Deck 34: Taxes and Investment Planning
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/84
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 34: Taxes and Investment Planning
1
The Roth IRA is an example of the Pension Model.
False
Explanation:After-tax dollars are invested in the Roth and qualified distributions are excluded from tax so a Roth IRA is an example of the Exempt Model.
Explanation:After-tax dollars are invested in the Roth and qualified distributions are excluded from tax so a Roth IRA is an example of the Exempt Model.
2
The Deferred Model offers two levels of tax deferral-the original contribution escapes current taxation as do the earnings on the underlying investment.
False
Explanation:This describes the Pension Model.In the Deferred Model,only taxes on investment earnings are deferred.
Explanation:This describes the Pension Model.In the Deferred Model,only taxes on investment earnings are deferred.
3
One characteristic of the Exempt Model is the fact that,like the Current and Deferred Models,only after-tax dollars are invested.
True
Explanation:After-tax dollars are invested under the Current,Deferred and Exempt Models.
Explanation:After-tax dollars are invested under the Current,Deferred and Exempt Models.
4
In the Deferred Model,investment earnings are taxed at the end of the investment period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the Current Model,investment earnings are taxed as they are earned.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
One of the characteristics of the Exempt Model is that earnings on the investment are exempt from explicit taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Savings accounts and money market funds are examples of investments taxed under the Current Model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An investment in a growth stock which does not pay dividends is an example of the Exempt Model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A single taxpayer earns a salary of $6,000.If he is taxed with a 10% flat rate,he has $5,400 of after-tax dollars available to invest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The nondeductible traditional IRA is a classic example of the Pension Model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the Exempt Model,the earnings are excluded from explicit taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Under the Pension Model,the entire accumulation,not just the earnings,is taxed at the end of the investment horizon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
One characteristic of the Pension Model is the fact that,like the Current and Deferred Models,only after-tax dollars are invested.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A taxpayer in the 25% marginal tax bracket invests $1,000 of after-tax dollars at 10% interest before taxes.At the end of year one,the taxpayer will have accumulated after-tax dollars of $1,075.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the Deferred Model,only after-tax dollars are invested.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Examples of the Exempt Model include deductible IRAs,H.R.10 (Keogh)plans,Sec.401(k)plans,and tax deferred annuities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Investments conforming to the Current Model provide no deferral advantages because earnings are taxed currently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Employer-sponsored qualified retirement plans and deductible IRAs fit the Pension Model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the Pension Model,the initial investment is deductible or excludible from gross income,and investment earnings are taxed currently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The Deferred Model investment outperforms the Current Model investment if interest rates and tax rates are constant over time because the interest on the Deferred Model investment grows tax free until withdrawal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Heidi invests $1,000 in a taxable bond for 5 years that earns 4% interest per year.Her marginal tax rate is 15%.What is her after-tax accumulated investment at the end of year 5 (assume that bond interest is reinvested at the same rate)?
A)$1,182
B)$1,143
C)$1,020
D)$1,762
A)$1,182
B)$1,143
C)$1,020
D)$1,762

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the Current Model
A)investment earnings are taxed currently.
B)the initial investment is deductible or excludible from gross income,and the investment earnings are taxed at the end of the investment period.
C)investment earnings are exempt from explicit taxation.
D)investment earnings are taxed at the end of the investment period.
A)investment earnings are taxed currently.
B)the initial investment is deductible or excludible from gross income,and the investment earnings are taxed at the end of the investment period.
C)investment earnings are exempt from explicit taxation.
D)investment earnings are taxed at the end of the investment period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the Exempt Model
A)investment earnings are taxed currently.
B)investment earnings are exempt from explicit taxation.
C)investment earnings are taxed at the end of the investment period.
D)the initial investment is deductible or excludible from gross income,and the investment earnings are taxed at the end of the investment period.
A)investment earnings are taxed currently.
B)investment earnings are exempt from explicit taxation.
C)investment earnings are taxed at the end of the investment period.
D)the initial investment is deductible or excludible from gross income,and the investment earnings are taxed at the end of the investment period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the Deferred Model
A)investment earnings are taxed currently.
B)investment earnings are exempt from explicit taxation.
C)investment earnings are taxed at the end of the investment period.
D)the initial investment is deductible or excludible from gross income,and the investment earnings are taxed at the end of the investment period.
A)investment earnings are taxed currently.
B)investment earnings are exempt from explicit taxation.
C)investment earnings are taxed at the end of the investment period.
D)the initial investment is deductible or excludible from gross income,and the investment earnings are taxed at the end of the investment period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Jan can invest $4,000 of after-tax dollars (AT$)directly in a taxable bond outside an IRA,or she can contribute the $4,000 to a nondeductible IRA and invest in the same bond through the IRA vehicle.In either case the bond yields an annual 4% before-tax rate of return (BTROR).Jan's marginal tax rate is 15%,and she expects it to remain so for the entire investment horizon of 25 years.What is her annualized after-tax rate of return (annualized ATROR)for the "bond inside the IRA"?
A)3)6%
B)4)5%
C)4%
D)None of the above.
A)3)6%
B)4)5%
C)4%
D)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Kate can invest $4,000 of after-tax dollars (AT$)directly in a taxable bond outside an IRA,or she can contribute the $4,000 to a nondeductible IRA and invest in the same bond through the IRA vehicle.In either case the bond yields an annual 3% before-tax rate of return (BTROR).Kate's marginal tax rate is 15%,and she expects it to remain so for the entire investment horizon of 25 years.What is the after-tax accumulation for the "bond outside the IRA" after 25 years (assume that bond interest is reinvested at the same rate)?
A)$5,585
B)$7,507
C)$8,375
D)None of the above.
A)$5,585
B)$7,507
C)$8,375
D)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Miles invests $20,000 in a taxable bond for 5 years that earns 5% interest per year.His marginal tax rate is 15%.What is his after-tax accumulated investment at the end of year 1?
A)$20,850
B)$21,000
C)$21,700
D)$22,000
A)$20,850
B)$21,000
C)$21,700
D)$22,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The general form of the annualized after-tax rate of return (annualized ATROR)for the Deferred Model can be expressed as
A)rann = [(1 + R)n(1 - tn)+ tn]1/n - 1.
B)rann = [(1 - R)n(1 - t)+ t]1/n - 1.
C)rann = [(1 + R)n(1 + t)+ t]1/n - 1.
D)rann = [(1 + R)n(1 + t)- t]1/n - 1.
A)rann = [(1 + R)n(1 - tn)+ tn]1/n - 1.
B)rann = [(1 - R)n(1 - t)+ t]1/n - 1.
C)rann = [(1 + R)n(1 + t)+ t]1/n - 1.
D)rann = [(1 + R)n(1 + t)- t]1/n - 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Nolan earns a salary of $80,000 and has a flat tax rate of 28%.The amount of after-tax dollars he has to invest is
A)$22,400.
B)$57,600.
C)$56,000.
D)$80,000.
A)$22,400.
B)$57,600.
C)$56,000.
D)$80,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The Deferred Model has all of the following characteristics except for
A)only after-tax dollars are invested.
B)the earnings on the investment are not taxed annually.
C)the accumulated earnings are taxed at the end of the investment horizon.
D)the Deferred Model will not outperform the Current Model given equal BTRORs and constant tax rates.
A)only after-tax dollars are invested.
B)the earnings on the investment are not taxed annually.
C)the accumulated earnings are taxed at the end of the investment horizon.
D)the Deferred Model will not outperform the Current Model given equal BTRORs and constant tax rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
At the beginning of year 1,Sandeep invests $10,000 in a money market fund that pays a 3% annual return before taxes.Sandeep's marginal tax rate is 25%,and he allows the after-tax earnings to remain in the money market fund.That is,he withdraws only enough cash to pay the taxes on the earnings.What is his after-tax accumulation at the end of year 2?
A)$10,455
B)$10,609
C)$10,690
D)None of the above
A)$10,455
B)$10,609
C)$10,690
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When given a choice between making a contribution to a Roth IRA or to a nondeductible traditional IRA,the taxpayer should choose the Roth IRA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If "R" equals the before-tax rate of return and "t" equals the investor's marginal tax rate,then the after-tax rate of return represented by "r" can be expressed as
A)r = R(1 - t).
B)r = R(1 + t).
C)r = (1 + t)R.
D)r = R - t.
A)r = R(1 - t).
B)r = R(1 + t).
C)r = (1 + t)R.
D)r = R - t.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The investment models discussed in the text include all of the following except for
A)the Deferred Model.
B)the Pension Model.
C)the Exempt Model.
D)the Non-Current Model.
A)the Deferred Model.
B)the Pension Model.
C)the Exempt Model.
D)the Non-Current Model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Charlene can invest $4,000 of after-tax dollars (AT$)directly in a taxable bond outside an IRA,or she can contribute the $4,000 to a nondeductible IRA and invest in the same bond through the IRA vehicle.In either case the bond yields an annual 7% before-tax rate of return (BTROR).Charlene's marginal tax rate is 20%,and she expects it to remain so for the entire investment horizon of 25 years.What is her annualized after-tax rate of return (annualized ATROR)for the "bond outside the IRA"?
A)5)6%
B)6%
C)6)5%
D)7%
A)5)6%
B)6%
C)6)5%
D)7%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Rich,an individual investor,lives in a land of no taxation and receive a $10,000 bonus.He invests this amount in a bond that pays interest of 4% per year and holds the bond for 5 years,reinvesting the interest annually at the same 4% return.At the end of 5 years the $10,000 original investment accumulates to
A)$10,400.
B)$12,625.
C)$12,763.
D)$12,167.
A)$10,400.
B)$12,625.
C)$12,763.
D)$12,167.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Vidya can invest $5,000 of after-tax dollars (AT$)directly in a taxable bond outside an IRA,or he can contribute the $5,000 to a nondeductible IRA and invest in the same bond through the IRA vehicle.In either case the bond yields an annual 5% before-tax rate of return (BTROR).Vidya's marginal tax rate is 15%,and he expects it to remain so for the entire investment horizon of 20 years.What is the after-tax accumulation for the "bond inside the IRA" after 20 years?
A)$12,027
B)$11,277
C)$10,062
D)None of the above.
A)$12,027
B)$11,277
C)$10,062
D)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The Current Model provides the future value of an investment having which of the following characteristics?
A)only after-tax dollars are invested
B)only before-tax dollars are invested
C)the earnings on the investment are taxed at the end of the investment period
D)investment earnings are exempt from taxation
A)only after-tax dollars are invested
B)only before-tax dollars are invested
C)the earnings on the investment are taxed at the end of the investment period
D)investment earnings are exempt from taxation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is a classic example of the Deferred Model?
A)a deductible traditional IRA
B)a 401(k)plan
C)a H.R.10 (Keogh)plan
D)a nondeductible traditional IRA
A)a deductible traditional IRA
B)a 401(k)plan
C)a H.R.10 (Keogh)plan
D)a nondeductible traditional IRA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In the Pension Model
A)investment earnings are taxed currently.
B)investment earnings are exempt from explicit taxation.
C)investment earnings are taxed at the end of the investment period.
D)the initial investment is deductible or excludible from gross income,and the investment earnings are taxed at the end of the investment period.
A)investment earnings are taxed currently.
B)investment earnings are exempt from explicit taxation.
C)investment earnings are taxed at the end of the investment period.
D)the initial investment is deductible or excludible from gross income,and the investment earnings are taxed at the end of the investment period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Rachel invests $5,000 in a money market account which earns a 5% before-tax return.Rachel has a 20% marginal tax rate.Rachel makes the one-time investment and leaves the funds in the account for 10 years.She allows all after-tax earnings to remain in the account.What is her after-tax accumulation after 10 years?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Melanie is in the 39.6% tax bracket and is ineligible to make deductible or Roth IRA contributions.Nevertheless,she wishes to contribute $5,500 to a traditional nondeductible IRA.How much taxable salary must she earn to have $5,500 left for the contribution?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What are the characteristics of the Pension Model?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Common examples of the Pension Model include all of the following except for
A)H)R.10 (Keogh)plans.
B)401(k)plans.
C)nondeductible traditional IRAs.
D)tax deferred annuities or 403(b)plans.
A)H)R.10 (Keogh)plans.
B)401(k)plans.
C)nondeductible traditional IRAs.
D)tax deferred annuities or 403(b)plans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Cooper can invest $10,000 after-tax dollars in a taxable bond either outside or inside a traditional nondeductible IRA.He will hold the investment for ten years.The bond yields 6% before taxes and Cooper's marginal tax rate is 33%.If he invests directly in the bond,he will withdraw an amount of interest each year sufficient to pay taxes and leave the remaining interest in the investment.What are the after-tax accumulations in the bond and in the IRA? Cooper will not be subject to the 10% penalty tax when the IRA withdrawal occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Earl invests $7,000 in a tax-exempt bond yielding 4% which matures in 15 years.What is Earl's after-tax accumulation at maturity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Elise contributes $1,000 to a deductible IRA.Her investment will earn 10% annually before taxes,and she will withdraw the accumulated amounts from the IRA after 20 years.She expects her tax rate to be 25% at that time and will not be subject to the 10% on early distributions.What is Elise's after-tax accumulation in the IRA?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Compare the characteristics of the Current and Deferred Models.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The formula for the after-tax accumulation (ATA)for the Exempt Model is
A)ATA = AT$ (1 - t)n.
B)ATA = AT$ (1 + t)n.
C)ATA = AT$ (1 + R)n.
D)ATA = AT$ (1 - R)n.
A)ATA = AT$ (1 - t)n.
B)ATA = AT$ (1 + t)n.
C)ATA = AT$ (1 + R)n.
D)ATA = AT$ (1 - R)n.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following characteristics belong(s)to the Exempt Model?
A)Only after-tax dollars are invested.
B)Only tax-free dollars are invested.
C)Earnings on the investment are exempt from explicit taxation.
D)both A and C
A)Only after-tax dollars are invested.
B)Only tax-free dollars are invested.
C)Earnings on the investment are exempt from explicit taxation.
D)both A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The Pension Model has all of the following characteristics except for
A)before-tax dollars are invested.
B)the annual earnings on the investment grow at the before-tax rate of return.
C)only the accumulated earnings are taxed at the end of the investment horizon when the investor cashes out of the investment.
D)the entire accumulation is taxed at the end of the investment horizon when the investor cashes out of the investment.
A)before-tax dollars are invested.
B)the annual earnings on the investment grow at the before-tax rate of return.
C)only the accumulated earnings are taxed at the end of the investment horizon when the investor cashes out of the investment.
D)the entire accumulation is taxed at the end of the investment horizon when the investor cashes out of the investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Taxpayers often have to decide between contributing to a traditional nondeductible IRA or a Roth IRA.In making the comparison between the two IRAs,which models should the taxpayer use?
A)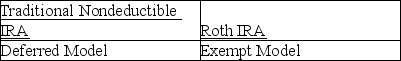
B)
C)
D)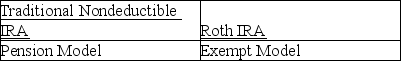
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Brianna purchases stock for $8,000.The stock appreciates (grows)at a 6% rate before taxes.Brianna sells the stock ten years later for $14,327.Brianna has a 39.6% marginal tax rate,but the stock sale is a LTCG taxed at 20%.Ignore the 3.8% Medicare surtax on net investment income.What are Brianna's after-tax proceeds?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Will invests $20,000 of after-tax dollars (AT$)in tax-exempt municipal bonds which yield 5% per year.He reinvests the interest in the same bonds and holds the bonds for two years.Will's marginal tax rate is 25%.What is his after-tax accumulation at the end of two years?
A)$21,000
B)$21,528
C)$22,000
D)$22,050
A)$21,000
B)$21,528
C)$22,000
D)$22,050

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Sylvia makes a one-time $2,000 deductible contribution into a deductible traditional IRA account,which will earn 8% annually before taxes.Twenty-five years later,at age 65,she withdraws all of the accumulation from the IRA when she is in the 15% marginal tax bracket.What is the total of her after-tax accumulated proceeds from the IRA?
A)$6,000
B)$8,541
C)$11,642
D)$13,697
A)$6,000
B)$8,541
C)$11,642
D)$13,697

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Jorge contributes $5,000 to a traditional nondeductible IRA in the current year and makes no subsequent contributions.Assume that the investment in the IRA yields 6% per year and that Jorge allows his investment to accumulate for 20 years.At the end of twenty years,he withdraws all of the amounts from the IRA when his marginal tax rate is 30%.What is his after-tax accumulation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If t0 is the tax rate in Year 0,tn is the tax rate in Year n,and ATA is after-tax accumulation,then which one of the following does not hold true?
A)if t0 = tn,ATA per Exempt Model = ATA per Pension Model
B)if t0 > tn,ATA per Exempt Model < ATA per Pension Model
C)if t0 < tn,ATA per Exempt Model > ATA per Pension Model
D)if t0 > tn,ATA per Exempt Model > ATA per Pension Model
A)if t0 = tn,ATA per Exempt Model = ATA per Pension Model
B)if t0 > tn,ATA per Exempt Model < ATA per Pension Model
C)if t0 < tn,ATA per Exempt Model > ATA per Pension Model
D)if t0 > tn,ATA per Exempt Model > ATA per Pension Model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Ken invests $10,000 in a deductible IRA which he will hold for 10 years.His current tax rate is 30% and he estimates that his tax rate will remain the same upon withdrawal.He will not be subject to the 10% penalty tax.Assume that the IRA will yield a before-tax return of 10%.What is the after-tax accumulation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Taxpayers often have to decide between contributing to a traditional deductible IRA or a Roth IRA.In making the comparison between the two IRAs,which models should the taxpayer use?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
State and local government obligations such as municipal bonds are classic examples of which model?
A)Deferred Model
B)Exempt Model
C)Current Model
D)Pension Model
A)Deferred Model
B)Exempt Model
C)Current Model
D)Pension Model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The difference between the BTRORs of fully-taxable and tax-favored investments is called
A)an explicit tax.
B)an implicit tax.
C)an effective tax.
D)a marginal tax.
A)an explicit tax.
B)an implicit tax.
C)an effective tax.
D)a marginal tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Given a choice between a fully-taxable investment and a tax-favored investment,investors will prefer the tax-favored investment,assuming the two investments are equally risky.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
When evaluating current salary versus deferred compensation,an employer considers the fact that a current salary is deducted in the current year and provides an immediate tax benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Willa is considering receiving either $20,000 of current salary or $30,000 of deferred compensation in two years.Her current tax rate is 35%,but she expects her tax rate to be 25% two years from now.Willa can invest any after-tax current salary at a 6% ATROR.If she receives the current salary and invests the after-tax amount,her investment will accumulate to
A)$16,854.
B)$14,607.
C)$22,472.
D)None of the above.
A)$16,854.
B)$14,607.
C)$22,472.
D)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Given that Dn is the amount of deferred compensation received in lieu of $1 currently,which one of the following decision rules can the employee and the employer apply when evaluating whether deferred compensation is preferable to current salary?
A)If the employee's indifference level of Dn exceeds the employer's indifference level of Dn,the employer will pay deferred compensation up to the employee's indifference level.
B)If the employee's indifference level of Dn is less than the employer's indifference level of Dn,the employee will only receive a current salary because the employer will not pay the employee's required deferred compensation.
C)If the employee's indifference level of Dn is less than the employer's indifference level of Dn,the employer can pay deferred compensation up to its indifference level.
D)None of the decision rules in A,B,or C above hold true.
A)If the employee's indifference level of Dn exceeds the employer's indifference level of Dn,the employer will pay deferred compensation up to the employee's indifference level.
B)If the employee's indifference level of Dn is less than the employer's indifference level of Dn,the employee will only receive a current salary because the employer will not pay the employee's required deferred compensation.
C)If the employee's indifference level of Dn is less than the employer's indifference level of Dn,the employer can pay deferred compensation up to its indifference level.
D)None of the decision rules in A,B,or C above hold true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The C Corporation Model is a variation of the
A)Current Model.
B)Pension Model.
C)Exempt Model.
D)Deferred Model.
A)Current Model.
B)Pension Model.
C)Exempt Model.
D)Deferred Model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Flow-through entities include partnerships,limited liability companies,limited liability partnerships,and C corporations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
While tax-exempt bonds are not subject to income tax under the Internal Revenue Code,they are subject to implicit taxes caused by increased demand driving up the price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Sophia's employer is considering paying her either $20,000 of current salary or $40,000 of deferred compensation in 12 years.Her employer's current tax rate is 34%,but the employer expects its tax rate to be 25% 12 years from now.The employer's ATROR is 11%.If the employer waits and pays the deferred compensation,its after-tax deferred compensation expense projected to Year 12 is
A)$20,000.
B)$26,400.
C)$30,000.
D)$40,000.
A)$20,000.
B)$26,400.
C)$30,000.
D)$40,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
An individual in the top tax bracket is planning to establish a new corporation and is weighing the choice between the C corporation form and the S corporation form.She expects the corporation to be profitable each year,with all profits reinvested except to the extent needed to pay corporate taxes or shareholder taxes on profits.The shareholder's plan is to sell the business after six years for a substantial gain.The C corporation will qualify as a small business corporation under Sec.1202.Applying the C Corporation Model and the Flow-Through Model
A)the C corporation form will provide a greater return for the period of ownership if the stock is sold after the six years.
B)the S corporation will provide the greater return for the period of ownership if the stock is sold after the six years.
C)the S corporation will provide the greater return for the period of ownership if the stock is instead sold before five years.
D)Both A and C are correct.
A)the C corporation form will provide a greater return for the period of ownership if the stock is sold after the six years.
B)the S corporation will provide the greater return for the period of ownership if the stock is sold after the six years.
C)the S corporation will provide the greater return for the period of ownership if the stock is instead sold before five years.
D)Both A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Judy is considering receiving either $20,000 of current salary or $40,000 of deferred compensation in 12 years.Her current tax rate is 33%,but she expects her tax rate to be 15% 12 years from now.Judy can invest any after-tax current salary at a 6% ATROR.If she receives the deferred compensation,her investment will accumulate to
A)$26,800.
B)$34,000.
C)$36,000.
D)$40,000.
A)$26,800.
B)$34,000.
C)$36,000.
D)$40,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Nontax issues to consider when evaluating current salary versus deferred compensation include
A)the employee may need the cash now.
B)deferred compensation carries some risk.
C)deferred compensation may,depending on the contract,lock the employee into continued employment.
D)All of the above are issues to be considered.
A)the employee may need the cash now.
B)deferred compensation carries some risk.
C)deferred compensation may,depending on the contract,lock the employee into continued employment.
D)All of the above are issues to be considered.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The Current Model most closely describes a flow-through entity while a variation of the Deferred Model describes a C corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The Flow-Through Model used for S corporations and partnerships is an application of the
A)Pension Model.
B)Current Model.
C)Deferred Model.
D)Exempt Model.
A)Pension Model.
B)Current Model.
C)Deferred Model.
D)Exempt Model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Discuss the decision rules for current salary versus deferred compensation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A flow-through entity's primary characteristic is that income escapes taxation at the entity level and flows-through to be taxed at the ownership level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Given that Dn is the amount of deferred compensation received in lieu of $1 currently,then if the employee's indifference level of Dn exceeds the employer's indifference level of Dn,the employee must accept current salary because the employer will not pay the employee's required deferred compensation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The C Corporation Model is a variation of the Flow-Through Model,where taxation occurs at both the entity and the owner levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The Flow-Through Model applies to a sole proprietorship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Flow-through entities include all of the following types of entities except
A)partnerships.
B)C corporations.
C)S corporations.
D)limited liability companies (LLCs).
A)partnerships.
B)C corporations.
C)S corporations.
D)limited liability companies (LLCs).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



