Deck 20: Amino Acid Metabolism
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/34
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Amino Acid Metabolism
1
Glucogenic amino acids include all of the following,except:
A)Glycine
B)Alanine
C)Aspartic acid
D)Leucine
E)All of these amino acids are glucogenic.
A)Glycine
B)Alanine
C)Aspartic acid
D)Leucine
E)All of these amino acids are glucogenic.
Leucine
2
The carbon chains of amino acids enter the major metabolic pathways through all of these compounds,except:
A)a-ketoglutarate
B)Pyruvate
C)Glyceraldehyde
D)Acetyl CoA
E)All of these are entry points for amino acid catabolism.
A)a-ketoglutarate
B)Pyruvate
C)Glyceraldehyde
D)Acetyl CoA
E)All of these are entry points for amino acid catabolism.
Glyceraldehyde
3
The formation of amino acids from proteins
A)occurs during anabolism.
B)is endergonic.
C)occurs during digestion.
D)is a cellular process.
E)all of these
A)occurs during anabolism.
B)is endergonic.
C)occurs during digestion.
D)is a cellular process.
E)all of these
occurs during digestion.
4
The coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)in its active form has all the following characteristics except:
A)It is covalently bonded to its enzyme.
B)It possesses a phosphate group.
C)It bonds to an amine group by means of the phosphate group.
D)All of these characteristics are true.
E)All of these characteristics are false.
A)It is covalently bonded to its enzyme.
B)It possesses a phosphate group.
C)It bonds to an amine group by means of the phosphate group.
D)All of these characteristics are true.
E)All of these characteristics are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The carbon skeletons of specific amino acids cannot be used to replenish which of the following species associated with the citric acid cycle?
A)pyruvate
B)citrate
C)fumarate
D)succinyl CoA
E)all of these can be used
A)pyruvate
B)citrate
C)fumarate
D)succinyl CoA
E)all of these can be used

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The following shows a part of the biosynthetic pathway of amino acids.If possible,draw an arrow to match the amino acid with its precursor.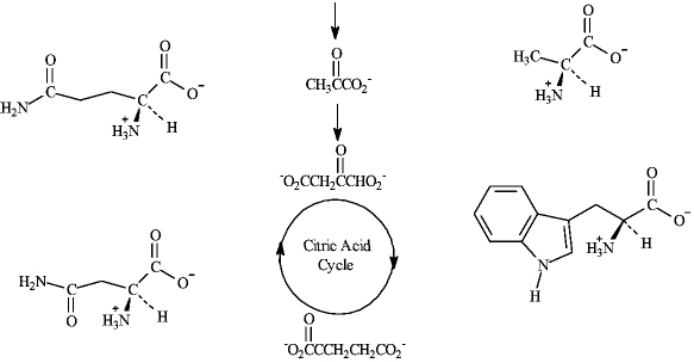


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
3-Phosphoglycerate contains the carbon skeleton used to make
A)serine
B)cysteine
C)glycine
D)all of these
A)serine
B)cysteine
C)glycine
D)all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Consider the deamination of serine to answer the following questions.
a) Draw the structure of the a-keto acid produced by the deamination of serine.
b) What is the fate of the amino group in serine when this conversion occurs in a mammalian system?
a) Draw the structure of the a-keto acid produced by the deamination of serine.
b) What is the fate of the amino group in serine when this conversion occurs in a mammalian system?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
By means of a semialdehyde intermediate,glutamate is involved in the synthesis of which of the following amino acids?
A)Arginine
B)Glutamine
C)Lysine
D)Proline
E)Both a and d.
A)Arginine
B)Glutamine
C)Lysine
D)Proline
E)Both a and d.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A coenzyme frequently encountered in transamination reactions is
A)tetrahydrofolate
B)pyridoxal phosphate
C)thiamine pyrophosphate
D)biotin
A)tetrahydrofolate
B)pyridoxal phosphate
C)thiamine pyrophosphate
D)biotin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The two nitrogens in urea arise directly from:
A)Ammonia and aspartic acid
B)Carbamoyl phosphate and glutamic acid
C)Ammonia and glutamic acid
D)Carbamoyl phosphate and glutamine
A)Ammonia and aspartic acid
B)Carbamoyl phosphate and glutamic acid
C)Ammonia and glutamic acid
D)Carbamoyl phosphate and glutamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Draw the structure of the product formed when the substance shown below undergoes amide formation.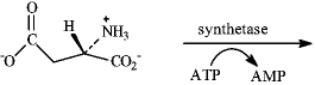
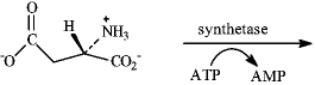

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
This many ATP equivalents are required to produce one molecule of urea from ammonia:
A)One ATP equivalent.
B)Two ATP equivalents.
C)Three ATP equivalents.
D)Four ATP equivalents.
E)Six ATP equivalents.
A)One ATP equivalent.
B)Two ATP equivalents.
C)Three ATP equivalents.
D)Four ATP equivalents.
E)Six ATP equivalents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Many biological reactions are endergonic.Explain how it is possible that these reactions occur spontaneously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What product would be obtained from enzymatic transamination of 3-hydroxy-2-ketopropanoic acid?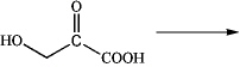


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
By a simple transamination reaction,intermediates in the Citric Acid Cycle can be converted in one step to all of these amino acids,except:
A)Alanine
B)Aspartic acid
C)Glutamic acid
D)Cysteine
E)All of these amino acids are only one step away from the major metabolic pathways.
A)Alanine
B)Aspartic acid
C)Glutamic acid
D)Cysteine
E)All of these amino acids are only one step away from the major metabolic pathways.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Consider the reaction below to answer the following questions.
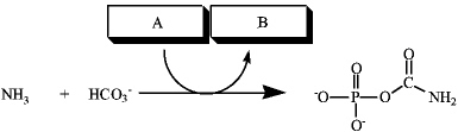
a) Which group of small molecules best fit the boxes associated with the reaction?

b) This reaction is part of:
a. the citric acid cycle.
b. the urea cycle.
c. a biosynthetic pathway of amino acids
d.the catabolism of amino acid carbon
chains.

a) Which group of small molecules best fit the boxes associated with the reaction?

b) This reaction is part of:
a. the citric acid cycle.
b. the urea cycle.
c. a biosynthetic pathway of amino acids
d.the catabolism of amino acid carbon
chains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is not an intermediate in the urea cycle?
A)arginine
B)citrulline
C)ornithine
D)lysine
A)arginine
B)citrulline
C)ornithine
D)lysine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Suppose that the formation of a dipeptide is endergonic by +14.7 kJ/mol.If this reaction is coupled with the hydrolysis of ATP,will the net reaction be spontaneous or nonspontaneous? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The key functional group in the PLP-dependent transamination of an a-amino acid is an activated
A)amine
B)imine
C)amide
D)enamine
A)amine
B)imine
C)amide
D)enamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What amino acid is the following a-keto acid derived from?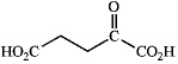 glutamic acid
glutamic acid
 glutamic acid
glutamic acid 
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Ornithine serves three metabolically important roles but is not found in proteins.Which of the following statements about ornithine is not true?
A)It is a precursor in the synthesis of citrulline.
B)It is an intermediate in the urea cycle.
C)It is a precursor in the synthesis of arginine.
D)It is biosynthesized from glutamine.
E)It is a product of arginine hydrolysis.
A)It is a precursor in the synthesis of citrulline.
B)It is an intermediate in the urea cycle.
C)It is a precursor in the synthesis of arginine.
D)It is biosynthesized from glutamine.
E)It is a product of arginine hydrolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The appropriate sequence in the biosynthesis of proline from glutamate is: 
A)4,2,1,3
B)4,1,2,3
C)1,4,3,2
D)1,4,2,3
E)2,3,1,4

A)4,2,1,3
B)4,1,2,3
C)1,4,3,2
D)1,4,2,3
E)2,3,1,4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Aspartate is formed from transamination of:
A)asparagine
B)aspartame
C)oxaloacetate
D)citrate
E)a-ketoglutarate
A)asparagine
B)aspartame
C)oxaloacetate
D)citrate
E)a-ketoglutarate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Write a mechanism for the formation of a-iminoglutarate from glutamate employing NAD+ as the oxidizing coenzyme.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the process of amino acid biosynthesis,how are glutamic acid,glutamine,proline,and arginine all related?
A)They are all derived from a-ketoglutarate.
B)They are all derivatives of acetyl CoA.
C)They are all derivatives of pyruvate.
D)They are all derived from aspartate.
E)They are all derivatives of 3-phosphoglycerate.
A)They are all derived from a-ketoglutarate.
B)They are all derivatives of acetyl CoA.
C)They are all derivatives of pyruvate.
D)They are all derived from aspartate.
E)They are all derivatives of 3-phosphoglycerate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Amino acids biosynthesized from aspartate include all except:
A)asparagine
B)threonine
C)methionine
D)lysine
E)glutamate
A)asparagine
B)threonine
C)methionine
D)lysine
E)glutamate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The reaction,2 NH4+ + a-ketoglutarate + NADPH + ATP ® glutamine + NADP+ + ADP + Pi + H2O,is the combined result of what two enzymes?
A)nitrogenase and glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH)
B)GDH and glutamine synthetase (GS)
C)GS and nitrogenase
D)GDH and nitrogenase
E)all of these are correct
A)nitrogenase and glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH)
B)GDH and glutamine synthetase (GS)
C)GS and nitrogenase
D)GDH and nitrogenase
E)all of these are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The term ketogenic amino acids refers to amino acids
A)that are precursors for glucose synthesis.
B)that are degraded to yield acetyl CoA or acetoacetate
C)that can not be converted to fatty acids or ketone bodies.
D)that are degraded to yield succinyl-CoA,pyruvate,a-ketoglutarate,fumarate and oxaloacetate.
E)None of these.
A)that are precursors for glucose synthesis.
B)that are degraded to yield acetyl CoA or acetoacetate
C)that can not be converted to fatty acids or ketone bodies.
D)that are degraded to yield succinyl-CoA,pyruvate,a-ketoglutarate,fumarate and oxaloacetate.
E)None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
All of the following are true of transamination except:
A)It is characterized by the transfer of an a-amino group from an amino acid to the a-keto position of an a-keto acid.
B)The amino donor becomes an a-keto acid.
C)The coenzyme needed is thiamine diphosphate.
D)The a-keto acid acceptor becomes an a-amino acid.
A)It is characterized by the transfer of an a-amino group from an amino acid to the a-keto position of an a-keto acid.
B)The amino donor becomes an a-keto acid.
C)The coenzyme needed is thiamine diphosphate.
D)The a-keto acid acceptor becomes an a-amino acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
All of the following are metabolic intermediates of a-amino acid carbon skeletons except:
A)pyridoxine
B)a-ketoglutarate
C)oxaloacetate
D)succinyl-CoA
E)fumarate
A)pyridoxine
B)a-ketoglutarate
C)oxaloacetate
D)succinyl-CoA
E)fumarate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Write a mechanism for the nonenzymatic transformation of glutamate semialdehyde into 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate.Which amino acid is synthesized from 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate in vivo? 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Transamination of pyruvate with glutamate as the nitrogen donor gives:
A)alanine
B)serine
C)cysteine
D)aspartate
E)tyrosine
A)alanine
B)serine
C)cysteine
D)aspartate
E)tyrosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What reaction does glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH)catalyze?
A)The oxidative deamination of glutamate to yield a-ketoglutarate.
B)Phosphorylation of carbamate to yield carbamoyl phosphate.
C)The amidation of the g carboxyl group of glutamate to form glutamine.
D)The deadenylation of glutamine synthetase (GS).
E)The adenylation of glutamine synthetase.
A)The oxidative deamination of glutamate to yield a-ketoglutarate.
B)Phosphorylation of carbamate to yield carbamoyl phosphate.
C)The amidation of the g carboxyl group of glutamate to form glutamine.
D)The deadenylation of glutamine synthetase (GS).
E)The adenylation of glutamine synthetase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



