Deck 8: Valuing Bonds
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/104
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Valuing Bonds
1
Consider a zero coupon bond with 20 years to maturity.The price this bond will trade for if the YTM is 6% is closest to:
A) $215
B) $312
C) $335
D) $306
A) $215
B) $312
C) $335
D) $306
$312
2
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The amount of each coupon payment is determined by the coupon rate of the bond.
B) Prior to its maturity date, the price of a zero-coupon bond is always greater than its face value.
C) The simplest type of bond is a zero-coupon bond.
D) Treasury bills are the Canadian government bonds with a maturity of up to one year.
A) The amount of each coupon payment is determined by the coupon rate of the bond.
B) Prior to its maturity date, the price of a zero-coupon bond is always greater than its face value.
C) The simplest type of bond is a zero-coupon bond.
D) Treasury bills are the Canadian government bonds with a maturity of up to one year.
Prior to its maturity date, the price of a zero-coupon bond is always greater than its face value.
3
Government of Canada Bonds are highly liquid investments which may be sold back by investors into the
A) primary market prior to maturity.
B) money market prior to maturity.
C) capital market prior to maturity.
D) secondary market prior to maturity.
A) primary market prior to maturity.
B) money market prior to maturity.
C) capital market prior to maturity.
D) secondary market prior to maturity.
secondary market prior to maturity.
4
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The bond certificate typically specifies that the coupons will be paid periodically until the maturity date of the bond.
B) The bond certificate indicates the amounts and dates of all payments to be made.
C) The only cash payments the investor will receive from a zero coupon bond are the interest payments that are paid up until the maturity date.
D) Usually the face value of a bond is repaid at maturity.
A) The bond certificate typically specifies that the coupons will be paid periodically until the maturity date of the bond.
B) The bond certificate indicates the amounts and dates of all payments to be made.
C) The only cash payments the investor will receive from a zero coupon bond are the interest payments that are paid up until the maturity date.
D) Usually the face value of a bond is repaid at maturity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Consider a zero-coupon bond with a $1000 face value and 10 years left until maturity.If the bond is currently trading for $459,then the yield to maturity on this bond is closest to:
A) 7.5%
B) 10.4%
C) 9.7%
D) 8.1%
A) 7.5%
B) 10.4%
C) 9.7%
D) 8.1%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Bond traders typically quote bond prices rather than bond yields.
B) Treasury bills are zero-coupon bonds.
C) Zero-coupon bonds always trade at a discount.
D) The yield to maturity is typically stated as an annual rate by multiplying the calculated YTM by the number of coupon payments per year, thereby converting it to an APR.
A) Bond traders typically quote bond prices rather than bond yields.
B) Treasury bills are zero-coupon bonds.
C) Zero-coupon bonds always trade at a discount.
D) The yield to maturity is typically stated as an annual rate by multiplying the calculated YTM by the number of coupon payments per year, thereby converting it to an APR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following formulas is incorrect?
A) Yield to maturity for an n-period zero-coupon bond =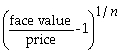
B) Price of an n-period bond =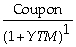 +
+ 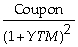 + ... +
+ ... + 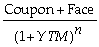
C) Price of an n-period bond = Coupon ×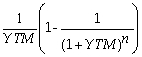 +
+ 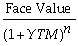
D) Coupon =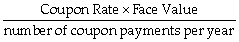
A) Yield to maturity for an n-period zero-coupon bond =
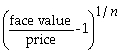
B) Price of an n-period bond =
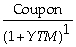 +
+ 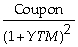 + ... +
+ ... + 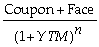
C) Price of an n-period bond = Coupon ×
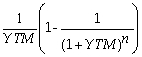 +
+ 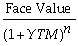
D) Coupon =
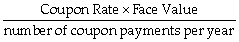

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Government of Canada Bonds pay coupons in every
A) month.
B) quarter.
C) half year.
D) year.
A) month.
B) quarter.
C) half year.
D) year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Most Canadian bonds are securities sold by governments and corporations to raise money from investors today in exchange for promised future payments.
B) By convention the coupon rate is expressed as an effective annual rate.
C) Bonds typically make two types of payments to their holders.
D) The time remaining until the repayment date is known as the term of the bond.
A) Most Canadian bonds are securities sold by governments and corporations to raise money from investors today in exchange for promised future payments.
B) By convention the coupon rate is expressed as an effective annual rate.
C) Bonds typically make two types of payments to their holders.
D) The time remaining until the repayment date is known as the term of the bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The coupon rate is the contractual rate of interest paid on the ________ of the bond.
A) present value
B) face value
C) price
D) prevailing rate of interest
A) present value
B) face value
C) price
D) prevailing rate of interest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Consider a zero-coupon bond with a $1000 face value and 10 years left until maturity.If the YTM of this bond is 10.4%,then the price of this bond is closest to:
A) $1000
B) $602
C) $1040
D) $372
A) $1000
B) $602
C) $1040
D) $372

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
For 10-year Canadian Savings Bonds,
A) the interest rate is guaranteed all the time until its maturity.
B) the interest rate is guaranteed for 5 years and fluctuates with market conditions for the remaining 5 years until its maturity.
C) the interest rate is guaranteed for 1 year and fluctuates with market conditions for the remaining 9 years until its maturity.
D) none of the above.
A) the interest rate is guaranteed all the time until its maturity.
B) the interest rate is guaranteed for 5 years and fluctuates with market conditions for the remaining 5 years until its maturity.
C) the interest rate is guaranteed for 1 year and fluctuates with market conditions for the remaining 9 years until its maturity.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Use the information for the question(s) below.
The Sisyphean Company has a bond outstanding with a face value of $1000 that reaches maturity in 15 years. The bond certificate indicates that the stated coupon rate for this bond is 8% and that the coupon payments are to be made semi-annually.
Assuming the appropriate YTM on the Sisyphean bond is 7.5%,then the price that this bond trades for will be closest to:
A) $1,045
B) $691
C) $1,000
D) $957
The Sisyphean Company has a bond outstanding with a face value of $1000 that reaches maturity in 15 years. The bond certificate indicates that the stated coupon rate for this bond is 8% and that the coupon payments are to be made semi-annually.
Assuming the appropriate YTM on the Sisyphean bond is 7.5%,then the price that this bond trades for will be closest to:
A) $1,045
B) $691
C) $1,000
D) $957

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The principal or face value of a bond is the notional amount we use to compute the interest payments.
B) Payments are made on bonds until a final repayment date, called the term date of the bond.
C) The coupon rate of a bond is set by the issuer and stated on the bond certificate.
D) The promised interest payments of a bond are called coupons.
A) The principal or face value of a bond is the notional amount we use to compute the interest payments.
B) Payments are made on bonds until a final repayment date, called the term date of the bond.
C) The coupon rate of a bond is set by the issuer and stated on the bond certificate.
D) The promised interest payments of a bond are called coupons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When the Canadian federal government issues a short term zero coupon bond,it is basically issuing a
A) treasury bill.
B) commercial paper.
C) promissory note.
D) bank acceptance.
A) treasury bill.
B) commercial paper.
C) promissory note.
D) bank acceptance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The IRR of an investment in a zero-coupon bond is the rate of return that investors will earn on their money if they buy a default-free bond at its current price and hold it to maturity.
B) The yield to maturity of a bond is the discount rate that sets the future value of the promised bond payments equal to the current market price of the bond.
C) Financial professionals also use the term spot interest rates to refer to the default-free zero-coupon yields.
D) When we calculate a bond's yield to maturity by solving the formula, Price of an n-period bond =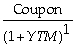 +
+ 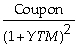 + ... +
+ ... + 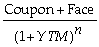 , the yield we compute will be a rate per coupon interval.
, the yield we compute will be a rate per coupon interval.
A) The IRR of an investment in a zero-coupon bond is the rate of return that investors will earn on their money if they buy a default-free bond at its current price and hold it to maturity.
B) The yield to maturity of a bond is the discount rate that sets the future value of the promised bond payments equal to the current market price of the bond.
C) Financial professionals also use the term spot interest rates to refer to the default-free zero-coupon yields.
D) When we calculate a bond's yield to maturity by solving the formula, Price of an n-period bond =
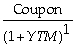 +
+ 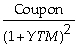 + ... +
+ ... + 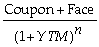 , the yield we compute will be a rate per coupon interval.
, the yield we compute will be a rate per coupon interval.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Zero-coupon bonds are also called pure discount bonds.
B) The IRR of an investment opportunity is the discount rate at which the NPV of the investment opportunity is equal to zero.
C) The yield to maturity for a zero-coupon bond is the return you will earn as an investor from holding the bond to maturity and receiving the promised face value payment.
D) When prices are quoted in the bond market, they are conventionally quoted in increments of $1000.
A) Zero-coupon bonds are also called pure discount bonds.
B) The IRR of an investment opportunity is the discount rate at which the NPV of the investment opportunity is equal to zero.
C) The yield to maturity for a zero-coupon bond is the return you will earn as an investor from holding the bond to maturity and receiving the promised face value payment.
D) When prices are quoted in the bond market, they are conventionally quoted in increments of $1000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements is false?
A) One advantage of quoting the yield to maturity rather than the price is that the yield is independent of the face value of the bond.
B) Unlike the case of bonds that pay coupons, for zero-coupon bonds there is no simple formula to solve for the yield to maturity directly.
C) Because we can convert any bond price into a yield, and vice versa, bond prices and yields are often used interchangeably.
D) The IRR of an investment in a bond is given a special name, the yield to maturity (YTM).
A) One advantage of quoting the yield to maturity rather than the price is that the yield is independent of the face value of the bond.
B) Unlike the case of bonds that pay coupons, for zero-coupon bonds there is no simple formula to solve for the yield to maturity directly.
C) Because we can convert any bond price into a yield, and vice versa, bond prices and yields are often used interchangeably.
D) The IRR of an investment in a bond is given a special name, the yield to maturity (YTM).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The yield to maturity of a bond is the same rate as ________.
A) the coupon rate
B) the effective rate of interest
C) the nominal interest rate
D) the internal rate of return
A) the coupon rate
B) the effective rate of interest
C) the nominal interest rate
D) the internal rate of return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Use the information for the question(s) below.
The Sisyphean Company has a bond outstanding with a face value of $1000 that reaches maturity in 15 years. The bond certificate indicates that the stated coupon rate for this bond is 8% and that the coupon payments are to be made semi-annually.
How much will each semi-annual coupon payment be?
A) $60
B) $40
C) $120
D) $80
The Sisyphean Company has a bond outstanding with a face value of $1000 that reaches maturity in 15 years. The bond certificate indicates that the stated coupon rate for this bond is 8% and that the coupon payments are to be made semi-annually.
How much will each semi-annual coupon payment be?
A) $60
B) $40
C) $120
D) $80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Use the table for the question(s) below.
The following table summarizes prices of various default-free zero-coupon bonds (expressed as a percentage of face value):
The yield to maturity for the three year zero-coupon bond is closest to:
A) 5.4%
B) 5.8%
C) 5.6%
D) 6.0%
The following table summarizes prices of various default-free zero-coupon bonds (expressed as a percentage of face value):

The yield to maturity for the three year zero-coupon bond is closest to:
A) 5.4%
B) 5.8%
C) 5.6%
D) 6.0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The value today of a bond equals the present value of all of its future cash flows.
B) The value today of a bond is smaller than the present value of all of its future cash flows.
C) The value today of a bond is greater than the present value of all of its future cash flows.
D) The value today of a bond equals the future value of all of its future cash flows.
A) The value today of a bond equals the present value of all of its future cash flows.
B) The value today of a bond is smaller than the present value of all of its future cash flows.
C) The value today of a bond is greater than the present value of all of its future cash flows.
D) The value today of a bond equals the future value of all of its future cash flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Use the information for the question(s) below.
The Sisyphean Company has a bond outstanding with a face value of $1000 that reaches maturity in 15 years. The bond certificate indicates that the stated coupon rate for this bond is 8% and that the coupon payments are to be made semi-annually.
How much are each of the semi-annual coupon payments? Assuming the appropriate YTM on the Sisyphean bond is 8.8%,then at what price should this bond trade for?
The Sisyphean Company has a bond outstanding with a face value of $1000 that reaches maturity in 15 years. The bond certificate indicates that the stated coupon rate for this bond is 8% and that the coupon payments are to be made semi-annually.
How much are each of the semi-annual coupon payments? Assuming the appropriate YTM on the Sisyphean bond is 8.8%,then at what price should this bond trade for?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following statements is false?
A) When a bond is trading at a discount, the price drop when a coupon is paid will be larger than the price increase between coupons, so the bond's discount will tend to decline as time passes.
B) When a bond trades at a price equal to its face value, it is said to trade at par.
C) As interest rates and bond yield rise, bond prices will fall.
D) Ultimately, the prices of all bonds approach the bond's face value when the bonds mature and their last coupons are paid.
A) When a bond is trading at a discount, the price drop when a coupon is paid will be larger than the price increase between coupons, so the bond's discount will tend to decline as time passes.
B) When a bond trades at a price equal to its face value, it is said to trade at par.
C) As interest rates and bond yield rise, bond prices will fall.
D) Ultimately, the prices of all bonds approach the bond's face value when the bonds mature and their last coupons are paid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following statements is false?
A) A bond trades at par when its coupon rate is equal to its yield to maturity.
B) The clean price of a bond is adjusted for accrued interest.
C) The price of the bond will drop by the amount of the coupon immediately after the coupon is paid.
D) If a coupon bond's yield to maturity exceeds its coupon rate, the present value of its cash flows at the yield to maturity will be greater than its face value.
A) A bond trades at par when its coupon rate is equal to its yield to maturity.
B) The clean price of a bond is adjusted for accrued interest.
C) The price of the bond will drop by the amount of the coupon immediately after the coupon is paid.
D) If a coupon bond's yield to maturity exceeds its coupon rate, the present value of its cash flows at the yield to maturity will be greater than its face value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Use the information for the question(s) below.
The Sisyphean Company has a bond outstanding with a face value of $1000 that reaches maturity in 15 years. The bond certificate indicates that the stated coupon rate for this bond is 8% and that the coupon payments are to be made semi-annually.
Assuming the appropriate YTM on the Sisyphean bond is 9.0%,then the price that this bond trades for will be closest to:
A) $946
B) $919
C) $1,086
D) $1,000
The Sisyphean Company has a bond outstanding with a face value of $1000 that reaches maturity in 15 years. The bond certificate indicates that the stated coupon rate for this bond is 8% and that the coupon payments are to be made semi-annually.
Assuming the appropriate YTM on the Sisyphean bond is 9.0%,then the price that this bond trades for will be closest to:
A) $946
B) $919
C) $1,086
D) $1,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Use the table for the question(s) below.
The following table summarizes prices of various default-free zero-coupon bonds (expressed as a percentage of face value):
Compute the yield to maturity for each of the five zero-coupon bonds.
The following table summarizes prices of various default-free zero-coupon bonds (expressed as a percentage of face value):

Compute the yield to maturity for each of the five zero-coupon bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following formulas is incorrect?
A) Invoice price = dirty price
B) Clean price = dirty price - accrued interest
C) Accrued interest = coupon amount ×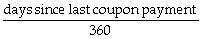
D) Cash price = clean price + accrued interest
A) Invoice price = dirty price
B) Clean price = dirty price - accrued interest
C) Accrued interest = coupon amount ×
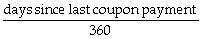
D) Cash price = clean price + accrued interest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Use the table for the question(s) below.
The following table summarizes prices of various default-free zero-coupon bonds (expressed as a percentage of face value):
The yield to maturity for the two year zero-coupon bond is closest to:
A) 6.0%
B) 5.8%
C) 5.6%
D) 5.5%
The following table summarizes prices of various default-free zero-coupon bonds (expressed as a percentage of face value):

The yield to maturity for the two year zero-coupon bond is closest to:
A) 6.0%
B) 5.8%
C) 5.6%
D) 5.5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements is false?
A) If a bond trades at a premium, its yield to maturity will exceed its coupon rate.
B) A bond that trades at a premium is said to trade above par.
C) When a coupon-paying bond is trading at a premium, an investor's return from the coupons is diminished by receiving a face value less than the price paid for the bond.
D) Holding fixed the bond's yield to maturity, for a bond not trading at par, the present value of the bond's remaining cash flows changes as the time to maturity decreases.
A) If a bond trades at a premium, its yield to maturity will exceed its coupon rate.
B) A bond that trades at a premium is said to trade above par.
C) When a coupon-paying bond is trading at a premium, an investor's return from the coupons is diminished by receiving a face value less than the price paid for the bond.
D) Holding fixed the bond's yield to maturity, for a bond not trading at par, the present value of the bond's remaining cash flows changes as the time to maturity decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Bond prices converge to the bond's face value due to the time effect, but simultaneously move up and down due to unpredictable changes in bond yields.
B) As interest rates and bond yields fall, bond prices will rise.
C) Bonds with higher coupon rates are more sensitive to interest rate changes.
D) Shorter maturity zero coupon bonds are less sensitive to changes in interest rates than are longer-term zero coupon bonds.
A) Bond prices converge to the bond's face value due to the time effect, but simultaneously move up and down due to unpredictable changes in bond yields.
B) As interest rates and bond yields fall, bond prices will rise.
C) Bonds with higher coupon rates are more sensitive to interest rate changes.
D) Shorter maturity zero coupon bonds are less sensitive to changes in interest rates than are longer-term zero coupon bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Use the information for the question(s) below.
The Sisyphean Company has a bond outstanding with a face value of $1000 that reaches maturity in 15 years. The bond certificate indicates that the stated coupon rate for this bond is 8% and that the coupon payments are to be made semi-annually.
Assuming the appropriate YTM on the Sisyphean bond is 9%,then this bond will trade at
A) a premium.
B) a discount.
C) par.
D) none of the above.
The Sisyphean Company has a bond outstanding with a face value of $1000 that reaches maturity in 15 years. The bond certificate indicates that the stated coupon rate for this bond is 8% and that the coupon payments are to be made semi-annually.
Assuming the appropriate YTM on the Sisyphean bond is 9%,then this bond will trade at
A) a premium.
B) a discount.
C) par.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Use the information for the question(s) below.
The Sisyphean Company has a bond outstanding with a face value of $1000 that reaches maturity in 15 years. The bond certificate indicates that the stated coupon rate for this bond is 8% and that the coupon payments are to be made semi-annually.
Assuming that this bond trades for $1,112,then the YTM for this bond is closest to:
A) 8.0%
B) 3.4%
C) 6.8%
D) 9.2%
The Sisyphean Company has a bond outstanding with a face value of $1000 that reaches maturity in 15 years. The bond certificate indicates that the stated coupon rate for this bond is 8% and that the coupon payments are to be made semi-annually.
Assuming that this bond trades for $1,112,then the YTM for this bond is closest to:
A) 8.0%
B) 3.4%
C) 6.8%
D) 9.2%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Use the information for the question(s) below.
The Sisyphean Company has a bond outstanding with a face value of $1000 that reaches maturity in 15 years. The bond certificate indicates that the stated coupon rate for this bond is 8% and that the coupon payments are to be made semi-annually.
Assuming that this bond trades for $903,then the YTM for this bond is closest to:
A) 8.0%
B) 6.8%
C) 9.9%
D) 9.2%
The Sisyphean Company has a bond outstanding with a face value of $1000 that reaches maturity in 15 years. The bond certificate indicates that the stated coupon rate for this bond is 8% and that the coupon payments are to be made semi-annually.
Assuming that this bond trades for $903,then the YTM for this bond is closest to:
A) 8.0%
B) 6.8%
C) 9.9%
D) 9.2%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Use the information for the question(s) below.
The Sisyphean Company has a bond outstanding with a face value of $1000 that reaches maturity in 15 years. The bond certificate indicates that the stated coupon rate for this bond is 8% and that the coupon payments are to be made semi-annually.
Assuming that this bond trades for $1,035.44,then the YTM for this bond is equal to:
The Sisyphean Company has a bond outstanding with a face value of $1000 that reaches maturity in 15 years. The bond certificate indicates that the stated coupon rate for this bond is 8% and that the coupon payments are to be made semi-annually.
Assuming that this bond trades for $1,035.44,then the YTM for this bond is equal to:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Use the information for the question(s) below.
The Sisyphean Company has a bond outstanding with a face value of $1000 that reaches maturity in 15 years. The bond certificate indicates that the stated coupon rate for this bond is 8% and that the coupon payments are to be made semi-annually.
Assuming the appropriate YTM on the Sisyphean bond is 7.5%,then this bond will trade at
A) par.
B) a discount.
C) a premium.
D) none of the above.
The Sisyphean Company has a bond outstanding with a face value of $1000 that reaches maturity in 15 years. The bond certificate indicates that the stated coupon rate for this bond is 8% and that the coupon payments are to be made semi-annually.
Assuming the appropriate YTM on the Sisyphean bond is 7.5%,then this bond will trade at
A) par.
B) a discount.
C) a premium.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Use the table for the question(s) below.
The following table summarizes prices of various default-free zero-coupon bonds (expressed as a percentage of face value):
What is the relationship between a bond's price and its yield to maturity?
The following table summarizes prices of various default-free zero-coupon bonds (expressed as a percentage of face value):

What is the relationship between a bond's price and its yield to maturity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Use the table for the question(s) below.
The following table summarizes prices of various default-free zero-coupon bonds (expressed as a percentage of face value):
Plot the zero-coupon yield curve (for the first five years).
The following table summarizes prices of various default-free zero-coupon bonds (expressed as a percentage of face value):

Plot the zero-coupon yield curve (for the first five years).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following statements is false?
A) If the bond trades at a discount, an investor who buys the bond will earn a return both from receiving the coupons and from receiving a face value that exceeds the price paid for the bond.
B) Most coupon bond issuers choose a coupon rate so that the bonds will initially trade at, or very near to, par.
C) Coupon bonds always trade for a discount.
D) At any point in time, changes in market interest rates affect a bond's yield to maturity and its price.
A) If the bond trades at a discount, an investor who buys the bond will earn a return both from receiving the coupons and from receiving a face value that exceeds the price paid for the bond.
B) Most coupon bond issuers choose a coupon rate so that the bonds will initially trade at, or very near to, par.
C) Coupon bonds always trade for a discount.
D) At any point in time, changes in market interest rates affect a bond's yield to maturity and its price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Use the table for the question(s) below.
The following table summarizes prices of various default-free zero-coupon bonds (expressed as a percentage of face value):
Based upon the information provided in the table above,you can conclude
A) that the yield curve is flat.
B) nothing about the shape of the yield curve.
C) that the yield curve is downward sloping.
D) that the yield curve is upward sloping.
The following table summarizes prices of various default-free zero-coupon bonds (expressed as a percentage of face value):

Based upon the information provided in the table above,you can conclude
A) that the yield curve is flat.
B) nothing about the shape of the yield curve.
C) that the yield curve is downward sloping.
D) that the yield curve is upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Consider a bond that pays annually an 8% coupon with 20 years to maturity.The amount that the price of the bond will change if its yield to maturity increases from 5% to 7% is closest to:
A) -$270
B) -$225
C) -$310
D) -$250
A) -$270
B) -$225
C) -$310
D) -$250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons: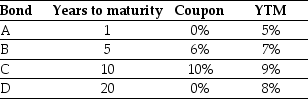
Consider a corporate bond with a $1000 face value,10% coupon with semiannual coupon payments,5 years until maturity,and which currently is selling for (has a cash price of)$1,113.80.The next coupon payment will be made in 63 days and there are 182 days in the current coupon period.The clean price for this bond is closest to:
A) $1146.50
B) $1065.70
C) $1113.80
D) $1081.10
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons:

Consider a corporate bond with a $1000 face value,10% coupon with semiannual coupon payments,5 years until maturity,and which currently is selling for (has a cash price of)$1,113.80.The next coupon payment will be made in 63 days and there are 182 days in the current coupon period.The clean price for this bond is closest to:
A) $1146.50
B) $1065.70
C) $1113.80
D) $1081.10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When the prevailing rate of return is below the coupon rate,the bond is sold at
A) premium price.
B) discounted price.
C) parity price.
D) none of the above.
A) premium price.
B) discounted price.
C) parity price.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The higher the market required return, the lower the price of the bond.
B) The higher the market required return, the higher the price of the bond.
C) The lower the market required return, the higher the price of the bond.
D) The lower the market required return, the lower the price of the bond.
A) The higher the market required return, the lower the price of the bond.
B) The higher the market required return, the higher the price of the bond.
C) The lower the market required return, the higher the price of the bond.
D) The lower the market required return, the lower the price of the bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Consider a bond that pays annually an 8% coupon with 20 years to maturity.The percentage change in the price of the bond if its yield to maturity increases from 5% to 7% is closest to:
A) 22%
B) 24%
C) -22%
D) -24%
A) 22%
B) 24%
C) -22%
D) -24%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The farther the bond's term is from its maturity, the farther the price is from its face value.
B) The closer the bond's term is to its maturity, the farther the price is from its face value.
C) The farther the bond's term is to its maturity, the closer the price is to its face value.
D) The closer the bond's term is to its maturity, the closer the price is to its face value.
A) The farther the bond's term is from its maturity, the farther the price is from its face value.
B) The closer the bond's term is to its maturity, the farther the price is from its face value.
C) The farther the bond's term is to its maturity, the closer the price is to its face value.
D) The closer the bond's term is to its maturity, the closer the price is to its face value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons:
The percentage change in the price of the bond "C" if its yield to maturity increases from 9% to 10% is closest to:
A) -17%
B) -6%
C) -4%
D) 4%
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons:

The percentage change in the price of the bond "C" if its yield to maturity increases from 9% to 10% is closest to:
A) -17%
B) -6%
C) -4%
D) 4%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Consider a zero coupon bond with 20 years to maturity.The amount that the price of the bond will change if its yield to maturity decreases from 7% to 5% is closest to:
A) $120
B) -$53
C) $53
D) $673
A) $120
B) -$53
C) $53
D) $673

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons:
The amount that the price of bond "D" will change if its yield to maturity increases from 8% to 9% is closest to:
A) -$36
B) -$39
C) $36
D) $9
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons:

The amount that the price of bond "D" will change if its yield to maturity increases from 8% to 9% is closest to:
A) -$36
B) -$39
C) $36
D) $9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons:
The percentage change in the price of the bond "A" if its yield to maturity increases from 5% to 6% is closest to:
A) -4%
B) -6%
C) -1%
D) 4%
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons:

The percentage change in the price of the bond "A" if its yield to maturity increases from 5% to 6% is closest to:
A) -4%
B) -6%
C) -1%
D) 4%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons:
Consider a corporate bond with a $1000 face value,8% coupon with semiannual coupon payments,7 years until maturity,and a YTM of 9%.It has been 57 days since the last coupon payment was made and there are 182 days in the current coupon period.The dirty (cash)price for this bond is closest to:
A) $949.70
B) $961.40
C) $936.40
D) $948.90
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons:

Consider a corporate bond with a $1000 face value,8% coupon with semiannual coupon payments,7 years until maturity,and a YTM of 9%.It has been 57 days since the last coupon payment was made and there are 182 days in the current coupon period.The dirty (cash)price for this bond is closest to:
A) $949.70
B) $961.40
C) $936.40
D) $948.90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The discount rate that sets the present value of the promised bond payments equal to the current market price of the bond is called
A) the current yield.
B) the yield to maturity.
C) the zero-coupon yield.
D) the discount yield.
A) the current yield.
B) the yield to maturity.
C) the zero-coupon yield.
D) the discount yield.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When the coupon rate of a bond is below the prevailing rate of return,the bond is sold at
A) premium price.
B) discounted price.
C) parity price.
D) none of the above.
A) premium price.
B) discounted price.
C) parity price.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If a bond is currently trading at its face (par)value,then it must be the case that
A) the bond's yield to maturity is less than its coupon rate.
B) the bond's yield to maturity is equal to its coupon rate.
C) the bond's yield to maturity is greater than its coupon rate.
D) the bond is a zero-coupon bond.
A) the bond's yield to maturity is less than its coupon rate.
B) the bond's yield to maturity is equal to its coupon rate.
C) the bond's yield to maturity is greater than its coupon rate.
D) the bond is a zero-coupon bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Consider a zero coupon bond with 20 years to maturity.The percentage change in the price of the bond if its yield to maturity decreases from 7% to 5% is closest to:
A) 46%
B) 17%
C) 22%
D) 38%
A) 46%
B) 17%
C) 22%
D) 38%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Prices of bonds with lower durations are more sensitive to interest rate changes.
B) When a bond is trading at a discount, the price increase between coupons will exceed the drop when a coupon is paid, so the bond's price will rise and its discount will decline as time passes.
C) Coupon bonds may trade at a discount, at a premium, or at par.
D) The sensitivity of a bond's price to changes in interest rates is the bond's duration.
A) Prices of bonds with lower durations are more sensitive to interest rate changes.
B) When a bond is trading at a discount, the price increase between coupons will exceed the drop when a coupon is paid, so the bond's price will rise and its discount will decline as time passes.
C) Coupon bonds may trade at a discount, at a premium, or at par.
D) The sensitivity of a bond's price to changes in interest rates is the bond's duration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons:
Which of the four bonds is the least sensitive to a one percent increase in the YTM?
A) Bond A
B) Bond B
C) Bond C
D) Bond D
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons:

Which of the four bonds is the least sensitive to a one percent increase in the YTM?
A) Bond A
B) Bond B
C) Bond C
D) Bond D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons:
The amount that the price of bond "B" will change if its yield to maturity increases from 7% to 8% is closest to:
A) -$36
B) $9
C) $36
D) $39
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons:

The amount that the price of bond "B" will change if its yield to maturity increases from 7% to 8% is closest to:
A) -$36
B) $9
C) $36
D) $39

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons:
Which of the four bonds is the most sensitive to a one percent increase in the YTM?
A) Bond A
B) Bond B
C) Bond C
D) Bond D
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons:

Which of the four bonds is the most sensitive to a one percent increase in the YTM?
A) Bond A
B) Bond B
C) Bond C
D) Bond D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons:
If its YTM does not change,how does a bond's cash price change between coupon payments?
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons:

If its YTM does not change,how does a bond's cash price change between coupon payments?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Bond ratings encourage widespread investor participation and relatively liquid markets.
B) Bonds in the top four categories are often referred to as investment grade bonds.
C) A bond's rating depends on the risk of bankruptcy as well as the bondholder's ability to lay claim to the firm's assets in the event of a bankruptcy.
D) Debt issues with a low-priority claim in bankruptcy will have a better rating than issues from the same company that have a higher priority in bankruptcy.
A) Bond ratings encourage widespread investor participation and relatively liquid markets.
B) Bonds in the top four categories are often referred to as investment grade bonds.
C) A bond's rating depends on the risk of bankruptcy as well as the bondholder's ability to lay claim to the firm's assets in the event of a bankruptcy.
D) Debt issues with a low-priority claim in bankruptcy will have a better rating than issues from the same company that have a higher priority in bankruptcy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The yield to maturity of a coupon bond is a weighted average of the yields on the zero-coupon bonds.
B) If the zero-coupon yield curve is downward sloping, the yield to maturity will decrease with the coupon rate.
C) The information in the zero-coupon yield curve is sufficient to price all other risk-free bonds.
D) When the yield curve is flat, all zero-coupon and coupon-paying bonds will have the same yield, independent of their maturities and coupon rates.
A) The yield to maturity of a coupon bond is a weighted average of the yields on the zero-coupon bonds.
B) If the zero-coupon yield curve is downward sloping, the yield to maturity will decrease with the coupon rate.
C) The information in the zero-coupon yield curve is sufficient to price all other risk-free bonds.
D) When the yield curve is flat, all zero-coupon and coupon-paying bonds will have the same yield, independent of their maturities and coupon rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Because the cash flows promised by the bond are the most that bondholders can hope to receive, the cash flows that a purchaser of a bond with credit risk expects to receive may be less than that amount.
B) By consulting bond ratings, investors can assess the credit-worthiness of a particular bond issue.
C) Because the yield to maturity for a bond is calculated using the promised cash flows, the yield of bonds with credit risk will be lower than that of otherwise identical default-free bonds.
D) A higher yield to maturity does not necessarily imply that a bond's expected return is higher.
A) Because the cash flows promised by the bond are the most that bondholders can hope to receive, the cash flows that a purchaser of a bond with credit risk expects to receive may be less than that amount.
B) By consulting bond ratings, investors can assess the credit-worthiness of a particular bond issue.
C) Because the yield to maturity for a bond is calculated using the promised cash flows, the yield of bonds with credit risk will be lower than that of otherwise identical default-free bonds.
D) A higher yield to maturity does not necessarily imply that a bond's expected return is higher.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the following zero-coupon yields on default-free securities:
The YTM of a 4-year default-free security with a face value of $1000 and an annual coupon rate of 5.25% is closest to:
A) 5.2%
B) 5.0%
C) 4.9%
D) 5.25%
Consider the following zero-coupon yields on default-free securities:

The YTM of a 4-year default-free security with a face value of $1000 and an annual coupon rate of 5.25% is closest to:
A) 5.2%
B) 5.0%
C) 4.9%
D) 5.25%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the following zero-coupon yields on default-free securities:
The YTM of a 3-year default-free security with a face value of $1000 and an annual coupon rate of 6% is closest to:
A) 5.5%
B) 5.8%
C) 5.5% .
D) 5.2%
Consider the following zero-coupon yields on default-free securities:

The YTM of a 3-year default-free security with a face value of $1000 and an annual coupon rate of 6% is closest to:
A) 5.5%
B) 5.8%
C) 5.5% .
D) 5.2%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the following zero-coupon yields on default-free securities:
A 3-year default-free security with a face value of $1000 and an annual coupon rate of 6% will trade
A) at a discount.
B) at a premium.
C) at par.
D) There is insufficient information provided to answer this question.
Consider the following zero-coupon yields on default-free securities:

A 3-year default-free security with a face value of $1000 and an annual coupon rate of 6% will trade
A) at a discount.
B) at a premium.
C) at par.
D) There is insufficient information provided to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons: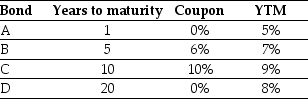
Assume that the YTM increases by 1% for each of the four bonds listed.Rank the bonds based upon the sensitivity of their prices from least to most sensitive.
Consider the following four bonds that pay annual coupons:

Assume that the YTM increases by 1% for each of the four bonds listed.Rank the bonds based upon the sensitivity of their prices from least to most sensitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the following zero-coupon yields on default-free securities:
The price today of a 3-year default-free security with a face value of $1000 and an annual coupon rate of 6% is closest to:
A) $1000
B) $1021
C) $1013
D) $1005
Consider the following zero-coupon yields on default-free securities:

The price today of a 3-year default-free security with a face value of $1000 and an annual coupon rate of 6% is closest to:
A) $1000
B) $1021
C) $1013
D) $1005

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A corporate bond which receives a BBB rating from Standard and Poor's is considered
A) a junk bond.
B) an investment grade bond.
C) a defaulted bond.
D) a high-yield bond.
A) a junk bond.
B) an investment grade bond.
C) a defaulted bond.
D) a high-yield bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Given the spot interest rates, we can determine the price and yield of any other default-free bond.
B) As the coupon increases, earlier cash flows become relatively less important than later cash flows in the calculation of the present value.
C) When the yield curve is flat, all zero-coupon and coupon-paying bonds will have the same yield, independent of their maturities and coupon rates.
D) When Canadian bond traders refer to "the yield curve," they are often referring to the coupon-paying treasury yield curve.
A) Given the spot interest rates, we can determine the price and yield of any other default-free bond.
B) As the coupon increases, earlier cash flows become relatively less important than later cash flows in the calculation of the present value.
C) When the yield curve is flat, all zero-coupon and coupon-paying bonds will have the same yield, independent of their maturities and coupon rates.
D) When Canadian bond traders refer to "the yield curve," they are often referring to the coupon-paying treasury yield curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the following zero-coupon yields on default-free securities:
What is the price today of a two-year,default-free security with a face value of $1000 and an annual coupon rate of 5.75%? Does this bond trade at a discount,premium,or at par?
Consider the following zero-coupon yields on default-free securities:

What is the price today of a two-year,default-free security with a face value of $1000 and an annual coupon rate of 5.75%? Does this bond trade at a discount,premium,or at par?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Investors pay less for bonds with credit risk than they would for an otherwise identical default-free bond.
B) The yield to maturity of a defaultable bond is equal to the expected return of investing in the bond.
C) The risk of default, which is known as the credit risk of the bond, means that the bond's cash flows are not known with certainty.
D) For corporate bonds, the issuer may default-that is, it might not pay back the full amount promised in the bond certificate.
A) Investors pay less for bonds with credit risk than they would for an otherwise identical default-free bond.
B) The yield to maturity of a defaultable bond is equal to the expected return of investing in the bond.
C) The risk of default, which is known as the credit risk of the bond, means that the bond's cash flows are not known with certainty.
D) For corporate bonds, the issuer may default-that is, it might not pay back the full amount promised in the bond certificate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the following zero-coupon yields on default-free securities:
The price of a five-year,zero-coupon,default-free security with a face value of $1000 is closest to:
A) $754
B) $772
C) $776
D) $791
Consider the following zero-coupon yields on default-free securities:

The price of a five-year,zero-coupon,default-free security with a face value of $1000 is closest to:
A) $754
B) $772
C) $776
D) $791

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The shape of the yield curve affects the price choice in the firm's financing decision.
B) The shape of the yield curve affects the cost choice in the firm's financing decision.
C) The shape of the yield curve affects the return choice in the firm's financing decision.
D) The shape of the yield curve affects the maturity choice in the firm's financing decision.
A) The shape of the yield curve affects the price choice in the firm's financing decision.
B) The shape of the yield curve affects the cost choice in the firm's financing decision.
C) The shape of the yield curve affects the return choice in the firm's financing decision.
D) The shape of the yield curve affects the maturity choice in the firm's financing decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following statements is false?
A) By convention, practitioners always plot the yield of the most senior issued bonds, termed the on-the-run-bonds.
B) We can determine the no-arbitrage price of a coupon bond by discounting its cash flows using the zero-coupon yields.
C) If the zero-coupon yield curve is upward sloping, the resulting yield to maturity decreases with the coupon rate of the bond.
D) The yield to maturity of a coupon bond is a weighted average of the yields on the zero-coupon bonds.
A) By convention, practitioners always plot the yield of the most senior issued bonds, termed the on-the-run-bonds.
B) We can determine the no-arbitrage price of a coupon bond by discounting its cash flows using the zero-coupon yields.
C) If the zero-coupon yield curve is upward sloping, the resulting yield to maturity decreases with the coupon rate of the bond.
D) The yield to maturity of a coupon bond is a weighted average of the yields on the zero-coupon bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the following zero-coupon yields on default-free securities:
The price today of a 4-year default-free security with a face value of $1000 and an annual coupon rate of 5.25% is closest to:
A) $1000
B) $1003
C) $1008
D) $987
Consider the following zero-coupon yields on default-free securities:

The price today of a 4-year default-free security with a face value of $1000 and an annual coupon rate of 5.25% is closest to:
A) $1000
B) $1003
C) $1008
D) $987

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The term structure of interest rate relates present value with the rate of return and the time to future value.
B) The term structure of interest rate separates present value from the rate of return and the time from future value.
C) The term structure of interest rate doubles present value with the rate of return and the time on future value.
D) The term structure of interest rate compounds present value with the rate of return and the time on future value.
A) The term structure of interest rate relates present value with the rate of return and the time to future value.
B) The term structure of interest rate separates present value from the rate of return and the time from future value.
C) The term structure of interest rate doubles present value with the rate of return and the time on future value.
D) The term structure of interest rate compounds present value with the rate of return and the time on future value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following statements is false?
A) We can use the law of one price to compute the price of a coupon bond from the prices of zero-coupon bonds.
B) The plot of the yields of coupon bonds of different maturities is called the coupon-paying yield curve.
C) It is possible to replicate the cash flows of a coupon bond using zero-coupon bonds.
D) Because the coupon bond provides cash flows at different points in time, the yield to maturity of a coupon bond is the simple average of the yields of the zero-coupon bonds of equal and shorter maturities.
A) We can use the law of one price to compute the price of a coupon bond from the prices of zero-coupon bonds.
B) The plot of the yields of coupon bonds of different maturities is called the coupon-paying yield curve.
C) It is possible to replicate the cash flows of a coupon bond using zero-coupon bonds.
D) Because the coupon bond provides cash flows at different points in time, the yield to maturity of a coupon bond is the simple average of the yields of the zero-coupon bonds of equal and shorter maturities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Use the table for the question(s) below.
Consider the following zero-coupon yields on default-free securities:
A 4-year default-free security with a face value of $1000 and an annual coupon rate of 5.25% will trade
A) at a premium.
B) at par.
C) at a discount.
D) There is insufficient information provided to answer this question.
Consider the following zero-coupon yields on default-free securities:

A 4-year default-free security with a face value of $1000 and an annual coupon rate of 5.25% will trade
A) at a premium.
B) at par.
C) at a discount.
D) There is insufficient information provided to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Generally speaking,in Canada,the risk of bonds issued by corporations is relatively ________ the risk of bonds issued by the governments.
A) higher than
B) lower than
C) equal to
D) none of the above
A) higher than
B) lower than
C) equal to
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



