Deck 28: Accounting for Group Structures
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 28: Accounting for Group Structures
1
AASB 127 "Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements" permits the reporting periods of entities in the group to be dissimilar as long as adjustments are made on consolidation to remove the impacts of different reporting periods.
False
2
When an acquirer makes a bargain purchase in a business combination,the excess that remains is recognised in profit or loss of the acquirer on acquisition date.
True
3
AASB 127 requires the parent company to have control of another entity in order for that entity's consolidation into the group accounts to be required.
True
4
The purpose of providing consolidated statements is to show the results and financial position of a group as if it were operating with a single source of finance:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
'Control' over a subsidiary,once determined as being in existence,can only be lost with a change in the level of ownership:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The consolidation concept adopted in AASB 127 is to include all the assets and liabilities of the parent entity and subsidiaries in the consolidation and to treat minority interests as part of the equity of the group:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The first step in the consolidation process is substituting the assets and liabilities of the subsidiary for the investment account that currently exists in the parent company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
As prescribed in AASB 3 "Business Combinations",when an acquirer makes a bargain purchase,the acquirer recognises the excess as goodwill on acquisition date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the consolidated financial statements of the parent entity and its controlled entities only transactions with assets and liabilities relating to parties external to the economic entity will be reflected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
AASB 127 notes that in preparing consolidated financial statements,an entity combines the financial statements of the parent and the subsidiaries line by line by adding together,in proportion to the degree of ownership,like items of assets,liabilities,income and expenses; but not equity balances:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Goodwill arises at acquisition date when the purchase price exceeds the identifiable assets acquired and the liabilities assumed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A subsidiary is an entity that is controlled by a parent entity:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Where separate entities in a group do not apply the same accounting methods,AASB 127 "Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements" prescribes adjustments to be made on consolidation to remove the impacts of different accounting policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The consolidation process does not involve any adjustments to the financial statements of the individual entities making up the group:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Under AASB 127 parent companies may choose whether to present one set of consolidated accounts or to provide two or more sub-sets of the consolidated accounts to cover the whole group:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
It is possible for one entity to control another entity under the AASB 3 definition without the controlling entity having any equity-ownership interest in the other entity:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Sullivan (1985)argued that the preparation of group accounts can proceed to the fulfilment of the true and fair notion only when partitioning is fully enforced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A company may own more than 50 per cent of the capital of another entity and not have effective control of that entity as defined in AASB 3:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Minority interests (minority interests)are defined as the equity in the parent company that is not provided by the group shareholders:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Control is defined in AASB 3 as the 'capacity to manage the policies of another entity':

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following consolidation concepts are described correctly?
A) The entity concept requires the inclusion of all the parent entity assets and the proportionate share of the assets and liabilities of the subsidiaries where the proportion is based on the direct ownership of the capital of the subsidiary by parent companies within the group.
B) The proprietary concept includes all the assets and liabilities of the parent company and subsidiaries as assets and liabilities of the group. Minority interest is treated as a liability of the group.
C) The parent-entity concept includes all assets and liabilities of the parent and its subsidiaries in the consolidated accounts. The minority interest is treated as a liability of the group.
D) The proprietary concept includes all the assets and liabilities of the parent company and subsidiaries as assets and liabilities of the group. Minority interest is treated as a liability of the group; the parent-entity concept includes all assets and liabilities of the parent and its subsidiaries in the consolidated accounts. The minority interest is treated as a liability of the group.
E) None of the given answers.
A) The entity concept requires the inclusion of all the parent entity assets and the proportionate share of the assets and liabilities of the subsidiaries where the proportion is based on the direct ownership of the capital of the subsidiary by parent companies within the group.
B) The proprietary concept includes all the assets and liabilities of the parent company and subsidiaries as assets and liabilities of the group. Minority interest is treated as a liability of the group.
C) The parent-entity concept includes all assets and liabilities of the parent and its subsidiaries in the consolidated accounts. The minority interest is treated as a liability of the group.
D) The proprietary concept includes all the assets and liabilities of the parent company and subsidiaries as assets and liabilities of the group. Minority interest is treated as a liability of the group; the parent-entity concept includes all assets and liabilities of the parent and its subsidiaries in the consolidated accounts. The minority interest is treated as a liability of the group.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Richer Ltd is owed a material amount by Poorer Partnership.Poorer is heavily in debt to Richer Ltd,but due to an unexpected economic downturn is unable to make repayments according to schedule.The board of Richer Ltd believes that Poorer has a good chance of trading out of its current economic difficulties as its management and product are sound and the current problems stem from external factors that are expected to pass within the next 12 to 18 months.Richer Ltd enters into an arrangement with Poorer to manage its finances until the economic situation reverses.At this stage it is not perceived as necessary for Richer Ltd to be otherwise involved in the running of Poorer.Given the situation described,what is Richer Ltd most likely to be required to do to account for Poorer under AASB 127?
A) As the control achieved is only temporary, under AASB 127 Richer would not be required to consolidate Poorer.
B) Richer Ltd should consolidate Poorer under AASB 127 because it has control over it by the definition of 'control' in that Standard.
C) Richer Ltd should not be required to consolidate Poorer as it does not have control as defined in AASB 127.
D) Richer Ltd does have temporary control of Poorer, but since Poorer is a partnership Richer is not required to include it in a consolidated set of financial statements.
E) None of the given answers.
A) As the control achieved is only temporary, under AASB 127 Richer would not be required to consolidate Poorer.
B) Richer Ltd should consolidate Poorer under AASB 127 because it has control over it by the definition of 'control' in that Standard.
C) Richer Ltd should not be required to consolidate Poorer as it does not have control as defined in AASB 127.
D) Richer Ltd does have temporary control of Poorer, but since Poorer is a partnership Richer is not required to include it in a consolidated set of financial statements.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
AASB 127 identifies a number of factors that may indicate the existence of control.These include:
A) The ability to appoint the CEO of another entity.
B) The power to dominate the composition of the board of directors or governing body of another entity.
C) The power to require another entity to purchase goods and services from an entity that results in a benefit to the controlling entity.
D) The ability to appoint the CEO of another entity and the power to dominate the composition of the board of directors or governing body of another entity.
E) None of the given answers.
A) The ability to appoint the CEO of another entity.
B) The power to dominate the composition of the board of directors or governing body of another entity.
C) The power to require another entity to purchase goods and services from an entity that results in a benefit to the controlling entity.
D) The ability to appoint the CEO of another entity and the power to dominate the composition of the board of directors or governing body of another entity.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following statements is an accurate description of the difference between a legal entity and an economic entity?
A) An economic entity is one that combines one or more legal entities with synergy such that they each make higher returns than they would individually. If an entity ceases to effectively produce increased returns in this way it becomes uneconomic. A legal entity is one that is recognised in law as having a separate existence from its owners.
B) A legal entity is one that uses appropriate corporate governance measures to ensure that it abides by legislative requirements and other legal regulations. An economic entity may span more than one legal entity, but is not a legal entity in itself.
C) An economic entity is one that is formed for the purpose of generating a profit and therefore a return to owners. A legal entity is one that is circumscribed by legal constitution or Accounting Standards as constituting a reporting entity.
D) A legal entity refers to an entity that has its own particular legal status such as a company, trust or partnership. The concept of an economic entity emphasises substance over legal form. It may operate as a co-ordinated entity and contain more than one legal entity.
E) None of the given answers.
A) An economic entity is one that combines one or more legal entities with synergy such that they each make higher returns than they would individually. If an entity ceases to effectively produce increased returns in this way it becomes uneconomic. A legal entity is one that is recognised in law as having a separate existence from its owners.
B) A legal entity is one that uses appropriate corporate governance measures to ensure that it abides by legislative requirements and other legal regulations. An economic entity may span more than one legal entity, but is not a legal entity in itself.
C) An economic entity is one that is formed for the purpose of generating a profit and therefore a return to owners. A legal entity is one that is circumscribed by legal constitution or Accounting Standards as constituting a reporting entity.
D) A legal entity refers to an entity that has its own particular legal status such as a company, trust or partnership. The concept of an economic entity emphasises substance over legal form. It may operate as a co-ordinated entity and contain more than one legal entity.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which consolidation concept mainly underlies the approach adopted in AASB 127?
A) The proprietary concept.
B) The accrual concept.
C) The entity concept.
D) The parent-entity concept.
E) None of the given answers.
A) The proprietary concept.
B) The accrual concept.
C) The entity concept.
D) The parent-entity concept.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The factors that are taken into consideration in determining whether or not an entity should be consolidated under AASB 127 include:
A) The nature of the legal form of the entity and whether or not the 'parent' entity owns enough of the equity in the entity to effectively control the benefits that flow from the relationship with the other entity.
B) Whether or not the potential 'parent' entity controls the other entity.
C) The number of members on the board under the control of the potential 'parent' entity, and whether or not the other entity has been partitioned by the potential 'parent' entity.
D) Whether or not the potential 'parent' entity controls the other entity and whether or not it is in a significantly different business to the potential 'parent'.
E) None of the given answers.
A) The nature of the legal form of the entity and whether or not the 'parent' entity owns enough of the equity in the entity to effectively control the benefits that flow from the relationship with the other entity.
B) Whether or not the potential 'parent' entity controls the other entity.
C) The number of members on the board under the control of the potential 'parent' entity, and whether or not the other entity has been partitioned by the potential 'parent' entity.
D) Whether or not the potential 'parent' entity controls the other entity and whether or not it is in a significantly different business to the potential 'parent'.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Jasper Ltd acquires all the issued capital of Carrot Ltd for a cash payment of $2,800,000 on 30 June 2004.The balance sheet of both entities at purchase date is: 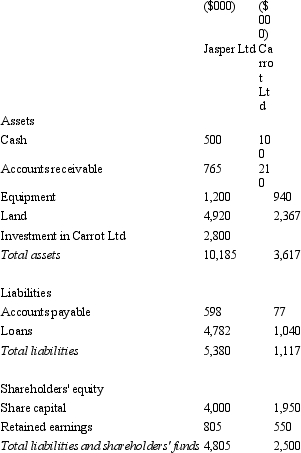 Assuming the assets of Carrot Ltd are recorded at fair value,what is the consolidated balance sheet at the date of purchase?
Assuming the assets of Carrot Ltd are recorded at fair value,what is the consolidated balance sheet at the date of purchase?
A)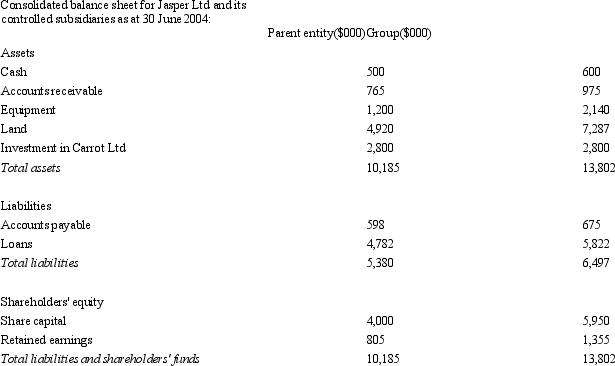
B)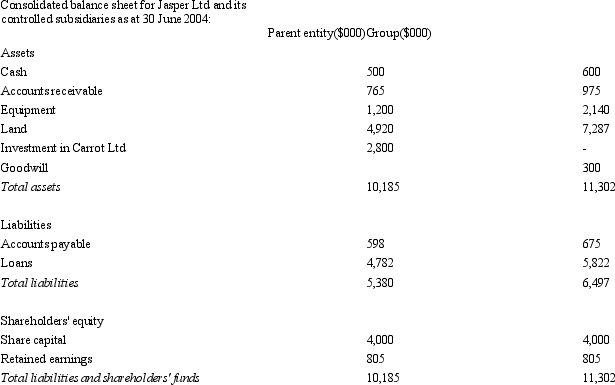
C)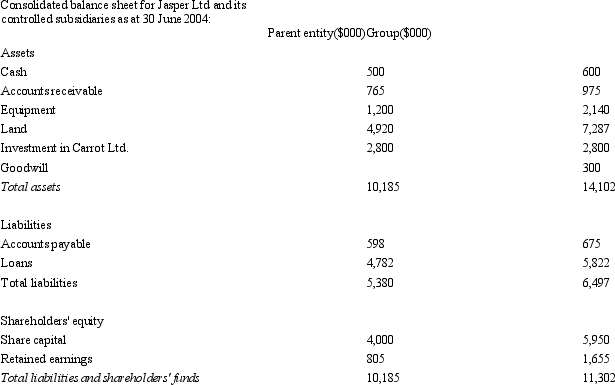
D)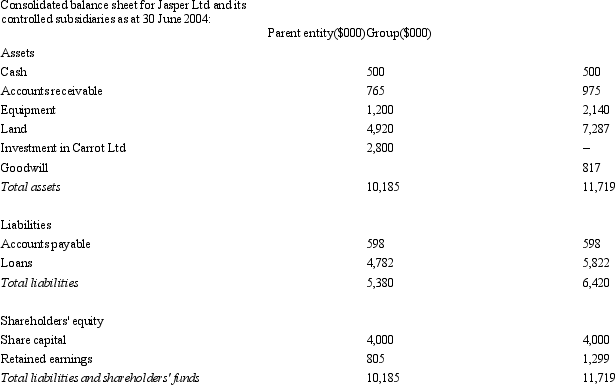
E) None of the given answers.
 Assuming the assets of Carrot Ltd are recorded at fair value,what is the consolidated balance sheet at the date of purchase?
Assuming the assets of Carrot Ltd are recorded at fair value,what is the consolidated balance sheet at the date of purchase?A)

B)

C)

D)

E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The partition effect in relation to a group of companies arose when:
A) It was not permitted under corporations law to consolidate an entity that was not a company. This resulted not only in the non-company entity not being consolidated, but also all the entities (company or otherwise) that it controlled not being consolidated.
B) The minority shareholders in a number of companies controlled by a parent entity organised themselves to block the transfer of funds within a group.
C) Companies in a group co-ordinated to transfer assets in such a way as to protect part of the group from being taxed, thus reducing the total tax owing for the group as a whole.
D) Dividends were declared and paid in such a way as to manage cash reserves within a group.
E) None of the given answers.
A) It was not permitted under corporations law to consolidate an entity that was not a company. This resulted not only in the non-company entity not being consolidated, but also all the entities (company or otherwise) that it controlled not being consolidated.
B) The minority shareholders in a number of companies controlled by a parent entity organised themselves to block the transfer of funds within a group.
C) Companies in a group co-ordinated to transfer assets in such a way as to protect part of the group from being taxed, thus reducing the total tax owing for the group as a whole.
D) Dividends were declared and paid in such a way as to manage cash reserves within a group.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Gouda Ltd acquires all the issued capital of Cheese Ltd for a cash payment of $2,545,000 on 30 June 2005.The balance sheet of Cheese Ltd at purchase date is: 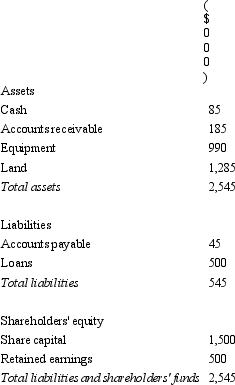 Assuming the assets are at fair value,what would be the consolidation entry to eliminate the investment in Cheese Ltd?
Assuming the assets are at fair value,what would be the consolidation entry to eliminate the investment in Cheese Ltd?
A)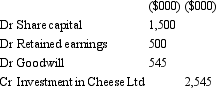
B)
C)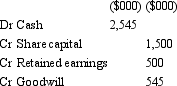
D)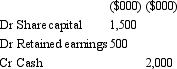
E) None of the given answers.
 Assuming the assets are at fair value,what would be the consolidation entry to eliminate the investment in Cheese Ltd?
Assuming the assets are at fair value,what would be the consolidation entry to eliminate the investment in Cheese Ltd?A)

B)

C)
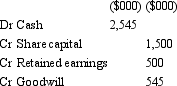
D)
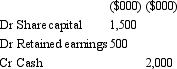
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
AASB 127 defines control as:
A) Governing the financial, operating and sustainability policies of an entity so as to benefit from its activities.
B) The capacity of an entity to dominate the decision-making of another entity by virtue of a majority shareholding or controlling ownership interest in some form.
C) The capacity and willingness to direct the decision-making of another entity with respect to its financial and operating policies to improve the performance and position of the controlling entity.
D) The power to govern the financial and operating policies of an entity so as to benefit from its activities.
E) None of the given answers.
A) Governing the financial, operating and sustainability policies of an entity so as to benefit from its activities.
B) The capacity of an entity to dominate the decision-making of another entity by virtue of a majority shareholding or controlling ownership interest in some form.
C) The capacity and willingness to direct the decision-making of another entity with respect to its financial and operating policies to improve the performance and position of the controlling entity.
D) The power to govern the financial and operating policies of an entity so as to benefit from its activities.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
'Passive' control implies that it is possible to exert control over another entity even though the option to exert such control may never be exercised.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Gigi Ltd is acting as a trustee for Bonberre trust.Gigi has complete control of the operating and financing decisions of the trust.The nominated beneficiaries of the trust are Mr and Mrs Bonberre,who each receive 50 per cent of the trust profits.Given the situation described,what is Gigi Ltd most likely to be required to do to account for the Bonberre trust under AASB 127?
A) Gigi Ltd should be required to consolidate the trust as it controls the operating and financing decisions.
B) Gigi Ltd should not be required to consolidate Bonberre trust because a trust cannot be a subsidiary under The Corporations Law.
C) Gigi Ltd should treat the trust as an investment in its books, valued at the present value of any future income streams expected to be received in return for managing the trust.
D) Gigi Ltd should not consolidate the trust because, while it does control the financing and operating decisions of the trust, it cannot do so in a way to benefit Gigi Ltd.
E) None of the given answers.
A) Gigi Ltd should be required to consolidate the trust as it controls the operating and financing decisions.
B) Gigi Ltd should not be required to consolidate Bonberre trust because a trust cannot be a subsidiary under The Corporations Law.
C) Gigi Ltd should treat the trust as an investment in its books, valued at the present value of any future income streams expected to be received in return for managing the trust.
D) Gigi Ltd should not consolidate the trust because, while it does control the financing and operating decisions of the trust, it cannot do so in a way to benefit Gigi Ltd.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Under AASB 127:
A) Management may agree with the auditors a flexible arrangement for the presentation of the group accounts where some companies or trusts within the group have a nature of business or location that makes their pattern of return and risk significantly different to the remaining entities in the group.
B) Companies that are non-homogeneous with the overall nature of the business of the group are prohibited from being consolidated and are required to have their financial statements presented separately.
C) Finance companies, which are highly geared by nature, are not required to be included in the consolidated accounts of groups that are not significantly involved in the finance business.
D) Companies within a group that are in distinctly different businesses do not have to be consolidated into a single set of consolidated accounts.
E) None of the given answers.
A) Management may agree with the auditors a flexible arrangement for the presentation of the group accounts where some companies or trusts within the group have a nature of business or location that makes their pattern of return and risk significantly different to the remaining entities in the group.
B) Companies that are non-homogeneous with the overall nature of the business of the group are prohibited from being consolidated and are required to have their financial statements presented separately.
C) Finance companies, which are highly geared by nature, are not required to be included in the consolidated accounts of groups that are not significantly involved in the finance business.
D) Companies within a group that are in distinctly different businesses do not have to be consolidated into a single set of consolidated accounts.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In what situation does an excess on acquisition arise and how does AASB 3 require it to be treated?
A) An excess arises when the fair value of the purchase consideration is greater than the nominal value of the assets purchased. AASB 3 requires an excess to be eliminated by recognising it as a gain in the period in which the entity was purchased.
B) An excess arises when the fair value of the purchase consideration is greater than the nominal value of the assets purchased. AASB 3 requires the fair values of the monetary assets acquired to be proportionately decreased until the excess is eliminated. If an excess balance remains it must be recognised as an expense in the income statement.
C) An excess arises when the cost of acquisition exceeds the fair value of the identifiable net assets purchased. AASB 3 requires the equity of the purchased entity to be proportionately decreased until the excess is eliminated.
D) An excess arises when the fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired by the entity exceeds the fair value of the consideration paid. AASB 3 requires a reassessment of the identification and measurement of the identifiable net assets, and a reassessment of the measurement of the fair value of the consideration paid. If an excess remains after the reassessment it must be recognised as income in profit or loss.
E) None of the given answers.
A) An excess arises when the fair value of the purchase consideration is greater than the nominal value of the assets purchased. AASB 3 requires an excess to be eliminated by recognising it as a gain in the period in which the entity was purchased.
B) An excess arises when the fair value of the purchase consideration is greater than the nominal value of the assets purchased. AASB 3 requires the fair values of the monetary assets acquired to be proportionately decreased until the excess is eliminated. If an excess balance remains it must be recognised as an expense in the income statement.
C) An excess arises when the cost of acquisition exceeds the fair value of the identifiable net assets purchased. AASB 3 requires the equity of the purchased entity to be proportionately decreased until the excess is eliminated.
D) An excess arises when the fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired by the entity exceeds the fair value of the consideration paid. AASB 3 requires a reassessment of the identification and measurement of the identifiable net assets, and a reassessment of the measurement of the fair value of the consideration paid. If an excess remains after the reassessment it must be recognised as income in profit or loss.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following statements accurately describes the elimination entry to eliminate pre-acquisition shareholders' funds?
A) It is made once at the time of the first consolidation of the economic entity's accounts in order to eliminate the parent entity's investment in the subsidiary against the non-monetary assets of the controlled entity.
B) It is made each time the consolidation is performed in order to adjust the carrying value of the controlled entity's non-current assets to their fair value.
C) It is carried out once at the date that control of the subsidiary is achieved in order to create the goodwill or discount and eliminate the parent entity's equity against the controlled entity's investment.
D) It is made each time the consolidation is performed in order to eliminate the parent entity's investment in the controlled entity against the equity of the controlled entity. Any adjustments necessary to bring the non-current assets of the controlled entity to fair value are made before the elimination entry and any difference between the consideration paid and the fair value of the net assets of the controlled entity are recognised.
E) None of the given answers.
A) It is made once at the time of the first consolidation of the economic entity's accounts in order to eliminate the parent entity's investment in the subsidiary against the non-monetary assets of the controlled entity.
B) It is made each time the consolidation is performed in order to adjust the carrying value of the controlled entity's non-current assets to their fair value.
C) It is carried out once at the date that control of the subsidiary is achieved in order to create the goodwill or discount and eliminate the parent entity's equity against the controlled entity's investment.
D) It is made each time the consolidation is performed in order to eliminate the parent entity's investment in the controlled entity against the equity of the controlled entity. Any adjustments necessary to bring the non-current assets of the controlled entity to fair value are made before the elimination entry and any difference between the consideration paid and the fair value of the net assets of the controlled entity are recognised.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What are the major consolidation concepts?
A) Entity, partnership and parent.
B) Equity, control and ownership.
C) Parent-entity, ownership and proprietary.
D) Entity, parent-entity and proprietary.
E) None of the given answers.
A) Entity, partnership and parent.
B) Equity, control and ownership.
C) Parent-entity, ownership and proprietary.
D) Entity, parent-entity and proprietary.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A consolidated entity is defined in the Corporations Act 2001 as:
A) The company and its subsidiaries at the end of the financial year. Subsidiaries are companies and trusts as defined in terms of this Act.
B) A company, registered management investment scheme or disclosing entity together with all the entities it is required by Accounting Standards to include in consolidated financial statements.
C) A trust or partnership registered as a management investment scheme and all the entities it controls at the end of the financial year.
D) The parent company, minority interests and subsidiaries owned by that parent company as at the end of the financial year.
E) None of the given answers.
A) The company and its subsidiaries at the end of the financial year. Subsidiaries are companies and trusts as defined in terms of this Act.
B) A company, registered management investment scheme or disclosing entity together with all the entities it is required by Accounting Standards to include in consolidated financial statements.
C) A trust or partnership registered as a management investment scheme and all the entities it controls at the end of the financial year.
D) The parent company, minority interests and subsidiaries owned by that parent company as at the end of the financial year.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
One important aim of releasing AAS 24 in 1991 and amendments made to The Corporations Law in the same year was to:
A) Require parent entities to consolidate companies that they controlled into one set of financial statements for the first time.
B) Change the treatment of minority interests to be reflected in the accounts as a liability.
C) Prevent companies from keeping debt off the balance sheet by interposing partnerships or trusts in the group structure.
D) Require the consolidation of the cash-flow statement as well as the balance sheet and income statement.
E) None of the given answers.
A) Require parent entities to consolidate companies that they controlled into one set of financial statements for the first time.
B) Change the treatment of minority interests to be reflected in the accounts as a liability.
C) Prevent companies from keeping debt off the balance sheet by interposing partnerships or trusts in the group structure.
D) Require the consolidation of the cash-flow statement as well as the balance sheet and income statement.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In the situation in which a subsidiary is only controlled temporarily,AASB 127 requires:
A) The investment be recorded at fair market value and any gain or loss on acquisition recognised immediately in the income statement.
B) The subsidiary to be treated as an associate and equity accounting applied.
C) The results of the subsidiary for the period of time that it was controlled should be included in the consolidated accounts.
D) The investment to be reported at cost and dividends be accrued when declared.
E) None of the given answers.
A) The investment be recorded at fair market value and any gain or loss on acquisition recognised immediately in the income statement.
B) The subsidiary to be treated as an associate and equity accounting applied.
C) The results of the subsidiary for the period of time that it was controlled should be included in the consolidated accounts.
D) The investment to be reported at cost and dividends be accrued when declared.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Growl Ltd acquires all the issued capital of Tiger Ltd for a cash payment of $5,000,000 on 30 June 2005.The balance sheet of Tiger Ltd at purchase date is: 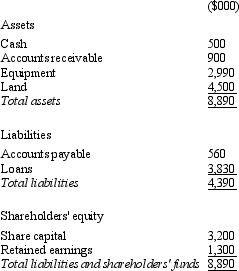 The fair value of the net assets at the date of purchase was $4,200,000.What amount of goodwill or excess would be recorded in the consolidated statements at the date of purchase?
The fair value of the net assets at the date of purchase was $4,200,000.What amount of goodwill or excess would be recorded in the consolidated statements at the date of purchase?
A) $500,000 goodwill
B) $300,000 discount
C) $800,000 goodwill
D) $389,000 discount
E) None of the given answers.
 The fair value of the net assets at the date of purchase was $4,200,000.What amount of goodwill or excess would be recorded in the consolidated statements at the date of purchase?
The fair value of the net assets at the date of purchase was $4,200,000.What amount of goodwill or excess would be recorded in the consolidated statements at the date of purchase?A) $500,000 goodwill
B) $300,000 discount
C) $800,000 goodwill
D) $389,000 discount
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Banderas Ltd acquires all the issued capital of Ryan Ltd for a cash payment of $2,900,000 on 30 June 2004.The balance sheet of Ryan Ltd at purchase date is: 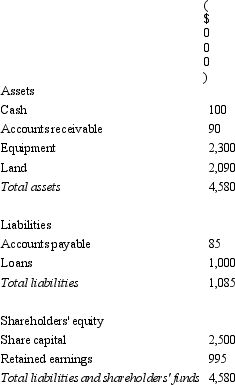 Assuming the assets are at fair value,what is the consolidation entry to eliminate the investment in Ryan Ltd?
Assuming the assets are at fair value,what is the consolidation entry to eliminate the investment in Ryan Ltd?
A)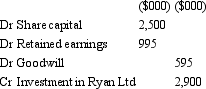
B)
C)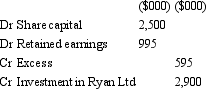
D)
E) None of the given answers.
 Assuming the assets are at fair value,what is the consolidation entry to eliminate the investment in Ryan Ltd?
Assuming the assets are at fair value,what is the consolidation entry to eliminate the investment in Ryan Ltd?A)
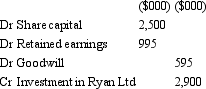
B)

C)
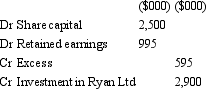
D)

E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following statements accurately describes important aspects of consolidation after the date of acquisition?
A) The elimination entry is made only the first time the consolidation is conducted. Any goodwill arising from the purchase is amortised over the appropriate period (not more than 20 years) and any excess will have been written off in the first year's elimination entry. Post-acquisition earnings are considered to be part of the group's earnings.
B) The elimination entry will be made each time the consolidation is undertaken. Goodwill arising on consolidation will be recognised and subject to annual impairment testing. If the controlled entity was purchased at a discount the excess is recognised in the first period's profit or loss, and in subsequent years in opening retained earnings.
C) The elimination entry is made each time the consolidation is undertaken. If an excess arises on consolidation it is completely written off in the first year and is not included in the consolidation worksheet entries again. If goodwill arises it is recognised for the full amount at acquisition and amortised over a period not exceeding 20 years. Any earnings made by the controlled entity after acquisition belongs to the parent entity and should be reflected in the consolidated accounts and the parent entity's books.
D) The elimination entry will be made each time the consolidation is undertaken, but the amount of goodwill or excess recognised each time will change. The excess will be written off in the first period and the goodwill amortised over an appropriate period (not exceeding 20 years). The goodwill expense will be recognised in the books of the parent company and matched against the post-acquisition earnings of the controlled entity. Any remaining surplus is treated as income in the consolidated accounts.
E) None of the given answers.
A) The elimination entry is made only the first time the consolidation is conducted. Any goodwill arising from the purchase is amortised over the appropriate period (not more than 20 years) and any excess will have been written off in the first year's elimination entry. Post-acquisition earnings are considered to be part of the group's earnings.
B) The elimination entry will be made each time the consolidation is undertaken. Goodwill arising on consolidation will be recognised and subject to annual impairment testing. If the controlled entity was purchased at a discount the excess is recognised in the first period's profit or loss, and in subsequent years in opening retained earnings.
C) The elimination entry is made each time the consolidation is undertaken. If an excess arises on consolidation it is completely written off in the first year and is not included in the consolidation worksheet entries again. If goodwill arises it is recognised for the full amount at acquisition and amortised over a period not exceeding 20 years. Any earnings made by the controlled entity after acquisition belongs to the parent entity and should be reflected in the consolidated accounts and the parent entity's books.
D) The elimination entry will be made each time the consolidation is undertaken, but the amount of goodwill or excess recognised each time will change. The excess will be written off in the first period and the goodwill amortised over an appropriate period (not exceeding 20 years). The goodwill expense will be recognised in the books of the parent company and matched against the post-acquisition earnings of the controlled entity. Any remaining surplus is treated as income in the consolidated accounts.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Gingimup Ltd purchased all the equity of Kindawansa Ltd on 30 June 2005.At that time the carrying value of the net assets of Kindawansa was $1,200,000.This amount was made up in equity as follows: share capital $1,000,000; retained earnings $200,000.Kindawansa has held some valuable land for a long time (purchased at $ 1,200,000),but has not revalued it.Its fair value at 30 June 2005 was $2,800,000 (all other non-current assets are recorded at fair value).Gingimup Ltd paid cash consideration of $3,000,000 for Kindawansa Ltd.Assuming that the land has not been revalued in the controlled entity's books,what are the elimination entries required to reflect the purchase of Kindawansa Ltd?
A)
B)
C)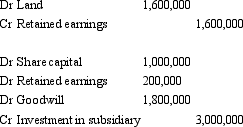
D)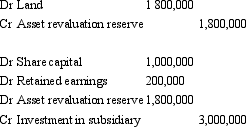
E) None of the given answers.
A)

B)

C)
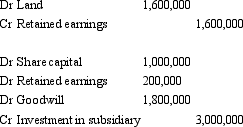
D)
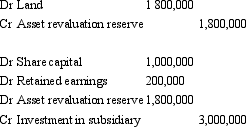
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The preparation of consolidated financial statements:
A) obviates the need for separate entities to prepare and release their own separate financial statements.
B) does not obviate the need for separate entities to prepare and release their own separate financial statements.
C) should be done in accordance with AASB 127.
D) obviates the need for separate entities to prepare and release their own separate financial statements and should be done in accordance with AASB 127.
E) does not obviate the need for separate entities to prepare and release their own separate financial statements and should be done in accordance with AASB 127.
A) obviates the need for separate entities to prepare and release their own separate financial statements.
B) does not obviate the need for separate entities to prepare and release their own separate financial statements.
C) should be done in accordance with AASB 127.
D) obviates the need for separate entities to prepare and release their own separate financial statements and should be done in accordance with AASB 127.
E) does not obviate the need for separate entities to prepare and release their own separate financial statements and should be done in accordance with AASB 127.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The lack of a direct link between levels of ownership and control (i.e.,the degree of ownership does not,of itself,determine if an entity has control of another):
A) is consistent with the AASB Framework's definition of assets, which relies on control and not legal ownership.
B) is consistent with the AASB Framework's definition of assets, which relies on legal ownership and not control.
C) is consistent with the AASB Framework's definition of equity, which recognises investments in other entities.
D) is consistent with the AASB Framework's definition of equity, which relies on control and not legal ownership.
E) is consistent with the AASB Framework's definition of assets, which identifies share ownership as being unimportant.
A) is consistent with the AASB Framework's definition of assets, which relies on control and not legal ownership.
B) is consistent with the AASB Framework's definition of assets, which relies on legal ownership and not control.
C) is consistent with the AASB Framework's definition of equity, which recognises investments in other entities.
D) is consistent with the AASB Framework's definition of equity, which relies on control and not legal ownership.
E) is consistent with the AASB Framework's definition of assets, which identifies share ownership as being unimportant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In the situation in which a subsidiary revalues its non-current assets to fair value in its books as part of being acquired by a parent entity,the accounting treatment is:
A) To treat the revaluation according to AASB 116 'Property, plant and equipment' in the books of the subsidiary entity.
B) To create an asset revaluation reserve in the consolidated accounts and write it off against the parent entity's investment in the subsidiary.
C) To adjust the investment recorded by the parent entity so that the entry balances in the elimination entry.
D) Determined by AASB 127 'Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements', which is concerned with the treatment of the revaluation in the books of the controlled entity. It requires the adjustment to fair value to be written off to the income statement.
E) None of the given answers.
A) To treat the revaluation according to AASB 116 'Property, plant and equipment' in the books of the subsidiary entity.
B) To create an asset revaluation reserve in the consolidated accounts and write it off against the parent entity's investment in the subsidiary.
C) To adjust the investment recorded by the parent entity so that the entry balances in the elimination entry.
D) Determined by AASB 127 'Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements', which is concerned with the treatment of the revaluation in the books of the controlled entity. It requires the adjustment to fair value to be written off to the income statement.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A subsidiary:
A) is excluded from consolidation because the investor is a venture capital organisation.
B) is not excluded from consolidation simply because the investor is a venture capital organisation.
C) is excluded from consolidation because its business activities are dissimilar from those of other entities within the group.
D) is not excluded from consolidation simply because the investor only has significant influence, and not control, over it.
E) is excluded from consolidation because the investor has no Board representation in the subsidiary.
A) is excluded from consolidation because the investor is a venture capital organisation.
B) is not excluded from consolidation simply because the investor is a venture capital organisation.
C) is excluded from consolidation because its business activities are dissimilar from those of other entities within the group.
D) is not excluded from consolidation simply because the investor only has significant influence, and not control, over it.
E) is excluded from consolidation because the investor has no Board representation in the subsidiary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Arthur Ltd acquires all the issued capital of Martha Ltd for a cash payment of $3,000,000 on 30 June 2005.The balance sheet of Martha Ltd at purchase date is: 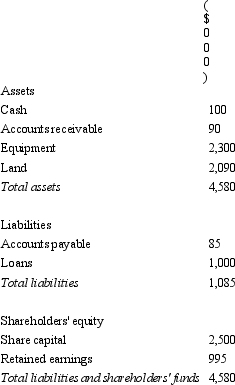 Assuming the assets are at fair value,what is the goodwill or excess on consolidation?
Assuming the assets are at fair value,what is the goodwill or excess on consolidation?
A) Goodwill of $500,000
B) Excess of $1 580,000
C) Goodwill of $510,000
D) Excess of $495,000
E) None of the given answers.
 Assuming the assets are at fair value,what is the goodwill or excess on consolidation?
Assuming the assets are at fair value,what is the goodwill or excess on consolidation?A) Goodwill of $500,000
B) Excess of $1 580,000
C) Goodwill of $510,000
D) Excess of $495,000
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
After initial recognition,goodwill is measured in which of the following ways?
A) At cost.
B) At fair value.
C) At cost less accumulated impairment losses.
D) At cost less accumulated amortisation.
E) In any of the ways mentioned above, at the discretion of entity management.
A) At cost.
B) At fair value.
C) At cost less accumulated impairment losses.
D) At cost less accumulated amortisation.
E) In any of the ways mentioned above, at the discretion of entity management.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In a situation where the net assets acquired in the controlled entity are not recorded at fair value,approaches that may be taken to account for this include:
A) Adjust the excess or goodwill so that the elimination entry balances.
B) Revalue the assets in the parent entity's books.
C) Revalue the assets during the consolidation process each period.
D) Adjust the depreciation on the assets to bring them to fair value in the consolidated accounts.
E) None of the given answers.
A) Adjust the excess or goodwill so that the elimination entry balances.
B) Revalue the assets in the parent entity's books.
C) Revalue the assets during the consolidation process each period.
D) Adjust the depreciation on the assets to bring them to fair value in the consolidated accounts.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Candle Ltd acquires all the issued capital of Wick Ltd for a cash payment of $4,500,000 on 30 June 2004.The balance sheet of Wick Ltd at purchase date is: 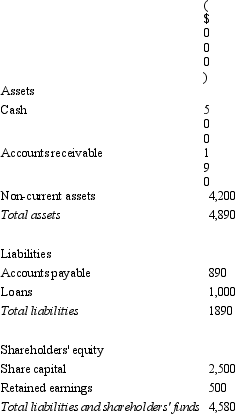 The fair value of the net assets of Wick Ltd as at 30 June 2004 is $3,800,000.What is the consolidation entry to eliminate the investment in Wick Ltd?
The fair value of the net assets of Wick Ltd as at 30 June 2004 is $3,800,000.What is the consolidation entry to eliminate the investment in Wick Ltd?
A)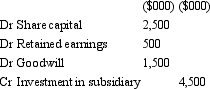
B)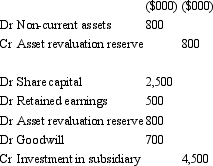
C)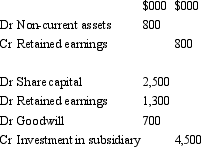
D)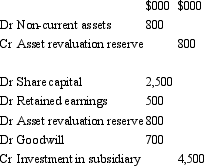
E) None of the given answers.
 The fair value of the net assets of Wick Ltd as at 30 June 2004 is $3,800,000.What is the consolidation entry to eliminate the investment in Wick Ltd?
The fair value of the net assets of Wick Ltd as at 30 June 2004 is $3,800,000.What is the consolidation entry to eliminate the investment in Wick Ltd?A)
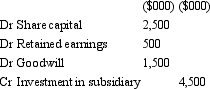
B)

C)
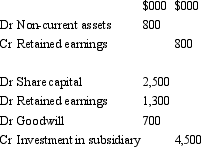
D)
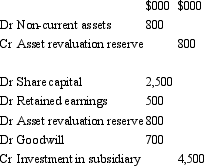
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A former loophole (now closed)that existed under the former s.9 of the Corporations Law:
A) required the preparation of one set of consolidated accounts for the group.
B) required the preparation of separate accounts for each body corporate in the group.
C) gave the choice of using full consolidation, proportional consolidation or the equity method of accounting.
D) gave the choice of one set, or two or more sets, of consolidated accounts; or separate accounts for each body corporate; or a combination.
E) meant that no group accounting was required whatsoever.
A) required the preparation of one set of consolidated accounts for the group.
B) required the preparation of separate accounts for each body corporate in the group.
C) gave the choice of using full consolidation, proportional consolidation or the equity method of accounting.
D) gave the choice of one set, or two or more sets, of consolidated accounts; or separate accounts for each body corporate; or a combination.
E) meant that no group accounting was required whatsoever.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
'Control' exists when the parent owns less than half of the voting power of an entity when:
A) no other entity owns more than half either.
B) there is power to govern the financial and operating policies of the entity under a statute.
C) there is power to govern the financial and operating policies of the entity under an agreement.
D) there is power to govern the financial and operating policies of the entity under a statute and there is power to govern the financial and operating policies of the entity under an agreement.
E) no other entity owns more than half either, there is power to govern the financial and operating policies of the entity under a statute and there is power to govern the financial and operating policies of the entity under an agreement.
A) no other entity owns more than half either.
B) there is power to govern the financial and operating policies of the entity under a statute.
C) there is power to govern the financial and operating policies of the entity under an agreement.
D) there is power to govern the financial and operating policies of the entity under a statute and there is power to govern the financial and operating policies of the entity under an agreement.
E) no other entity owns more than half either, there is power to govern the financial and operating policies of the entity under a statute and there is power to govern the financial and operating policies of the entity under an agreement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A) A group comprises a parent and all of its subsidiaries.
B) Consolidated financial statements are financial statements of a group of entities presented as if that group was acting as a single economic entity.
C) A subsidiary is an entity that is controlled by another entity.
D) A parent is an entity that has more than one subsidiary.
E) None of the given answers; they are all correct statements.
A) A group comprises a parent and all of its subsidiaries.
B) Consolidated financial statements are financial statements of a group of entities presented as if that group was acting as a single economic entity.
C) A subsidiary is an entity that is controlled by another entity.
D) A parent is an entity that has more than one subsidiary.
E) None of the given answers; they are all correct statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Sigmund Ltd acquires all the issued capital of Freud Ltd for a cash payment of $1,900,000 on 30 June 2004.The financial statements of both entities on 30 June 2005 are:  The fair value of the net tangible assets of Freud Ltd on 30 June 2004 was $1,332,000.The equity of Freud at that time was made up of share capital of $1,172,000 and retained earnings of $160,000.Goodwill had been determined to have been impaired by $56,800 during the period.During the period ended 30 June 2005 there were no intragroup transactions.Which of the following consolidated financial statements is correct?
The fair value of the net tangible assets of Freud Ltd on 30 June 2004 was $1,332,000.The equity of Freud at that time was made up of share capital of $1,172,000 and retained earnings of $160,000.Goodwill had been determined to have been impaired by $56,800 during the period.During the period ended 30 June 2005 there were no intragroup transactions.Which of the following consolidated financial statements is correct?
A)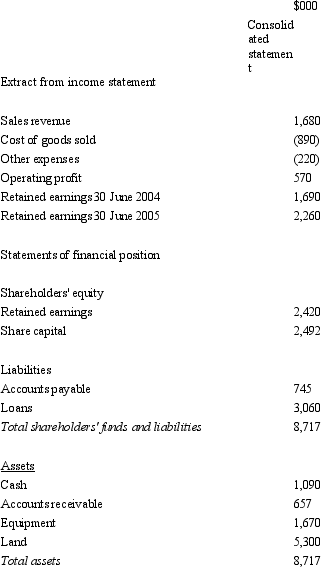
B)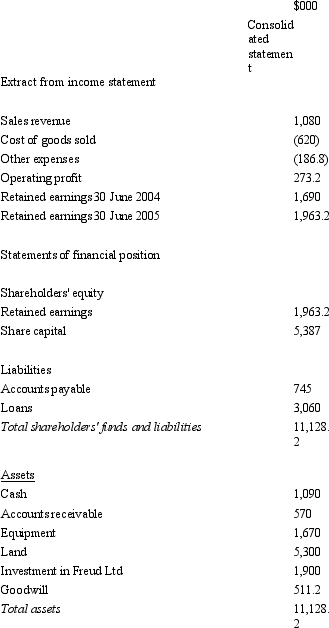
C)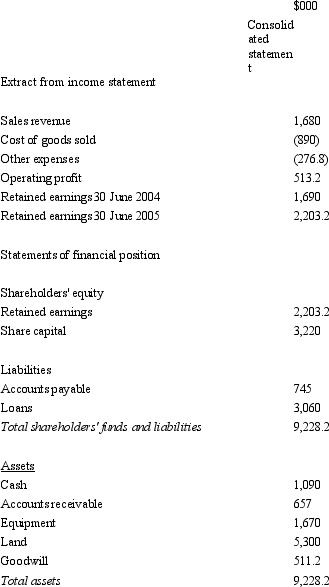
D)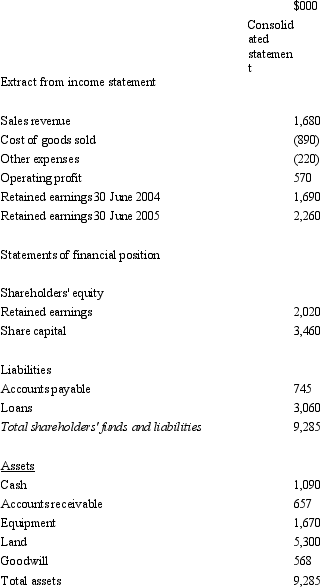
E) None of the given answers.
 The fair value of the net tangible assets of Freud Ltd on 30 June 2004 was $1,332,000.The equity of Freud at that time was made up of share capital of $1,172,000 and retained earnings of $160,000.Goodwill had been determined to have been impaired by $56,800 during the period.During the period ended 30 June 2005 there were no intragroup transactions.Which of the following consolidated financial statements is correct?
The fair value of the net tangible assets of Freud Ltd on 30 June 2004 was $1,332,000.The equity of Freud at that time was made up of share capital of $1,172,000 and retained earnings of $160,000.Goodwill had been determined to have been impaired by $56,800 during the period.During the period ended 30 June 2005 there were no intragroup transactions.Which of the following consolidated financial statements is correct?A)

B)

C)

D)

E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Minority interests are defined is AASB 127 as:
A) that portion of profit or loss and net assets of a subsidiary attributable to equity interests that are not owned directly by the parent.
B) that portion of net assets of a subsidiary attributable to equity interests that are not owned, directly or indirectly through subsidiaries, by the parent.
C) that portion of profit or loss and net assets of a subsidiary attributable to equity interests that are not owned, directly or indirectly through subsidiaries, by the parent.
D) that portion of profit or loss and net assets of a subsidiary attributable to equity interests that are not owned indirectly through subsidiaries, by the parent.
E) the largest single shareholding, less fifty per cent, not owned, directly or indirectly through subsidiaries, by the parent.
A) that portion of profit or loss and net assets of a subsidiary attributable to equity interests that are not owned directly by the parent.
B) that portion of net assets of a subsidiary attributable to equity interests that are not owned, directly or indirectly through subsidiaries, by the parent.
C) that portion of profit or loss and net assets of a subsidiary attributable to equity interests that are not owned, directly or indirectly through subsidiaries, by the parent.
D) that portion of profit or loss and net assets of a subsidiary attributable to equity interests that are not owned indirectly through subsidiaries, by the parent.
E) the largest single shareholding, less fifty per cent, not owned, directly or indirectly through subsidiaries, by the parent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Where the controlled entity's non-current assets were not at fair value at the date of purchase and they have not been revalued in the controlled entity's accounts,the treatment in the consolidation entry may include which of the following entries?
A)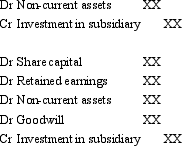
B)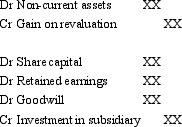
C)
D)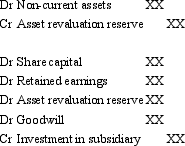
E) None of the given answers.
A)

B)

C)

D)

E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
'Goodwill' is:
A) an intangible asset, as defined in AASB 138.
B) future economic benefits arising from assets that are not capable of being separately recognised or individually identified
C) determined as being the excess of the fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired over the cost of an acquisition.
D) recognised by the acquirer, at acquisition date, as an asset in its own books.
E) All of the given answers.
A) an intangible asset, as defined in AASB 138.
B) future economic benefits arising from assets that are not capable of being separately recognised or individually identified
C) determined as being the excess of the fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired over the cost of an acquisition.
D) recognised by the acquirer, at acquisition date, as an asset in its own books.
E) All of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In determining control,'potential voting rights':
A) include those rights embedded in such instruments as share call options and share warrants.
B) which are currently exercisable should be taken into account.
C) even if they are not currently exercisable should be taken into account.
D) include those rights embedded in such instruments as share call options and share warrants and which are currently exercisable should be taken into account.
E) include those rights embedded in such instruments as share call options and share warrants, which are currently exercisable should be taken into account and C above and even if they are not currently exercisable should be taken into account.
A) include those rights embedded in such instruments as share call options and share warrants.
B) which are currently exercisable should be taken into account.
C) even if they are not currently exercisable should be taken into account.
D) include those rights embedded in such instruments as share call options and share warrants and which are currently exercisable should be taken into account.
E) include those rights embedded in such instruments as share call options and share warrants, which are currently exercisable should be taken into account and C above and even if they are not currently exercisable should be taken into account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Fresco Ltd acquires all the issued capital of Indoor Ltd for a cash payment of $1,000,000 on 30 June 2005.The balance sheet of Indoor Ltd at purchase date is: 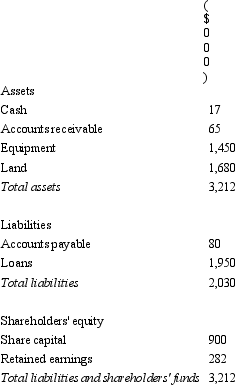 Assuming the assets of Indoor Ltd are at fair value,what is the entry to eliminate the investment in Fresco Ltd?
Assuming the assets of Indoor Ltd are at fair value,what is the entry to eliminate the investment in Fresco Ltd?
A)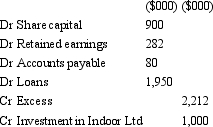
B)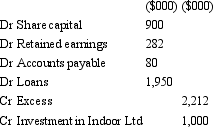
C)
D)
E) None of the given answers.
 Assuming the assets of Indoor Ltd are at fair value,what is the entry to eliminate the investment in Fresco Ltd?
Assuming the assets of Indoor Ltd are at fair value,what is the entry to eliminate the investment in Fresco Ltd?A)

B)

C)

D)

E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
When group members do not apply the same accounting methods,the consolidation process requires which of the following to be done?
A) All group members must change their accounting policies to be consistent.
B) Adjustments must be made on consolidation to remove the impacts of the different policies.
C) Two sets of consolidated accounts need to be presenteD. the first done on the basis of the inconsistent policies; the second done after the subsidiaries have adjusted their policies in line with the parent.
D) A choice is to be made by the parent's management between any of the three other options listed.
E) Nothing needs to be done.
A) All group members must change their accounting policies to be consistent.
B) Adjustments must be made on consolidation to remove the impacts of the different policies.
C) Two sets of consolidated accounts need to be presenteD. the first done on the basis of the inconsistent policies; the second done after the subsidiaries have adjusted their policies in line with the parent.
D) A choice is to be made by the parent's management between any of the three other options listed.
E) Nothing needs to be done.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following statements is not in accordance with AASB 3 "Business Combinations"?
A) An entity shall account for each business combination by applying the acquisition method.
B) For each business combination, one of the combining entities shall be identified as the acquirer.
C) The acquirer is required to recognise, separately from goodwill, the identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed and any non-controlling interest in the acquiree.
D) The acquirer shall measure the identifiable assets acquired and the liabilities assumed at their acquisition-date agreed values.
E) None of the given answers.
A) An entity shall account for each business combination by applying the acquisition method.
B) For each business combination, one of the combining entities shall be identified as the acquirer.
C) The acquirer is required to recognise, separately from goodwill, the identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed and any non-controlling interest in the acquiree.
D) The acquirer shall measure the identifiable assets acquired and the liabilities assumed at their acquisition-date agreed values.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following statements is not in accordance with AASB 127 "Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements"?
A) A parent need not present consolidated financial statements if the parent is itself a wholly-owned subsidiary, or is a partially-owned subsidiary of another entity.
B) Control is presumed to exist when the parent owns, directly or indirectly through subsidiaries, more than half of the voting power of an entity.
C) A parent consolidates subsidiaries that satisfy the criteria to be classified as assets held for sale.
D) Intragroup balances, transactions, income and expenses are eliminated in full for wholly-owned subsidiaries and in proportion to ownership for partially-owned subsidiaries.
E) None of the given answers.
A) A parent need not present consolidated financial statements if the parent is itself a wholly-owned subsidiary, or is a partially-owned subsidiary of another entity.
B) Control is presumed to exist when the parent owns, directly or indirectly through subsidiaries, more than half of the voting power of an entity.
C) A parent consolidates subsidiaries that satisfy the criteria to be classified as assets held for sale.
D) Intragroup balances, transactions, income and expenses are eliminated in full for wholly-owned subsidiaries and in proportion to ownership for partially-owned subsidiaries.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following statements about post-acquisition earnings is(are)incorrect?
A) They form part of earnings of the economic entity.
B) They are the earnings produced subsequent to the acquisition date by members of the group.
C) They are eliminated against the parent's earnings, in a similar fashion to pre-acquisition earnings.
D) They form part of earnings of the economic entity and they are eliminated against the parent's earnings, in a similar fashion to pre-acquisition earnings.
E) None of the given answers; they are all correct.
A) They form part of earnings of the economic entity.
B) They are the earnings produced subsequent to the acquisition date by members of the group.
C) They are eliminated against the parent's earnings, in a similar fashion to pre-acquisition earnings.
D) They form part of earnings of the economic entity and they are eliminated against the parent's earnings, in a similar fashion to pre-acquisition earnings.
E) None of the given answers; they are all correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
On 1 July 2012,Felix Ltd acquires all shares in Oscar Ltd for $800 000.The fair value of net assets acquired is $620 000 comprised of $400,000 in share capital and $220 000 in retained earnings.What is the appropriate elimination entry for this investment that is in accordance with AASB 3 "Business Combinations" and AASB 127 "Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements"?
A)
B)
C)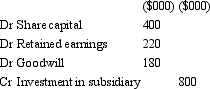
D)
E) None of the given answers.
A)

B)

C)
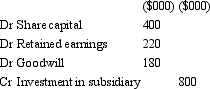
D)

E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
On consolidation,the investment in subsidiary,shown in the investor's books,shall be eliminated in full against which of the following?
A) Assets and liabilities of the subsidiary.
B) Post-acquisition shareholders' funds of the subsidiary.
C) Share capital of the subsidiary acquired by the parent only.
D) Goodwill amount created on acquisition.
E) None of the given answers.
A) Assets and liabilities of the subsidiary.
B) Post-acquisition shareholders' funds of the subsidiary.
C) Share capital of the subsidiary acquired by the parent only.
D) Goodwill amount created on acquisition.
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
On 1 July 2012,Carol Ltd acquires all shares in Alice Ltd for $400 000.The fair value of net assets acquired is $320 000 comprised of $200,000 in share capital and $120 000 in retained earnings.On the date of purchase,a contingent liability is not recoded in the books of the acquiree but assumed by the acquirer.The contingent liability is estimated at $20 000 and likely to eventuate after acquisition.What is the appropriate elimination entry for this investment that is in accordance with AASB 3 "Business Combinations" and AASB 127 "Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements"?
A)
B)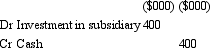
C)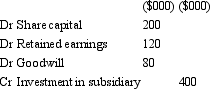
D)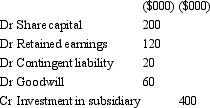
E) None of the given answers.
A)

B)
C)
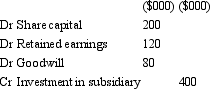
D)
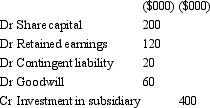
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
On 1 July 2012,Bob Ltd acquires all shares in Ted Ltd for $600 000.The fair value of net assets acquired is $500 000 comprised of $400,000 in share capital and $100 000 in retained earnings.What is the appropriate elimination entry for this investment that is in accordance with AASB 3 "Business Combinations" and AASB 127 "Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements"?
A)
B)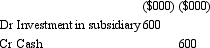
C)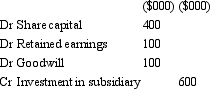
D)
E) None of the given answers.
A)

B)
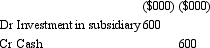
C)
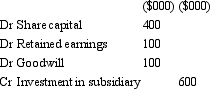
D)

E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
On 1 July 2012,Goliath Ltd acquires all shares in David Ltd for $800 000.The fair value of net assets acquired is $920 000 comprised of $600,000 in share capital and $320 000 in retained earnings.What is the appropriate elimination entry for this investment that is in accordance with AASB 3 "Business Combinations" and AASB 127 "Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements"?
A)
B)
C)
D)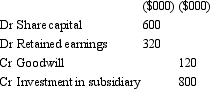
E) None of the given answers.
A)

B)

C)

D)
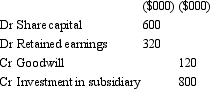
E) None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



