Deck 26: Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/83
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
1
The sugar found in an RNA nucleotide is
A)d-ribose.
B)2-deoxy-d-ribose.
C)d-rhamnose.
D)d-raffinose.
E)all of the above
A)d-ribose.
B)2-deoxy-d-ribose.
C)d-rhamnose.
D)d-raffinose.
E)all of the above
d-ribose.
2
Which base is normally found in RNA but not in DNA?
A)thymine
B)adenine
C)guanine
D)uracil
E)cytosine
A)thymine
B)adenine
C)guanine
D)uracil
E)cytosine
uracil
3
This question has three parts:
A)Describe the similarities and differences of purines and pyrimidines.
B)List the specific bases in each category that are important in nucleic acids.
C)Describe their interactions in DNA and RNA.
A)Describe the similarities and differences of purines and pyrimidines.
B)List the specific bases in each category that are important in nucleic acids.
C)Describe their interactions in DNA and RNA.
A) A purine is a molecule that consists of a five-membered and a six-membered ring structure joined at one side with four carbon atoms replaced by nitrogen.A pyrimidine is a six-membered ring structure in which two carbons are replaced by nitrogen atoms.
B) The specific purines found in nucleic acids are adenine and guanine;each of these has different functional groups on the ring structure.The specific pyrimidines found in nucleic acids are cytosine,thymine,and uracil.As in purines,each of these has specific functional groups on the ring structure.
C) In DNA,these bases interact by forming hydrogen bonds: thymine and adenine form two hydrogen bonds,and cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds,except in RNA,uracil replaces thymine.Each of these base pairs is about the same size,allowing their interactions to join two separate strands of DNA with a constant distance between the sugar-phosphate backbones.Hydrogen bonds allow the two-stranded molecule to be reasonably sturdy,but to be able to separate without a prohibitive expenditure of energy.Similar interactions between the bases occur in transcription,when DNA produces RNA.
B) The specific purines found in nucleic acids are adenine and guanine;each of these has different functional groups on the ring structure.The specific pyrimidines found in nucleic acids are cytosine,thymine,and uracil.As in purines,each of these has specific functional groups on the ring structure.
C) In DNA,these bases interact by forming hydrogen bonds: thymine and adenine form two hydrogen bonds,and cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds,except in RNA,uracil replaces thymine.Each of these base pairs is about the same size,allowing their interactions to join two separate strands of DNA with a constant distance between the sugar-phosphate backbones.Hydrogen bonds allow the two-stranded molecule to be reasonably sturdy,but to be able to separate without a prohibitive expenditure of energy.Similar interactions between the bases occur in transcription,when DNA produces RNA.
4
A nucleotide is composed of a ________ with a ________ added to it.
A)pentose;phosphate group
B)pentose;nitrogen base
C)nucleoside;nitrogen base
D)nucleoside;phosphate group
E)phosphate group;nitrogen base
A)pentose;phosphate group
B)pentose;nitrogen base
C)nucleoside;nitrogen base
D)nucleoside;phosphate group
E)phosphate group;nitrogen base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is a nucleoside which would be found in DNA?
A)adenosine triphosphate
B)UMP
C)deoxyguanosine
D)deoxyribose
E)deoxythymidine diphosphate
A)adenosine triphosphate
B)UMP
C)deoxyguanosine
D)deoxyribose
E)deoxythymidine diphosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The purine bases are
A)fused 5 and 6 membered ring systems containing 4 ring nitrogens.
B)6 membered ring systems containing 2 ring nitrogens.
C)6 membered ring systems containing 4 ring nitrogens.
D)fused 5 and 6 membered ring systems containing 2 nitrogens.
E)none of the above
A)fused 5 and 6 membered ring systems containing 4 ring nitrogens.
B)6 membered ring systems containing 2 ring nitrogens.
C)6 membered ring systems containing 4 ring nitrogens.
D)fused 5 and 6 membered ring systems containing 2 nitrogens.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A region on the DNA strand that carries the information needed for the synthesis of a specific protein is called a
A)codon.
B)gene.
C)chromosome.
D)complementary base unit.
E)chromatid.
A)codon.
B)gene.
C)chromosome.
D)complementary base unit.
E)chromatid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
All of the following are components of nucleotides except
A)aldopentoses in the form of five-membered rings.
B)heterocyclic nitrogen bases consisting of six-membered rings.
C)heterocyclic nitrogen bases consisting of two fused rings.
D)phosphate groups.
E)metal ions.
A)aldopentoses in the form of five-membered rings.
B)heterocyclic nitrogen bases consisting of six-membered rings.
C)heterocyclic nitrogen bases consisting of two fused rings.
D)phosphate groups.
E)metal ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When a β-N-glycosidic bond forms between guanine and deoxyribose,the resulting molecule is called
A)riboguanine.
B)deoxyriboguanine.
C)deoxyriboguanosine.
D)guanosine.
E)deoxyguanidine.
A)riboguanine.
B)deoxyriboguanine.
C)deoxyriboguanosine.
D)guanosine.
E)deoxyguanidine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The chemical combination of ribose and one of the five nitrogen bases results in formation of a
A)nucleotide.
B)nucleoside.
C)DNA molecule.
D)chromosome.
E)gene.
A)nucleotide.
B)nucleoside.
C)DNA molecule.
D)chromosome.
E)gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Chromatin is
A)nuclear material composed of DNA and histones.
B)the portion of a chromosome that codes for a specific trait.
C)a protein found on the surface of a cell.
D)the fluid part of a cell that surrounds the organelles.
E)a component of cell membranes.
A)nuclear material composed of DNA and histones.
B)the portion of a chromosome that codes for a specific trait.
C)a protein found on the surface of a cell.
D)the fluid part of a cell that surrounds the organelles.
E)a component of cell membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
DNA is primarily located in what part of the cell?
A)cytoplasm
B)mitochondrion
C)nucleus
D)ribosome
E)cell membrane
A)cytoplasm
B)mitochondrion
C)nucleus
D)ribosome
E)cell membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A chromosome is a(an)
A)complex of DNA and histones formed in a cell nucleus before cell division.
B)segment of DNA that directs synthesis of a specific peptide or protein.
C)list of locations of markers that relate to inheritable traits.
D)set of identical copies of DNA segments from a single ancestor.
E)ordered list of the nucleotides in a segment of DNA.
A)complex of DNA and histones formed in a cell nucleus before cell division.
B)segment of DNA that directs synthesis of a specific peptide or protein.
C)list of locations of markers that relate to inheritable traits.
D)set of identical copies of DNA segments from a single ancestor.
E)ordered list of the nucleotides in a segment of DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is a major function of nucleic acids?
A)storage and transfer of genetic information
B)storage and intracellular transfer of energy
C)catalysis of virtually all biochemical reactions
D)structural support in both plants and animals
E)long-term storage of energy
A)storage and transfer of genetic information
B)storage and intracellular transfer of energy
C)catalysis of virtually all biochemical reactions
D)structural support in both plants and animals
E)long-term storage of energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The pyrimidine bases are
A)6 membered ring systems containing 2 ring nitrogens.
B)fused 5 and 6 membered ring systems containing 4 ring nitrogens.
C)6 membered ring systems containing 4 ring nitrogens.
D)fused 5 and 6 membered ring systems containing 2 nitrogens.
E)none of the above
A)6 membered ring systems containing 2 ring nitrogens.
B)fused 5 and 6 membered ring systems containing 4 ring nitrogens.
C)6 membered ring systems containing 4 ring nitrogens.
D)fused 5 and 6 membered ring systems containing 2 nitrogens.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The most characteristic feature of all the bases found in either DNA or RNA is that they
A)are all nitrogen-containing 6 membered ring compounds.
B)are all six membered rings.
C)are all fused five and six membered rings.
D)all bond to the sugar ring through the number 1 carbon of the base.
E)all have at least one carbonyl group attached to the six-membered ring.
A)are all nitrogen-containing 6 membered ring compounds.
B)are all six membered rings.
C)are all fused five and six membered rings.
D)all bond to the sugar ring through the number 1 carbon of the base.
E)all have at least one carbonyl group attached to the six-membered ring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which base is normally found in DNA but not in RNA?
A)thymine
B)adenine
C)guanine
D)uracil
E)cytosine
A)thymine
B)adenine
C)guanine
D)uracil
E)cytosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The initials DNA stand for
A)deribosenucleic acid.
B)deoxyribonucleic acid.
C)deoxyribonuclear acid.
D)deribonucleic acid.
E)none of these
A)deribosenucleic acid.
B)deoxyribonucleic acid.
C)deoxyribonuclear acid.
D)deribonucleic acid.
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What are the repeating units in nucleic acids?
A)monosaccharides
B)amino acids
C)nucleotides
D)nucleosides
E)nitrogen bases
A)monosaccharides
B)amino acids
C)nucleotides
D)nucleosides
E)nitrogen bases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A nucleotide is a(an)
A)amide of a nitrogen base and a fatty acid.
B)amide of a nucleoside and a fatty acid.
C)ester of a nucleoside and a fatty acid.
D)5'-monophosphate ester of a nucleoside.
E)polymer of alternating ribose and purine or pyrimidine units.
A)amide of a nitrogen base and a fatty acid.
B)amide of a nucleoside and a fatty acid.
C)ester of a nucleoside and a fatty acid.
D)5'-monophosphate ester of a nucleoside.
E)polymer of alternating ribose and purine or pyrimidine units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The number of hydrogen bonds between guanine and adenine in DNA is
A)0.
B)1.
C)2.
D)3.
E)4.
A)0.
B)1.
C)2.
D)3.
E)4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A)Identify if the following structure is a nucleotide or a nucleoside.
B)What is the name of this molecule?
C)Label the components.
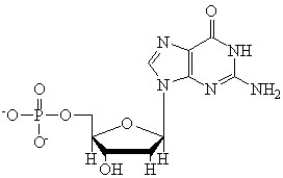
B)What is the name of this molecule?
C)Label the components.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is(are)a pyrmidine base found in nucleic acids?
A)
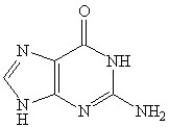
B)
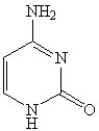
C)
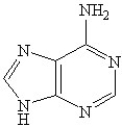
D)
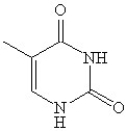
E)B and D
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)B and D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The bonding forces between the two DNA strands in a double helix are
A)polar bonds.
B)peptide linkages.
C)phosphate bonds.
D)hydrogen bonds.
E)ester bonds.
A)polar bonds.
B)peptide linkages.
C)phosphate bonds.
D)hydrogen bonds.
E)ester bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In DNA,a DNA sequence complementary to the strand shown below (reading '3 to 5')is
5' C-G-G-T-T-A-G 3'
A)G-C-C-A-A-T-C.
B)C-G-G-T-T-A-G.
C)A-T-T-G-G-C-T.
D)G-C-C-U-U-U-C.
E)G-C-C-U-U-A-C.
5' C-G-G-T-T-A-G 3'
A)G-C-C-A-A-T-C.
B)C-G-G-T-T-A-G.
C)A-T-T-G-G-C-T.
D)G-C-C-U-U-U-C.
E)G-C-C-U-U-A-C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the name of the base at the 5' end of the sequence G-A-C-T-T-A?
A)adenine
B)thymine
C)cytosine
D)guanine
E)uracil
A)adenine
B)thymine
C)cytosine
D)guanine
E)uracil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The number of hydrogen bonds between cytosine and guanine in DNA is
A)0.
B)1.
C)2.
D)3.
E)4.
A)0.
B)1.
C)2.
D)3.
E)4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the difference between deoxyribose and ribose?
A)Deoxyribose is a d form,whereas ribose is an l form.
B)Deoxyribose has one less oxygen atom than does ribose.
C)Ribose is found in the straight chain structure,whereas deoxyribose is not.
D)Ribose is a monosaccharide,but deoxyribose is a polysaccharide.
E)All statements are incorrect.
A)Deoxyribose is a d form,whereas ribose is an l form.
B)Deoxyribose has one less oxygen atom than does ribose.
C)Ribose is found in the straight chain structure,whereas deoxyribose is not.
D)Ribose is a monosaccharide,but deoxyribose is a polysaccharide.
E)All statements are incorrect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The backbone of a nucleic acid molecule consists of
A)alternating sugar and phosphate groups linked by phosphate ester bonds.
B)alternating sugar and nitrogen base groups linked by amide bonds.
C)alternating nitrogen bases and phosphate groups linked by amide bonds and strengthened by hydrogen bonds.
D)sugar molecules bonded from the #3 carbon of one molecule to the #5 carbon of the other by glycosidic linkages.
E)complementary bases joined by hydrogen bonds.
A)alternating sugar and phosphate groups linked by phosphate ester bonds.
B)alternating sugar and nitrogen base groups linked by amide bonds.
C)alternating nitrogen bases and phosphate groups linked by amide bonds and strengthened by hydrogen bonds.
D)sugar molecules bonded from the #3 carbon of one molecule to the #5 carbon of the other by glycosidic linkages.
E)complementary bases joined by hydrogen bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In a molecule of DNA,the sugar of one nucleotide binds through its ________ hydroxyl group to the ________ hydroxyl group of the next nucleotide by forming a phosphate ester.
A)3';5'
B)3';3'
C)5';5'
D)1';3'
E)1';5'
A)3';5'
B)3';3'
C)5';5'
D)1';3'
E)1';5'

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
One pair of nitrogen bases in DNA is
A)adenine and thymine.
B)adenine and guanine.
C)adenine and uracil.
D)adenine and cytosine.
E)none of the above
A)adenine and thymine.
B)adenine and guanine.
C)adenine and uracil.
D)adenine and cytosine.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Draw the structure for the dCMP nucleotide.Label all parts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
One pair of nitrogen bases in DNA is
A)guanine and adenine.
B)guanine and thymine.
C)guanine and cytosine.
D)guanine and uracil.
E)none of the above
A)guanine and adenine.
B)guanine and thymine.
C)guanine and cytosine.
D)guanine and uracil.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The number of hydrogen bonds between adenine and thymine in DNA is
A)0.
B)1.
C)2.
D)3.
E)4.
A)0.
B)1.
C)2.
D)3.
E)4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which statement does not correctly describe structural differences between DNA and RNA?
A)RNA contains uracil instead of thymine.
B)RNA molecules have a lower molecular mass than DNA molecules.
C)RNA molecules are generally single-stranded.
D)The sugar in RNA has one more hydroxyl group than the sugar in DNA.
E)All of the statements are correct.
A)RNA contains uracil instead of thymine.
B)RNA molecules have a lower molecular mass than DNA molecules.
C)RNA molecules are generally single-stranded.
D)The sugar in RNA has one more hydroxyl group than the sugar in DNA.
E)All of the statements are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is(are)a purine base found in nucleic acids?
A)
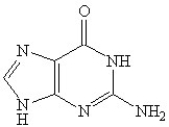
B)
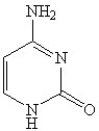
C)
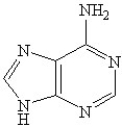
D)
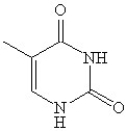
E)A and C
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the name of the base at the 3' end of the sequence G-A-C-T-T-A?
A)adenine
B)thymine
C)cytosine
D)guanine
E)uracil
A)adenine
B)thymine
C)cytosine
D)guanine
E)uracil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the complementary strand for a single DNA strand with the sequence 5' TCGA 3'?
A)3' TGCA 5'
B)3' AGCT 5'
C)3' CTAC 5'
D)3' GATC 5'
E)3' TCGA 5'
A)3' TGCA 5'
B)3' AGCT 5'
C)3' CTAC 5'
D)3' GATC 5'
E)3' TCGA 5'

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Draw the structure for the UMP nucleotide.Label all parts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Draw the full structure of the dinucleotide C-G.Identify the 5' and 3' ends of this dinucleotide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The process in which information contained in RNA is used to manufacture proteins is called
A)mutation.
B)replication.
C)transcription.
D)translation.
E)translocation.
A)mutation.
B)replication.
C)transcription.
D)translation.
E)translocation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Distinguish between the forms of RNA that exist in a typical cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
During the process of transcription,the base adenine in DNA pairs with the base ________ in the new mRNA.
A)guanine
B)thymine
C)cytosine
D)uracil
E)adenine
A)guanine
B)thymine
C)cytosine
D)uracil
E)adenine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The type of nucleic acid that carries the information for protein synthesis from the nucleus to the cytoplasm is
A)DNA.
B)mRNA.
C)rRNA.
D)tRNA.
E)RNA.
A)DNA.
B)mRNA.
C)rRNA.
D)tRNA.
E)RNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Draw the structure illustrating the hydrogen bonding that occurs between the base pairs cytosine and guanine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Explain the term base pairing and its relationship to replication of DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In replication of DNA,each new double strand consists of one template strand and one new strand.Therefore,replication is said to be
A)repetitive.
B)semiconservative.
C)polymeric.
D)catabolic.
E)none of these
A)repetitive.
B)semiconservative.
C)polymeric.
D)catabolic.
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The type of nucleic acid that carries the amino acids to the protein chain that is growing in the ribosome is called
A)DNA.
B)mRNA.
C)rRNA.
D)tRNA.
E)RNA.
A)DNA.
B)mRNA.
C)rRNA.
D)tRNA.
E)RNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Replication of DNA produces two daughter DNA molecules in which
A)one daughter molecule contains both parent strands and one daughter molecule contains both newly synthesized strands.
B)each daughter molecule contains one parent strand and one newly synthesized strand.
C)each daughter molecule contains two newly synthesized strands.
D)each daughter molecule contains both parent strand.
E)None of the above happens during replication.
A)one daughter molecule contains both parent strands and one daughter molecule contains both newly synthesized strands.
B)each daughter molecule contains one parent strand and one newly synthesized strand.
C)each daughter molecule contains two newly synthesized strands.
D)each daughter molecule contains both parent strand.
E)None of the above happens during replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
All of the statements about RNA are correct except
A)RNA can exist in three forms: rRNA,tRNA,and mRNA.
B)RNA molecules are smaller than DNA molecules,but form double helices like DNA.
C)RNA does not contain thymine.
D)transfer RNA delivers amino acids to the protein chain as it is being manufactured.
E)messenger RNA is complementary to the template strand of its DNA,and almost identical to the informational strand of the DNA.
A)RNA can exist in three forms: rRNA,tRNA,and mRNA.
B)RNA molecules are smaller than DNA molecules,but form double helices like DNA.
C)RNA does not contain thymine.
D)transfer RNA delivers amino acids to the protein chain as it is being manufactured.
E)messenger RNA is complementary to the template strand of its DNA,and almost identical to the informational strand of the DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The number of hydrogen bonds between cytosine and thymine in DNA is
A)0.
B)1.
C)2.
D)3.
E)4.
A)0.
B)1.
C)2.
D)3.
E)4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
rRNA is associated with what part of the cell?
A)cytoplasm
B)mitochondrion
C)nucleus
D)ribosome
E)cell membrane
A)cytoplasm
B)mitochondrion
C)nucleus
D)ribosome
E)cell membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
RNA differs from DNA in that
A)it is single stranded.
B)the sugar is ribose.
C)there are three types of RNA.
D)thymine is replaced by uracil.
E)all of the above
A)it is single stranded.
B)the sugar is ribose.
C)there are three types of RNA.
D)thymine is replaced by uracil.
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The enzyme involved in catalyzing the 5' phosphate reaction with the 3' hydroxyl group of the incoming base is called
A)DNA ligase.
B)DNA polymerase.
C)DNA gyrase.
D)helicase.
E)none of the above
A)DNA ligase.
B)DNA polymerase.
C)DNA gyrase.
D)helicase.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The process of manufacturing an identical copy of a DNA molecule is called
A)mutation.
B)replication.
C)transcription.
D)translation.
E)translocation.
A)mutation.
B)replication.
C)transcription.
D)translation.
E)translocation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
All of the following are associated with replication of DNA except
A)DNA polymerase.
B)DNA ligase.
C)hydrogen bonds.
D)replication fork.
E)amino acids.
A)DNA polymerase.
B)DNA ligase.
C)hydrogen bonds.
D)replication fork.
E)amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The process in which information from DNA is used to manufacture RNA is called
A)mutation.
B)replication.
C)transcription.
D)translation.
E)translocation.
A)mutation.
B)replication.
C)transcription.
D)translation.
E)translocation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Transcription is
A)copying of DNA molecules to make an exact duplicate.
B)production of a single strand of RNA identical to the information strand of DNA.
C)production of a single strand of RNA from the template strand of DNA.
D)making a protein molecule based on information contained in RNA.
E)breakdown of damaged nucleic acids to prevent mutations.
A)copying of DNA molecules to make an exact duplicate.
B)production of a single strand of RNA identical to the information strand of DNA.
C)production of a single strand of RNA from the template strand of DNA.
D)making a protein molecule based on information contained in RNA.
E)breakdown of damaged nucleic acids to prevent mutations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The central belief of molecular genetics states that
A)every copy of DNA is an exact replica of the parent molecule.
B)DNA stores genetic information and RNA reads,decodes,and uses that information.
C)in DNA and RNA adenine always pairs with thymine and cytosine always pairs with guanine.
D)each amino acid is coded by a unique set of three base pairs.
E)replication of DNA is a semiconservative process.
A)every copy of DNA is an exact replica of the parent molecule.
B)DNA stores genetic information and RNA reads,decodes,and uses that information.
C)in DNA and RNA adenine always pairs with thymine and cytosine always pairs with guanine.
D)each amino acid is coded by a unique set of three base pairs.
E)replication of DNA is a semiconservative process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When a new strand of RNA is transcribed from the DNA strand shown,its base sequence will be
Informational strand of DNA: 5' TTACGGAT 3'
Template strand of DNA: 3' AATGCCTA 5'
A)5' TTACGGAT 3'.
B)5' AATGCCTA 3'.
C)5' UUACGGAU 3'.
D)5' AAUGCCUA 3'.
E)5' UUTGCCTU 3'.
Informational strand of DNA: 5' TTACGGAT 3'
Template strand of DNA: 3' AATGCCTA 5'
A)5' TTACGGAT 3'.
B)5' AATGCCTA 3'.
C)5' UUACGGAU 3'.
D)5' AAUGCCUA 3'.
E)5' UUTGCCTU 3'.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match the following.
pyrimidine bases
A)a group of three nucleotides in RNA that code for specific amino acids or for termination of the protein chain
B)the type of ribonucleic acid that is part of the ribosome and protein complex that synthesizes other proteins
C)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose,one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids,and one or more phosphate groups
D)the sequence of nucleotides that specifies sequences of amino acids in protein synthesis
E)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose and one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids
F)the ribonucleic acid whose function is to deliver the amino acids into position for protein synthesis
G)one of three specific bases consisting of a heterocyclic ring with various substituted functional groups and found in DNA and RNA
H)one of two specific bases consisting of two interlocked heterocyclic rings and found in DNA and RNA
I)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule
J)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule fused with a 5-membered heterocyclic molecule
K)the ribonucleic acid that carries the code transcribed from DNA and directs protein synthesis
pyrimidine bases
A)a group of three nucleotides in RNA that code for specific amino acids or for termination of the protein chain
B)the type of ribonucleic acid that is part of the ribosome and protein complex that synthesizes other proteins
C)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose,one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids,and one or more phosphate groups
D)the sequence of nucleotides that specifies sequences of amino acids in protein synthesis
E)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose and one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids
F)the ribonucleic acid whose function is to deliver the amino acids into position for protein synthesis
G)one of three specific bases consisting of a heterocyclic ring with various substituted functional groups and found in DNA and RNA
H)one of two specific bases consisting of two interlocked heterocyclic rings and found in DNA and RNA
I)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule
J)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule fused with a 5-membered heterocyclic molecule
K)the ribonucleic acid that carries the code transcribed from DNA and directs protein synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match the following.
nucleoside
A)a group of three nucleotides in RNA that code for specific amino acids or for termination of the protein chain
B)the type of ribonucleic acid that is part of the ribosome and protein complex that synthesizes other proteins
C)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose,one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids,and one or more phosphate groups
D)the sequence of nucleotides that specifies sequences of amino acids in protein synthesis
E)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose and one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids
F)the ribonucleic acid whose function is to deliver the amino acids into position for protein synthesis
G)one of three specific bases consisting of a heterocyclic ring with various substituted functional groups and found in DNA and RNA
H)one of two specific bases consisting of two interlocked heterocyclic rings and found in DNA and RNA
I)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule
J)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule fused with a 5-membered heterocyclic molecule
K)the ribonucleic acid that carries the code transcribed from DNA and directs protein synthesis
nucleoside
A)a group of three nucleotides in RNA that code for specific amino acids or for termination of the protein chain
B)the type of ribonucleic acid that is part of the ribosome and protein complex that synthesizes other proteins
C)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose,one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids,and one or more phosphate groups
D)the sequence of nucleotides that specifies sequences of amino acids in protein synthesis
E)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose and one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids
F)the ribonucleic acid whose function is to deliver the amino acids into position for protein synthesis
G)one of three specific bases consisting of a heterocyclic ring with various substituted functional groups and found in DNA and RNA
H)one of two specific bases consisting of two interlocked heterocyclic rings and found in DNA and RNA
I)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule
J)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule fused with a 5-membered heterocyclic molecule
K)the ribonucleic acid that carries the code transcribed from DNA and directs protein synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Match the following.
nucleotide
A)a group of three nucleotides in RNA that code for specific amino acids or for termination of the protein chain
B)the type of ribonucleic acid that is part of the ribosome and protein complex that synthesizes other proteins
C)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose,one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids,and one or more phosphate groups
D)the sequence of nucleotides that specifies sequences of amino acids in protein synthesis
E)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose and one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids
F)the ribonucleic acid whose function is to deliver the amino acids into position for protein synthesis
G)one of three specific bases consisting of a heterocyclic ring with various substituted functional groups and found in DNA and RNA
H)one of two specific bases consisting of two interlocked heterocyclic rings and found in DNA and RNA
I)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule
J)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule fused with a 5-membered heterocyclic molecule
K)the ribonucleic acid that carries the code transcribed from DNA and directs protein synthesis
nucleotide
A)a group of three nucleotides in RNA that code for specific amino acids or for termination of the protein chain
B)the type of ribonucleic acid that is part of the ribosome and protein complex that synthesizes other proteins
C)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose,one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids,and one or more phosphate groups
D)the sequence of nucleotides that specifies sequences of amino acids in protein synthesis
E)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose and one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids
F)the ribonucleic acid whose function is to deliver the amino acids into position for protein synthesis
G)one of three specific bases consisting of a heterocyclic ring with various substituted functional groups and found in DNA and RNA
H)one of two specific bases consisting of two interlocked heterocyclic rings and found in DNA and RNA
I)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule
J)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule fused with a 5-membered heterocyclic molecule
K)the ribonucleic acid that carries the code transcribed from DNA and directs protein synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Match the following.
purine
A)a group of three nucleotides in RNA that code for specific amino acids or for termination of the protein chain
B)the type of ribonucleic acid that is part of the ribosome and protein complex that synthesizes other proteins
C)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose,one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids,and one or more phosphate groups
D)the sequence of nucleotides that specifies sequences of amino acids in protein synthesis
E)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose and one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids
F)the ribonucleic acid whose function is to deliver the amino acids into position for protein synthesis
G)one of three specific bases consisting of a heterocyclic ring with various substituted functional groups and found in DNA and RNA
H)one of two specific bases consisting of two interlocked heterocyclic rings and found in DNA and RNA
I)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule
J)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule fused with a 5-membered heterocyclic molecule
K)the ribonucleic acid that carries the code transcribed from DNA and directs protein synthesis
purine
A)a group of three nucleotides in RNA that code for specific amino acids or for termination of the protein chain
B)the type of ribonucleic acid that is part of the ribosome and protein complex that synthesizes other proteins
C)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose,one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids,and one or more phosphate groups
D)the sequence of nucleotides that specifies sequences of amino acids in protein synthesis
E)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose and one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids
F)the ribonucleic acid whose function is to deliver the amino acids into position for protein synthesis
G)one of three specific bases consisting of a heterocyclic ring with various substituted functional groups and found in DNA and RNA
H)one of two specific bases consisting of two interlocked heterocyclic rings and found in DNA and RNA
I)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule
J)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule fused with a 5-membered heterocyclic molecule
K)the ribonucleic acid that carries the code transcribed from DNA and directs protein synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following represents the correct order in the flow of genetic information?
A)tRNA → DNA → proteins
B)mRNA → tRNA → proteins
C)DNA → mRNA → proteins
D)rRNA → mRNA → proteins
E)DNA → tRNA → mRNA
A)tRNA → DNA → proteins
B)mRNA → tRNA → proteins
C)DNA → mRNA → proteins
D)rRNA → mRNA → proteins
E)DNA → tRNA → mRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The nucleotide sequence of a gene that codes for the protein of interest is called a(n)
A)intron.
B)exon.
C)heterogenous nuclear RNA.
D)gene.
A)intron.
B)exon.
C)heterogenous nuclear RNA.
D)gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The nucleotide sequence in the mRNA that does not code for part of a protein is a(n)
A)intron.
B)exon.
C)heterogenous nuclear RNA.
D)gene.
A)intron.
B)exon.
C)heterogenous nuclear RNA.
D)gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Transcription and translation of the mRNA involved in protein synthesis occur in two different locations in the cell.Translation occurs in the
A)nucleus.
B)mitochondria.
C)cytoplasm.
D)cell's membrane.
A)nucleus.
B)mitochondria.
C)cytoplasm.
D)cell's membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Match the following.
pyrimidine
A)a group of three nucleotides in RNA that code for specific amino acids or for termination of the protein chain
B)the type of ribonucleic acid that is part of the ribosome and protein complex that synthesizes other proteins
C)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose,one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids,and one or more phosphate groups
D)the sequence of nucleotides that specifies sequences of amino acids in protein synthesis
E)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose and one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids
F)the ribonucleic acid whose function is to deliver the amino acids into position for protein synthesis
G)one of three specific bases consisting of a heterocyclic ring with various substituted functional groups and found in DNA and RNA
H)one of two specific bases consisting of two interlocked heterocyclic rings and found in DNA and RNA
I)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule
J)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule fused with a 5-membered heterocyclic molecule
K)the ribonucleic acid that carries the code transcribed from DNA and directs protein synthesis
pyrimidine
A)a group of three nucleotides in RNA that code for specific amino acids or for termination of the protein chain
B)the type of ribonucleic acid that is part of the ribosome and protein complex that synthesizes other proteins
C)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose,one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids,and one or more phosphate groups
D)the sequence of nucleotides that specifies sequences of amino acids in protein synthesis
E)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose and one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids
F)the ribonucleic acid whose function is to deliver the amino acids into position for protein synthesis
G)one of three specific bases consisting of a heterocyclic ring with various substituted functional groups and found in DNA and RNA
H)one of two specific bases consisting of two interlocked heterocyclic rings and found in DNA and RNA
I)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule
J)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule fused with a 5-membered heterocyclic molecule
K)the ribonucleic acid that carries the code transcribed from DNA and directs protein synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Translation is
A)copying of DNA molecules to make an exact duplicate.
B)production of a single strand of RNA identical to the information strand of DNA.
C)production of a single strand of RNA from the template strand of DNA.
D)making a protein molecule based on information contained in RNA.
E)breakdown of damaged nucleic acids to prevent mutations.
A)copying of DNA molecules to make an exact duplicate.
B)production of a single strand of RNA identical to the information strand of DNA.
C)production of a single strand of RNA from the template strand of DNA.
D)making a protein molecule based on information contained in RNA.
E)breakdown of damaged nucleic acids to prevent mutations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The introns are removed from the mRNA by the action of a(n)
A)polymerase.
B)gyrase.
C)spliceosome.
D)ligase.
A)polymerase.
B)gyrase.
C)spliceosome.
D)ligase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following codons signals the end of translation?
A)CAG
B)UAA
C)UCA
D)GUA
E)UGC
A)CAG
B)UAA
C)UCA
D)GUA
E)UGC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which nucleic acid carries the codon for protein synthesis?
A)DNA
B)rRNA
C)tRNA
D)mRNA
A)DNA
B)rRNA
C)tRNA
D)mRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Match the following.
purine bases
A)a group of three nucleotides in RNA that code for specific amino acids or for termination of the protein chain
B)the type of ribonucleic acid that is part of the ribosome and protein complex that synthesizes other proteins
C)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose,one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids,and one or more phosphate groups
D)the sequence of nucleotides that specifies sequences of amino acids in protein synthesis
E)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose and one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids
F)the ribonucleic acid whose function is to deliver the amino acids into position for protein synthesis
G)one of three specific bases consisting of a heterocyclic ring with various substituted functional groups and found in DNA and RNA
H)one of two specific bases consisting of two interlocked heterocyclic rings and found in DNA and RNA
I)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule
J)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule fused with a 5-membered heterocyclic molecule
K)the ribonucleic acid that carries the code transcribed from DNA and directs protein synthesis
purine bases
A)a group of three nucleotides in RNA that code for specific amino acids or for termination of the protein chain
B)the type of ribonucleic acid that is part of the ribosome and protein complex that synthesizes other proteins
C)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose,one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids,and one or more phosphate groups
D)the sequence of nucleotides that specifies sequences of amino acids in protein synthesis
E)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose and one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids
F)the ribonucleic acid whose function is to deliver the amino acids into position for protein synthesis
G)one of three specific bases consisting of a heterocyclic ring with various substituted functional groups and found in DNA and RNA
H)one of two specific bases consisting of two interlocked heterocyclic rings and found in DNA and RNA
I)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule
J)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule fused with a 5-membered heterocyclic molecule
K)the ribonucleic acid that carries the code transcribed from DNA and directs protein synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Match the following.
tRNA
A)a group of three nucleotides in RNA that code for specific amino acids or for termination of the protein chain
B)the type of ribonucleic acid that is part of the ribosome and protein complex that synthesizes other proteins
C)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose,one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids,and one or more phosphate groups
D)the sequence of nucleotides that specifies sequences of amino acids in protein synthesis
E)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose and one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids
F)the ribonucleic acid whose function is to deliver the amino acids into position for protein synthesis
G)one of three specific bases consisting of a heterocyclic ring with various substituted functional groups and found in DNA and RNA
H)one of two specific bases consisting of two interlocked heterocyclic rings and found in DNA and RNA
I)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule
J)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule fused with a 5-membered heterocyclic molecule
K)the ribonucleic acid that carries the code transcribed from DNA and directs protein synthesis
tRNA
A)a group of three nucleotides in RNA that code for specific amino acids or for termination of the protein chain
B)the type of ribonucleic acid that is part of the ribosome and protein complex that synthesizes other proteins
C)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose,one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids,and one or more phosphate groups
D)the sequence of nucleotides that specifies sequences of amino acids in protein synthesis
E)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose and one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids
F)the ribonucleic acid whose function is to deliver the amino acids into position for protein synthesis
G)one of three specific bases consisting of a heterocyclic ring with various substituted functional groups and found in DNA and RNA
H)one of two specific bases consisting of two interlocked heterocyclic rings and found in DNA and RNA
I)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule
J)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule fused with a 5-membered heterocyclic molecule
K)the ribonucleic acid that carries the code transcribed from DNA and directs protein synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
After initiation of protein production,the correct order for the steps in the manufacture of proteins is
I.elongation
II.peptide bond formation
III.termination
IV.tRNA binding with ribosome
A)I,II,III,IV
B)I,IV,II,III
C)IV,II,I,III
D)IV,I,II,III
E)II,I,IV,III
I.elongation
II.peptide bond formation
III.termination
IV.tRNA binding with ribosome
A)I,II,III,IV
B)I,IV,II,III
C)IV,II,I,III
D)IV,I,II,III
E)II,I,IV,III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Match the following.
mRNA
A)a group of three nucleotides in RNA that code for specific amino acids or for termination of the protein chain
B)the type of ribonucleic acid that is part of the ribosome and protein complex that synthesizes other proteins
C)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose,one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids,and one or more phosphate groups
D)the sequence of nucleotides that specifies sequences of amino acids in protein synthesis
E)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose and one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids
F)the ribonucleic acid whose function is to deliver the amino acids into position for protein synthesis
G)one of three specific bases consisting of a heterocyclic ring with various substituted functional groups and found in DNA and RNA
H)one of two specific bases consisting of two interlocked heterocyclic rings and found in DNA and RNA
I)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule
J)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule fused with a 5-membered heterocyclic molecule
K)the ribonucleic acid that carries the code transcribed from DNA and directs protein synthesis
mRNA
A)a group of three nucleotides in RNA that code for specific amino acids or for termination of the protein chain
B)the type of ribonucleic acid that is part of the ribosome and protein complex that synthesizes other proteins
C)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose,one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids,and one or more phosphate groups
D)the sequence of nucleotides that specifies sequences of amino acids in protein synthesis
E)a specific chemical combination of ribose or deoxyribose and one of the five purine or pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids
F)the ribonucleic acid whose function is to deliver the amino acids into position for protein synthesis
G)one of three specific bases consisting of a heterocyclic ring with various substituted functional groups and found in DNA and RNA
H)one of two specific bases consisting of two interlocked heterocyclic rings and found in DNA and RNA
I)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule
J)a category of base found in nucleic acids consisting of a 6-membered heterocyclic molecule fused with a 5-membered heterocyclic molecule
K)the ribonucleic acid that carries the code transcribed from DNA and directs protein synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Codons provide the information needed to synthesize
A)nucleic acids.
B)carbohydrates.
C)lipids.
D)proteins.
A)nucleic acids.
B)carbohydrates.
C)lipids.
D)proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A codon is
A)a sequence of three amino acids that translates to a specific nucleotide in RNA.
B)a complex of proteins and DNA which is associated with cell division.
C)all the segments of DNA needed to direct the production of a specific protein.
D)a sequence of three nucleotides in RNA that codes for a specific amino acid or for chain termination.
E)the collection of DNA that stores all the genetic information for an individual organism.
A)a sequence of three amino acids that translates to a specific nucleotide in RNA.
B)a complex of proteins and DNA which is associated with cell division.
C)all the segments of DNA needed to direct the production of a specific protein.
D)a sequence of three nucleotides in RNA that codes for a specific amino acid or for chain termination.
E)the collection of DNA that stores all the genetic information for an individual organism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
How many three letter combinations are there present in the genetic code?
A)32
B)64
C)16
D)88
A)32
B)64
C)16
D)88

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



