the number of defects in units at the Wright Company.
A)147 defective units
B)980 defective units
C)9,800 defective units
D)980,000 defective units
E)9,800,000 defective units
A)147 defective units
B)980 defective units
C)9,800 defective units
D)980,000 defective units
E)9,800,000 defective units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The Nutcracker Company manufactures two types of bolts: Top Point,the premium bolt,and a less competitive bolt,Bottom Point.The managerial accountant uses activity-based costing system (ABC)to calculate the manufacturing cost of Top Point.The product is very similar to other products produced in the marketplace.Does the company operate in a competitive market or a noncompetitive market? How does the manager determine prices? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Market-based pricing starts with:
A)target price.
B)listing price.
C)selling price.
D)strategic price.
E)consumer price.
A)target price.
B)listing price.
C)selling price.
D)strategic price.
E)consumer price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In reference to locked-in cost curves and the cost-incurrence curves,the top curve plots:
A)single locked-in costs.
B)cumulative locked-in costs.
C)single cost per unit.
D)cumulative cost per unit.
E)double cost per unit.
A)single locked-in costs.
B)cumulative locked-in costs.
C)single cost per unit.
D)cumulative cost per unit.
E)double cost per unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the target operating income per unit? What is the difference in target operating income per unit compared to the target cost per unit?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The cost that,if eliminated,would reduce actual or perceived value or utility customers experience from using the product or service is ________.
A)value-added cost
B)locked-in cost
C)designed-in cost
D)conversion costs
E)non-value added costs
A)value-added cost
B)locked-in cost
C)designed-in cost
D)conversion costs
E)non-value added costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Companies operating in less competitive markets offer products or services that differ from each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The Cedar Manufacturing Company reported a target cost of $600 per unit of fence material.The existing unit cost is $750.What should the manager do to reach the target cost?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The Coffee Distribution Company charges $1,200 to distribute coffee to customers.The managers at the company expect competitors to reduce prices to $1,025.The managers at the Coffee Distribution Company decide to remain competitive and reduce the cost of their coffee by 20%.
Required:
Compute the new cost the Coffee Distribution Company will charge based on the 20% price reduction.As a result of the cost reduction,should the managerial accountants at the Coffee Distribution forecast an increase or a decrease in annual sales per unit?
A)$900;decrease
B)$925;increase
C)$960;increase
D)$985;decrease
E)$1,025;decrease
Required:
Compute the new cost the Coffee Distribution Company will charge based on the 20% price reduction.As a result of the cost reduction,should the managerial accountants at the Coffee Distribution forecast an increase or a decrease in annual sales per unit?
A)$900;decrease
B)$925;increase
C)$960;increase
D)$985;decrease
E)$1,025;decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Value engineering entails improvements in product designs,changes in materials specifications,and modifications in process methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Target costs include all future costs,variable costs,and costs that are fixed in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Why is it important for managers to understand customers and competitors?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Why do managers perform cost analysis to implement cost reduction strategies to target cost reduction?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
To earn the target return on capital,the Moore Company needs to earn 12% operating income per unit on the total units they need to sell.The managerial accountant reported that the target price is $750 per unit.Compute the target operating income per unit and the target cost per unit.
A)$80 operating income per unit;$650 per unit
B)$90 operating income per unit;$660 per unit
C)$100 operating income per unit;$670 per unit
D)$110 operating income per unit;$680 per unit
E)$120 operating income per unit;$690 per unit
A)$80 operating income per unit;$650 per unit
B)$90 operating income per unit;$660 per unit
C)$100 operating income per unit;$670 per unit
D)$110 operating income per unit;$680 per unit
E)$120 operating income per unit;$690 per unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A systematic evaluation of all aspects of the value chain,with the objective of reducing costs and achieving a quality level that satisfies customers is ________.
A)cost engineering
B)price engineering
C)value engineering
D)product engineering
E)promotion engineering
A)cost engineering
B)price engineering
C)value engineering
D)product engineering
E)promotion engineering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Costs that have not yet been incurred but will be incurred in the future based on decisions that have already been made are:
A)value-added costs.
B)locked-in costs.
C)non-value-added costs.
D)targeted costs.
E)conversion costs.
A)value-added costs.
B)locked-in costs.
C)non-value-added costs.
D)targeted costs.
E)conversion costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is meant by the term reverse engineer?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A non-value-added-cost is a cost that,if eliminated,would reduce the actual or perceived value or utility that customers gain from using the product or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The Ivy Company manufactures two types of artificial ivy vines: Long Ivy,the long vine,and Thin Ivy,a smaller vine.The managerial accountant said that the company operates in a less competitive market.How does the managerial accountant decide on the margin that is added to costs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The estimated price for a product or service that customers are willing to pay is:
A)target price.
B)listing price.
C)selling price.
D)strategic price.
E)consumer price.
A)target price.
B)listing price.
C)selling price.
D)strategic price.
E)consumer price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The target cost per unit is never lower than the existing full cost of the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What can managerial accountants do to avoid the undesirable effects of value engineering and target costing?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What do managers do when activities and costs do not fall neatly into value-added or non-value added categories? What is the risk involved with this decision?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The reporting and assessment of revenues earned from customers and the costs incurred to earn those revenues is:
A)price discount.
B)whale curve.
C)price markups.
D)customer-cost hierarchy.
E)customer-profitability analysis.
A)price discount.
B)whale curve.
C)price markups.
D)customer-cost hierarchy.
E)customer-profitability analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In the time-and-materials method,individual jobs are priced based on materials and labor time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The Board Manufacturing Company reported investment capital of $80,000,000 and a 16% (pretax)target rate of return on the investment of 150,000 units of Product Y.
Required:
Compute the targeted annual operating income and the target operating income per unit of Product Y.
A)$5 operating income;$85.33 operating income per unit
B)$12,000,000 operating income;$85.33 operating income per unit
C)$12,500,000 operating income;$85.33 operating income per unit
D)$12,800,000 operating income;$85.33 operating income per unit
E)$12,850,000 operating income;$85.33 operating income per unit
Required:
Compute the targeted annual operating income and the target operating income per unit of Product Y.
A)$5 operating income;$85.33 operating income per unit
B)$12,000,000 operating income;$85.33 operating income per unit
C)$12,500,000 operating income;$85.33 operating income per unit
D)$12,800,000 operating income;$85.33 operating income per unit
E)$12,850,000 operating income;$85.33 operating income per unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is cost incurrence? What does cost incurrence measure?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The Heritage Foundation reported the following information:
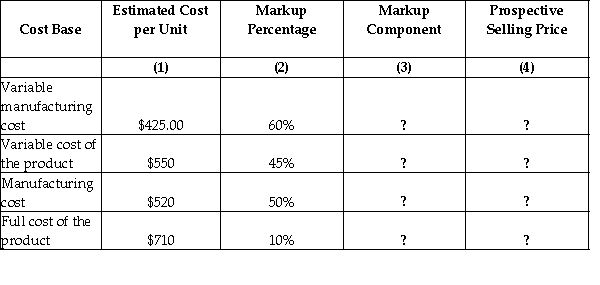
Required:
Compute the markup component and the prospective selling price for each cost base at the Heritage Foundation.
A)Markup components for each cost base: $255;$247.50;$260;$71
Prospective selling price for each cost base: $680;$797.50;$780;$781
B)Markup components for each cost base: $260;$257.50;$270;$481
Prospective selling price for each cost base: $690;$797.50;$785;$785
C)Markup components for each cost base: $265;$262.50;$275;$491
Prospective selling price for each cost base: $700;$825.50;$795;$790
D)Markup components for each cost base: $270;$262.50;$280;$495
Prospective selling price for each cost base: $705: $830.50;$800;$795
E)Markup components for each cost base: $275;$267.50;$285;$500
Prospective selling price for each cost base: $710;$835.50;$805;$800

Required:
Compute the markup component and the prospective selling price for each cost base at the Heritage Foundation.
A)Markup components for each cost base: $255;$247.50;$260;$71
Prospective selling price for each cost base: $680;$797.50;$780;$781
B)Markup components for each cost base: $260;$257.50;$270;$481
Prospective selling price for each cost base: $690;$797.50;$785;$785
C)Markup components for each cost base: $265;$262.50;$275;$491
Prospective selling price for each cost base: $700;$825.50;$795;$790
D)Markup components for each cost base: $270;$262.50;$280;$495
Prospective selling price for each cost base: $705: $830.50;$800;$795
E)Markup components for each cost base: $275;$267.50;$285;$500
Prospective selling price for each cost base: $710;$835.50;$805;$800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In contrast to cost-plus pricing,target pricing never determines product characteristics and target price on the basis of customer preferences and expected competitor responses,and then computes a target cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Value engineering decreases both value-added costs and non-value-added costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What are the key steps in value engineering?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The general formula for setting a cost-based selling price adds a markup component to the cost base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Target annual operating income divided by invested capital is ________.
A)target price
B)locked in costs
C)target cost per unit
D)target operating income per unit
E)target rate of return on investment
A)target price
B)locked in costs
C)target cost per unit
D)target operating income per unit
E)target rate of return on investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Kaizen is a continuous improvement technique used to reduce the time it takes to do a task,eliminate waste,and improve operating efficiency and productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The Walter Foundation invested $3,500,000 in a plant to remanufacture refrigerators.The target operating income from the plant is $250,000 annually.The company plans actual sales of 800 refrigerators at $1,100.00 each.
Required:
Compute the target rate of return on the investment at the Walter Foundation.
A)6.14 %
B)7.14 %
C)8.14 %
D)9.14 %
E)10.14 %
Required:
Compute the target rate of return on the investment at the Walter Foundation.
A)6.14 %
B)7.14 %
C)8.14 %
D)9.14 %
E)10.14 %

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Amarillo Manufacturing uses a 13% markup on the full unit cost of Product X to compute the selling price.The full unit cost of Product X is $850.
Required:
Compute the markup component and the prospective selling price.
A)$95.50;$925.50
B)$110.50;$960.50
C)$115.50;$965.50
D)$120.50;$970.50
E)$125.50;$975.50
Required:
Compute the markup component and the prospective selling price.
A)$95.50;$925.50
B)$110.50;$960.50
C)$115.50;$965.50
D)$120.50;$970.50
E)$125.50;$975.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Do service companies use cost-plus pricing?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The Kensington Corporation invested $2,500,000 in an operation to make wooden planks.The target operating income desired at the plant is $245,000 annually.The company plans actual sales of 700 planks at $500 each.The managerial accountant reported a target rate of return on the investment of 15%.
Required:
Compute the markup percentage as a percentage of the full cost for the Kensington Corporation.
A)2.00%
B)2.13%
C)2.33%
D)2.43%
E)2.53%
Required:
Compute the markup percentage as a percentage of the full cost for the Kensington Corporation.
A)2.00%
B)2.13%
C)2.33%
D)2.43%
E)2.53%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The reduction in selling price below list selling price to encourage customers to purchase more quantities is:
A)price discount.
B)whale curve.
C)price markups.
D)customer-cost hierarchy.
E)customer-profitability analysis.
A)price discount.
B)whale curve.
C)price markups.
D)customer-cost hierarchy.
E)customer-profitability analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Mark Manufacturing had a product design that resulted in a $740 full cost of Product B.Assuming a markup of 10%,what is the prospective price of Product B?
A)$800
B)$804
C)$814
D)$824
E)$834
A)$800
B)$804
C)$814
D)$824
E)$834

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Companies seek to minimize non-value added costs because they do not provide benefits to customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
________ spans the time from initial R&D on a product to when customer service and support is no longer offered for that product.
A)Product life cycle
B)Life-cycle budgeting
C)Life-cycle costing
D)Customer life-cycle costs
E)Price discrimination
A)Product life cycle
B)Life-cycle budgeting
C)Life-cycle costing
D)Customer life-cycle costs
E)Price discrimination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A customer cost hierarchy categorizes costs related to customers into different cost pools on the basis of different types of cost drivers,or cost allocation bases,or different degrees of difficulty determining cause-and-effect or benefits-received relationships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The costs that influence prices a company can charge for its products is:
A)product life-cycle costing.
B)life-cycle budgeting.
C)customer life-cycle costs.
D)life-cycle costing.
E)price discrimination.
A)product life-cycle costing.
B)life-cycle budgeting.
C)customer life-cycle costs.
D)life-cycle costing.
E)price discrimination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What are the first three categories of the customer-cost hierarchy? Why do managers want to analyze customer-level indirect costs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which category of indirect costs in the customer-cost hierarchy are costs incurred to process orders or to make deliveries?
A)Customer output unit-level costs.
B)Customer batch-level costs.
C)Customer-sustaining costs.
D)Distribution-channel costs.
E)Corporate-division-sustaining costs.
A)Customer output unit-level costs.
B)Customer batch-level costs.
C)Customer-sustaining costs.
D)Distribution-channel costs.
E)Corporate-division-sustaining costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The Premier Sales Company reported $6,250,000 on the sales order activity in 2012.The activity included negotiating,finalizing,issuing,and collecting on 5,500 sales orders.
Required:
Compute the cost per sales order.What type of costs are sales-order costs?
A)$950.37;distribution-channel costs
B)$1050.37;customer-sustaining costs
C)$1,136.37;batch-level costs
D)$1,250.37;customer-sustaining costs
E)$1,330.37;corporate-sustaining costs
Required:
Compute the cost per sales order.What type of costs are sales-order costs?
A)$950.37;distribution-channel costs
B)$1050.37;customer-sustaining costs
C)$1,136.37;batch-level costs
D)$1,250.37;customer-sustaining costs
E)$1,330.37;corporate-sustaining costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In life-cycle budgeting,managers estimate the revenues and business function costs across the entire value chain from a product's initial R&D to its final customer service and support.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which category of indirect costs in the customer-cost hierarchy are costs of visits to customers or costs of displays at customer sites?
A)Customer output unit-level costs.
B)Customer batch-level costs.
C)Customer-sustaining costs.
D)Distribution-channel costs.
E)Corporate division-sustaining costs.
A)Customer output unit-level costs.
B)Customer batch-level costs.
C)Customer-sustaining costs.
D)Distribution-channel costs.
E)Corporate division-sustaining costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The manager at Renovations Incorporated reported the following information about life-cycle costs:
Assume the following budgeted amounts for General Ledger over a 6-year product life cycle:
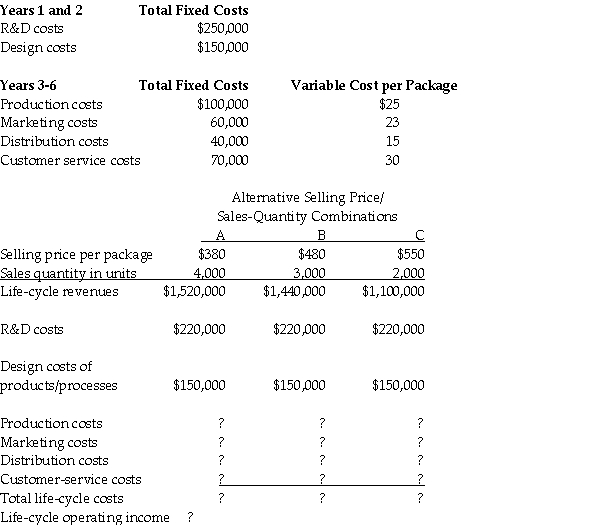
Required:
Compute the life-cycle costs for Production costs,Marketing costs,Distribution costs,Customer-service costs,and total costs.Compute the life-cycle operating income.
Assume the following budgeted amounts for General Ledger over a 6-year product life cycle:

Required:
Compute the life-cycle costs for Production costs,Marketing costs,Distribution costs,Customer-service costs,and total costs.Compute the life-cycle operating income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
________ tracks and accumulates business function costs across the entire value chain from a product's initial R&D to its final customer service and support.
A)Product life cycle
B)Life-cycle budgeting
C)Customer life-cycle costs
D)Life-cycle costing
E)Price discrimination
A)Product life cycle
B)Life-cycle budgeting
C)Customer life-cycle costs
D)Life-cycle costing
E)Price discrimination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which category of indirect costs in the customer-cost hierarchy is the cost of the salary of a manager in a wholesale distribution channel?
A)Customer output unit-level costs.
B)Customer batch-level costs.
C)Customer-sustaining costs.
D)Distribution-channel costs.
E)Corporate division-sustaining costs.
A)Customer output unit-level costs.
B)Customer batch-level costs.
C)Customer-sustaining costs.
D)Distribution-channel costs.
E)Corporate division-sustaining costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The costs that provide useful information for strategically evaluating pricing decisions are:
A)product life-cycle costs.
B)discretionary costs.
C)customer life-cycle costs.
D)life-cycle costs.
E)budgeted life-cycle costs.
A)product life-cycle costs.
B)discretionary costs.
C)customer life-cycle costs.
D)life-cycle costs.
E)budgeted life-cycle costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Price discounts are not a function of multiple factors,including the volume of product purchased and the desire to sell to a customer who might help promote sales to other customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Sales-order costs are:
A)output unit-level costs.
B)batch-level costs.
C)customer-sustaining costs.
D)distribution-channel costs.
E)corporate-sustaining costs.
A)output unit-level costs.
B)batch-level costs.
C)customer-sustaining costs.
D)distribution-channel costs.
E)corporate-sustaining costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Customer-Profitability Analysis for Consumer Banking Clients

Required:
Compute the Customer-Level Operating Income.

Required:
Compute the Customer-Level Operating Income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Stripe Engineering reported the following budgeted life-cycle revenues to report alternative selling-price/sales-quantity combinations:
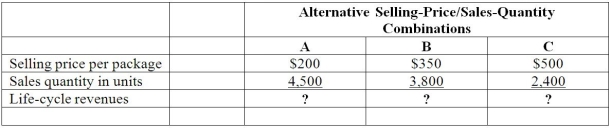
Required:
Compute the life-cycle revenues for A,B,and C.
A)$500;$1,000,500;$1,110,000
B)$900,000;$1,330,000;$1,200,000
C)$925,000;$1,360,000;$1,250,000
D)$950,000;$1,360,000;$1,275,000
E)$975,000;$1,370,000;$1,285,000

Required:
Compute the life-cycle revenues for A,B,and C.
A)$500;$1,000,500;$1,110,000
B)$900,000;$1,330,000;$1,200,000
C)$925,000;$1,360,000;$1,250,000
D)$950,000;$1,360,000;$1,275,000
E)$975,000;$1,370,000;$1,285,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which category of indirect costs in the customer-cost hierarchy are product handling costs of each computer sold?
A)Customer output unit-level costs.
B)Customer batch-level costs.
C)Customer-sustaining costs.
D)Distribution-channel costs.
E)Corporate-division sustaining costs.
A)Customer output unit-level costs.
B)Customer batch-level costs.
C)Customer-sustaining costs.
D)Distribution-channel costs.
E)Corporate-division sustaining costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Budgeted life-cycle costs provide useful information for strategically evaluating pricing decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Tracking price discounts by customer and by salesperson has no impact on customer profitability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
________ focus on total costs incurred by a customer to acquire,use,maintain,and dispose of a product or service.
A)Product life-cycle
B)Life-cycle budgeting
C)Customer life-cycle costs
D)Life-cycle costing
E)Price discrimination
A)Product life-cycle
B)Life-cycle budgeting
C)Customer life-cycle costs
D)Life-cycle costing
E)Price discrimination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



