Deck 16: Option Contracts
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Option Contracts
1
The 'volatility smile' behaviour of options documented by Rubinstein (1985)suggests that implied volatility increases with the difference between the current asset price and the exercise price.
True
Explanation: Rubinstein (1985)suggests that some form of combined model could counter these problems.There is also evidence of the so-called volatility smile,where the implied volatility increases with the difference between the current asset price and the exercise price.
Explanation: Rubinstein (1985)suggests that some form of combined model could counter these problems.There is also evidence of the so-called volatility smile,where the implied volatility increases with the difference between the current asset price and the exercise price.
2
If the exercise price is equal to the underlying asset price,the option is said to be:


D
Explanation: If the intrinsic value is zero the option is said to be either at-the-money or out-of-the-money.An option is said to be at-the-money if the exercise price is equal to the underlying asset price (or at least very near);otherwise it is out-of-the-money.Where the intrinsic value of the option is positive,it is said to be in-the-money.A call option is in-the-money when the underlying asset price exceeds the exercise price.A put option is in-the-money when the underlying asset price is less than the exercise price.
Explanation: If the intrinsic value is zero the option is said to be either at-the-money or out-of-the-money.An option is said to be at-the-money if the exercise price is equal to the underlying asset price (or at least very near);otherwise it is out-of-the-money.Where the intrinsic value of the option is positive,it is said to be in-the-money.A call option is in-the-money when the underlying asset price exceeds the exercise price.A put option is in-the-money when the underlying asset price is less than the exercise price.
3
Put-call parity states that,other things being equal,the price of a put will equal that of a call.
False
Explanation: As equation 16.5,shows,comparison of the cost of the two portfolios gives rise to the put-call parity relationship:
Explanation: As equation 16.5,shows,comparison of the cost of the two portfolios gives rise to the put-call parity relationship:
4
A futures contract differs from an option contract in that the holder of a futures contract has a right but not an obligation to settle on a particular date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The option valuation model of Black and Scholes allows for changes in the standard deviation of the underlying asset over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Assume an option with a price of $4.10 and current pay-off,if exercised today of $0.65.Given a risk-free rate of 5%,the time value of the option now is:
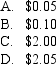
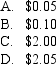

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The difference between the exercise price and the underlying asset price is called the:
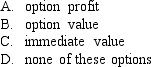
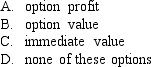

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An American option can only be exercised on the expiration date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In relation to hedging when the short futures position is combined with the long asset position,the net effect is that wealth is not altered with changes in price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
All else the same,an American style option will be ______ valuable than a ______ style option.
A)more;European-
B)less;European-
C)more;Canadian-
D)less;Canadian-
A)more;European-
B)less;European-
C)more;Canadian-
D)less;Canadian-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The method of estimating standard deviation advocated by Kritzman (1991)for use in the Black-Scholes model is based on historical time series.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Three of the most important characteristics of options are:



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following factors affects the price of an option?
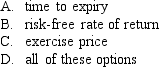
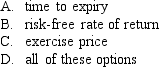

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The writer of a put option _______________.
A)agrees to sell shares at a set price if the option holder desires
B)agrees to buy shares at a set price if the option holder desires
C)has the right to buy shares at a set price
D)has the right to sell shares at a set price
A)agrees to sell shares at a set price if the option holder desires
B)agrees to buy shares at a set price if the option holder desires
C)has the right to buy shares at a set price
D)has the right to sell shares at a set price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In general,most Australian exchange-traded options have no protection against dividends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The option pay-off diagram illustrates:



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An American put option gives its holder the right to _________.
A)buy the underlying asset at the exercise price on or before the expiration date
B)buy the underlying asset at the exercise price only at the expiration date
C)sell the underlying asset at the exercise price on or before the expiration date
D)sell the underlying asset at the exercise price only at the expiration date
A)buy the underlying asset at the exercise price on or before the expiration date
B)buy the underlying asset at the exercise price only at the expiration date
C)sell the underlying asset at the exercise price on or before the expiration date
D)sell the underlying asset at the exercise price only at the expiration date

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A bought bull spread can be created by buying a call option and selling a call option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Figure 16.10 Panel A.As the price rises,the pay-off from the short futures position decreases because the futures position locks in a selling price.As the price falls wealth rises.When the short futures position is combined with the long asset position,the net effect is that wealth is not altered with changes in price.
Given an expected price fall in the underlying asset,a reasonable strategy to profit from this information would be to sell a call written on the asset.
Given an expected price fall in the underlying asset,a reasonable strategy to profit from this information would be to sell a call written on the asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The __________ with shorter time to expiry may have greater value than otherwise identical options.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A put option with 60 days to maturity,exercise price of $12.00 and the risk-free rate is 5% p.a.If a call option is trading at $2.30 and a put option with $0.06 and the current share price is $14.00,what is the arbitrage possible per contract according to put-call parity?
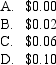
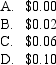

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The premium of an American put option is generally greater than that of the European put option because:



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Assume a one-period world with current share price of $5.00,interest rate of 8% over the period and a price increase factor of 1.25.Given this information,the current premium on a call option with an exercise price of $4.50 using the binomial model is:



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A compound option is:



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Using the Black-Scholes model,the delta of a call option is:
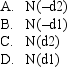
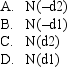

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
is created by combining a call option and a put option with the same time to maturity,but with the call strike price being greater than the put strike price.
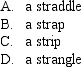
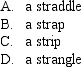

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Assume a two-period world with a current share price of $21.00,an interest rate of 6.5% over the period,a price increase factor of 1.43 and a price decrease factor of 0.55.What are the possible end-of-period prices?
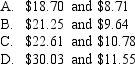


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A call option with 60 days to maturity,exercise price of $12.00,underlying spot price of 14.00 p.a.is valued at $2.24.If the put option with these characteristics is trading at $0.06,at what risk-free rate will put-call parity hold? (Assume the call option premium is correctly priced and there are no dividends. )
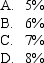
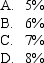

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
For a call option,the rate of increase in the share price is 2%,while the rate of decrease in the share price is 1%.If the share price increases,the call price is $10.10,while the call price will be $9.95 if the share price decreases.Given this information,and that the asset price is currently $10.00 and the risk-free rate is 5% p.a. ,calculate the risk-free hedge ratio.
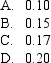


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
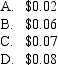
30
A call option with 60 days to maturity,exercise price of $12.00,underlying spot price of $14.00 and risk-free rate of 7% p.a.is valued at $2.20.What is the value of a put option with the same characteristics? (Assume the call option premium is correctly priced and there are no dividends. )


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A combination of purchasing a call and put option with the same exercise price and time to expiry is called:
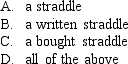
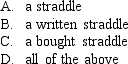

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A call option has a price of $2.50 with exercise price of $14.00 and underlying asset price of $15.00.If the time to maturity is 60 days and the risk-free return is 7% p.a. ,what is the pricing bounds error?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A put option with 60 days to maturity,exercise price of $12.00,underlying spot price of 14.00 and risk-free rate of 7% p.a.is valued at $0.10.What is the value of a call option with the same characteristics? (Assume the put option premium is correctly priced and there are no dividends. )
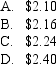
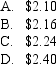

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A put option has a price of $2.50 with exercise price of $14.00 and underlying asset price of $12.00.If the time to maturity is 30 days and the risk-free return is 7% p.a. ,what is the pricing bounds error?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A call option has a price of $0.50 with exercise price of $14.00 and underlying asset price of $15.00.If the time to maturity is 60 days and the risk-free return is 7% p.a. ,what is the pricing bound error?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A call option has a price of $4.50 with exercise price of $14.00 and underlying asset price of $15.00.If the time to maturity is 60 days and the risk-free return is 7% p.a. ,what is the pricing bounds error?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The most difficult parameter to estimate in the Black-Scholes model is the:
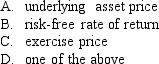
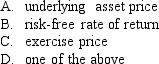

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Using the Black-Scholes model,the delta of a put option is:
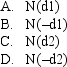
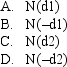

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A put option with 60 days to maturity,exercise price of $12.00,and the risk-free rate is 7% p.a.If a call option is trading at $2.24 and a put option with $0.06,what is the share price that will result in put-call parity holding?
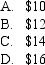
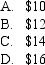

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A put option has a price of $1.50,with exercise price of $14.00 and underlying asset price of $12.00.If the time to maturity is 30 days and the risk-free return is 7% p.a. ,what is the pricing bounds error?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



