Deck 25: DNA Structure and Gene Expression
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/93
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: DNA Structure and Gene Expression
1
If a species contains 23% A in its DNA,what is the percentage of guanine it would contain?
A)23%
B)46%
C)25%
D)44%
E)27%
A) 23%
B) 46%
C)
C) 25%
C) So, if the DNA is 23% A it is also 23% for a total of 46%. This means that the other 54% is composed of G and C in equal amounts. This means that 27% is G and 27% is
A)23%
B)46%
C)25%
D)44%
E)27%
A) 23%
B) 46%
C)
C) 25%
C) So, if the DNA is 23% A it is also 23% for a total of 46%. This means that the other 54% is composed of G and C in equal amounts. This means that 27% is G and 27% is
E
2
In semi-conservative DNA replication,each new double helix formed will have
A) two new strands and two old strands.
B) one new and one old strand in each helix.
C) three new strands in one helix and three old strands in the second helix.
D) two new and one old strand in one helix and two old and one new strand in second helix.
E) two new strands in one helix and two old strands in the other helix.
A) two new strands and two old strands.
B) one new and one old strand in each helix.
C) three new strands in one helix and three old strands in the second helix.
D) two new and one old strand in one helix and two old and one new strand in second helix.
E) two new strands in one helix and two old strands in the other helix.
B
Explanation: The term semi-conservative replication is used to describe the replication of DNA since each newly made DNA molecule is composed of one strand that serves as the template and one strand that has been newly formed by DNA polymerase. Thus every molecule of DNA is one half parent DNA and one half newly made strand.Bloom's
Explanation: The term semi-conservative replication is used to describe the replication of DNA since each newly made DNA molecule is composed of one strand that serves as the template and one strand that has been newly formed by DNA polymerase. Thus every molecule of DNA is one half parent DNA and one half newly made strand.Bloom's
3
Chargaff's rules of DNA structure states that
A)A + T = G + C.
B)A + G = T + C.
C)A = C,T = G.
D)A = G,T = C.
E)the number of purines in DNA never equals the number of pyrimidines.
A)A + T = G + C.
B)A + G = T + C.
C)A = C,T = G.
D)A = G,T = C.
E)the number of purines in DNA never equals the number of pyrimidines.
B
Explanation: Erwin Chargaff determined that the amount of adenine equals the amount of thymine (A = T), and the amount of guanine equals the amount of cytosine (G = C). These findings came to be known as Chargaff's rules.Bloom's
Explanation: Erwin Chargaff determined that the amount of adenine equals the amount of thymine (A = T), and the amount of guanine equals the amount of cytosine (G = C). These findings came to be known as Chargaff's rules.Bloom's
4
Which of the following statements about DNA replication is NOT correct?
A) Unwinding of the DNA molecule occurs as hydrogen bonds break.
B) Replication occurs as each base is paired with another exactly like it.
C) The process is known as semi-conservative replication because one old strand is conserved in the new molecule.
D) The enzyme that catalyzes DNA replication is DNA polymerase.
E) Complementary base pairs are held together with hydrogen bonds.
A) Unwinding of the DNA molecule occurs as hydrogen bonds break.
B) Replication occurs as each base is paired with another exactly like it.
C) The process is known as semi-conservative replication because one old strand is conserved in the new molecule.
D) The enzyme that catalyzes DNA replication is DNA polymerase.
E) Complementary base pairs are held together with hydrogen bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The amount of adenine is always equal to the amount of ____ in DNA.
A) cytosine
B) uracil
C) guanine
D) thymine
E) ATP
A) cytosine
B) uracil
C) guanine
D) thymine
E) ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which does NOT describe a function of the DNA polymerase molecule?
A) recognize the free nucleotide that pairs with the base on the old strand of DNA
B) read the strand of old DNA and recognize the base there
C) proofread to ensure that the proper base has been incorporated
D) make the proper nucleotide to match with the base read on the old strand
E) nucleotides are joined by hydrogen bonds
A) recognize the free nucleotide that pairs with the base on the old strand of DNA
B) read the strand of old DNA and recognize the base there
C) proofread to ensure that the proper base has been incorporated
D) make the proper nucleotide to match with the base read on the old strand
E) nucleotides are joined by hydrogen bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which statement is NOT correct about the results of the Hershey-Chase experiment with the T2 virus?
A) Radioactively labeled protein was found in the bacteria, not in the virus coats.
B) Radioactively labeled DNA was found in the bacteria, not in the virus coats.
C) DNA was labeled with radioactive phosphorus.
D) Protein was labeled with radioactive sulfur.
E) Two separate experiments were actually run, one with radioactive phosphorus and one with radioactive sulfur.
A) Radioactively labeled protein was found in the bacteria, not in the virus coats.
B) Radioactively labeled DNA was found in the bacteria, not in the virus coats.
C) DNA was labeled with radioactive phosphorus.
D) Protein was labeled with radioactive sulfur.
E) Two separate experiments were actually run, one with radioactive phosphorus and one with radioactive sulfur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The enzyme that is used to join complementary DNA nucleotides together is
A) DNA polymerase.
B) RNA polymerase.
C) helicase.
D) ribozyme.
E) lipase.
A) DNA polymerase.
B) RNA polymerase.
C) helicase.
D) ribozyme.
E) lipase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is NOT true about DNA?
A) has a double helix
B) bases held together by hydrogen bonds
C) bases are complementary to each other
D) has a deoxyribose sugar
E) contains adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil
A) has a double helix
B) bases held together by hydrogen bonds
C) bases are complementary to each other
D) has a deoxyribose sugar
E) contains adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The X-ray diffraction photography of Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins was critical evidence
A) indicating that DNA has a double helix structure.
B) showing the bases of DNA were held together by hydrogen bonds.
C) showing equal numbers of purines and pyrimidines.
D) revealing the structure of the deoxyribose sugar.
E) of the location of each adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine.
A) indicating that DNA has a double helix structure.
B) showing the bases of DNA were held together by hydrogen bonds.
C) showing equal numbers of purines and pyrimidines.
D) revealing the structure of the deoxyribose sugar.
E) of the location of each adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the Watson-Crick model of DNA,the "sides" of the ladder are composed of
A) sugars.
B) bases.
C) hydrogen bonds.
D) sugar-phosphate molecules.
E) phosphate groups.
A) sugars.
B) bases.
C) hydrogen bonds.
D) sugar-phosphate molecules.
E) phosphate groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Information from X-ray crystallographic data collected by _______ was used by Watson and Crick in their development of the model of DNA.
A) Chargaff
B) Griffith
C) McClintock
D) Franklin
E) Hershey and Chase
A) Chargaff
B) Griffith
C) McClintock
D) Franklin
E) Hershey and Chase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The individual(s)credited with the discovery of the structure of DNA is (are)
A) Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase.
B) James Watson and Francis Crick.
C) Erwin Chargaff.
D) Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins.
E) Charles Darwin and Gregor Mendel.
A) Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase.
B) James Watson and Francis Crick.
C) Erwin Chargaff.
D) Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins.
E) Charles Darwin and Gregor Mendel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Hershey and Chase experimented with radioactively labeled phosphorus and sulfur to determine that DNA and not protein is the genetic material.Which of the following would NOT be an essential part of this experiment?
A) Sulfur is present in amino acids in the protein coat of bacteria.
B) Phosphorus is present in high amounts in DNA.
C) Sulfur is not present in DNA.
D) Phosphorus is not present in amino acids in the protein coat of bacteria.
E) DNA contains nitrogen.
A) Sulfur is present in amino acids in the protein coat of bacteria.
B) Phosphorus is present in high amounts in DNA.
C) Sulfur is not present in DNA.
D) Phosphorus is not present in amino acids in the protein coat of bacteria.
E) DNA contains nitrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If the protein coat of a virus that infects a bacterium is labeled with radioactive sulfur and the DNA of the virus is labeled with radioactive phosphorus,over time
A) both the sulfur and the phosphorus will be found within the bacterium.
B) only the sulfur will be found inside the bacterium.
C) only the phosphorus will be found inside the bacterium.
D) both the sulfur and the phosphorus will be found outside the bacterium.
E) the radioactivity of the sulfur and phosphorus will decay very quickly and not be detectable.
A) both the sulfur and the phosphorus will be found within the bacterium.
B) only the sulfur will be found inside the bacterium.
C) only the phosphorus will be found inside the bacterium.
D) both the sulfur and the phosphorus will be found outside the bacterium.
E) the radioactivity of the sulfur and phosphorus will decay very quickly and not be detectable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Because one original strand of the double-stranded helix is found in each daughter cell,the replication process is called
A) proofreading.
B) semi-conservative.
C) redundant.
D) freeing of DNA.
E) mutation positive.
A) proofreading.
B) semi-conservative.
C) redundant.
D) freeing of DNA.
E) mutation positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The hereditary material found in all cells is
A) DNA.
B) rRNA.
C) mRNA.
D) tRNA.
E) ATP.
A) DNA.
B) rRNA.
C) mRNA.
D) tRNA.
E) ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following have nitrogenous bases correctly paired in DNA?
A)adenine-guanine; thymine-cytosine
B)adenine-uracil; guanine-cytosine
C)adenine-thymine; guanine-cytosine
D)adenine-adenine; guanine-guanine
E)adenine-cytosine; guanine-thymine
A) adenine-guanine; thymine-cytosine
B) adenine-uracil; guanine-cytosine
C) adenine-thymine; guanine-cytosine
D) adenine-adenine; guanine-guanine
E) adenine-cytosine; guanine-thymine Since the amount of adenine (A) equals the amount of thymine (T) and the amount of guanine (G) equals the amount of cytosine (C) this means that A must pair with T and C with
A)adenine-guanine; thymine-cytosine
B)adenine-uracil; guanine-cytosine
C)adenine-thymine; guanine-cytosine
D)adenine-adenine; guanine-guanine
E)adenine-cytosine; guanine-thymine
A) adenine-guanine; thymine-cytosine
B) adenine-uracil; guanine-cytosine
C) adenine-thymine; guanine-cytosine
D) adenine-adenine; guanine-guanine
E) adenine-cytosine; guanine-thymine Since the amount of adenine (A) equals the amount of thymine (T) and the amount of guanine (G) equals the amount of cytosine (C) this means that A must pair with T and C with

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A nucleotide contains
A) DNA and RNA.
B) a sugar and a phosphate.
C) complementary purines and pyrimidines.
D) RNA, protein, and lipids.
E) a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogen base.
A) DNA and RNA.
B) a sugar and a phosphate.
C) complementary purines and pyrimidines.
D) RNA, protein, and lipids.
E) a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogen base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The fact that for a given species the amount of purines in the DNA always matches the number of pyrimidines was first determined by
A) Watson and Crick.
B) Franklin and Wilkins.
C) Hershey and Chase.
D) Chargaff.
E) Mendel.
A) Watson and Crick.
B) Franklin and Wilkins.
C) Hershey and Chase.
D) Chargaff.
E) Mendel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the classes of RNA molecules carries the genetic information as it is needed for the construction of a protein?
A) ribosomal RNA
B) transfer RNA
C) messenger RNA
D) primary mRNA transcript
E) mature RNA
A) ribosomal RNA
B) transfer RNA
C) messenger RNA
D) primary mRNA transcript
E) mature RNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
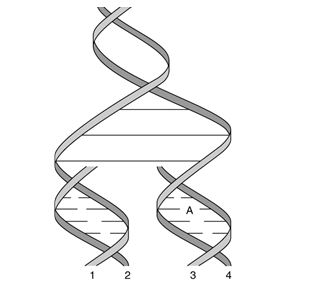
In Figure 25.4,when replication is finished,strand 1 will have the same base composition as strand ___ while strand 2 will have the same base composition as strand ____.
A) 2; 3
B) 1; 3
C) 3; 4
D) 1; 4
E) 2; 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Transcription of part of a DNA molecule with a nucleotide sequence of AAACAACTT results in a mRNA molecule with the complementary sequence of
A)GGGAGAACC.
B)UUUGUUGAA.
C)TTTGAAGCC.
D)CCCACCTCC.
E)AAACAACTT.
A)GGGAGAACC.
B)UUUGUUGAA.
C)TTTGAAGCC.
D)CCCACCTCC.
E)AAACAACTT.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The function of transfer RNA is to
A) carry amino acids to ribosomes.
B) transfer nucleotides to the nucleus.
C) transmit coded information to the cytoplasm.
D) turn DNA on and off.
E) act as the site for protein synthesis.
A) carry amino acids to ribosomes.
B) transfer nucleotides to the nucleus.
C) transmit coded information to the cytoplasm.
D) turn DNA on and off.
E) act as the site for protein synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An intervening sequence of DNA that is not expressed is called a(n)
A) exon.
B) intron.
C) replicon.
D) promoter.
E) gene.
A) exon.
B) intron.
C) replicon.
D) promoter.
E) gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The ______ contain(s)the information for the structure of the protein.
A) introns
B) exons
C) promoter
D) ribosomes
E) nucleoli
A) introns
B) exons
C) promoter
D) ribosomes
E) nucleoli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A gene is physically located on the _____ of the cell.
A) DNA
B) messenger RNA
C) enzymes
D) proteins
E) nucleus
A) DNA
B) messenger RNA
C) enzymes
D) proteins
E) nucleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Prior to protein synthesis,the DNA
A) attracts tRNAs with appropriate amino acids.
B) serves as a template for the production of mRNA.
C) adheres to ribosomes for protein synthesis.
D) contains anticodons that become codons.
E) must first undergo replication.
A) attracts tRNAs with appropriate amino acids.
B) serves as a template for the production of mRNA.
C) adheres to ribosomes for protein synthesis.
D) contains anticodons that become codons.
E) must first undergo replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following nucleotide bases is found only in RNA,not in DNA?
A) guanine
B) adenine
C) thymine
D) uracil
E) cytosine
A) guanine
B) adenine
C) thymine
D) uracil
E) cytosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is NOT true about RNA?
A) RNA transfers messages from DNA to ribosomes.
B) RNA contains the sugar ribose.
C) RNA contains adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine.
D) RNA is single stranded.
E) RNA forms a helix.
A) RNA transfers messages from DNA to ribosomes.
B) RNA contains the sugar ribose.
C) RNA contains adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine.
D) RNA is single stranded.
E) RNA forms a helix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The _____ enzyme is responsible for unwinding the double-helix structure of DNA during replication.
A) helicase
B) polymerase
C) ligase
D) extendase
E) windase
A) helicase
B) polymerase
C) ligase
D) extendase
E) windase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the classes of RNA molecules carries the amino acids that are added to the growing polypeptide chain?
A) ribosomal RNA
B) transfer RNA
C) messenger RNA
D) primary mRNA transcript
E) ribozyme
A) ribosomal RNA
B) transfer RNA
C) messenger RNA
D) primary mRNA transcript
E) ribozyme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In modern biochemical genetics,the flow of inherited information is from
A) protein RNA DNA.
B) DNA RNA protein.
C) DNA protein RNA.
D) RNA DNA protein.
E) RNA protein DNA.
A) protein RNA DNA.
B) DNA RNA protein.
C) DNA protein RNA.
D) RNA DNA protein.
E) RNA protein DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
During the process of transcription,the information in
A) a protein is converted into RNA information.
B) RNA is converted into protein information.
C) RNA is converted into DNA information.
D) DNA is converted into RNA information.
E) DNA is converted into protein information.
A) a protein is converted into RNA information.
B) RNA is converted into protein information.
C) RNA is converted into DNA information.
D) DNA is converted into RNA information.
E) DNA is converted into protein information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Artificial RNA with a known base sequence was added to a medium containing bacterial ribosomes and a mixture of amino acids.By chemical identification of the resulting polypeptide,researchers could discover the
A) transcription factors involved.
B) mutation rate.
C) codon.
D) Chargaff rule.
E) difference between DNA and RNA.
A) transcription factors involved.
B) mutation rate.
C) codon.
D) Chargaff rule.
E) difference between DNA and RNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the classes of RNA molecules is linked with proteins in forming the large and small subunits of a cytoplasmic structure?
A) ribosomal RNA
B) transfer RNA
C) messenger RNA
D) primary mRNA transcript
E) ribozymes
A) ribosomal RNA
B) transfer RNA
C) messenger RNA
D) primary mRNA transcript
E) ribozymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

In Figure 25.4,if adenine is located on strand 4,then on strand 2 at the same location ____ must be present.
A) adenine
B) thymine
C) cytosine
D) guanine
E) uracil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If one strand of DNA has the base sequence AAGCAA,the complementary strand has which of the following sequences?
A)UUCGUU
B)TTCGTT
C)AAGCAA
D)UTCGTU
E)TTCGTG
A)UUCGUU
B)TTCGTT
C)AAGCAA
D)UTCGTU
E)TTCGTG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is NOT part of gene expression?
A) transcription
B) replication
C) translation
D) amino acids
E) protein synthesis
A) transcription
B) replication
C) translation
D) amino acids
E) protein synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following nucleotide bases is found only in DNA,not in RNA?
A) guanine
B) adenine
C) thymine
D) uracil
E) cytosine
A) guanine
B) adenine
C) thymine
D) uracil
E) cytosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Segments of DNA that are NOT part of the gene are called
A) exons.
B) introns.
C) transposons.
D) inducers.
E) promoters.
A) exons.
B) introns.
C) transposons.
D) inducers.
E) promoters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following does NOT occur when lactose is present in the environment of
A) The lac repressor binds to the operator.
B) The RNA polymerase binds to the promoter.
C) Three different genes are transcribed.
D) The repressor binds to lactose.
E) The enzymes that break down lactose are synthesized.
A) The lac repressor binds to the operator.
B) The RNA polymerase binds to the promoter.
C) Three different genes are transcribed.
D) The repressor binds to lactose.
E) The enzymes that break down lactose are synthesized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Initiation,elongation,and termination are three stages in
A) DNA replication.
B) error correction by proofreading enzymes.
C) mRNA processing.
D) translation.
E) intron removal.
A) DNA replication.
B) error correction by proofreading enzymes.
C) mRNA processing.
D) translation.
E) intron removal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Gene mutations are
A) always deleterious.
B) always beneficial.
C) radiation-induced changes only.
D) alterations in the normal sequence of bases within a gene.
E) alterations in the normal sequence of bases outside a gene.
A) always deleterious.
B) always beneficial.
C) radiation-induced changes only.
D) alterations in the normal sequence of bases within a gene.
E) alterations in the normal sequence of bases outside a gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which is the process that synthesizes mRNA?
A) translation
B) transcription
C) transposition
D) transformation
E) translocation
A) translation
B) transcription
C) transposition
D) transformation
E) translocation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The correct sequence of events in the production of a polypeptide is
A) initiation termination elongation.
B) elongation termination initiation.
C) termination elongation initiation.
D) elongation initiation termination.
E) initiation elongation termination.
A) initiation termination elongation.
B) elongation termination initiation.
C) termination elongation initiation.
D) elongation initiation termination.
E) initiation elongation termination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following processes does NOT take place during translation?
A) attachment of a ribosome to mRNA
B) growth of a polypeptide chain
C) binding of two tRNA molecules/ribosome
D) liberation of polypeptide from ribosome
E) production of mRNA
A) attachment of a ribosome to mRNA
B) growth of a polypeptide chain
C) binding of two tRNA molecules/ribosome
D) liberation of polypeptide from ribosome
E) production of mRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which is most directly responsible for the sequence of amino acids in a protein?
A) the sequence of the anticodons
B) the number of codons in mRNA
C) the enzyme that attaches the amino acid to tRNA
D) the proteins associated with rRNA
E) the sequence of codons in mRNA
A) the sequence of the anticodons
B) the number of codons in mRNA
C) the enzyme that attaches the amino acid to tRNA
D) the proteins associated with rRNA
E) the sequence of codons in mRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
For translation to take place,which of the following would NOT be required to be present?
A) DNA
B) mRNA
C) tRNA amino acid complex
D) rRNA
E) ribosome
A) DNA
B) mRNA
C) tRNA amino acid complex
D) rRNA
E) ribosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which is the process by which a protein is constructed in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells?
A) translation
B) transcription
C) transposition
D) transformation
E) translocation
A) translation
B) transcription
C) transposition
D) transformation
E) translocation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If the normal nucleotide sequence was TACGGCATG,what type of gene mutation is present if the resulting sequence becomes TAGGCATG?
A) chromosomal mutation
B) germinal mutation
C) addition mutation
D) deletion mutation
E) substitution mutation
A) chromosomal mutation
B) germinal mutation
C) addition mutation
D) deletion mutation
E) substitution mutation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The addition of a poly-A tail to mRNA occurs after which of the following?
A) replication
B) transcription
C) translation
D) translocation
E) termination
A) replication
B) transcription
C) translation
D) translocation
E) termination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of these is NOT a form of a point mutation?
A) nonsense mutation
B) missense mutation
C) silent mutation
D) frameshift mutation
E) UAC becomes UAU
A) nonsense mutation
B) missense mutation
C) silent mutation
D) frameshift mutation
E) UAC becomes UAU

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The genetic code consists of ____ bases that stand for one amino acid.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 20
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is NOT a frameshift mutation of the nucleotide sequence CATUAUCCC?
A) CATTUAUCCC
B) ATUAUCCC
C) CTUAUCCC
D) CATUAUCGC
E) CCATUAUCCC
A) CATTUAUCCC
B) ATUAUCCC
C) CTUAUCCC
D) CATUAUCGC
E) CCATUAUCCC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Specific DNA sequences that have the ability to move within and out of chromosomes are called
A) transposons.
B) introns.
C) exons.
D) operators.
E) ribozymes.
A) transposons.
B) introns.
C) exons.
D) operators.
E) ribozymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The ____ of a tRNA molecule will base pair with the codon of a mRNA molecule.
A) DNA sequence
B) anticodon
C) amino acid binding site
D) RNA polymerase
E) promoter site
A) DNA sequence
B) anticodon
C) amino acid binding site
D) RNA polymerase
E) promoter site

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The site of translation is the
A) nucleus.
B) nucleolus.
C) ribosome.
D) ribozyme.
E) mitochondria.
A) nucleus.
B) nucleolus.
C) ribosome.
D) ribozyme.
E) mitochondria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which is NOT true about the genetic code?
A) It is exactly the same in all organisms.
B) It is composed of a triplet code of three bases per codon.
C) It produces 64 different possibilities of codon sequences.
D) Some amino acids are coded for by more than one codon.
E) It contains start and stop codons as instructions.
A) It is exactly the same in all organisms.
B) It is composed of a triplet code of three bases per codon.
C) It produces 64 different possibilities of codon sequences.
D) Some amino acids are coded for by more than one codon.
E) It contains start and stop codons as instructions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Messenger RNA is produced in the
A) cytoplasm.
B) ribosomes.
C) nucleus.
D) endoplasmic reticulum.
E) lysosome.
A) cytoplasm.
B) ribosomes.
C) nucleus.
D) endoplasmic reticulum.
E) lysosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Active genes are found in the _______ of eukaryotic chromosomes.
A) heterochromatin
B) euchromatin
C) Barr bodies
D) promoters
E) operons
A) heterochromatin
B) euchromatin
C) Barr bodies
D) promoters
E) operons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Two strains of E.coli-one of which can turn on its lactase production and one that cannot-are grown together with lactose in the medium.If all other conditions are equal,what will occur?
A) Both strains will continue to be present in equal amounts.
B) The two strains will kill each other off.
C) The strain that can turn on lactase production will overgrow the culture and be the only one left.
D) The strain that cannot turn on lactase production will overgrow the culture and be the only one left.
E) The strain that can turn on lactase production will make its own lactose once the lactose present in the medium is completely used.
A) Both strains will continue to be present in equal amounts.
B) The two strains will kill each other off.
C) The strain that can turn on lactase production will overgrow the culture and be the only one left.
D) The strain that cannot turn on lactase production will overgrow the culture and be the only one left.
E) The strain that can turn on lactase production will make its own lactose once the lactose present in the medium is completely used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which level of primary control in eukaryotic gene activity involves processing early RNA transcripts to mRNA and control of the rate at which mRNA leaves the nucleus?
A) feedback control
B) translational control
C) transcriptional control
D) posttranscriptional control
E) posttranslational control
A) feedback control
B) translational control
C) transcriptional control
D) posttranscriptional control
E) posttranslational control

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
According to the operon theory,the function of the regulator gene is to
A) code for enzymes in a metabolic pathway.
B) serve as an on/off switch for transcription.
C) code for a repressor molecule that can bind to the operator.
D) bind to the RNA polymerase molecule.
E) bind to the promoter.
A) code for enzymes in a metabolic pathway.
B) serve as an on/off switch for transcription.
C) code for a repressor molecule that can bind to the operator.
D) bind to the RNA polymerase molecule.
E) bind to the promoter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
DNA segments called _____ are at the ends of chromosomes and eventually signal the cell to enter apoptosis.
A) transposons
B) mutagens
C) activated chromatin
D) operons
E) telomeres
A) transposons
B) mutagens
C) activated chromatin
D) operons
E) telomeres

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Eukaryotic transcription factors assist the ______ in binding to the _________.
A) repressor; operator
B) RNA polymerase; promoter
C) DNA polymerase; promoter
D) helicases; operator
E) operator; repressor
A) repressor; operator
B) RNA polymerase; promoter
C) DNA polymerase; promoter
D) helicases; operator
E) operator; repressor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If the gene product needed is either transfer RNA or ribosomal RNA,the most efficient way to produce this product is
A) activating chromatin.
B) increasing transcription factors.
C) increasing the rate mRNA matures.
D) increasing translational control.
E) increasing posttranscriptional control.
A) activating chromatin.
B) increasing transcription factors.
C) increasing the rate mRNA matures.
D) increasing translational control.
E) increasing posttranscriptional control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
____________ regulation occurs within a cell when the newly formed protein is modified.
A) Transcriptional
B) Posttranscriptional
C) Translational
D) Posttranslational
E) Operon
A) Transcriptional
B) Posttranscriptional
C) Translational
D) Posttranslational
E) Operon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following serve to directly accelerate the cell cycle?
A) tumor suppressor genes
B) carcinogens
C) repressors
D) proto-oncogene proteins
E) p53 gene
A) tumor suppressor genes
B) carcinogens
C) repressors
D) proto-oncogene proteins
E) p53 gene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which part of an operon is incorrectly matched with its function?
A) promoter-where RNA polymerase first binds to DNA
B) regulator-binds to the repressor protein
C) structural-makes mRNA by transcription
D) operator-if unbound, allows RNA polymerase to bind to DNA
E) all are incorrectly matched with its function
A) promoter-where RNA polymerase first binds to DNA
B) regulator-binds to the repressor protein
C) structural-makes mRNA by transcription
D) operator-if unbound, allows RNA polymerase to bind to DNA
E) all are incorrectly matched with its function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following levels of control involves the use of a poly-A tail?
A) protein activity
B) translation of mRNA
C) mRNA processing
D) transcriptional control
E) chromatin structure
A) protein activity
B) translation of mRNA
C) mRNA processing
D) transcriptional control
E) chromatin structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which level of primary control in eukaryotic gene activity involves the lifespan of the mRNA molecule and the ability of the mRNA to bind to ribosomes?
A) feedback control
B) translational control
C) transcriptional control
D) posttranscriptional control
E) posttranslational control
A) feedback control
B) translational control
C) transcriptional control
D) posttranscriptional control
E) posttranslational control

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which is NOT associated with cancer?
A) It can establish new tumors distant from the site of the primary tumor.
B) It forms new blood vessels and brings nutrients and oxygen to the tumor.
C) Cancer cells can undergo cell division repeatedly and indefinitely.
D) Tumors invade surrounding tissues and are filtered by lymph nodes.
E) A malignant mass of cells is encapsulated and does not invade adjacent tissue.
A) It can establish new tumors distant from the site of the primary tumor.
B) It forms new blood vessels and brings nutrients and oxygen to the tumor.
C) Cancer cells can undergo cell division repeatedly and indefinitely.
D) Tumors invade surrounding tissues and are filtered by lymph nodes.
E) A malignant mass of cells is encapsulated and does not invade adjacent tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In eukaryotes,control of gene expression is NOT by
A) translational control in cytoplasm after mRNA leaves the nucleus and before protein is produced.
B) transcriptional control in the nucleus based on which genes are transcribed and how fast they are transcribed.
C) posttranscriptional control in the nucleus after DNA is transcribed, including the speed with which mRNA leaves the nucleus.
D) posttranslational control in the cytoplasm that occurs after protein synthesis.
E) the use of repressor proteins and operators.
A) translational control in cytoplasm after mRNA leaves the nucleus and before protein is produced.
B) transcriptional control in the nucleus based on which genes are transcribed and how fast they are transcribed.
C) posttranscriptional control in the nucleus after DNA is transcribed, including the speed with which mRNA leaves the nucleus.
D) posttranslational control in the cytoplasm that occurs after protein synthesis.
E) the use of repressor proteins and operators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Apoptosis refers to cell death and
A) is always biologically detrimental to an organism.
B) can be programmed and is essential to normal development.
C) is the accumulation of genetic errors.
D) is a failure in the translation or transcription mechanism.
E) is any failure of the genetic machinery to work correctly.
A) is always biologically detrimental to an organism.
B) can be programmed and is essential to normal development.
C) is the accumulation of genetic errors.
D) is a failure in the translation or transcription mechanism.
E) is any failure of the genetic machinery to work correctly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
When the sheep Dolly was successfully cloned,it was produced by growing an in vitro fertilized egg where the normal egg nucleus had been removed and replaced by a nucleus from an adult.Since this nucleus is from an old mature animal,we would expect it to ______.Interestingly,tests show that this did not happen,a fact that currently puzzles researchers.
A) have additional Barr bodies
B) be mutated
C) have shorter telomeres
D) have longer telomeres
E) express transcription and translation more rapidly
A) have additional Barr bodies
B) be mutated
C) have shorter telomeres
D) have longer telomeres
E) express transcription and translation more rapidly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following is NOT true about oncogenes?
A) They are normal genes that have undergone a mutation.
B) They cause growth factors or growth factor receptors on a cell to malfunction.
C) When mutated oncogenes turn into proto-oncogenes.
D) They cause a cell to divide repeatedly.
E) They are not alien to the cell.
A) They are normal genes that have undergone a mutation.
B) They cause growth factors or growth factor receptors on a cell to malfunction.
C) When mutated oncogenes turn into proto-oncogenes.
D) They cause a cell to divide repeatedly.
E) They are not alien to the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
____________ bind to enhancers in eukaryotic cells to increase the rate of transcription.
A) Repressors
B) RNA polymerases
C) Ligases
D) Transcription activators
E) DNA polymerases
A) Repressors
B) RNA polymerases
C) Ligases
D) Transcription activators
E) DNA polymerases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which level of primary control in eukaryotic gene activity involves changes in the polypeptide chain before it becomes functional?
A) feedback control
B) translational control
C) transcriptional control
D) posttranscriptional control
E) posttranslational control
A) feedback control
B) translational control
C) transcriptional control
D) posttranscriptional control
E) posttranslational control

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following is NOT true about cancer cells?
A) They exhibit uncontrolled growth.
B) They can form benign or malignant tumors.
C) They exhibit disorganized growth.
D) They exhibit contact inhibition.
E) They may undergo metastasis.
A) They exhibit uncontrolled growth.
B) They can form benign or malignant tumors.
C) They exhibit disorganized growth.
D) They exhibit contact inhibition.
E) They may undergo metastasis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



