Deck 22: Accounting for Superannuation Plans
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/77
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Accounting for Superannuation Plans
1
The maximum period a defined benefit plan can have between detailed actuarial reviews of the accrued benefits is 2 years.
False
2
When a member remains in a defined benefit plan until retirement,the amount paid out is determined by reference to their contributions and investment earnings thereon.
False
3
According to AAS 25,the revenue of a superannuation fund should include the changes in net market value of all plan assets over the period.
True
4
A defined benefit plan is also known as an accumulation fund.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
AAS 25 permits use of cost or revalued basis in measuring assets of a defined contribution plan and a defined benefit plan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Accounting standards regulate the provision of reports by superannuation plans,including information on the performance and position of the plan and individual members' contributions and entitlements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
It is common for superannuation plans to recognise depreciation expense for its non-current assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
AAS 25 requires all liabilities of a superannuation plan to be discounted to their present value at reporting date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
AAS 25 Financial Reporting by Superannuation Plans deals with accounting in an employer's financial reports for employee entitlements,including retirement benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Wear and tear of assets is not considered when determining market values of assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The purpose of all superannuation plans is to guarantee a specified level of retirement,death or disability benefits for members of the plan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
AAS 25 requires the disclosure of at least a summary of the most recent actuarial report for defined contribution plans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A superannuation plan is defined in AAS 25 as an arrangement whereby it is agreed between trustees and employers,employees or self-employed persons,that benefits be provided upon the retirement of plan members or upon their resignation,death,disablement or other specified events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For a defined contribution plan and a defined benefit plan,the changes in net market values of the plan's financial liabilities since the beginning of the reporting period shall be included in the profit or loss for the reporting period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In a defined contribution plan,accrued benefits are the difference between the carrying amount of the assets and the sum of all other liabilities of the superannuation plan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The accrued benefits of a defined benefit superannuation plan are the accumulated assets that will be used to meet the plan's obligations to its members.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Accrued benefits in a defined contribution plan encompass amounts which have been allocated and amounts which have not been allocated to members of the plan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Defined benefit plans must disclose actuarial information in their financial statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When a superannuation fund has inventories recognised as an asset,this should be valued at lower of cost or net realisable value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Superannuation funds are monitored and regulated by the Australian Vigilance Regulation Authority and the Australian Securities and Investments Commission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Happy Days Superannuation Plan provides the following information regarding its assets and receipts for the year ended 30 June 2014: 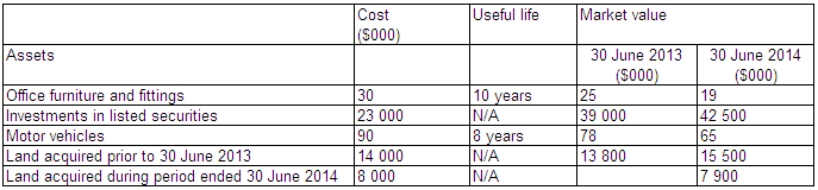 During the period land acquired before 30 June 2013 was sold.The land had a cost of $4 million,a market value at 30 June 2013 of $4.5 million,and was sold for $6 million.What is the revenue of the superannuation plan for the period in accordance with AAS 25?
During the period land acquired before 30 June 2013 was sold.The land had a cost of $4 million,a market value at 30 June 2013 of $4.5 million,and was sold for $6 million.What is the revenue of the superannuation plan for the period in accordance with AAS 25?
A) $12 600 000
B) $6 585 750
C) $11 081 000
D) $6 581 000
 During the period land acquired before 30 June 2013 was sold.The land had a cost of $4 million,a market value at 30 June 2013 of $4.5 million,and was sold for $6 million.What is the revenue of the superannuation plan for the period in accordance with AAS 25?
During the period land acquired before 30 June 2013 was sold.The land had a cost of $4 million,a market value at 30 June 2013 of $4.5 million,and was sold for $6 million.What is the revenue of the superannuation plan for the period in accordance with AAS 25?A) $12 600 000
B) $6 585 750
C) $11 081 000
D) $6 581 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Situations in which a superannuation plan may be considered not to be a reporting entity include:
A) where there is only a single member of the plan.
B) where the trust assets are secured by guarantees and the plan only invests in risk-free government bonds.
C) where plan members are employed by entities other than public companies, and the plan members and the owners of the employer entity are an identical group.
D) where there is only a single member of the plan and plans where plan members are employed by entities other than public companies, and the plan members and the owners of the employer entity are an identical group.
A) where there is only a single member of the plan.
B) where the trust assets are secured by guarantees and the plan only invests in risk-free government bonds.
C) where plan members are employed by entities other than public companies, and the plan members and the owners of the employer entity are an identical group.
D) where there is only a single member of the plan and plans where plan members are employed by entities other than public companies, and the plan members and the owners of the employer entity are an identical group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
How are the accrued benefits of a defined contribution plan measured?
A) They are measured as the market value of the assets of the plan with no accumulated depreciation deducted.
B) They are a residual amount: the difference between the carrying amount of the assets and the sum of the income tax and sundry liabilities of the plan.
C) They are measured in a detailed actuarial review to determine the present value of expected future benefit payments arising as a result of membership of the fund up to measurement date.
D) They are measured as the difference between the carrying value of the plan's assets and the liability to pay funds out to members on retirement.
A) They are measured as the market value of the assets of the plan with no accumulated depreciation deducted.
B) They are a residual amount: the difference between the carrying amount of the assets and the sum of the income tax and sundry liabilities of the plan.
C) They are measured in a detailed actuarial review to determine the present value of expected future benefit payments arising as a result of membership of the fund up to measurement date.
D) They are measured as the difference between the carrying value of the plan's assets and the liability to pay funds out to members on retirement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A defined benefit plan is one in which:
A) The contributions by employees are defined in advance and the employers agree to increase their contribution to the fund to compensate for changes in the consumer price index.
B) The benefits to be paid to members on retirement are determined by the performance of the fund over the period of employee membership. This ensures that the member enjoys the benefits of the investments made by the plan.
C) The amounts to be paid to members at normal retirement age are specified or determined, at least in part, by reference to members' years of membership and/or salary levels.
D) The amounts to be contributed by employees are determined by the plan trustees based on members' years of membership and/or salary levels.
A) The contributions by employees are defined in advance and the employers agree to increase their contribution to the fund to compensate for changes in the consumer price index.
B) The benefits to be paid to members on retirement are determined by the performance of the fund over the period of employee membership. This ensures that the member enjoys the benefits of the investments made by the plan.
C) The amounts to be paid to members at normal retirement age are specified or determined, at least in part, by reference to members' years of membership and/or salary levels.
D) The amounts to be contributed by employees are determined by the plan trustees based on members' years of membership and/or salary levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The revenue recognition and asset valuation methods specified in AAS 25 are likely to increase the volatility of reported earnings.This is because:
A) Revenue is to be recognised when it is received and depreciation is to be calculated on a units-of-usage basis.
B) The short-term variation in market prices of assets intended to be held long-term are reported as revenues or expenses each year.
C) The asset valuation is to be based on the lower of cost and net realisable value, so that there are often lump-sum write-offs to the statement of comprehensive income.
D) Preparers of accounts for superannuation plans argue that the revenues should be smoothed over a 7-year period rather than all reported as earned in a period.
A) Revenue is to be recognised when it is received and depreciation is to be calculated on a units-of-usage basis.
B) The short-term variation in market prices of assets intended to be held long-term are reported as revenues or expenses each year.
C) The asset valuation is to be based on the lower of cost and net realisable value, so that there are often lump-sum write-offs to the statement of comprehensive income.
D) Preparers of accounts for superannuation plans argue that the revenues should be smoothed over a 7-year period rather than all reported as earned in a period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the case of a defined benefit plan,the statements the trustees must provide if a detailed actuarial review has not been conducted at balance date include:
A) an operating statement and a statement of financial position.
B) a statement of net assets and an operating statement.
C) a statement of changes in net assets and a statement of net assets.
D) a statement of changes in net assets and a statement of financial position.
A) an operating statement and a statement of financial position.
B) a statement of net assets and an operating statement.
C) a statement of changes in net assets and a statement of net assets.
D) a statement of changes in net assets and a statement of financial position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A contributory superannuation plan is one in which:
A) the employer contributes periodic payments to the trust fund.
B) the employees contribute periodic payments to the trust fund.
C) the government contributes a percentage of the employees' contribution.
D) the benefits accumulate at a compound rate.
A) the employer contributes periodic payments to the trust fund.
B) the employees contribute periodic payments to the trust fund.
C) the government contributes a percentage of the employees' contribution.
D) the benefits accumulate at a compound rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
AAS 25 requires that all the assets of superannuation plans be measured at:
A) historical cost, depreciated where appropriate.
B) replacement cost net of accumulated depreciation where appropriate.
C) net market value.
D) net realisable value if they are investments. Operating assets are to be valued at historical cost and depreciated where appropriate.
A) historical cost, depreciated where appropriate.
B) replacement cost net of accumulated depreciation where appropriate.
C) net market value.
D) net realisable value if they are investments. Operating assets are to be valued at historical cost and depreciated where appropriate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The argument in support of AAS 25's selected method of measuring assets for superannuation plans is that:
A) Reliability is important to members of a plan because they are relying on the plan for income in their retirement.
B) It is more relevant to the users.
C) Using a market measure introduces subjectivity into the financial reports.
D) Reliability is important to members of a plan because they are relying on the plan for income in their retirement and it is more relevant to the users.
A) Reliability is important to members of a plan because they are relying on the plan for income in their retirement.
B) It is more relevant to the users.
C) Using a market measure introduces subjectivity into the financial reports.
D) Reliability is important to members of a plan because they are relying on the plan for income in their retirement and it is more relevant to the users.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
According to AAS 25,beneficiaries of a defined contribution plan will be interested in evaluating:
A) the performance of trust management in preserving the plan's assets.
B) the plan's ability to meet its obligations to members and beneficiaries.
C) the plan's ability to meet its debts as they fall due.
D) the plan's ability to provide an adequate level of benefits for members and beneficiaries.
A) the performance of trust management in preserving the plan's assets.
B) the plan's ability to meet its obligations to members and beneficiaries.
C) the plan's ability to meet its debts as they fall due.
D) the plan's ability to provide an adequate level of benefits for members and beneficiaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In what way is the asset measurement requirement in AAS 25 Financial Reporting by Superannuation Plans inconsistent with the treatment required in AASB 1023 Financial Reporting of General Insurance Activities?
A) The requirement in AAS 25 is to measure assets at net market value whereas AASB 1023 requires the application of net realisable value.
B) AAS 25 requires market values to be used for all investments, whereas in AASB 1023 market values are required for investments integral to the entity's general insurance activities.
C) AAS 25 requires the use of market values whereas AASB 1023 requires the use of modified historical cost.
D) The requirement in AAS 25 relates to all assets of the entity, whereas in AASB 1023 it relates only to investments integral to the entity's general insurance activities.
A) The requirement in AAS 25 is to measure assets at net market value whereas AASB 1023 requires the application of net realisable value.
B) AAS 25 requires market values to be used for all investments, whereas in AASB 1023 market values are required for investments integral to the entity's general insurance activities.
C) AAS 25 requires the use of market values whereas AASB 1023 requires the use of modified historical cost.
D) The requirement in AAS 25 relates to all assets of the entity, whereas in AASB 1023 it relates only to investments integral to the entity's general insurance activities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
AAS 25 is relevant for superannuation plans that are reporting entities.A reporting entity is one for which:
A) A minimum of 25 per cent of the members of the fund have voted in favour of the provision of general purpose financial reports.
B) It is reasonable to expect the existence of users who are dependent on general purpose financial reports for information that will be useful for them for making and evaluating decisions about the allocation of scarce resources.
C) There has not been a vote carried by 75 per cent or more of the members releasing the trustees from the responsibility to provide general purpose financial reports.
D) It is reasonable to expect the existence of users who need specific purpose reports in order to make and evaluate decisions about the allocation of scarce resources.
A) A minimum of 25 per cent of the members of the fund have voted in favour of the provision of general purpose financial reports.
B) It is reasonable to expect the existence of users who are dependent on general purpose financial reports for information that will be useful for them for making and evaluating decisions about the allocation of scarce resources.
C) There has not been a vote carried by 75 per cent or more of the members releasing the trustees from the responsibility to provide general purpose financial reports.
D) It is reasonable to expect the existence of users who need specific purpose reports in order to make and evaluate decisions about the allocation of scarce resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
According to AAS 25,superannuation plans must provide a statement of financial position,an operating statement and a statement of cash flows in which of the following situations?
A) In the case of a defined contribution fund; if it has had an actuarial assessment of the accrued benefits owed to members in the current period it must provide these reports.
B) In the case of a defined benefit plan; the trustees may choose to provide these statements if they have had an actuarial review of the accrued benefits at balance date.
C) In the case of a defined contribution fund these reports are required if the plan is a reporting entity.
D) In the case of a defined benefit plan; the trustees may choose to provide these statements if they have had an actuarial review of the accrued benefits at balance date and in the case of a defined contribution fund these reports are required if the plan is a reporting entity.
A) In the case of a defined contribution fund; if it has had an actuarial assessment of the accrued benefits owed to members in the current period it must provide these reports.
B) In the case of a defined benefit plan; the trustees may choose to provide these statements if they have had an actuarial review of the accrued benefits at balance date.
C) In the case of a defined contribution fund these reports are required if the plan is a reporting entity.
D) In the case of a defined benefit plan; the trustees may choose to provide these statements if they have had an actuarial review of the accrued benefits at balance date and in the case of a defined contribution fund these reports are required if the plan is a reporting entity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How are the accrued benefits of a defined benefit plan measured?
A) They are measured as the difference between the carrying value of the plan's assets and the liability to pay funds out to members on retirement.
B) They are measured as the market value of the assets of the plan with no accumulated depreciation deducted.
C) They are a residual amount: the difference between the carrying amount of the assets and the sum of the income tax and sundry liabilities of the plan.
D) They are measured in a detailed actuarial review to determine the present value of expected future benefit payments arising as a result of membership of the fund up to measurement date.
A) They are measured as the difference between the carrying value of the plan's assets and the liability to pay funds out to members on retirement.
B) They are measured as the market value of the assets of the plan with no accumulated depreciation deducted.
C) They are a residual amount: the difference between the carrying amount of the assets and the sum of the income tax and sundry liabilities of the plan.
D) They are measured in a detailed actuarial review to determine the present value of expected future benefit payments arising as a result of membership of the fund up to measurement date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The measurement of the accrued benefits of a defined benefit plan involves assumptions about factors including:
A) expected value of benefits to be paid as a result of early withdrawal from the plan.
B) future salary levels and membership turnover.
C) mortality rates.
D) all of the given answers.
A) expected value of benefits to be paid as a result of early withdrawal from the plan.
B) future salary levels and membership turnover.
C) mortality rates.
D) all of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A description of the regulatory framework relevant to superannuation plans in Australia is:
A) AAS 25 provides legally backed, mandatory requirements for financial reporting by superannuation funds. The reporting required covers both general purpose financial reporting and statements of contributions and entitlements for individual members. APRA and ASIC have a role in supervising and monitoring superannuation plans in line with legislation contained in the Superannuation Industry Supervision Act 1993.
B) ASIC has a supervisory role and APRA monitors trusts that are superannuation plans. Regulations regarding the plans are set out in the Superannuation Industry Supervision Act 1993. AAS 25 provides guidance for reporting for general purpose users and individual members and it is recommended by APRA that plans conform with AAS 25.
C) APRA is the regulatory body that supervises reporting and financial standards for superannuation trusts. ASIC monitors those superannuation plans established as companies. In general, superannuation plans are regulated through the Superannuation Industry Supervision Act 1993. This Act mandates compliance with AAS 25 for all superannuation plans.
D) Superannuation plans are monitored and regulated by APRA and ASIC, with specific regulations set out in the Superannuation Industry Supervision Act 1993. AAS 25 provides guidance for general purpose financial reports and it is recommended by APRA that plans follow AAS 25.
A) AAS 25 provides legally backed, mandatory requirements for financial reporting by superannuation funds. The reporting required covers both general purpose financial reporting and statements of contributions and entitlements for individual members. APRA and ASIC have a role in supervising and monitoring superannuation plans in line with legislation contained in the Superannuation Industry Supervision Act 1993.
B) ASIC has a supervisory role and APRA monitors trusts that are superannuation plans. Regulations regarding the plans are set out in the Superannuation Industry Supervision Act 1993. AAS 25 provides guidance for reporting for general purpose users and individual members and it is recommended by APRA that plans conform with AAS 25.
C) APRA is the regulatory body that supervises reporting and financial standards for superannuation trusts. ASIC monitors those superannuation plans established as companies. In general, superannuation plans are regulated through the Superannuation Industry Supervision Act 1993. This Act mandates compliance with AAS 25 for all superannuation plans.
D) Superannuation plans are monitored and regulated by APRA and ASIC, with specific regulations set out in the Superannuation Industry Supervision Act 1993. AAS 25 provides guidance for general purpose financial reports and it is recommended by APRA that plans follow AAS 25.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The types of reports that a superannuation plan provides fall into which two categories?
A) reports that relate to the financial performance and position of the plan
B) accrual accounting reports and statements of cash flow
C) individual contributions and entitlements of each member and the performance and position of the plan itself
D) government reporting requirements and general purpose financial reports
A) reports that relate to the financial performance and position of the plan
B) accrual accounting reports and statements of cash flow
C) individual contributions and entitlements of each member and the performance and position of the plan itself
D) government reporting requirements and general purpose financial reports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Long-lived Superannuation Plan provides the following information regarding its assets and receipts for the year ended 30 June 2014: 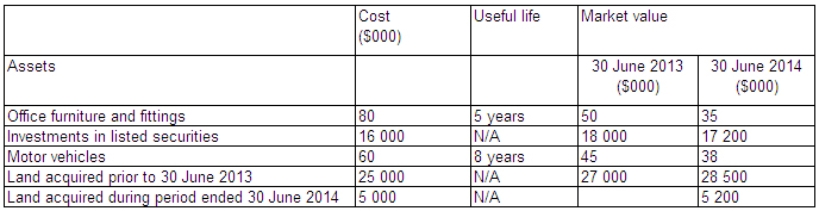 During the period,land acquired before 30 June 2013 was sold.The land had a cost of $1 million,a market value at 30 June 2013 of $2 million,and was sold for $2.8 million.What is the revenue of the superannuation plan for the period in accordance with AAS 25?
During the period,land acquired before 30 June 2013 was sold.The land had a cost of $1 million,a market value at 30 June 2013 of $2 million,and was sold for $2.8 million.What is the revenue of the superannuation plan for the period in accordance with AAS 25?
A) $3 700 000
B) $3 678 000
C) $2 676 500
D) $1 678 000
 During the period,land acquired before 30 June 2013 was sold.The land had a cost of $1 million,a market value at 30 June 2013 of $2 million,and was sold for $2.8 million.What is the revenue of the superannuation plan for the period in accordance with AAS 25?
During the period,land acquired before 30 June 2013 was sold.The land had a cost of $1 million,a market value at 30 June 2013 of $2 million,and was sold for $2.8 million.What is the revenue of the superannuation plan for the period in accordance with AAS 25?A) $3 700 000
B) $3 678 000
C) $2 676 500
D) $1 678 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A defined contribution plan is one in which:
A) The amounts to be paid to members at normal retirement age are determined by reference to the accumulated contributions made by and/or on behalf of members, together with investment earnings thereon.
B) The amounts to be paid to members at normal retirement age are determined by reference to the percentage level of salary contributed over the period of membership of the plan.
C) The amounts to be contributed by employees are determined by the plan trustees based on members' years of membership and/or salary levels.
D) The amounts to be paid to members at normal retirement age are specified or determined, at least in part, by reference to members' years of membership and/or salary levels.
A) The amounts to be paid to members at normal retirement age are determined by reference to the accumulated contributions made by and/or on behalf of members, together with investment earnings thereon.
B) The amounts to be paid to members at normal retirement age are determined by reference to the percentage level of salary contributed over the period of membership of the plan.
C) The amounts to be contributed by employees are determined by the plan trustees based on members' years of membership and/or salary levels.
D) The amounts to be paid to members at normal retirement age are specified or determined, at least in part, by reference to members' years of membership and/or salary levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The requirements of AAS 25 mean that some other standards do not apply to superannuation plans.These standards include:
A) AAS 4 Depreciation and AAS 17 Leases.
B) AAS 21 Acquisitions of Assets and AAS 17 Leases.
C) AAS 28 Statement of Cash Flows and AAS 10 Revaluation of Non-current Assets.
D) AAS 10 Revaluation of Non-current Assets and AAS 4 Depreciation.
A) AAS 4 Depreciation and AAS 17 Leases.
B) AAS 21 Acquisitions of Assets and AAS 17 Leases.
C) AAS 28 Statement of Cash Flows and AAS 10 Revaluation of Non-current Assets.
D) AAS 10 Revaluation of Non-current Assets and AAS 4 Depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The discount rate that AAS 25 recommends for use is:
A) a current, market-determined, risk-adjusted discount rate appropriate to the plan.
B) the inflation-adjusted, current, risk-free government bond rate.
C) the rate of return earned by high quality corporate bonds.
D) the rate of interest charged by banks on loans with matching maturities to the accrued benefits.
A) a current, market-determined, risk-adjusted discount rate appropriate to the plan.
B) the inflation-adjusted, current, risk-free government bond rate.
C) the rate of return earned by high quality corporate bonds.
D) the rate of interest charged by banks on loans with matching maturities to the accrued benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The accounting treatment for the sale of non-current assets by a superannuation fund involves the following steps:
A) Update the asset's depreciation expense; calculate the gain or loss by comparing the proceeds from sale with the asset's carrying amount.
B) Update the asset's depreciation expense; perform impairment test; calculate the gain or loss by comparing the assets carrying amount with proceeds from sale.
C) Revalue the asset to its net market value immediately prior to sale and recognise changes as part of revenue; calculate the gain or loss by comparing the assets carrying amount with proceeds from sale.
D) Revalue the asset to its net market value immediately prior to sale and recognise changes as part of revenue; recognise sale of non-current assets.
A) Update the asset's depreciation expense; calculate the gain or loss by comparing the proceeds from sale with the asset's carrying amount.
B) Update the asset's depreciation expense; perform impairment test; calculate the gain or loss by comparing the assets carrying amount with proceeds from sale.
C) Revalue the asset to its net market value immediately prior to sale and recognise changes as part of revenue; calculate the gain or loss by comparing the assets carrying amount with proceeds from sale.
D) Revalue the asset to its net market value immediately prior to sale and recognise changes as part of revenue; recognise sale of non-current assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The following information relates to the Old Fogey's Superannuation Plan,which is a defined benefit scheme.Amounts given for all assets are at net market value. At balance date the scheme is owed from the current period. During the period shares in listed companies that had a net realisable value of $5 million at the beginning of the period were sold for $6.2 million.Shares were purchased during the period for $2 million. Actuarial reports on the fund are undertaken annually at balance date.The actuarial estimate of the accrued benefits were:
What is the total revenue for the plan for the period ended 30 June 2015?
A) $6 555 000
B) $2 709 000
C) $8 200 000
D) $1 685 000
What is the total revenue for the plan for the period ended 30 June 2015?
A) $6 555 000
B) $2 709 000
C) $8 200 000
D) $1 685 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The disclosure requirements for a defined contribution plan include:
A) a statement of cash flows and an operating statement.
B) a statement of net assets.
C) a statement of changes in net assets.
D) a statement of cash flows and an operating statement and a statement of net assets.
A) a statement of cash flows and an operating statement.
B) a statement of net assets.
C) a statement of changes in net assets.
D) a statement of cash flows and an operating statement and a statement of net assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The assets of a superannuation fund include:
A) contributions receivable from employer and employees.
B) cash and other monetary assets.
C) investments of the plan.
D) all of the given answers.
A) contributions receivable from employer and employees.
B) cash and other monetary assets.
C) investments of the plan.
D) all of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following combinations complies with the measurement rules of assets held by a superannuation fund?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
AAS 25 requires a defined benefit plan to append to its financial statements an actuarial report that contains the following information:
A) the effective date of the report.
B) the name and qualifications of the actuary.
C) the relationship of the market value of the net assets to meet accrued benefits of the plan at the date of valuation of the plan's assets.
D) all of the given answers.
A) the effective date of the report.
B) the name and qualifications of the actuary.
C) the relationship of the market value of the net assets to meet accrued benefits of the plan at the date of valuation of the plan's assets.
D) all of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Maestro Superannuation Plan provides the following information relating to the period ended 30 June 2014: The actuarial assumption used to calculate the liability was that the individual would take the benefit as a lump sum on retirement in 9 years' time.What is the present value of the expected future benefit payment (rounded to the nearest dollar)?
A) $153 894
B) $182 673
C) $141 423
D) $39 907
A) $153 894
B) $182 673
C) $141 423
D) $39 907

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The following information relates to the Retiree's Retreat Superannuation Plan,which is a defined benefit scheme.Amounts given for all assets are at net market value. At balance date the scheme is owed from the current period. During the period shares in listed companies that had a net realisable value of $5 million at the beginning of the period were sold for $6.2 million.Shares were purchased during the period for $2 million. Actuarial reports on the fund are undertaken annually at balance date.The actuarial estimate of the accrued benefits were:
What is the total expense for the period ended 30 June 2015 assuming that the plan's trustees have elected to prepare a statement of comprehensive income?
A) $8 269 000
B) $9 325 000
C) $8 364 000
D) $9 681 000
What is the total expense for the period ended 30 June 2015 assuming that the plan's trustees have elected to prepare a statement of comprehensive income?
A) $8 269 000
B) $9 325 000
C) $8 364 000
D) $9 681 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
For a defined contribution plan to satisfy the reporting requirements of AAS 25 it must provide:
A) a statement of financial position, an operating statement and accompanying notes.
B) a statement of financial position, an operating statement and a statement of cash flows.
C) a statement of net assets, a statement of changes in net assets and accompanying notes.
D) a statement of financial position, an operating statement and accompanying notes or a statement of net assets, a statement of changes in net assets and accompanying notes.
A) a statement of financial position, an operating statement and accompanying notes.
B) a statement of financial position, an operating statement and a statement of cash flows.
C) a statement of net assets, a statement of changes in net assets and accompanying notes.
D) a statement of financial position, an operating statement and accompanying notes or a statement of net assets, a statement of changes in net assets and accompanying notes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Do-it-Yourself Defined Contribution Plan owns the following assets with the following values: The fund sold its motor vehicles for $70 000.
What amount of revenue for changes in net market value of assets should Do-it-Yourself Defined Contribution Plan recognise for the year ended 30 June 2013?
A) $10 000
B) $20 000
C) $50 000
D) $80 000
What amount of revenue for changes in net market value of assets should Do-it-Yourself Defined Contribution Plan recognise for the year ended 30 June 2013?
A) $10 000
B) $20 000
C) $50 000
D) $80 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A defined benefit superannuation plan is required to provide additional disclosures in the actuarial report most recently prepared for the plan.These disclosures include:
A) the opinion of the actuary as to the financial condition of the plan at balance date.
B) the trustee's opinion of the qualification of the actuary.
C) the fees paid to the actuary.
D) the trustee's opinion of the qualification of the actuary and the fees paid to the actuary.
A) the opinion of the actuary as to the financial condition of the plan at balance date.
B) the trustee's opinion of the qualification of the actuary.
C) the fees paid to the actuary.
D) the trustee's opinion of the qualification of the actuary and the fees paid to the actuary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The required disclosures for a defined benefit plan include:
A) a statement of comprehensive income and a statement of financial position.
B) a note disclosure of the liability for accrued benefits and the date at which it was measured.
C) an operating statement.
D) a note disclosure of the liability for accrued benefits and the date at which it was measured and an operating statement.
A) a statement of comprehensive income and a statement of financial position.
B) a note disclosure of the liability for accrued benefits and the date at which it was measured.
C) an operating statement.
D) a note disclosure of the liability for accrued benefits and the date at which it was measured and an operating statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Revenues of superannuation plans include:
A) investment revenue.
B) contribution revenue.
C) gain on sale of non-current assets.
D) investment revenue and contribution revenue.
A) investment revenue.
B) contribution revenue.
C) gain on sale of non-current assets.
D) investment revenue and contribution revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Happy-go-lucky Superannuation Plan provides the following information relating to the period ended 30 June 2014: The actuarial assumption used to calculate the liability was that the individual would take the benefit as a lump sum on retirement in 6 years' time.What is the present value of the expected future benefit payment (rounded to the nearest dollar)?
A) $333 171
B) $298 134
C) $373 108
D) $121 613
A) $333 171
B) $298 134
C) $373 108
D) $121 613

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
A) AAS 25 requires that the obligations for accrued benefits of a defined benefit plan be discounted to their present value but there is no specific requirement to discount other liabilities.
B) AAS 25 requires all assets of superannuation plans to be measured at net market values.
C) AAS 25 requires changes in assets of superannuation plans to be recognised as revenue for the reporting period.
D) All of the give answers are correct.
A) AAS 25 requires that the obligations for accrued benefits of a defined benefit plan be discounted to their present value but there is no specific requirement to discount other liabilities.
B) AAS 25 requires all assets of superannuation plans to be measured at net market values.
C) AAS 25 requires changes in assets of superannuation plans to be recognised as revenue for the reporting period.
D) All of the give answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The following information relates to the Montigo Superannuation Plan,which is a defined benefit scheme.Amounts given for all assets are at net market value. At balance date the scheme is owed from the current period. During the period shares in listed companies that had a net realisable value of $7 million at the beginning of the period were sold for $8.5 million.Shares were purchased during the period for $3 million. The fund has not had an actuarial review undertaken as at balance date.What are the net assets available to pay benefits at 30 June 2015?
A) $22 290 000
B) $22 498 000
C) $22 453 000
D) $26 998 000
A) $22 290 000
B) $22 498 000
C) $22 453 000
D) $26 998 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following items is not reported as a liability in the financial reports of a defined contribution plan?
A) Income tax payable.
B) Accounts payable.
C) Accrued member benefits.
D) None of the given choices are correct.
A) Income tax payable.
B) Accounts payable.
C) Accrued member benefits.
D) None of the given choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is the key distinction between a defined benefit superannuation plan and a defined contribution superannuation plan?
A) A defined benefit plan accumulates funds through investments in real assets such as land and buildings whereas a defined contribution plan accumulates funds through investments in shares and other more liquid assets.
B) A defined benefit plan is run by professional trustees who seek the support of investment advisors and consultants. A defined contribution plan is normally run by trustees appointed by the employer and focuses on simple formulas for investment.
C) The assets of a defined benefit plan are the focus in determining the benefits that will be paid out to members, whereas for a defined contribution plan the benefits are measured through the liability to members.
D) A defined benefit plan's accrued benefits are determined by reference to the provisions of the superannuation plan trust deed's payment formulas. A defined contribution plan's accrued benefits are determined as the difference between the assets and other liabilities of the fund.
A) A defined benefit plan accumulates funds through investments in real assets such as land and buildings whereas a defined contribution plan accumulates funds through investments in shares and other more liquid assets.
B) A defined benefit plan is run by professional trustees who seek the support of investment advisors and consultants. A defined contribution plan is normally run by trustees appointed by the employer and focuses on simple formulas for investment.
C) The assets of a defined benefit plan are the focus in determining the benefits that will be paid out to members, whereas for a defined contribution plan the benefits are measured through the liability to members.
D) A defined benefit plan's accrued benefits are determined by reference to the provisions of the superannuation plan trust deed's payment formulas. A defined contribution plan's accrued benefits are determined as the difference between the assets and other liabilities of the fund.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Use of professional judgment to establish the net market values of assets is not permitted on which of the following matters?
A) market price of unquoted securities
B) discount factor to use for long-term monetary assets
C) market price of quoted securities
D) costs of expected disposal
A) market price of unquoted securities
B) discount factor to use for long-term monetary assets
C) market price of quoted securities
D) costs of expected disposal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following statements is not in accordance with AAS 25 Financial Reporting by Superannuation Plans?
A) Assets of a defined contribution plan and a defined benefit plan are measured at net market values as at the reporting date.
B) Obligations for accrued benefits of a defined benefit plan should be discounted to their present value, but there is no requirement to discount other liabilities at the reporting date.
C) For a defined contribution plan the change in net market values of the plan's financial liabilities since the beginning of the reporting period is included in the profit or loss for the reporting period.
D) For a defined benefit plan, the change in net market values of the plan's financial liabilities since the beginning of the reporting period, included equity for the reporting period.
A) Assets of a defined contribution plan and a defined benefit plan are measured at net market values as at the reporting date.
B) Obligations for accrued benefits of a defined benefit plan should be discounted to their present value, but there is no requirement to discount other liabilities at the reporting date.
C) For a defined contribution plan the change in net market values of the plan's financial liabilities since the beginning of the reporting period is included in the profit or loss for the reporting period.
D) For a defined benefit plan, the change in net market values of the plan's financial liabilities since the beginning of the reporting period, included equity for the reporting period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Discuss the options available for defined benefit superannuation plans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
AAS 25 requires that all the assets of superannuation plans be measured at:
A) net market value.
B) replacement cost .
C) historical cost.
D) net realisable value.
A) net market value.
B) replacement cost .
C) historical cost.
D) net realisable value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
AAS 25 requires a defined contribution plan to disclose which of the following items on the face of the operating statement or by way of note?
A) investment revenue and its individual components, including changes in net market values for each class of investment
B) amounts contributed by employers
C) amounts contributed by members
D) none of the given answers
A) investment revenue and its individual components, including changes in net market values for each class of investment
B) amounts contributed by employers
C) amounts contributed by members
D) none of the given answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Maestro Superannuation Plan provides the following information relating to the period ended 30 June 2014: The actuarial assumption used to calculate the liability was that the individual would take the benefit as a lump sum on retirement in 10 years' time.What is the present value of the expected future benefit payment (rounded to the nearest dollar)?
A) $245 565
B) $203 339
C) $185 277
D) $370 370
A) $245 565
B) $203 339
C) $185 277
D) $370 370

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Contrast the measurement rules that apply to assets of superannuation funds from assets held for backing general insurance liabilities.What effects would these have on the qualitative characteristics of financial reports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following items would not be classified as an asset in a defined benefit fund?
A) government securities
B) fixed interest securities
C) amounts contributed by members
D) fixtures and fitting
A) government securities
B) fixed interest securities
C) amounts contributed by members
D) fixtures and fitting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What is the accounting treatment for sale of non-current assets in a superannuation plan?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Maestro Superannuation Plan provides the following information relating to the period ended 30 June 2014: The actuarial assumption used to calculate the liability was that the individual would take the benefit as a lump sum on retirement in 8 years' time.What is the present value of the expected future benefit payment (rounded to the nearest dollar)?
A) $270 355
B) $232 142
C) $250 430
D) $349 056
A) $270 355
B) $232 142
C) $250 430
D) $349 056

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Discuss what is referred to as accrued benefits to members of a (a)defined benefit plan and (b)defined contribution plan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Discuss why the Australian Accounting Standards Board decided not to adopt IAS 26 Accounting and Reporting by Retirement Benefit Plans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Discuss the rationale for providing two presentation formats in preparing a financial report for defined benefit plans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Contrast the measurement of assets as required in AAS 25 for superannuation funds with that required in AASB 1023 for general insurers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What are the implications of not having the force of law in adopting the requirements of AAS 25 on financial reports?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following measurement rules is not in accordance with AAS 25 Financial Reporting by Superannuation Plans?
A) Assets of a defined contribution plan and a defined benefit plan are measured at net market values as at the reporting date.
B) Accrued benefits of a defined contribution plan shall be shown as an amount equivalent to the difference between the carrying amount of the assets and the sum of all other liabilities.
C) Obligations for accrued benefits of a defined benefit plan are discounted to the present value of expected future payments arising from membership date to reporting date.
D) Long-term liabilities of a defined benefit plan are discounted to their present value at reporting date.
A) Assets of a defined contribution plan and a defined benefit plan are measured at net market values as at the reporting date.
B) Accrued benefits of a defined contribution plan shall be shown as an amount equivalent to the difference between the carrying amount of the assets and the sum of all other liabilities.
C) Obligations for accrued benefits of a defined benefit plan are discounted to the present value of expected future payments arising from membership date to reporting date.
D) Long-term liabilities of a defined benefit plan are discounted to their present value at reporting date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The Commonwealth government guaranteed securities rate attaching to those securities is considered to be:
A) a market rate.
B) a risk-free rate.
C) a conservative rate.
D) a competitive rate.
A) a market rate.
B) a risk-free rate.
C) a conservative rate.
D) a competitive rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Discuss the disclosure requirements for defined benefit plans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



