Deck 20: Electrochemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/114
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Electrochemistry
1
Table 20.2 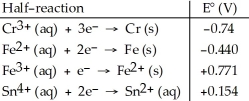
Which of the following reactions will occur spontaneously as written?
A)3Fe2+ (aq) + Cr3+ (aq) → Cr (s) + 3Fe3+ (aq)
B)2Cr3+ (aq) + 3Sn2+ (aq) → 3Sn4+ (aq) + 2Cr (s)
C)Sn4+ (aq) + Fe2+ (s) → Sn2+ (aq) + Fe (s)
D)Sn2+ (aq) + Fe2+ (s) → Sn4+ (aq) + Fe3+ (aq)
E)2Cr (s) + 3Fe2+ (s) → 3Fe (s) + 2Cr3+ (aq)
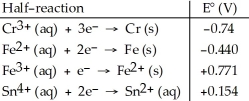
Which of the following reactions will occur spontaneously as written?
A)3Fe2+ (aq) + Cr3+ (aq) → Cr (s) + 3Fe3+ (aq)
B)2Cr3+ (aq) + 3Sn2+ (aq) → 3Sn4+ (aq) + 2Cr (s)
C)Sn4+ (aq) + Fe2+ (s) → Sn2+ (aq) + Fe (s)
D)Sn2+ (aq) + Fe2+ (s) → Sn4+ (aq) + Fe3+ (aq)
E)2Cr (s) + 3Fe2+ (s) → 3Fe (s) + 2Cr3+ (aq)
2Cr (s) + 3Fe2+ (s) → 3Fe (s) + 2Cr3+ (aq)
2
Table 20.1
Half Reaction E°(V)
F2 (g) + 2e- → 2F- (aq)+2.87
Cl2 (g) + 2e- → 2Cl- (aq)+1.359
Br2 (l) + 2e- → 2Br- (aq)+1.065
O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq) + 4e- → 2H2O (l) +1.23
Ag+ + e- → Ag (s)+0.799
Fe3+ (aq) + e- → Fe2+ (aq)+0.771
I2 (s) + 2e- → 2I- (aq)+0.536
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu (s)+0.34
2H+ + 2e- → H2 (g) 0
Pb2+ + 2e- → Pb (s)-0.126
Ni2+ + 2e- → Ni (s)-0.28
Li+ + e- → Li (s)-3.05
Which one of the following is the best oxidizing agent?
A)H2
B)Na
C)O2
D)Li
E)Ca
Half Reaction E°(V)
F2 (g) + 2e- → 2F- (aq)+2.87
Cl2 (g) + 2e- → 2Cl- (aq)+1.359
Br2 (l) + 2e- → 2Br- (aq)+1.065
O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq) + 4e- → 2H2O (l) +1.23
Ag+ + e- → Ag (s)+0.799
Fe3+ (aq) + e- → Fe2+ (aq)+0.771
I2 (s) + 2e- → 2I- (aq)+0.536
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu (s)+0.34
2H+ + 2e- → H2 (g) 0
Pb2+ + 2e- → Pb (s)-0.126
Ni2+ + 2e- → Ni (s)-0.28
Li+ + e- → Li (s)-3.05
Which one of the following is the best oxidizing agent?
A)H2
B)Na
C)O2
D)Li
E)Ca
O2
3
Which element is reduced in the reaction below? Fe2+ + H+ + Cr2O72- → Fe3+ + Cr3+ + H2O
A)Fe
B)Cr
C)O
D)H
A)Fe
B)Cr
C)O
D)H
Cr
4
Which transformation could take place at the anode of an electrochemical cell?
A)NO → NO3-
B)CO2 → C2O42-
C)VO2+ → VO2+
D)H2AsO4 → H3AsO3
E)O2 → H2O2
A)NO → NO3-
B)CO2 → C2O42-
C)VO2+ → VO2+
D)H2AsO4 → H3AsO3
E)O2 → H2O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which element is reduced in the reaction below? Fe(CO)5 (l) + 2HI (g) → Fe(CO)4I2 (s) + CO (g) + H2 (g)
A)Fe
B)C
C)O
D)H
E)I
A)Fe
B)C
C)O
D)H
E)I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which substance is the oxidizing agent in the following reaction? Fe2S3 + 12HNO3 → 2Fe(NO3)3 + 3S + 6NO2 + 6H2O
A)HNO3
B)S
C)NO2
D)Fe2S3
E)H2O
A)HNO3
B)S
C)NO2
D)Fe2S3
E)H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The purpose of the salt bridge in an electrochemical cell is to ________.
A)maintain electrical neutrality in the half-cells via migration of ions
B)provide a source of ions to react at the anode and cathode
C)provide oxygen to facilitate oxidation at the anode
D)provide a means for electrons to travel from the anode to the cathode
E)provide a means for electrons to travel from the cathode to the anode
A)maintain electrical neutrality in the half-cells via migration of ions
B)provide a source of ions to react at the anode and cathode
C)provide oxygen to facilitate oxidation at the anode
D)provide a means for electrons to travel from the anode to the cathode
E)provide a means for electrons to travel from the cathode to the anode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which transformation could take place at the anode of an electrochemical cell?
A)Cr2O72- → Cr2+
B)F2 to F-
C)O2 to H2O
D)HAsO2 to As
E)None of the above could take place at the anode.
A)Cr2O72- → Cr2+
B)F2 to F-
C)O2 to H2O
D)HAsO2 to As
E)None of the above could take place at the anode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which one of the following reactions is a redox reaction?
A)NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
B)Pb2+ + 2Cl- → PbCl2
C)AgNO3 + HCl → HNO3 + AgCl
D)None of the above is a redox reaction.
A)NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
B)Pb2+ + 2Cl- → PbCl2
C)AgNO3 + HCl → HNO3 + AgCl
D)None of the above is a redox reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Table 20.1
Half Reaction E°(V)
F2 (g) + 2e- → 2F- (aq)+2.87
Cl2 (g) + 2e- → 2Cl- (aq)+1.359
Br2 (l) + 2e- → 2Br- (aq)+1.065
O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq) + 4e- → 2H2O (l) +1.23
Ag+ + e- → Ag (s)+0.799
Fe3+ (aq) + e- → Fe2+ (aq)+0.771
I2 (s) + 2e- → 2I- (aq)+0.536
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu (s)+0.34
2H+ + 2e- → H2 (g) 0
Pb2+ + 2e- → Pb (s)-0.126
Ni2+ + 2e- → Ni (s)-0.28
Li+ + e- → Li (s)-3.05
Which one of the following types of elements is most likely to be a good oxidizing agent?
A)alkali metals
B)lanthanides
C)alkaline earth elements
D)transition elements
E)halogens
Half Reaction E°(V)
F2 (g) + 2e- → 2F- (aq)+2.87
Cl2 (g) + 2e- → 2Cl- (aq)+1.359
Br2 (l) + 2e- → 2Br- (aq)+1.065
O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq) + 4e- → 2H2O (l) +1.23
Ag+ + e- → Ag (s)+0.799
Fe3+ (aq) + e- → Fe2+ (aq)+0.771
I2 (s) + 2e- → 2I- (aq)+0.536
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu (s)+0.34
2H+ + 2e- → H2 (g) 0
Pb2+ + 2e- → Pb (s)-0.126
Ni2+ + 2e- → Ni (s)-0.28
Li+ + e- → Li (s)-3.05
Which one of the following types of elements is most likely to be a good oxidizing agent?
A)alkali metals
B)lanthanides
C)alkaline earth elements
D)transition elements
E)halogens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Consider an electrochemical cell based on the reaction: 2H+ (aq) + Sn (s) → Sn2+ (aq) + H2 (g)
Which of the following actions would change the measured cell potential?
A)increasing the pH in the cathode compartment
B)lowering the pH in the cathode compartment
C)increasing the [Sn2+] in the anode compartment
D)increasing the pressure of hydrogen gas in the cathode compartment
E)Any of the above will change the measure cell potential.
Which of the following actions would change the measured cell potential?
A)increasing the pH in the cathode compartment
B)lowering the pH in the cathode compartment
C)increasing the [Sn2+] in the anode compartment
D)increasing the pressure of hydrogen gas in the cathode compartment
E)Any of the above will change the measure cell potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the coefficient of the permanganate ion when the following equation is balanced? MnO4- + Br- → Mn2+ + Br2 (acidic solution)
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)5
E)4
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)5
E)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following reactions is a redox reaction? (a) K2CrO4 + BaCl2 → BaCrO4 + 2KCl
(b) Pb22+ + 2Br- → PbBr
(c) Cu + S → CuS
A)(a)only
B)(b)only
C)(c)only
D)(a)and (c)
E)(b)and (c)
(b) Pb22+ + 2Br- → PbBr
(c) Cu + S → CuS
A)(a)only
B)(b)only
C)(c)only
D)(a)and (c)
E)(b)and (c)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which transformation could take place at the cathode of an electrochemical cell?
A)MnO2 → MnO4-
B)Br2 → BrO3-
C)NO → HNO2
D)HSO4- → H2SO3
E)Mn2+ → MnO4-
A)MnO2 → MnO4-
B)Br2 → BrO3-
C)NO → HNO2
D)HSO4- → H2SO3
E)Mn2+ → MnO4-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Table 20.1
Half Reaction E°(V)
F2 (g) + 2e- → 2F- (aq)+2.87
Cl2 (g) + 2e- → 2Cl- (aq)+1.359
Br2 (l) + 2e- → 2Br- (aq)+1.065
O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq) + 4e- → 2H2O (l) +1.23
Ag+ + e- → Ag (s)+0.799
Fe3+ (aq) + e- → Fe2+ (aq)+0.771
I2 (s) + 2e- → 2I- (aq)+0.536
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu (s)+0.34
2H+ + 2e- → H2 (g) 0
Pb2+ + 2e- → Pb (s)-0.126
Ni2+ + 2e- → Ni (s)-0.28
Li+ + e- → Li (s)-3.05
Which of the halogens in Table 20.1 is the strongest oxidizing agent?
A)Cl2
B)Br2
C)F2
D)I2
E)All of the halogens have equal strength as oxidizing agents.
Half Reaction E°(V)
F2 (g) + 2e- → 2F- (aq)+2.87
Cl2 (g) + 2e- → 2Cl- (aq)+1.359
Br2 (l) + 2e- → 2Br- (aq)+1.065
O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq) + 4e- → 2H2O (l) +1.23
Ag+ + e- → Ag (s)+0.799
Fe3+ (aq) + e- → Fe2+ (aq)+0.771
I2 (s) + 2e- → 2I- (aq)+0.536
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu (s)+0.34
2H+ + 2e- → H2 (g) 0
Pb2+ + 2e- → Pb (s)-0.126
Ni2+ + 2e- → Ni (s)-0.28
Li+ + e- → Li (s)-3.05
Which of the halogens in Table 20.1 is the strongest oxidizing agent?
A)Cl2
B)Br2
C)F2
D)I2
E)All of the halogens have equal strength as oxidizing agents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consider an electrochemical cell based on the reaction: 2H+ (aq) + Sn (s) → Sn2+ (aq) + H2 (g)
Which of the following actions would not change the measured cell potential?
A)lowering the pH in the cathode compartment
B)addition of more tin metal to the anode compartment
C)increasing the tin (II)ion concentration in the anode compartment
D)increasing the pressure of hydrogen gas in the cathode compartment
E)Any of the above will change the measured cell potential.
Which of the following actions would not change the measured cell potential?
A)lowering the pH in the cathode compartment
B)addition of more tin metal to the anode compartment
C)increasing the tin (II)ion concentration in the anode compartment
D)increasing the pressure of hydrogen gas in the cathode compartment
E)Any of the above will change the measured cell potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the coefficient of Fe3+ when the following equation is balanced? CN- + Fe3+ → CNO- + Fe2+ (basic solution)
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Table 20.2 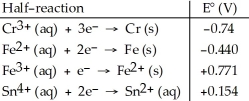
Which of the following reactions will occur spontaneously as written?
A)Sn4+ (aq) + Fe3+ (aq) → Sn2+ (aq) + Fe2+ (aq)
B)3Fe (s) + 2Cr3+ (aq) → 2Cr (s) + 3Fe2+ (aq)
C)Sn4+ (aq) + Fe2+ (aq) → Sn2+ (aq) + Fe (s)
D)3Sn4+ (aq) + 2Cr (s) → 2Cr3+ (aq) + 3Sn2+ (aq)
E)3Fe2+ (aq) → Fe (s) + 2Fe3+ (aq)
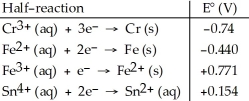
Which of the following reactions will occur spontaneously as written?
A)Sn4+ (aq) + Fe3+ (aq) → Sn2+ (aq) + Fe2+ (aq)
B)3Fe (s) + 2Cr3+ (aq) → 2Cr (s) + 3Fe2+ (aq)
C)Sn4+ (aq) + Fe2+ (aq) → Sn2+ (aq) + Fe (s)
D)3Sn4+ (aq) + 2Cr (s) → 2Cr3+ (aq) + 3Sn2+ (aq)
E)3Fe2+ (aq) → Fe (s) + 2Fe3+ (aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the coefficient of the dichromate ion when the following equation is balanced? Fe2+ + Cr2O72- → Fe3+ + Cr3+ (acidic solution)
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)5
E)6
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)5
E)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which element is reduced in the reaction below? I- + MnO4- + H+ → I2 + MnO2 + H2O
A)I
B)Mn
C)O
D)H
A)I
B)Mn
C)O
D)H

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the oxidation number of oxygen in H2O2?
A)-1
B)-2
C)+1
D)+2
E)-1/2
A)-1
B)-2
C)+1
D)+2
E)-1/2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the oxidation number of manganese in MnO2?
A)+3
B)+2
C)+1
D)+4
E)+7
A)+3
B)+2
C)+1
D)+4
E)+7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
________ is the oxidizing agent in the reaction below. Cr2O72- + 6S2O32- + 14H+ → 2Cr3+ + 3S4O62- + 7H2O
A)Cr2O72-
B)S2O32-
C)H+
D)Cr3+
E)S4O62-
A)Cr2O72-
B)S2O32-
C)H+
D)Cr3+
E)S4O62-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The gain of electrons by an element is called ________.
A)reduction
B)oxidation
C)disproportionation
D)fractionation
E)sublimation
A)reduction
B)oxidation
C)disproportionation
D)fractionation
E)sublimation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Cathodic protection of a metal pipe against corrosion usually entails ________.
A)attaching an active metal to make the pipe the anode in an electrochemical cell
B)coating the pipe with another metal whose standard reduction potential is less negative than that of the pipe
C)attaching an active metal to make the pipe the cathode in an electrochemical cell
D)attaching a dry cell to reduce any metal ions which might be formed
E)coating the pipe with a fluoropolymer to act as a source of fluoride ion (since the latter is so hard to oxidize)
A)attaching an active metal to make the pipe the anode in an electrochemical cell
B)coating the pipe with another metal whose standard reduction potential is less negative than that of the pipe
C)attaching an active metal to make the pipe the cathode in an electrochemical cell
D)attaching a dry cell to reduce any metal ions which might be formed
E)coating the pipe with a fluoropolymer to act as a source of fluoride ion (since the latter is so hard to oxidize)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which substance is the reducing agent in the reaction below? Pb + PbO2 + 2H2SO4 → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O
A)Pb
B)H2SO4
C)PbO2
D)PbSO4
E)H2O
A)Pb
B)H2SO4
C)PbO2
D)PbSO4
E)H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which substance is serving as the reducing agent in the following reaction? 14H+ + Cr2O72- + 3Ni → 3Ni2+ + 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
A)Ni
B)H+
C)Cr2O72-
D)H2O
E)Ni2+
A)Ni
B)H+
C)Cr2O72-
D)H2O
E)Ni2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the oxidation number of potassium in KMnO4?
A)0
B)+1
C)+2
D)-1
E)+3
A)0
B)+1
C)+2
D)-1
E)+3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
________ is reduced in the following reaction: Cr2O72- + 6S2O32- + 14H+ → 2Cr3+ + 3S4O62 + 7H2O
A)Cr6+
B)S2+
C)H+
D)O2-
E)S4O62-
A)Cr6+
B)S2+
C)H+
D)O2-
E)S4O62-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
________ is the reducing agent in the reaction below. Cr2O72- + 6S2O32- + 14H+ → 2Cr3+ + 3S4O62- + 7H2O
A)Cr2O72-
B)S2O32-
C)H+
D)Cr3+
E)S4O62-
A)Cr2O72-
B)S2O32-
C)H+
D)Cr3+
E)S4O62-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the cathode in the hydrogen fuel cell?
A)O2
B)KOH
C)Li
D)H2
E)Pt
A)O2
B)KOH
C)Li
D)H2
E)Pt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the cathode in an alkaline battery?
A)MnO2
B)KOH
C)Zn powder
D)Mn2O3
E)Pt
A)MnO2
B)KOH
C)Zn powder
D)Mn2O3
E)Pt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which substance is serving as the oxidizing agent in the following reaction? 14H+ + Cr2O72- + 3Ni → 3Ni2+ + 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
A)Ni
B)H+
C)Cr2O72-
D)H2O
E)Ni2+
A)Ni
B)H+
C)Cr2O72-
D)H2O
E)Ni2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the oxidation number of manganese in the MnO41- ion?
A)+1
B)+2
C)+5
D)+4
E)+7
A)+1
B)+2
C)+5
D)+4
E)+7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which substance is the oxidizing agent in the reaction below? Pb + PbO2 + 2H2SO4 → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O
A)Pb
B)H2SO4
C)PbO2
D)PbSO4
E)H2O
A)Pb
B)H2SO4
C)PbO2
D)PbSO4
E)H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the anode in an alkaline battery?
A)MnO2
B)KOH
C)Zn powder
D)Mn2O3
E)Pt
A)MnO2
B)KOH
C)Zn powder
D)Mn2O3
E)Pt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In a lead-acid battery, the electrodes are consumed. In this battery, ________.
A)the anode is Pb
B)the anode is PbSO4
C)the anode is PbO2
D)the cathode is PbSO4
E)the cathode is Pb
A)the anode is Pb
B)the anode is PbSO4
C)the anode is PbO2
D)the cathode is PbSO4
E)the cathode is Pb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
One of the differences between a voltaic cell and an electrolytic cell is that in an electrolytic cell, ________.
A)an electric current is produced by a chemical reaction
B)electrons flow toward the anode
C)a nonspontaneous reaction is forced to occur
D)O2 gas is produced at the cathode
E)oxidation occurs at the cathode
A)an electric current is produced by a chemical reaction
B)electrons flow toward the anode
C)a nonspontaneous reaction is forced to occur
D)O2 gas is produced at the cathode
E)oxidation occurs at the cathode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
________ is oxidized in the following reaction: Cr2O72- + 6S2O32- + 14H+ → 2Cr3+ + 3S4O62- + 7H2O
A)Cr6+
B)S2+
C)H+
D)O2-
E)S4O62-
A)Cr6+
B)S2+
C)H+
D)O2-
E)S4O62-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the oxidation number of chromium in Cr2O72- ion?
A)+3
B)+12
C)+7
D)+6
E)+14
A)+3
B)+12
C)+7
D)+6
E)+14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In a voltaic cell, electrons flow from the ________ to the ________.
A)salt bride, anode
B)anode, salt bridge
C)cathode, anode
D)salt bridge, cathode
E)anode, cathode
A)salt bride, anode
B)anode, salt bridge
C)cathode, anode
D)salt bridge, cathode
E)anode, cathode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
1V = ________.
A)1 amp ∙ s
B)1 J/s
C)96485 C
D)1 J/C
E)1 C/J
A)1 amp ∙ s
B)1 J/s
C)96485 C
D)1 J/C
E)1 C/J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The electrode at which oxidation occurs is called the ________.
A)oxidizing agent
B)cathode
C)reducing agent
D)anode
E)voltaic cell
A)oxidizing agent
B)cathode
C)reducing agent
D)anode
E)voltaic cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Table 20.2 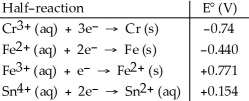
The standard cell potential (E°cell)for the voltaic cell based on the reaction below is ________ V. Cr (s) + 3Fe3+ (aq) → 3Fe2+ (aq) + Cr3+ (aq)
A)-1.45
B)+2.99
C)+1.51
D)+3.05
E)+1.57
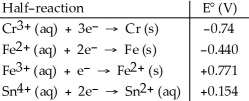
The standard cell potential (E°cell)for the voltaic cell based on the reaction below is ________ V. Cr (s) + 3Fe3+ (aq) → 3Fe2+ (aq) + Cr3+ (aq)
A)-1.45
B)+2.99
C)+1.51
D)+3.05
E)+1.57

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Table 20.2 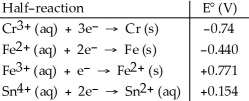
The standard cell potential (E°cell)for the voltaic cell based on the reaction below is ________ V. 2Cr (s) + 3Fe2+ (aq) → 3Fe (s) + 2Cr3+ (aq)
A)+0.30
B)+2.80
C)+3.10
D)+0.83
E)-0.16
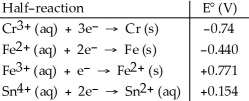
The standard cell potential (E°cell)for the voltaic cell based on the reaction below is ________ V. 2Cr (s) + 3Fe2+ (aq) → 3Fe (s) + 2Cr3+ (aq)
A)+0.30
B)+2.80
C)+3.10
D)+0.83
E)-0.16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The balanced half-reaction in which sulfate ion is reduced to sulfite ion is a ________ process.
A)four-electron
B)one-electron
C)two-electron
D)three-electron
E)six-electron
A)four-electron
B)one-electron
C)two-electron
D)three-electron
E)six-electron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The half-reaction occurring at the anode in the balanced reaction shown below is ________. 3MnO4- (aq) + 24H+ (aq) + 5Fe (s) → 3Mn2+ (aq) + 5Fe3+ (aq) + 12H2O (l)
A)MnO4- (aq) + 8H+ (aq) + 5e- → Mn2+ (aq) + 4H2O (l)
B)2MnO4- (aq) + 12H+ (aq) + 6e- → 2Mn2+ (aq) + 3H2O (l)
C)Fe (s) → Fe3+ (aq) + 3e-
D)Fe (s) → Fe2+ (aq) + 2e-
E)Fe2+ (aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + e-
A)MnO4- (aq) + 8H+ (aq) + 5e- → Mn2+ (aq) + 4H2O (l)
B)2MnO4- (aq) + 12H+ (aq) + 6e- → 2Mn2+ (aq) + 3H2O (l)
C)Fe (s) → Fe3+ (aq) + 3e-
D)Fe (s) → Fe2+ (aq) + 2e-
E)Fe2+ (aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + e-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The relationship between the change in Gibbs free energy and the emf of an electrochemical cell is given by ________.
A)ΔG =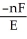
B)ΔG =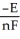
C)ΔG = -nFE
D)ΔG = -nRTF
E)ΔG =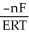
A)ΔG =
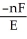
B)ΔG =
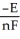
C)ΔG = -nFE
D)ΔG = -nRTF
E)ΔG =
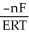

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Table 20.2 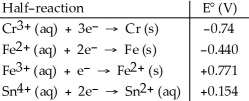
The standard cell potential (E°cell)for the voltaic cell based on the reaction below is ________ V. 3Sn4+ (aq) + 2Cr (s) → 2Cr3+ (aq) + 3Sn2+ (aq)
A)+1.94
B)+0.89
C)+2.53
D)-0.59
E)-1.02
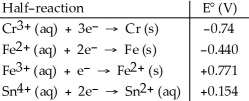
The standard cell potential (E°cell)for the voltaic cell based on the reaction below is ________ V. 3Sn4+ (aq) + 2Cr (s) → 2Cr3+ (aq) + 3Sn2+ (aq)
A)+1.94
B)+0.89
C)+2.53
D)-0.59
E)-1.02

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The standard cell potential (E°cell)of the reaction below is -0.34 V. The value of ΔG° for the reaction is ________ kJ/mol. Cu (s) + 2H+ (aq) → Cu2+ (aq) + H2 (g)
A)-0.34
B)+66
C)-130
D)+130
E)none of the above
A)-0.34
B)+66
C)-130
D)+130
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The more ________ the value of E°red, the greater the driving force for reduction.
A)positive
B)negative
C)exothermic
D)endothermic
E)extensive
A)positive
B)negative
C)exothermic
D)endothermic
E)extensive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Table 20.2 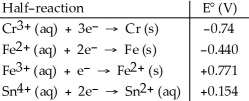
The standard cell potential (E°cell)for the voltaic cell based on the reaction below is ________ V. Sn2+ (aq) + 2Fe3+ (aq) → 2Fe2+ (aq) + Sn4+ (aq)
A)+0.46
B)+0.617
C)+1.39
D)-0.46
E)+1.21
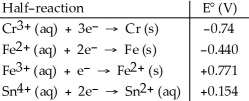
The standard cell potential (E°cell)for the voltaic cell based on the reaction below is ________ V. Sn2+ (aq) + 2Fe3+ (aq) → 2Fe2+ (aq) + Sn4+ (aq)
A)+0.46
B)+0.617
C)+1.39
D)-0.46
E)+1.21

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The standard cell potential (E°cell)of the reaction below is -0.55 V. The value of ΔG° for the reaction is ________ J/mol. I2 (s) + 2Br- (aq) → 2I- (aq) + Br2 (l)
A)0.54
B)0.55
C)5.5 × 10-6
D)1.1 × 105
E)none of the above
A)0.54
B)0.55
C)5.5 × 10-6
D)1.1 × 105
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The reduction half reaction occurring in the standard hydrogen electrode is ________.
A)H2 (g, 1 atm) → 2H+ (aq, 1M) + 2e-
B)2H+ (aq) + 2OH- → H2O (l)
C)O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq)+ 4e- → 2H2O (l)
D)2H+ (aq, 1M) + 2e- → H2 (g, 1 atm)
E)2H+ (aq, 1M) + Cl2 (aq) → 2HCl (aq)
A)H2 (g, 1 atm) → 2H+ (aq, 1M) + 2e-
B)2H+ (aq) + 2OH- → H2O (l)
C)O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq)+ 4e- → 2H2O (l)
D)2H+ (aq, 1M) + 2e- → H2 (g, 1 atm)
E)2H+ (aq, 1M) + Cl2 (aq) → 2HCl (aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
________ electrons appear in the following half-reaction when it is balanced. S4O62- → 2S2O32-
A)6
B)2
C)4
D)1
E)3
A)6
B)2
C)4
D)1
E)3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The standard cell potential (E°cell)of the reaction below is +0.126 V. The value of ΔG° for the reaction is ________ kJ/mol. Pb (s) + 2H+(aq) → Pb2+ (aq) + H2 (g)
A)-24.3
B)+24.3
C)-12.6
D)+12.6
E)-50.8
A)-24.3
B)+24.3
C)-12.6
D)+12.6
E)-50.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The balanced half-reaction in which chlorine gas is reduced to the aqueous chloride ion is a ________ process.
A)one-electron
B)two-electron
C)four-electron
D)three-electron
E)six-electron
A)one-electron
B)two-electron
C)four-electron
D)three-electron
E)six-electron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The half-reaction occurring at the cathode in the balanced reaction shown below is ________. 3MnO4- (aq) + 24H+ (aq) + 5Fe (s) → 3Mn2+ (aq) + 5Fe3+ (aq) + 12H2O (l)
A)MnO4- (aq) + 8H+ (aq) + 5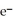 → Mn2+ (aq) + 4H2O (l)
→ Mn2+ (aq) + 4H2O (l)
B)2MnO4- (aq) + 12H+ (aq) + 6e- → 2Mn2+ (aq) + 3H2O (l)
C)Fe (s) → Fe3+ (aq) + 3e-
D)Fe (s) → Fe2+ (aq) + 2e-
E)Fe2+ (aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + e-
A)MnO4- (aq) + 8H+ (aq) + 5
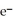 → Mn2+ (aq) + 4H2O (l)
→ Mn2+ (aq) + 4H2O (l)B)2MnO4- (aq) + 12H+ (aq) + 6e- → 2Mn2+ (aq) + 3H2O (l)
C)Fe (s) → Fe3+ (aq) + 3e-
D)Fe (s) → Fe2+ (aq) + 2e-
E)Fe2+ (aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + e-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The balanced half-reaction in which dichromate ion is reduced to chromium (III)ion is a ________ process.
A)four-electron
B)twelve-electron
C)three-electron
D)six-electron
E)two-electron
A)four-electron
B)twelve-electron
C)three-electron
D)six-electron
E)two-electron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The balanced half-reaction in which dichromate ion is reduced to chromium metal is a ________ process.
A)two-electron
B)six-electron
C)three-electron
D)four-electron
E)twelve-electron
A)two-electron
B)six-electron
C)three-electron
D)four-electron
E)twelve-electron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the oxidation number of phosphorous in the PH3 molecule?
A)-3
B)-4
C)-5
D)+1
E)0
A)-3
B)-4
C)-5
D)+1
E)0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which element is oxidized in the reaction below? I- + MnO4- + H+ → I2 + MnO2 + cO
A)I
B)Mn
C)O
D)H
A)I
B)Mn
C)O
D)H

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which substance is the oxidizing agent in the reaction below? Fe(CO)5 (l) + 2HI (g) → Fe(CO)4I2 (s) + CO (g) + H2 (g)
A)HI
B)Fe(CO)5
C)Fe(CO)4I2
D)CO
E)H2
A)HI
B)Fe(CO)5
C)Fe(CO)4I2
D)CO
E)H2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The standard cell potential (E° cell)for the reaction below is +0.63 V. The cell potential for this reaction is ________ V when [ Zn2+] = 3.0 M and [Pb2+] = 2.0 × 10-4 M. Pb2+ (aq) + Zn (s) → Zn2+ (aq) + Pb (s)
A)0.51
B)0.86
C)0.40
D)0.75
E)0.63
A)0.51
B)0.86
C)0.40
D)0.75
E)0.63

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is the oxidation number of sulfur in the S2O32- ion?
A)+2
B)+1
C)0
D)-1
E)-2
A)+2
B)+1
C)0
D)-1
E)-2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In the galvanic cell using the redox reaction below, the reduction half-reaction is ________. Zn (s) + Cu2+ (aq) → Zn2+ (aq) + Cu (s)
A)Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu
B)Zn → Zn2+ + 2e-
C)Cu2+ → Cu + 2e-
D)Zn + 2e- → Zn2+
A)Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu
B)Zn → Zn2+ + 2e-
C)Cu2+ → Cu + 2e-
D)Zn + 2e- → Zn2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What is the correct coefficient for the electrons in the following half-reaction: Ni6+ + ___e- → Ni
A)6
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)5
A)6
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What is the oxidation number of bromine in the HBrO molecule?
A)+1
B)+2
C)0
D)-1
E)-2
A)+1
B)+2
C)0
D)-1
E)-2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which element is reduced in the following reaction? Fe2S3 + 12HNO3 → 2Fe(NO3)3 + 3S + 6NO2 + 6H2O
A)N
B)S
C)H
D)O
E)NO2
A)N
B)S
C)H
D)O
E)NO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What is the oxidation number of nitrogen in the NH2OH molecule?
A)-1
B)-2
C)-3
D)0
E)+1
A)-1
B)-2
C)-3
D)0
E)+1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A voltaic cell is constructed with two silver-silver chloride electrodes, where the half-reaction is AgCl (s) + e- → Ag (s) + Cl- (aq)E° = +0.222 V
The concentrations of chloride ion in the two compartments are 0.0100 M and 1.55 M, respectively. The cell emf is ________ V.
A)0.216
B)0.130
C)0.00143
D)34.4
E)0.228
The concentrations of chloride ion in the two compartments are 0.0100 M and 1.55 M, respectively. The cell emf is ________ V.
A)0.216
B)0.130
C)0.00143
D)34.4
E)0.228

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In the electrochemical cell using the redox reaction below, the oxidation half reaction is ________. Sn4+ (aq) + Fe (s)→ Sn2+ (aq) + Fe2+ (aq)
A)Sn4+ + 2e- → Sn2+
B)Fe → Fe2+ + 2e-
C)Sn4+ → Sn2+ + 2e-
D)Fe + 2e- → Fe2+
E)Fe + 2e- → Sn2+
A)Sn4+ + 2e- → Sn2+
B)Fe → Fe2+ + 2e-
C)Sn4+ → Sn2+ + 2e-
D)Fe + 2e- → Fe2+
E)Fe + 2e- → Sn2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In the electrochemical cell using the redox reaction below, the cathode half-reaction is ________. 2H+ (s) + Sn (s) → Sn2+ (aq) + H2 (g)
A)2H+ + 2e- → H2
B)Sn → Sn2+ + 2e-
C)2H+ → H2 + 2e-
D)Sn + 2e- → Sn2+
E)Sn + 2e- → H2
A)2H+ + 2e- → H2
B)Sn → Sn2+ + 2e-
C)2H+ → H2 + 2e-
D)Sn + 2e- → Sn2+
E)Sn + 2e- → H2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Galvanized iron is iron coated with ________.
A)magnesium
B)zinc
C)chromium
D)phosphate
E)iron oxide
A)magnesium
B)zinc
C)chromium
D)phosphate
E)iron oxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which element is reduced in the reaction below? Fe2+ + H+ + Cr2O72- → Fe3+ + Cr3+ + H2O
A)Cr
B)Fe
C)H
D)O
A)Cr
B)Fe
C)H
D)O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The standard cell potential (E° cell)for the reaction below is +1.10 V. The cell potential for this reaction is ________ V when the concentration of [Cu2+] = 1.0 × 10-5 M and [Zn2+] = 3.0 M. Zn (s) + Cu2+ (aq) → Cu (s) + Zn2+ (aq)
A)1.42
B)1.26
C)0.94
D)0.78
E)1.10
A)1.42
B)1.26
C)0.94
D)0.78
E)1.10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The standard cell potential (E°cell)of the reaction below is +1.34 V. The value of ΔG° for the reaction is ________ kJ/mol. 3 Cu (s) + 2 MnO4- (aq)+ 8H+ (aq) → 3 Cu2+ (aq)+ 2 MnO2 (s) + 4 H2O (l)
A)-24.3
B)+259
C)-259
D)+776
E)-776
A)-24.3
B)+259
C)-259
D)+776
E)-776

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The lead-containing reactant(s)consumed during recharging of a lead-acid battery is/are ________.
A)Pb (s)only
B)PbO2 (s)only
C)PbSO4 (s)only
D)both PbO2 (s)and PbSO4 (s)
E)both Pb (s)and PbO2 (s)
A)Pb (s)only
B)PbO2 (s)only
C)PbSO4 (s)only
D)both PbO2 (s)and PbSO4 (s)
E)both Pb (s)and PbO2 (s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The standard cell potential (E°)of a voltaic cell constructed using the cell reaction below is 0.76 V: Zn (s) + 2H+ (aq) → Zn2+ (aq) + H2 (g)
With PH2 = 1.0 atm and [Zn2+] = 1.0 M, the cell potential is 0.53 V. The concentration of H+ in the cathode compartment is ________ M.
A)1.3 × 10-4
B)1.7 × 10-8
C)1.1 × 10-2
D)7.7 × 103
E)1.3 × 10-11
With PH2 = 1.0 atm and [Zn2+] = 1.0 M, the cell potential is 0.53 V. The concentration of H+ in the cathode compartment is ________ M.
A)1.3 × 10-4
B)1.7 × 10-8
C)1.1 × 10-2
D)7.7 × 103
E)1.3 × 10-11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Corrosion of iron is retarded by ________.
A)the presence of salts
B)high pH conditions
C)low pH conditions
D)both the presence of salts and high pH conditions
E)both the presence of salts and low pH conditions
A)the presence of salts
B)high pH conditions
C)low pH conditions
D)both the presence of salts and high pH conditions
E)both the presence of salts and low pH conditions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



