Deck 27: Protein and Amino Acid Metabolism
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/47
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 27: Protein and Amino Acid Metabolism
1
What percentage of a healthy adult's energy need is met by metabolism of protein?
A)less than 5
B)10-20
C)35-45
D)65-75
E)more than 90
A)less than 5
B)10-20
C)35-45
D)65-75
E)more than 90
10-20
2
Two key amino acids in the catabolism of nitrogen atoms in amino acids are
A)aspartate and phenylalanine.
B)aspartate and tyrosine.
C)aspartate and glutamate.
D)glutamate and asparagine.
E)alanine and valine.
A)aspartate and phenylalanine.
B)aspartate and tyrosine.
C)aspartate and glutamate.
D)glutamate and asparagine.
E)alanine and valine.
aspartate and glutamate.
3
The enzyme that removes an amine group from an amino acid and moves it to α-ketoglutarate is classified as a
A)ligase.
B)phosphatase.
C)transaminase.
D)dehydrogenase.
E)kinase.
A)ligase.
B)phosphatase.
C)transaminase.
D)dehydrogenase.
E)kinase.
transaminase.
4
When the amino acid alanine is deaminated,it is converted to
A)glutamate.
B)acetate.
C)pyruvate.
D)oxaloacetate.
E)urea.
A)glutamate.
B)acetate.
C)pyruvate.
D)oxaloacetate.
E)urea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When an amine group is transferred to α-ketoglutarate,one product is always
A)glycine.
B)glutamate.
C)aspartate.
D)alanine.
E)leucine.
A)glycine.
B)glutamate.
C)aspartate.
D)alanine.
E)leucine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If nitrogen is to be excreted from the body,it is converted to which chemical?
A)ammonia
B)arginine
C)glycine
D)α-ketoglutarate
E)urea
A)ammonia
B)arginine
C)glycine
D)α-ketoglutarate
E)urea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The first step in amino acid catabolism is ________.
A)transamination
B)decarboxylation
C)oxidation
D)esterification
E)tautomerization
A)transamination
B)decarboxylation
C)oxidation
D)esterification
E)tautomerization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When α-ketoglutarate accepts an amine group,it is converted to
A)glutamate.
B)pyruvate.
C)acetyl.
D)transaminase.
E)urea.
A)glutamate.
B)pyruvate.
C)acetyl.
D)transaminase.
E)urea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
α-ketoglutarate is converted to glutamate by
A)loss of a carbonyl group.
B)loss of a carboxyl group.
C)accepting an acetyl group.
D)loss of an amide linkage.
E)accepting an amine group.
A)loss of a carbonyl group.
B)loss of a carboxyl group.
C)accepting an acetyl group.
D)loss of an amide linkage.
E)accepting an amine group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When the amine group of glutamate is replaced with a carbonyl group,the process is called
A)hydrolysis.
B)oxidative deamination.
C)reductive deamination.
D)oxidative decarboxylation.
E)phosphorylation.
A)hydrolysis.
B)oxidative deamination.
C)reductive deamination.
D)oxidative decarboxylation.
E)phosphorylation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
α-ketoacids are produced as a result of a transamination reaction with ________ acting as the donor molecule.
A)glutamate
B)aspartate
C)urea
D)ornithine
E)oxaloacetate
A)glutamate
B)aspartate
C)urea
D)ornithine
E)oxaloacetate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The amino acid pool is the collection of
A)all amino acids available from the diet.
B)amino acids produced from breakdown of proteins and available for reuse.
C)essential amino acids available from the diet or from breakdown of other proteins.
D)all free amino acids in the body.
E)all amino acids in the body,whether free or part of proteins.
A)all amino acids available from the diet.
B)amino acids produced from breakdown of proteins and available for reuse.
C)essential amino acids available from the diet or from breakdown of other proteins.
D)all free amino acids in the body.
E)all amino acids in the body,whether free or part of proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following enzymes is not involved in the digestion of proteins?
A)pepsin
B)amylase
C)trypsin
D)carboxypeptidase
E)chymotrypsin
A)pepsin
B)amylase
C)trypsin
D)carboxypeptidase
E)chymotrypsin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
One of the most important functions of amino acids is for the synthesis of
A)glucose.
B)pyruvate for energy.
C)body proteins.
D)purines and pyrimidines.
A)glucose.
B)pyruvate for energy.
C)body proteins.
D)purines and pyrimidines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The process of oxidative deamination of an amino acid produces which of the following?
A)urea
B)CO2 and H2O
C)NH4+
D)aspartate
E)glutamate
A)urea
B)CO2 and H2O
C)NH4+
D)aspartate
E)glutamate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The common features of catabolism of all amino acids include
A)removal of the amine group and conversion of the carbon skeleton to intermediates which can enter the citric acid cycle.
B)hydrolysis of peptide linkages and production of CO2 as waste.
C)hydrolysis of peptide linkages and production of urea as waste.
D)diversion of the carbon skeletons into gluconeogenesis.
E)diversion of the carbon skeletons into ketogenesis.
A)removal of the amine group and conversion of the carbon skeleton to intermediates which can enter the citric acid cycle.
B)hydrolysis of peptide linkages and production of CO2 as waste.
C)hydrolysis of peptide linkages and production of urea as waste.
D)diversion of the carbon skeletons into gluconeogenesis.
E)diversion of the carbon skeletons into ketogenesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The structural formula of glutamate is ________.
A)
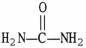
B)NH4+
C)
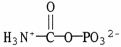
D)
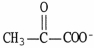
E)
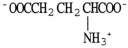
A)
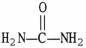
B)NH4+
C)

D)
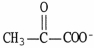
E)
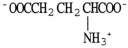

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which statement best summarizes the digestion of proteins?
A)Amine groups are removed from all amino acids.
B)All peptide linkages are hydrolyzed to produce a mixture of amino acids.
C)Proteins are denatured by stomach acid.
D)Amino acids are combined to produce proteins or enzymes.
E)none of the above
A)Amine groups are removed from all amino acids.
B)All peptide linkages are hydrolyzed to produce a mixture of amino acids.
C)Proteins are denatured by stomach acid.
D)Amino acids are combined to produce proteins or enzymes.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which is the correct order for the steps in digestion and absorption of proteins?
I.hydrolysis by pancreatic lipases
II.denaturation by stomach acid
III.hydrolysis by pepsin
IV.active transport into the bloodstream
A)I,II,III,IV
B)IV,II,III,I
C)II,I,III,IV
D)II,III,I,IV
E)III,II,IV,I
I.hydrolysis by pancreatic lipases
II.denaturation by stomach acid
III.hydrolysis by pepsin
IV.active transport into the bloodstream
A)I,II,III,IV
B)IV,II,III,I
C)II,I,III,IV
D)II,III,I,IV
E)III,II,IV,I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When glutamate acts as the source of an amino group,the enzyme involved is a
A)transferase.
B)lipase.
C)pepsin.
D)synthetase.
E)dehydrogenase.
A)transferase.
B)lipase.
C)pepsin.
D)synthetase.
E)dehydrogenase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is the usual reactant in the urea cycle?
A)NH4+
B)glutamate
C)pyruvate
D)carbamoyl phosphate
E)CO2
A)NH4+
B)glutamate
C)pyruvate
D)carbamoyl phosphate
E)CO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Each of the following metabolic intermediates is a precursor to one or more amino acids except
A)fumarate.
B)α-ketoglutarate.
C)oxaloacetate.
D)3-phosphoglycerate.
E)pyruvate.
A)fumarate.
B)α-ketoglutarate.
C)oxaloacetate.
D)3-phosphoglycerate.
E)pyruvate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
An essential amino acid is one that
A)is required for the synthesis of all proteins.
B)must be obtained in the diet because the human body cannot synthesize it.
C)can safely be omitted from the diet because the human body can produce it in unlimited amounts.
D)must be provided in the diet for individuals with specific hereditary enzyme deficiencies.
E)has a relatively simple carbon skeleton.
A)is required for the synthesis of all proteins.
B)must be obtained in the diet because the human body cannot synthesize it.
C)can safely be omitted from the diet because the human body can produce it in unlimited amounts.
D)must be provided in the diet for individuals with specific hereditary enzyme deficiencies.
E)has a relatively simple carbon skeleton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
All of the following chemicals are part of the urea cycle except
A)carbamoyl phosphate.
B)citrulline.
C)arginine.
D)fumarate.
E)acetyl-SCoA.
A)carbamoyl phosphate.
B)citrulline.
C)arginine.
D)fumarate.
E)acetyl-SCoA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Ketogenic amino acids cannot be converted into which of the following?
A)fatty acids
B)glucose
C)ketone bodies
D)acetyl CoA
E)They can be converted into all of the above.
A)fatty acids
B)glucose
C)ketone bodies
D)acetyl CoA
E)They can be converted into all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The conversion of nitrogen derivatives to urea takes place in the
A)blood.
B)kidneys.
C)liver.
D)brain.
E)intestines.
A)blood.
B)kidneys.
C)liver.
D)brain.
E)intestines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The urea cycle is ________ because it ________.
A)exergonic; costs 3 ATP
B)exergonic; releases 3 ATP
C)endergonic; costs 3 ATP
D)endergonic; releases 3 ATP
E)neither exergonic nor endergonic; consumes 3 ATP in an early step and releases 3 ATP in a later step
A)exergonic; costs 3 ATP
B)exergonic; releases 3 ATP
C)endergonic; costs 3 ATP
D)endergonic; releases 3 ATP
E)neither exergonic nor endergonic; consumes 3 ATP in an early step and releases 3 ATP in a later step

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Explain the difference between ketogenic and glucogenic amino acids.Identify the amino acids in each category.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following types of compounds do not require nitrogen for their biosynthesis?
A)purines
B)pyrimidines
C)neurotransmitters
D)urea
E)All of these require nitrogen.
A)purines
B)pyrimidines
C)neurotransmitters
D)urea
E)All of these require nitrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The urea cycle is part of the metabolic breakdown of ________.
A)amino acids
B)pyrimidines
C)purines
D)lipids
E)carbohydrates
A)amino acids
B)pyrimidines
C)purines
D)lipids
E)carbohydrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Gout is a disease state that results from the precipitation of compounds containing ________ in joints in the hands and feet.
A)urate
B)urea
C)glutamate
D)oxalate
E)acetate
A)urate
B)urea
C)glutamate
D)oxalate
E)acetate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following processes is important when new amino acids are produced in the body?
A)deamination
B)transamination
C)urea cycle
D)phosphorylation
A)deamination
B)transamination
C)urea cycle
D)phosphorylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In the anabolism of amino acids,________ is the source of the amine group.
A)aspartate
B)urea
C)glutamate
D)arginine
E)phenylalanine
A)aspartate
B)urea
C)glutamate
D)arginine
E)phenylalanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
PKU,phenylketonuria,is caused by a defect in the enzyme that converts
A)alanine to serine.
B)phenylalanine to tyrosine.
C)tryptophan to tyrosine.
D)alanine to phenylalanine.
A)alanine to serine.
B)phenylalanine to tyrosine.
C)tryptophan to tyrosine.
D)alanine to phenylalanine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Amino acids that can be synthesized in the body are called ______ amino acids.
A)essential
B)glycogenic
C)ketogenic
D)nonessential
A)essential
B)glycogenic
C)ketogenic
D)nonessential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Complementary sources of protein are
A)single foods that contain all of the essential amino acids.
B)single foods that contain all of the nonessential amino acids.
C)single foods that contain none of the essential amino acids.
D)single foods that contain none of the nonessential amino acids.
E)combinations of foods that provide all of the amino acids,both essential and nonessential.
A)single foods that contain all of the essential amino acids.
B)single foods that contain all of the nonessential amino acids.
C)single foods that contain none of the essential amino acids.
D)single foods that contain none of the nonessential amino acids.
E)combinations of foods that provide all of the amino acids,both essential and nonessential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The source of nitrogen for the synthesis of nonessential amino acids is
A)glutamate.
B)acetate.
C)pyruvate.
D)oxaloacetate.
E)urea.
A)glutamate.
B)acetate.
C)pyruvate.
D)oxaloacetate.
E)urea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
All of the carbon backbones from amino acids end up as intermediates in the ________.
A)citric acid cycle
B)urea cycle
C)β-oxidation sequence
D)both A and C
E)none of the above
A)citric acid cycle
B)urea cycle
C)β-oxidation sequence
D)both A and C
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The structural formula of urea is ________.
A)
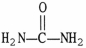
B)NH4+
C)
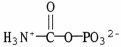
D)
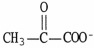
E)
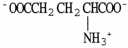
A)
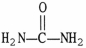
B)NH4+
C)

D)
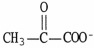
E)
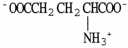

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Glucogenic amino acids can be converted into which of the following?
A)glucose
B)fatty acids
C)acetyl CoA
D)ketone bodies
E)They can be converted into all of the above.
A)glucose
B)fatty acids
C)acetyl CoA
D)ketone bodies
E)They can be converted into all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Match the following.
nonessential amino acid
A)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate,which ultimately becomes glucose
B)the transfer of an amine group from an amino acid to an α-keto acid
C)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate that later becomes a ketone body or a fatty acid
D)the collection of all the free amino acids in the body
E)an amino acid that must be obtained in the diet because humans do not have the appropriate anabolic pathways for its synthesis
F)the biochemical pathway that converts nitrogen and its derivatives to a less toxic form for excretion
G)an amino acid which can be synthesized by the human body as needed
nonessential amino acid
A)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate,which ultimately becomes glucose
B)the transfer of an amine group from an amino acid to an α-keto acid
C)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate that later becomes a ketone body or a fatty acid
D)the collection of all the free amino acids in the body
E)an amino acid that must be obtained in the diet because humans do not have the appropriate anabolic pathways for its synthesis
F)the biochemical pathway that converts nitrogen and its derivatives to a less toxic form for excretion
G)an amino acid which can be synthesized by the human body as needed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Match the following.
amino acid pool
A)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate,which ultimately becomes glucose
B)the transfer of an amine group from an amino acid to an α-keto acid
C)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate that later becomes a ketone body or a fatty acid
D)the collection of all the free amino acids in the body
E)an amino acid that must be obtained in the diet because humans do not have the appropriate anabolic pathways for its synthesis
F)the biochemical pathway that converts nitrogen and its derivatives to a less toxic form for excretion
G)an amino acid which can be synthesized by the human body as needed
amino acid pool
A)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate,which ultimately becomes glucose
B)the transfer of an amine group from an amino acid to an α-keto acid
C)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate that later becomes a ketone body or a fatty acid
D)the collection of all the free amino acids in the body
E)an amino acid that must be obtained in the diet because humans do not have the appropriate anabolic pathways for its synthesis
F)the biochemical pathway that converts nitrogen and its derivatives to a less toxic form for excretion
G)an amino acid which can be synthesized by the human body as needed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Match the following.
glucogenic amino acid
A)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate,which ultimately becomes glucose
B)the transfer of an amine group from an amino acid to an α-keto acid
C)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate that later becomes a ketone body or a fatty acid
D)the collection of all the free amino acids in the body
E)an amino acid that must be obtained in the diet because humans do not have the appropriate anabolic pathways for its synthesis
F)the biochemical pathway that converts nitrogen and its derivatives to a less toxic form for excretion
G)an amino acid which can be synthesized by the human body as needed
glucogenic amino acid
A)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate,which ultimately becomes glucose
B)the transfer of an amine group from an amino acid to an α-keto acid
C)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate that later becomes a ketone body or a fatty acid
D)the collection of all the free amino acids in the body
E)an amino acid that must be obtained in the diet because humans do not have the appropriate anabolic pathways for its synthesis
F)the biochemical pathway that converts nitrogen and its derivatives to a less toxic form for excretion
G)an amino acid which can be synthesized by the human body as needed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Match the following.
urea cycle
A)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate,which ultimately becomes glucose
B)the transfer of an amine group from an amino acid to an α-keto acid
C)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate that later becomes a ketone body or a fatty acid
D)the collection of all the free amino acids in the body
E)an amino acid that must be obtained in the diet because humans do not have the appropriate anabolic pathways for its synthesis
F)the biochemical pathway that converts nitrogen and its derivatives to a less toxic form for excretion
G)an amino acid which can be synthesized by the human body as needed
urea cycle
A)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate,which ultimately becomes glucose
B)the transfer of an amine group from an amino acid to an α-keto acid
C)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate that later becomes a ketone body or a fatty acid
D)the collection of all the free amino acids in the body
E)an amino acid that must be obtained in the diet because humans do not have the appropriate anabolic pathways for its synthesis
F)the biochemical pathway that converts nitrogen and its derivatives to a less toxic form for excretion
G)an amino acid which can be synthesized by the human body as needed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Match the following.
essential amino acid
A)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate,which ultimately becomes glucose
B)the transfer of an amine group from an amino acid to an α-keto acid
C)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate that later becomes a ketone body or a fatty acid
D)the collection of all the free amino acids in the body
E)an amino acid that must be obtained in the diet because humans do not have the appropriate anabolic pathways for its synthesis
F)the biochemical pathway that converts nitrogen and its derivatives to a less toxic form for excretion
G)an amino acid which can be synthesized by the human body as needed
essential amino acid
A)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate,which ultimately becomes glucose
B)the transfer of an amine group from an amino acid to an α-keto acid
C)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate that later becomes a ketone body or a fatty acid
D)the collection of all the free amino acids in the body
E)an amino acid that must be obtained in the diet because humans do not have the appropriate anabolic pathways for its synthesis
F)the biochemical pathway that converts nitrogen and its derivatives to a less toxic form for excretion
G)an amino acid which can be synthesized by the human body as needed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Match the following.
transamination
A)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate,which ultimately becomes glucose
B)the transfer of an amine group from an amino acid to an α-keto acid
C)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate that later becomes a ketone body or a fatty acid
D)the collection of all the free amino acids in the body
E)an amino acid that must be obtained in the diet because humans do not have the appropriate anabolic pathways for its synthesis
F)the biochemical pathway that converts nitrogen and its derivatives to a less toxic form for excretion
G)an amino acid which can be synthesized by the human body as needed
transamination
A)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate,which ultimately becomes glucose
B)the transfer of an amine group from an amino acid to an α-keto acid
C)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate that later becomes a ketone body or a fatty acid
D)the collection of all the free amino acids in the body
E)an amino acid that must be obtained in the diet because humans do not have the appropriate anabolic pathways for its synthesis
F)the biochemical pathway that converts nitrogen and its derivatives to a less toxic form for excretion
G)an amino acid which can be synthesized by the human body as needed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Match the following.
ketogenic amino acid
A)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate,which ultimately becomes glucose
B)the transfer of an amine group from an amino acid to an α-keto acid
C)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate that later becomes a ketone body or a fatty acid
D)the collection of all the free amino acids in the body
E)an amino acid that must be obtained in the diet because humans do not have the appropriate anabolic pathways for its synthesis
F)the biochemical pathway that converts nitrogen and its derivatives to a less toxic form for excretion
G)an amino acid which can be synthesized by the human body as needed
ketogenic amino acid
A)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate,which ultimately becomes glucose
B)the transfer of an amine group from an amino acid to an α-keto acid
C)an amino acid whose carbon skeleton can be converted to a citric acid cycle intermediate that later becomes a ketone body or a fatty acid
D)the collection of all the free amino acids in the body
E)an amino acid that must be obtained in the diet because humans do not have the appropriate anabolic pathways for its synthesis
F)the biochemical pathway that converts nitrogen and its derivatives to a less toxic form for excretion
G)an amino acid which can be synthesized by the human body as needed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



