Deck 10: An Overview of Accounting for Liabilities
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/78
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: An Overview of Accounting for Liabilities
1
A necessary condition to recognise a present obligation in the financial statements is that the identity of the party to whom the present obligation is owed must be known.
False
2
A discount on debentures issued arises when the market required rate of return is less than the coupon rate.
False
3
In accordance with AASB 137 Provisions,Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets,a contingent liability must be disclosed in the financial statement even when the likelihood of a present obligation occurring in future is remote.
False
4
In a constructive obligation where the entity retains discretion to avoid any future sacrifice of economic benefits,no liability should be recognised in the financial statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Under AASB 101 something may be classified as a current liability even when it is not expected to be settled for a period in excess of 12 months.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A guarantee provided to a financier for a loan taken out by another entity,where default on that loan is uncertain as at the reporting date,is an example of a contingent liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Entities are only required to record a liability if there has been a past transaction that has created a present obligation to another entity that is expected to result in an outflow of future economic benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The defining characteristic of a 'provision' as opposed to other liabilities is that the existence of an obligation is uncertain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The market will only pay a premium for debentures if the par value of those debentures is lower than the market interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Provisions are established to allow for future sacrifices such as repairs and maintenance of machinery and may be recognised as liabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In AASB 137 Provisions,Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets,there is symmetry in the treatment of contingent liabilities and contingent assets where both are required to be disclosed when the contingent event is probable to occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In terms of accounting treatment debentures and bonds are the same thing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Executory contracts are within the scope of AASB 137 Provisions,Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A provision shall be recognised when an entity may have a future obligation as a result of a past event.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A necessary condition for a provision to be recognised is that there is a legal obligation to make a future sacrifice of economic benefits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Convertible notes may be best described as having characteristics of both liabilities and bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An entity shall classify a liability as current when it holds the liability primarily for the purpose of trading.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In accordance with AASB 137 Provisions,Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets some present obligations are allowed to be disclosed in the notes to the financial statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When determining whether a liability exists,the intentions or actions of management need to be taken into account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Some researchers have found that firms can benefit from being in financial distress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
One recognised approach to reducing the level of debt that has been adopted in the past was to:
A) attempt to report the debt as equity, often in the form of preference shares.
B) create reserves and draw on them later as a source of funding.
C) treat as many liabilities as possible as provisions.
D) record liabilities as an increase in cash and a decrease in revenues.
A) attempt to report the debt as equity, often in the form of preference shares.
B) create reserves and draw on them later as a source of funding.
C) treat as many liabilities as possible as provisions.
D) record liabilities as an increase in cash and a decrease in revenues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Examples of contingent liabilities include:
A) future payments arising under employee entitlements for long service leave.
B) past tax deductions claimed that are under review by the Australian Taxation Office, but which the entity intends to dispute if disallowed.
C) out of court settlements in the case of liability for damage to health due to products manufactured by the entity.
D) past tax deductions claimed that are under review by the Australian Taxation Office, but which the entity intends to dispute if disallowed and out of court settlements in the case of liability for damage to health due to products manufactured by the entity
A) future payments arising under employee entitlements for long service leave.
B) past tax deductions claimed that are under review by the Australian Taxation Office, but which the entity intends to dispute if disallowed.
C) out of court settlements in the case of liability for damage to health due to products manufactured by the entity.
D) past tax deductions claimed that are under review by the Australian Taxation Office, but which the entity intends to dispute if disallowed and out of court settlements in the case of liability for damage to health due to products manufactured by the entity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Grindle Ltd has total assets of $1.5 million and liabilities of $0.9 million before it issues $300 000 in preference shares.What is the debt-to-asset ratio assuming that the preference shares have no voting rights and offer a fixed dividend rate of 10% and (a)are redeemable at the discretion of the issuer and (b)have a scheduled date for mandatory redemption?
A) (a) 60%; (b) 80%
B) (a) 50%; (b) 67%
C) (a) 80%; (b) 60%
D) (a) 67%; (b) 50%
A) (a) 60%; (b) 80%
B) (a) 50%; (b) 67%
C) (a) 80%; (b) 60%
D) (a) 67%; (b) 50%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Preference shares,as noted in AASB 132:
A) should be regarded as debt when redemption is at the option of the holder or on a specified date.
B) will be classified as debt or equity based on their legal form rather than the substance of the financial instrument.
C) exhibit the characteristics of equity when they are non-redeemable.
D) will have their classification as debt or equity affected by the intention to make distributions in the future.
A) should be regarded as debt when redemption is at the option of the holder or on a specified date.
B) will be classified as debt or equity based on their legal form rather than the substance of the financial instrument.
C) exhibit the characteristics of equity when they are non-redeemable.
D) will have their classification as debt or equity affected by the intention to make distributions in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following provisions satisfy the requirements to be recognised as a liability under AASB 137?
A) provisions for repairs and overhauls
B) provisions for warranties
C) provisions for maintenance
D) provisions for refurbishment costs
A) provisions for repairs and overhauls
B) provisions for warranties
C) provisions for maintenance
D) provisions for refurbishment costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
All things being equal,firms would typically prefer to disclose low levels of debt because:
A) Any debt is a bad thing in the capital structure of a business.
B) Additional debt may lead to a technical breach of a firm's contractual agreements with existing debt-holders and lead to the possible wind-up of the business or the need to renegotiate the contract.
C) The level of recognised debt will affect the profitability of the business.
D) Recognising debt in the income statement may lead to a decrease in management bonuses that are based on the times-interest-earned and debt-to-assets ratios.
A) Any debt is a bad thing in the capital structure of a business.
B) Additional debt may lead to a technical breach of a firm's contractual agreements with existing debt-holders and lead to the possible wind-up of the business or the need to renegotiate the contract.
C) The level of recognised debt will affect the profitability of the business.
D) Recognising debt in the income statement may lead to a decrease in management bonuses that are based on the times-interest-earned and debt-to-assets ratios.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Tissues and Co has elected to issue preference shares to the value of $220 000.Prior to the share issue the company has assets of $780 000,liabilities of $370 000 and equity recorded at $410 000.The terms of the share issue state that these shares are non-redeemable but a guaranteed cumulative dividend of 8% of share value is payable.Calculate the debt-to-asset ratio immediately before and after the share issue.
A) before-47.4%; after - 47.4%
B) before-47.4%; after - 37%
C) before-52.6%; after - 63%
D) before-47.4%; after - 59%
A) before-47.4%; after - 47.4%
B) before-47.4%; after - 37%
C) before-52.6%; after - 63%
D) before-47.4%; after - 59%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The interest that a debenture holder receives at the time of each payment made by the issuer is:
A) the coupon rate multiplied by the face value of the net debenture liability.
B) the market rate of interest multiplied by the present value of the opening balance of the net debenture liability.
C) the market rate of interest multiplied by the present value of the closing balance of the net debenture liability.
D) the coupon rate of interest multiplied by the present value of the opening balance of the net debenture liability.
A) the coupon rate multiplied by the face value of the net debenture liability.
B) the market rate of interest multiplied by the present value of the opening balance of the net debenture liability.
C) the market rate of interest multiplied by the present value of the closing balance of the net debenture liability.
D) the coupon rate of interest multiplied by the present value of the opening balance of the net debenture liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The present obligation component of a liability must be based on:
A) a legal obligation only.
B) a social obligation.
C) a contractual obligation.
D) none of the given answers.
A) a legal obligation only.
B) a social obligation.
C) a contractual obligation.
D) none of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The par or face value of a debenture is:
A) the amount that debenture holders will receive on maturity of the debenture.
B) the amount that a debenture holder would be prepared to pay for a debenture when the coupon rate is below the interest rate the debenture holder considers appropriate.
C) the amount debenture holders will receive annually until the debenture matures.
D) the amount that a debenture holder would be prepared to pay for a debenture when the coupon rate is above the interest rate the debenture holder considers appropriate.
A) the amount that debenture holders will receive on maturity of the debenture.
B) the amount that a debenture holder would be prepared to pay for a debenture when the coupon rate is below the interest rate the debenture holder considers appropriate.
C) the amount debenture holders will receive annually until the debenture matures.
D) the amount that a debenture holder would be prepared to pay for a debenture when the coupon rate is above the interest rate the debenture holder considers appropriate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Examples of equitable or constructive obligations include:
A) A state government promises economic support to householders and businesses affected by recent bushfires. It has in the past provided at least this level of support.
B) Management of a retail store decides to offer compensation to customers as a result of faulty scooters purchased from the store and causing injury. The manufacturers are normally considered liable for this type of fault.
C) A company that has published policies regarding support for the environment and has in the past rehabilitated polluted sites has identified contamination it has caused in land surrounding one of its production sites. Not correcting the problem with the site will lead to serious difficulties with the local community.
D) A state government promises economic support to householders and businesses affected by recent bushfires. A company that has published policies regarding support for the environment and has in the past rehabilitated polluted sites has identified contamination it has caused in land surrounding one of its production sites. Not correcting the problem with the site will lead to serious difficulties with the local community.
A) A state government promises economic support to householders and businesses affected by recent bushfires. It has in the past provided at least this level of support.
B) Management of a retail store decides to offer compensation to customers as a result of faulty scooters purchased from the store and causing injury. The manufacturers are normally considered liable for this type of fault.
C) A company that has published policies regarding support for the environment and has in the past rehabilitated polluted sites has identified contamination it has caused in land surrounding one of its production sites. Not correcting the problem with the site will lead to serious difficulties with the local community.
D) A state government promises economic support to householders and businesses affected by recent bushfires. A company that has published policies regarding support for the environment and has in the past rehabilitated polluted sites has identified contamination it has caused in land surrounding one of its production sites. Not correcting the problem with the site will lead to serious difficulties with the local community.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Some provisions traditionally recorded by entities may not be considered liabilities under the AASB Framework because:
A) their amounts are not considered probable.
B) they do not involve a future sacrifice of economic benefits.
C) the identity of the external party to whom the present obligation is owed is unknown.
D) there is no entity other than the reporting entity involved in the present obligation as a result of past transactions or other past events.
A) their amounts are not considered probable.
B) they do not involve a future sacrifice of economic benefits.
C) the identity of the external party to whom the present obligation is owed is unknown.
D) there is no entity other than the reporting entity involved in the present obligation as a result of past transactions or other past events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If future cash flows are not discounted the effect in the financial statements is to:
A) report amounts of cash outflows that are the same but occur over different time periods as the same amount.
B) report net cash flows at their future value rather than their present value.
C) understate the amount of the present obligation.
D) report net cash flows at their future value rather than their present value and understate the amount of the present obligation.
A) report amounts of cash outflows that are the same but occur over different time periods as the same amount.
B) report net cash flows at their future value rather than their present value.
C) understate the amount of the present obligation.
D) report net cash flows at their future value rather than their present value and understate the amount of the present obligation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Some research has shown that being in financial distress may not be all bad news for an entity because:
A) Investors will see this as an opportunity to buy into a company that can really only improve.
B) Existing managers will want to be released from their contracts allowing new ideas to be employed.
C) There will be no requirement to consider the social costs of retrenching employees because the accounting numbers show it is necessary.
D) It will provide the stimulus to rethink activities that may in turn lead to improved future performance.
A) Investors will see this as an opportunity to buy into a company that can really only improve.
B) Existing managers will want to be released from their contracts allowing new ideas to be employed.
C) There will be no requirement to consider the social costs of retrenching employees because the accounting numbers show it is necessary.
D) It will provide the stimulus to rethink activities that may in turn lead to improved future performance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An equitable or constructive obligation arises when:
A) Social or moral sanctions or custom leaves the entity no realistic alternative other than to make a sacrifice of future benefits.
B) Management makes a discretionary decision to make a future sacrifice of economic benefits.
C) Management communicates its decision to commit to the future sacrifice of economic benefits to the parties concerned.
D) Social or moral sanctions or custom leaves the entity no realistic alternative other than to make a sacrifice of future benefits and management communicates its decision to commit to the future sacrifice of economic benefits to the parties concerned.
A) Social or moral sanctions or custom leaves the entity no realistic alternative other than to make a sacrifice of future benefits.
B) Management makes a discretionary decision to make a future sacrifice of economic benefits.
C) Management communicates its decision to commit to the future sacrifice of economic benefits to the parties concerned.
D) Social or moral sanctions or custom leaves the entity no realistic alternative other than to make a sacrifice of future benefits and management communicates its decision to commit to the future sacrifice of economic benefits to the parties concerned.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the treatment of contingent liabilities in the financial statements?
A) Contingent liabilities are to be recognised as a separate category in the statement of financial position, with a clear note disclosure of the factors that constitute the contingent event for each material contingent liability.
B) Contingent liabilities are required to be disclosed in the notes to the financial statement when the amount of the obligation cannot be measured with sufficient reliability.
C) Material contingent liabilities only are required to be recognised in the financial statements under AASB 137.
D) Contingent liabilities are to be disclosed in the notes to the accounts in categories that reflect their nature and possible timing.
A) Contingent liabilities are to be recognised as a separate category in the statement of financial position, with a clear note disclosure of the factors that constitute the contingent event for each material contingent liability.
B) Contingent liabilities are required to be disclosed in the notes to the financial statement when the amount of the obligation cannot be measured with sufficient reliability.
C) Material contingent liabilities only are required to be recognised in the financial statements under AASB 137.
D) Contingent liabilities are to be disclosed in the notes to the accounts in categories that reflect their nature and possible timing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A debenture will be issued at par value:
A) because that is the offer price; if the rate offered is too low the offer will be under-subscribed, so those who take it up will receive more interest.
B) on most occasions, because management is careful to issue the debentures at an amount close to the market rate.
C) on those rare occasions when the coupon rate is the same as the market rate.
D) on those occasions when the offer rate is equal to the coupon rate.
A) because that is the offer price; if the rate offered is too low the offer will be under-subscribed, so those who take it up will receive more interest.
B) on most occasions, because management is careful to issue the debentures at an amount close to the market rate.
C) on those rare occasions when the coupon rate is the same as the market rate.
D) on those occasions when the offer rate is equal to the coupon rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Outside the situation where specific types of provisions are covered in standards,a provision exists when and only when:
A) The entity has a present legal, equitable or constructive obligation to make a future sacrifice of economic benefits to other entities as a result of past transactions or other past events; and the amount or timing of the future sacrifice of economic benefits that will be made to satisfy the present obligation is uncertain.
B) There is a legal or constructive obligation to make a future sacrifice of economic benefits within the entity as a result of past transactions or other past events, the amount or timing of which is uncertain.
C) The entity has a present legal obligation to make a future sacrifice of economic benefits to other entities as a result of past transactions or other past events; and the amount or timing of the future sacrifice of economic benefits that will be made to satisfy the present obligation is uncertain.
D) The amount, timing and entity to whom the obligation to sacrifice future economic benefits as a result of a past legal or constructive obligation are unknown.
A) The entity has a present legal, equitable or constructive obligation to make a future sacrifice of economic benefits to other entities as a result of past transactions or other past events; and the amount or timing of the future sacrifice of economic benefits that will be made to satisfy the present obligation is uncertain.
B) There is a legal or constructive obligation to make a future sacrifice of economic benefits within the entity as a result of past transactions or other past events, the amount or timing of which is uncertain.
C) The entity has a present legal obligation to make a future sacrifice of economic benefits to other entities as a result of past transactions or other past events; and the amount or timing of the future sacrifice of economic benefits that will be made to satisfy the present obligation is uncertain.
D) The amount, timing and entity to whom the obligation to sacrifice future economic benefits as a result of a past legal or constructive obligation are unknown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is not listed in AASB 101 to determine if a liability should be classified as current?
A) If the liability is guaranteed to be settled within 12 months.
B) If the liability is held primarily for the purpose of being traded.
C) If the entity does not have an unconditional right to defer settlement of the liability for at least 12 months.
D) If the liability is expected to be settled in the entity's normal operating cycle.
A) If the liability is guaranteed to be settled within 12 months.
B) If the liability is held primarily for the purpose of being traded.
C) If the entity does not have an unconditional right to defer settlement of the liability for at least 12 months.
D) If the liability is expected to be settled in the entity's normal operating cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If the entity is offering a higher interest rate on debentures than the market believes is appropriate,the market will:
A) be prepared to pay more than the par value of the debentures, offering a discount.
B) be prepared to pay less than the par value of the debentures, offering a discount.
C) be prepared to pay more than the par value of the debentures, offering a premium.
D) be prepared to pay less than the par value of the debentures, offering a premium.
A) be prepared to pay more than the par value of the debentures, offering a discount.
B) be prepared to pay less than the par value of the debentures, offering a discount.
C) be prepared to pay more than the par value of the debentures, offering a premium.
D) be prepared to pay less than the par value of the debentures, offering a premium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Dubbin Ltd issues $3 million in 5-year,8%,semi-annual coupon debentures.The rate of return required by the market is 6% per annum.What is the journal entry to record the issue of the debentures (rounded to the nearest dollar)?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When an entity's management resolves that the entity will offer to repair a defect it has recently discovered in one of its products,even though the nature of the defect is such that purchasers of the product would not expect the entity to do so:
A) it must immediately recognise a liability.
B) it must immediately recognise a liability, if it can be measured reliably.
C) it will never recognise a liability as the offer to repair was not part of the contract of sale.
D) it will only need to recognise a liability when the entity makes the offer public, or commits itself in some other way to make the repairs.
A) it must immediately recognise a liability.
B) it must immediately recognise a liability, if it can be measured reliably.
C) it will never recognise a liability as the offer to repair was not part of the contract of sale.
D) it will only need to recognise a liability when the entity makes the offer public, or commits itself in some other way to make the repairs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When debentures are issued at a discount:
A) the discount represents the cost of attracting the funds and should be recognised as an expense.
B) no further entries are required because the discount is calculated prior to receipt of the funds and therefore will not be recorded.
C) the effect interest method is used to calculate the amortised cost of the financial liability.
D) the discount amount can be used to offset any gains shown when debentures have been issued at a premium.
A) the discount represents the cost of attracting the funds and should be recognised as an expense.
B) no further entries are required because the discount is calculated prior to receipt of the funds and therefore will not be recorded.
C) the effect interest method is used to calculate the amortised cost of the financial liability.
D) the discount amount can be used to offset any gains shown when debentures have been issued at a premium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the appropriate treatment for convertible notes in accordance with AASB 132 Financial Instruments: Presentation?
A) as a financial liability
B) as equity
C) as part debt and part equity
D) as a financial liability and disclosure of conversion option
A) as a financial liability
B) as equity
C) as part debt and part equity
D) as a financial liability and disclosure of conversion option

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Banshee Ltd issues $12 million in 8-year,8%,semi-annual coupon debentures.The rate of return required by the market is 12%.What is the journal entry to record the first payment of interest assuming that Banshee uses the effective-interest method to amortise any discount or premium (round to the nearest dollar)?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Evaluate whether the following situations will give rise to a present obligation:
I: Bona Bay Ltd is a large manufacturer of surfboards and provides a two year warranty for all its products from the time of purchase by offering to repair or replace the item.
II: Sea Eagle Ltd operates its offshore oil rigs near Curlew Beach.During the reporting period,there was a major oil spill and the company had publicly announced to undertake clean-up of all the contamination that it caused.There is no environmental legislation on oil spills.
III: A customer sued Neck Bay Ltd for damages from a faulty product.The company hired a legal team to dispute this claim.
IV:
Whitehaven Ltd had guaranteed a bank loan to an associated company.
In compliance with AASB 137 Provisions,Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets,which of the above situations requires recognition in the financial statements?
A) I, II and III
B) I and II
C) II and III
D) III and IV
I: Bona Bay Ltd is a large manufacturer of surfboards and provides a two year warranty for all its products from the time of purchase by offering to repair or replace the item.
II: Sea Eagle Ltd operates its offshore oil rigs near Curlew Beach.During the reporting period,there was a major oil spill and the company had publicly announced to undertake clean-up of all the contamination that it caused.There is no environmental legislation on oil spills.
III: A customer sued Neck Bay Ltd for damages from a faulty product.The company hired a legal team to dispute this claim.
IV:
Whitehaven Ltd had guaranteed a bank loan to an associated company.
In compliance with AASB 137 Provisions,Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets,which of the above situations requires recognition in the financial statements?
A) I, II and III
B) I and II
C) II and III
D) III and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Where the change in the carrying amount of a liability is due to the impacts of using present values,the change shall be recognised as a(n):
A) gain on sale of liability.
B) revaluation reserve adjustment.
C) adjustment to opening retained earnings.
D) borrowing cost.
A) gain on sale of liability.
B) revaluation reserve adjustment.
C) adjustment to opening retained earnings.
D) borrowing cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Convertible notes are:
A) essentially the same as debentures and need to be recorded as liabilities.
B) a form of asset.
C) are often referred to as hybrid securities and should be recorded as equity as they will eventually be converted into shares.
D) part debt and part equity and should be disclosed as such according to AAB 132.
A) essentially the same as debentures and need to be recorded as liabilities.
B) a form of asset.
C) are often referred to as hybrid securities and should be recorded as equity as they will eventually be converted into shares.
D) part debt and part equity and should be disclosed as such according to AAB 132.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Melville Ltd received a material claim for damages from a customer for not delivering ordered goods on time.The customer insists that Melville Ltd's late delivery resulted in significant losses to the customer.Melville Ltd admits to the delay but disputes the material damages being claimed.What is the appropriate accounting treatment for the claim that is in accordance with AASB 137?
A) Ignore the claim.
B) Recognise the minimum amount of the liability.
C) Recognise the maximum amount of the liability.
D) Recognise the best estimate of the liability.
A) Ignore the claim.
B) Recognise the minimum amount of the liability.
C) Recognise the maximum amount of the liability.
D) Recognise the best estimate of the liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following statements is consistent with the positive accounting theory paradigm?
A) Managers avoid future sacrifice of economic benefits debt covenants when the company is close to violation of debt covenants.
B) Managers avoid constructive obligations in the presence of accounting based debt covenants even though there is no realistic alternative to making future sacrifice of economic benefits.
C) Managers choose accounting methods that will decrease income to reduce the probability of debt covenant violation.
D) Managers avoid income increasing accounting methods to reduce the probability of debt covenant violation.
A) Managers avoid future sacrifice of economic benefits debt covenants when the company is close to violation of debt covenants.
B) Managers avoid constructive obligations in the presence of accounting based debt covenants even though there is no realistic alternative to making future sacrifice of economic benefits.
C) Managers choose accounting methods that will decrease income to reduce the probability of debt covenant violation.
D) Managers avoid income increasing accounting methods to reduce the probability of debt covenant violation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Edgar Ltd issues $7 million in 6-year,10%,semi-annual coupon debentures.The rate of return required by the market is 8% per annum.What is the journal entry to record the first payment of interest assuming using the effective-interest method to amortise any discount or premium (rounded to the nearest dollar)?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In accordance with AASB 137 Provisions,Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets,which of the following statements is correct?
A) Contingent liabilities and provisions are required by AASB 137 to be disclosed in the financial statements.
B) Contingent assets where realisation of economic benefits is probable should be recognised in the financial statements.
C) Constructive obligations are recognised when entities have no realistic alternative to making future sacrifice of economic benefits.
D) Provisions for future necessary repairs and maintenance should be recognised in the financial statements.
A) Contingent liabilities and provisions are required by AASB 137 to be disclosed in the financial statements.
B) Contingent assets where realisation of economic benefits is probable should be recognised in the financial statements.
C) Constructive obligations are recognised when entities have no realistic alternative to making future sacrifice of economic benefits.
D) Provisions for future necessary repairs and maintenance should be recognised in the financial statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Spoton Co Ltd issues $5 million in 2-year,8%,semi-annual coupon debentures to the public.The market required rate of return is also 8%.The money is received on application and the debentures are allotted on the same day: 30 June 2013.What are the journal entries to record (a)the receipt of funds and allotment of debentures on 30 June 2013,(b)the payment of interest on 31 December 2013 and (c)the redemption of the debentures on 30 June 2015?
A)
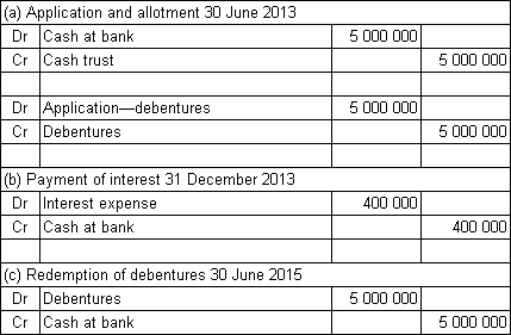
B)
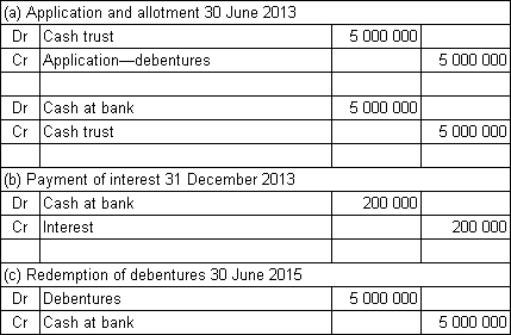
C)
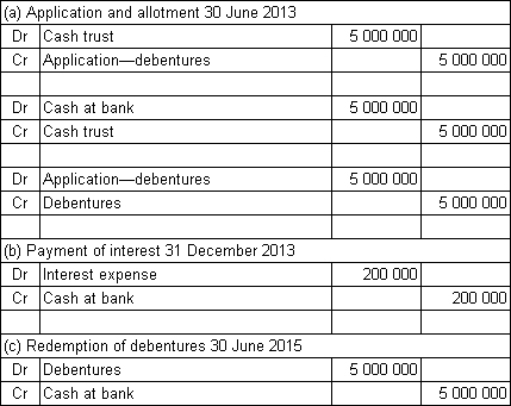
D)
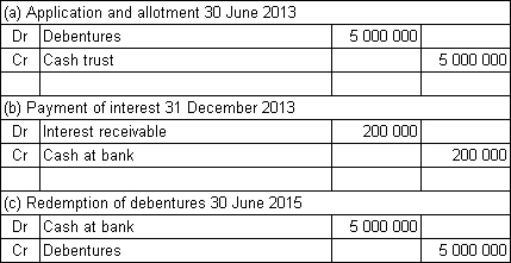
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In disclosing liabilities,a reporting entity:
A) discloses on the basis of the current/non-current liability dichotomy.
B) has a choice, based on the notions of relevance and reliability to disclose liabilities either on the basis of the current/non-current liability dichotomy or on the basis of order of liquidity.
C) has a choice, based on the principle of conservatism to disclose liabilities either on the basis of the current/non-current liability dichotomy or on the basis of order of liquidity.
D) discloses on the basis of order of liquidity.
A) discloses on the basis of the current/non-current liability dichotomy.
B) has a choice, based on the notions of relevance and reliability to disclose liabilities either on the basis of the current/non-current liability dichotomy or on the basis of order of liquidity.
C) has a choice, based on the principle of conservatism to disclose liabilities either on the basis of the current/non-current liability dichotomy or on the basis of order of liquidity.
D) discloses on the basis of order of liquidity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Pearl Ltd issues $8 million in 5-year debentures that pay interest every 6 months at a coupon rate of 12% per annum.The required market rate of return is 16% per annum.What is the issue price of the debentures (rounded to the nearest dollar)?
A) $6 926 387
B) $8 000 000
C) $9 177 614
D) $8 673 978
A) $6 926 387
B) $8 000 000
C) $9 177 614
D) $8 673 978

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When measuring a liability at present values,the discount rate to be used,according to paragraph 47 of AASB 137,is:
A) the pre-tax rate that reflects the current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the liability.
B) the after-tax rate that reflects the current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the liability.
C) the pre-tax rate that reflects the current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the liability, and shall also reflect risks for which future cash flows have already been adjusted.
D) the pre-tax risk free rate.
A) the pre-tax rate that reflects the current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the liability.
B) the after-tax rate that reflects the current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the liability.
C) the pre-tax rate that reflects the current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the liability, and shall also reflect risks for which future cash flows have already been adjusted.
D) the pre-tax risk free rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
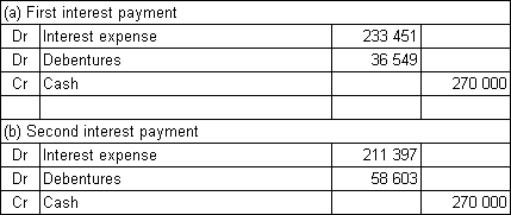
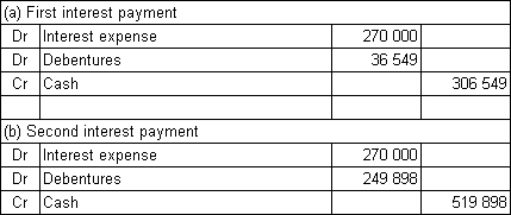
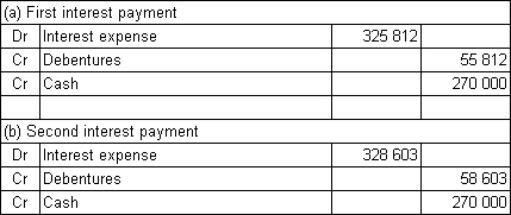
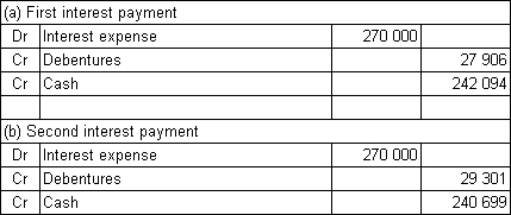
Buderup Ltd issues $9 million in 12-year,6%,semi-annual coupon debentures.The rate of return required by the market is 10% per annum.What are the journal entries to record the first and second payments of interest assuming that Buderup uses the effective-interest method to amortise any discount or premium (rounded to the nearest dollar)?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Risky Ltd issues $8 million in 5-year,6%,semi-annual coupon debentures in a private placement.The rate of return required by the debenture holder is 8%.What is the journal entry to record the issue of the debentures (round to the nearest dollar)?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A present obligation,as one of the criteria for recognising a liability,implies:
A) there must be a legal obligation.
B) a legally binding contractual arrangement between two parties: the entity and another party.
C) the involvement of two separate parties-the entity and another party-of which the identity of the latter needs not necessarily to be known.
D) the involvement of two separate parties-the entity and another party-of which the identity of the latter must be known.
A) there must be a legal obligation.
B) a legally binding contractual arrangement between two parties: the entity and another party.
C) the involvement of two separate parties-the entity and another party-of which the identity of the latter needs not necessarily to be known.
D) the involvement of two separate parties-the entity and another party-of which the identity of the latter must be known.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In accordance with AASB 137 Provisions,Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets,which of the following is considered a contingent liability?
A) Guarantee provided by the parent entity on behalf of a solvent subsidiary.
B) Settlement of a legal case where the company is likely to be held liable for damages in court.
C) Best estimate of likely claims for warranty by customers.
D) Guarantee of an associate's bank overdraft where the associate has declared bankruptcy.
A) Guarantee provided by the parent entity on behalf of a solvent subsidiary.
B) Settlement of a legal case where the company is likely to be held liable for damages in court.
C) Best estimate of likely claims for warranty by customers.
D) Guarantee of an associate's bank overdraft where the associate has declared bankruptcy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Explain,in the context of the latest AASB 137,why 'provisions' for items such as future repairs and maintenance are no longer permitted to be recognised.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Unless the probability of any outflow in a settlement is remote,an entity needs to disclose for each class of contingent liability:
A) the possibility of any reimbursement.
B) an indication of the timing and amount uncertainties.
C) an estimate of its financial effect.
D) All of the given answers must be disclosed.
A) the possibility of any reimbursement.
B) an indication of the timing and amount uncertainties.
C) an estimate of its financial effect.
D) All of the given answers must be disclosed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An essential characteristic of a liability is the existence of a present obligation.What does this mean?
Discuss the different types of obligations that may be considered 'present' obligations.
Discuss the different types of obligations that may be considered 'present' obligations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A compound instrument,such as a convertible note,comprises two components.They are:
A) a financial liability (contractual arrangement to deliver cash or another financial liability) and an equity instrument (a call option granting the holder the right, for a specified period of time, to convert it into a fixed number of ordinary shares of the entity).
B) a financial liability (contractual arrangement to deliver cash or another financial asset) and an equity instrument (a call option granting the holder the right, for a specified period of time, to convert it into a fixed number of ordinary shares of the entity).
C) a financial liability (contractual arrangement to deliver cash or another financial asset) and an equity instrument (a call option granting the holder the right, for a specified period of time, to convert it into a variable number of ordinary shares of the entity).
D) a financial liability (contractual arrangement to deliver cash or another financial asset) and an equity instrument (a put option granting the holder the right, for a specified period of time, to convert it into a fixed number of ordinary shares of the entity).
A) a financial liability (contractual arrangement to deliver cash or another financial liability) and an equity instrument (a call option granting the holder the right, for a specified period of time, to convert it into a fixed number of ordinary shares of the entity).
B) a financial liability (contractual arrangement to deliver cash or another financial asset) and an equity instrument (a call option granting the holder the right, for a specified period of time, to convert it into a fixed number of ordinary shares of the entity).
C) a financial liability (contractual arrangement to deliver cash or another financial asset) and an equity instrument (a call option granting the holder the right, for a specified period of time, to convert it into a variable number of ordinary shares of the entity).
D) a financial liability (contractual arrangement to deliver cash or another financial asset) and an equity instrument (a put option granting the holder the right, for a specified period of time, to convert it into a fixed number of ordinary shares of the entity).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The fact that a preference share is redeemable:
A) makes it a financial liability.
B) makes it an equity instrument.
C) makes it a compound financial instrument.
D) does not automatically mean that it is a financial liability. Conditions and rights attaching to the share need to be considered before it can be classified as either a financial liability or equity instrument.
A) makes it a financial liability.
B) makes it an equity instrument.
C) makes it a compound financial instrument.
D) does not automatically mean that it is a financial liability. Conditions and rights attaching to the share need to be considered before it can be classified as either a financial liability or equity instrument.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Discuss the criteria required to classify a liability as current.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In determining the amount to be assigned to the equity component of a compound financial instrument,you must:
A) add the face value of the financial liability to the fair value of the compound financial instrument as a whole.
B) deduct the face value of the financial liability from the fair value of the compound financial instrument as a whole.
C) deduct the face value of the financial liability from the face value of the compound financial instrument as a whole.
D) deduct the fair value of the financial liability from the fair value of the compound financial instrument as a whole.
A) add the face value of the financial liability to the fair value of the compound financial instrument as a whole.
B) deduct the face value of the financial liability from the fair value of the compound financial instrument as a whole.
C) deduct the face value of the financial liability from the face value of the compound financial instrument as a whole.
D) deduct the fair value of the financial liability from the fair value of the compound financial instrument as a whole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Adopting the effective-interest method means that the balance of the debenture liability represents:
A) the par value of the debenture.
B) the present value of the liability throughout the debenture term.
C) the adjustment to the debenture par value.
D) the borrowing cost.
A) the par value of the debenture.
B) the present value of the liability throughout the debenture term.
C) the adjustment to the debenture par value.
D) the borrowing cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
From the following extract of an amortisation schedule pertaining to a compound financial instrument,what is the net liability (assuming the debenture has not yet been repaid),at the end of Period 10?
A) Nil
B) 9 500 000
C) 9 905 582
D) 10 000 000
A) Nil
B) 9 500 000
C) 9 905 582
D) 10 000 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In accordance with AASB 137 Provisions,Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets,differentiate provisions from accruals and provide one example for each type of liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Discuss the substance-over-firm approach in AASB 132 Financial Instruments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Explain,in the context of Positive Accounting Theory,the implications of making professional judgments in respect to recognising and measuring liabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
From the following extract of an amortisation schedule pertaining to a compound financial instrument,what is the effective-interest rate embodied in the instrument?
A) 6%
B) 5%
C) Variable, as shown in the table it has increased from 5.5837% in Period 1 to 6.2738% in Period 3.
D) 4%.
A) 6%
B) 5%
C) Variable, as shown in the table it has increased from 5.5837% in Period 1 to 6.2738% in Period 3.
D) 4%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Explain in what situations,and why,some provisions should be measured at present values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If liabilities are disclosed as current on the basis of the entity's operating cycle,and this cycle is greater than 12 months it should:
A) adjust the statement of financial position for a 12 month period.
B) disclose the length of the operating cycle.
C) apply the 12-month test.
D) None of the given answers are correct.
A) adjust the statement of financial position for a 12 month period.
B) disclose the length of the operating cycle.
C) apply the 12-month test.
D) None of the given answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
AASB 13 defines fair value measurement as:
A) the price that would be received to buy an asset or received to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the due date.
B) the price that would be paid to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the due date.
C) the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date.
D) the price that would be estimated to sell an asset or to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date.
A) the price that would be received to buy an asset or received to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the due date.
B) the price that would be paid to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the due date.
C) the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date.
D) the price that would be estimated to sell an asset or to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Discuss the necessary conditions prescribed in AASB 137 Provisions,Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets to recognise provisions.Illustrate how these conditions are satisfied in a product warranty example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Explain,providing an example,the 'effective-interest method' used to amortise debenture discount and debenture premium accounts.What is the implication of using this method for the balance of the net liability throughout the debenture term?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



