Deck 15: The Autonomic Nervous System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: The Autonomic Nervous System
1
Which of the following types of neurons would normally have the shortest axon?
A)Somatic motor neurons
B)Preganglionic parasympathetic neurons
C)Postganglionic sympathetic neurons
D)Preganglionic sympathetic neurons
E)Somatosensory neurons.
A)Somatic motor neurons
B)Preganglionic parasympathetic neurons
C)Postganglionic sympathetic neurons
D)Preganglionic sympathetic neurons
E)Somatosensory neurons.
D
2
A postganglionic neuron in the ANS
A)releases neurotransmitter that binds to the effector cell.
B)is the first part of an autonomic motor pathway.
C)has its cell body in the brain or spinal cord.
D)has its axons exiting the CNS through cranial nerves.
E)carries information into the sympathetic chain ganglia.
A)releases neurotransmitter that binds to the effector cell.
B)is the first part of an autonomic motor pathway.
C)has its cell body in the brain or spinal cord.
D)has its axons exiting the CNS through cranial nerves.
E)carries information into the sympathetic chain ganglia.
A
3
The autonomic nervous system is NOT involved in controlling
A)exocrine glands.
B)skeletal muscle.
C)cardiac muscle.
D)smooth muscle.
E)endocrine glands.
A)exocrine glands.
B)skeletal muscle.
C)cardiac muscle.
D)smooth muscle.
E)endocrine glands.
B
4
The two main neurotransmitters of the autonomic nervous system are
A)nicotine and adrenaline.
B)muscarine and acetylcholine.
C)norepinephrine and muscarine.
D)norepinephrine and acetylcholine.
E)somatostatin and nicotine.
A)nicotine and adrenaline.
B)muscarine and acetylcholine.
C)norepinephrine and muscarine.
D)norepinephrine and acetylcholine.
E)somatostatin and nicotine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following terms is used to designate an effector that is innervated by both the parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions of the ANS?
A)Preganglionic stimulation
B)Biganglion excitation
C)Multi-autonomic output
D)Bipolar innervation
E)Dual innervation
A)Preganglionic stimulation
B)Biganglion excitation
C)Multi-autonomic output
D)Bipolar innervation
E)Dual innervation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which autonomic plexus is located anterior to the fifth lumbar vertebra and serves the pelvic viscera?
A)Inferior mesenteric plexus
B)Renal plexus
C)Celiac plexus
D)Hypogastric plexus
E)Superior mesenteric plexus
A)Inferior mesenteric plexus
B)Renal plexus
C)Celiac plexus
D)Hypogastric plexus
E)Superior mesenteric plexus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following descriptions of a preganglionic neuron is NOT correct?
A)Has axons that exit the CNS in a cranial or spinal nerve.
B)Has myelinated axons.
C)Forms the first part of an autonomic motor pathway.
D)Has its cell body in the brain or spinal cord.
E)Forms gap junctions with postganglionic neurons in autonomic ganglia.
A)Has axons that exit the CNS in a cranial or spinal nerve.
B)Has myelinated axons.
C)Forms the first part of an autonomic motor pathway.
D)Has its cell body in the brain or spinal cord.
E)Forms gap junctions with postganglionic neurons in autonomic ganglia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Interoceptors are found in
A)blood vessels
B)visceral organs
C)muscles
D)all of these choices
E)none of these choices
A)blood vessels
B)visceral organs
C)muscles
D)all of these choices
E)none of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is NOT a parasympathetic terminal ganglion?
A)Ciliary ganglion
B)Pterygopalatine ganglion
C)Submandibular ganglion
D)Otic ganglion
E)All are parasympathetic terminal ganglia
A)Ciliary ganglion
B)Pterygopalatine ganglion
C)Submandibular ganglion
D)Otic ganglion
E)All are parasympathetic terminal ganglia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which ganglia contain the cell bodies of the parasympathetic postganglionic neurons that serve the parotid salivary glands?
A)Ciliary ganglia
B)Pterygopalatine ganglia
C)Submandibular ganglia
D)Otic ganglia
E)None of these choices
A)Ciliary ganglia
B)Pterygopalatine ganglia
C)Submandibular ganglia
D)Otic ganglia
E)None of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following does NOT describe the parasympathetic division of the ANS?
A)Long preganglionic neurons
B)Synapses with smooth muscle in blood vessels walls
C)Vagus nerve output
D)Ganglia found near visceral effectors
E)Sacral spinal cord output
A)Long preganglionic neurons
B)Synapses with smooth muscle in blood vessels walls
C)Vagus nerve output
D)Ganglia found near visceral effectors
E)Sacral spinal cord output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following are structures containing sympathetic preganglionic axons that connect the anterior ramus of the spinal nerve with the ganglia of the sympathetic trunk?
A)Lumbar splanchnic nerve
B)Greater splanchnic nerve
C)Inferior cervical ganglion
D)White rami communicantes
E)Gray rami communicantes
A)Lumbar splanchnic nerve
B)Greater splanchnic nerve
C)Inferior cervical ganglion
D)White rami communicantes
E)Gray rami communicantes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following does NOT describe the sympathetic division of the ANS?
A)Ganglia primarily found in the head
B)Stimulates sweat glands
C)Synapses with smooth muscle in blood vessel walls
D)Short preganglionic neurons
E)Thoracolumbar output
A)Ganglia primarily found in the head
B)Stimulates sweat glands
C)Synapses with smooth muscle in blood vessel walls
D)Short preganglionic neurons
E)Thoracolumbar output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Autonomic motor neurons regulate visceral activities by
1)increasing activities in effector tissue.
2)decreasing activities in effector tissue.
3)changing the direction of impulse conduction across synapses.
A)1 only
B)2 only
C)3 only
D)Both 1 and 2
E)None of these choices
1)increasing activities in effector tissue.
2)decreasing activities in effector tissue.
3)changing the direction of impulse conduction across synapses.
A)1 only
B)2 only
C)3 only
D)Both 1 and 2
E)None of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Acetylcholine is released by _____ postganglionic neurons and is removed from the synaptic cleft at a _____ rate than norepinephrine.
A)sympathetic;slower
B)sympathetic;faster
C)parasympathetic;slower
D)parasympathetic;faster
E)both parasympathetic and sympathetic;slower
A)sympathetic;slower
B)sympathetic;faster
C)parasympathetic;slower
D)parasympathetic;faster
E)both parasympathetic and sympathetic;slower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is NOT a sympathetic prevertebral ganglion?
A)Celiac ganglion
B)Ciliary ganglion
C)Superior mesenteric ganglion
D)Inferior mesenteric ganglion
E)All are prevertebral ganglia
A)Celiac ganglion
B)Ciliary ganglion
C)Superior mesenteric ganglion
D)Inferior mesenteric ganglion
E)All are prevertebral ganglia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The largest autonomic plexus is called the
A)superior mesenteric plexus.
B)renal plexus.
C)cardiac plexus.
D)celiac plexus.
E)hypogastric plexus.
A)superior mesenteric plexus.
B)renal plexus.
C)cardiac plexus.
D)celiac plexus.
E)hypogastric plexus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following are types of cholinergic receptors?
A)Nicotinic and adrenergic receptors
B)Muscarinic and somatic receptors
C)Adrenergic and somatic receptors
D)Nicotinic and muscarinic receptors
E)Somatostatic and nicotinic receptors
A)Nicotinic and adrenergic receptors
B)Muscarinic and somatic receptors
C)Adrenergic and somatic receptors
D)Nicotinic and muscarinic receptors
E)Somatostatic and nicotinic receptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Autonomic tone is regulated by the
A)medulla oblongata.
B)cerebellum.
C)cerebrum.
D)vermis.
E)hypothalamus.
A)medulla oblongata.
B)cerebellum.
C)cerebrum.
D)vermis.
E)hypothalamus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following responses is NOT caused by activation of the parasympathetic division of the ANS?
A)Decreased heart rate
B)Airway dilation
C)Decreased pupil diameter
D)Increased secretion of digestive juices
E)Increased gastric motility
A)Decreased heart rate
B)Airway dilation
C)Decreased pupil diameter
D)Increased secretion of digestive juices
E)Increased gastric motility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Explain why the sympathetic division of the ANS has more widespread and longer-lasting effects than the parasympathetic division.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following responses is NOT caused by activation of the sympathetic division?
A)Increased heart rate
B)Airway constriction
C)Decreased blood flow to kidneys and gastrointestinal tract
D)Increased blood flow to skeletal muscle,cardiac muscle,liver and fat
E)Increased blood glucose level
A)Increased heart rate
B)Airway constriction
C)Decreased blood flow to kidneys and gastrointestinal tract
D)Increased blood flow to skeletal muscle,cardiac muscle,liver and fat
E)Increased blood glucose level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
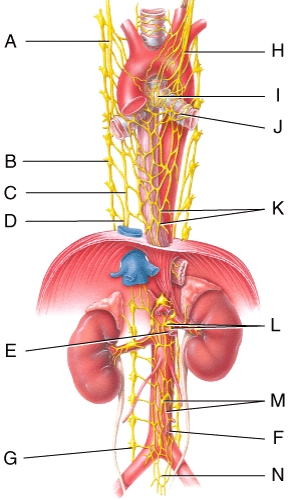
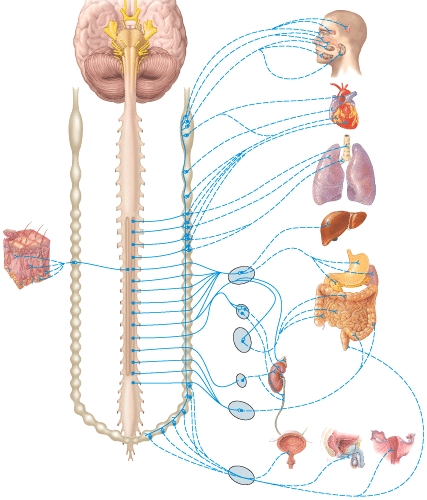
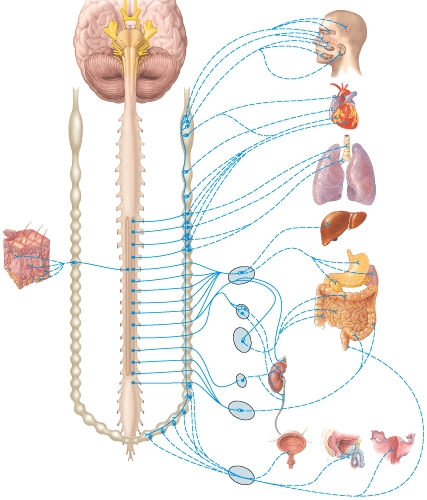
Where is the inferior mesenteric ganglion and plexus in the figure?
A)E
B)F
C)G
D)M
E)N

A)E
B)F
C)G
D)M
E)N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following labeled structures is the right sympathetic trunk ganglion?
A)E
B)B
C)L
D)M
E)N

A)E
B)B
C)L
D)M
E)N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Where is the hypogastric plexus in the figure?
A)J
B)K
C)D
D)F
E)N

A)J
B)K
C)D
D)F
E)N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The superior mesenteric ganglion receives nervous input from the
A)lesser splanchnic nerve.
B)least splanchnic nerve.
C)greater thoracic splanchnic nerve
D)a and b only
E)a,b,and c

A)lesser splanchnic nerve.
B)least splanchnic nerve.
C)greater thoracic splanchnic nerve
D)a and b only
E)a,b,and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Preganglionic neurons are supplied to the submandibular ganglion by which cranial nerve?
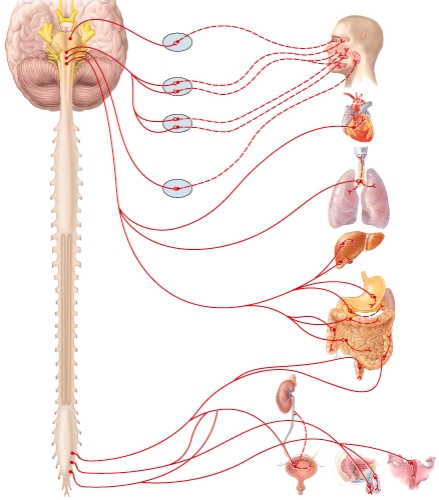
A)Oculomotor (III)nerve (cranial nerve III)
B)Facial (VII)nerve (cranial nerve VII)
C)Glossopharyngeal (IX)nerve (cranial nerve IX)
D)Vagus (X)nerve (cranial nerve X)
E)None of these choices

A)Oculomotor (III)nerve (cranial nerve III)
B)Facial (VII)nerve (cranial nerve VII)
C)Glossopharyngeal (IX)nerve (cranial nerve IX)
D)Vagus (X)nerve (cranial nerve X)
E)None of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following nerves provides innervation for the external genitals?
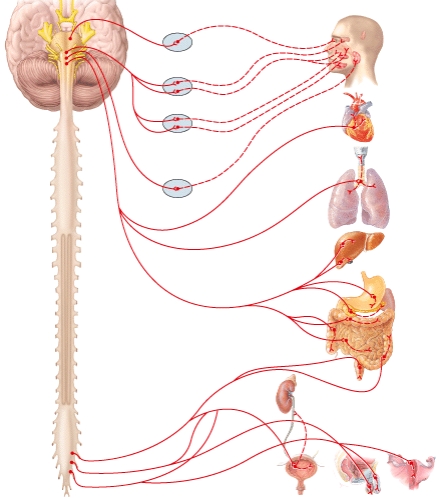
A)Oculomotor (III)nerve (cranial nerve III)
B)Facial (VII)nerve (cranial nerve VII)
C)Glossopharyngeal (IX)nerve (cranial nerve IX)
D)Vagus (X)nerve (cranial nerve X)
E)Pelvic splanchnic nerve

A)Oculomotor (III)nerve (cranial nerve III)
B)Facial (VII)nerve (cranial nerve VII)
C)Glossopharyngeal (IX)nerve (cranial nerve IX)
D)Vagus (X)nerve (cranial nerve X)
E)Pelvic splanchnic nerve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
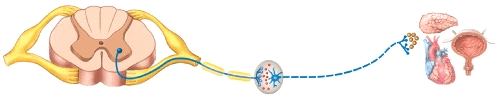
29
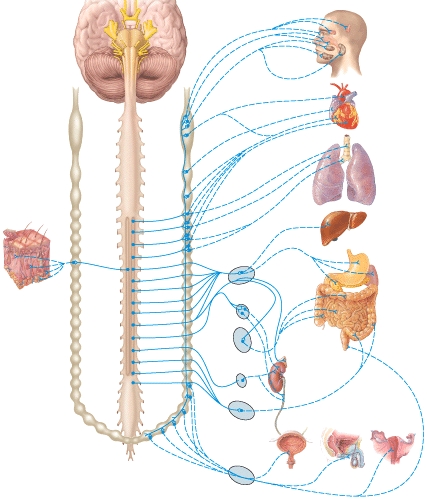
What type of nervous system pathway is shown in this figure?

A)Somatic motor pathway
B)Somatic sensory pathway
C)Autonomic motor pathway
D)Autonomic sensory pathway
E)None of these choices

A)Somatic motor pathway
B)Somatic sensory pathway
C)Autonomic motor pathway
D)Autonomic sensory pathway
E)None of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What type of neurotransmitter is used by the pathway shown in the figure?

A)Norepinephrine
B)Acetylcholine
C)Epinephrine
D)Dopamine
E)Serotonin

A)Norepinephrine
B)Acetylcholine
C)Epinephrine
D)Dopamine
E)Serotonin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Describe the possible ways in which the axon of a sympathetic preganglionic neuron connects with postganglionic neurons after it reaches the sympathetic trunk ganglia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which ganglion supplies the stomach with postganglionic neurons?
A)Middle cervical ganglion
B)Inferior cervical ganglion
C)Celiac ganglion
D)Inferior mesenteric ganglion
E)Ciliary ganglion

A)Middle cervical ganglion
B)Inferior cervical ganglion
C)Celiac ganglion
D)Inferior mesenteric ganglion
E)Ciliary ganglion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which nerve supplies the inferior mesenteric ganglion with preganglionic neurons?
A)Lumbar splanchnic nerve
B)Lesser splanchnic nerve
C)Greater splanchnic nerve
D)Cardiac accelerator
E)Phrenic nerve

A)Lumbar splanchnic nerve
B)Lesser splanchnic nerve
C)Greater splanchnic nerve
D)Cardiac accelerator
E)Phrenic nerve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What region does the superior cervical ganglion primarily serve?
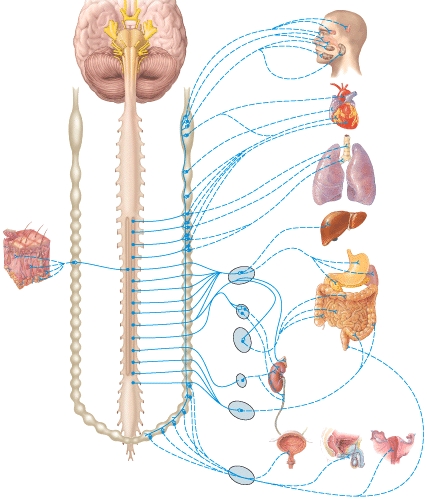
A)Abdominal
B)Pelvic
C)Skin
D)Head
E)None of these choices

A)Abdominal
B)Pelvic
C)Skin
D)Head
E)None of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Describe the potential roles that autonomic neurons that release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine perform in the ANS.Be sure to describe the types of postsynaptic effector cells including their receptors that could be potentially activated by acetylcholine release from autonomic neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Parasympathetic innervation of the liver occurs through
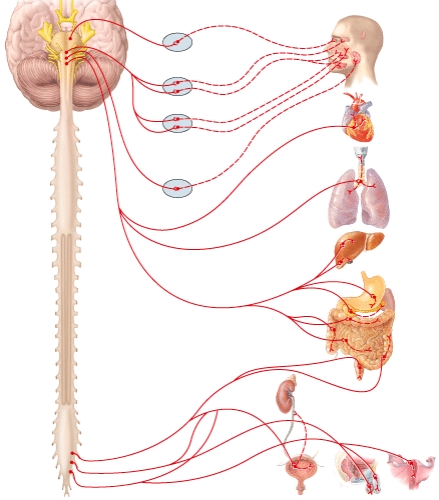
A)oculomotor (III)nerve (cranial nerve III).
B)facial (VII)nerve (cranial nerve VII).
C)glossopharyngeal (IX)nerve (cranial nerve IX).
D)vagus (X)nerve (cranial nerve X).
E)pelvic splanchnic nerve.

A)oculomotor (III)nerve (cranial nerve III).
B)facial (VII)nerve (cranial nerve VII).
C)glossopharyngeal (IX)nerve (cranial nerve IX).
D)vagus (X)nerve (cranial nerve X).
E)pelvic splanchnic nerve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
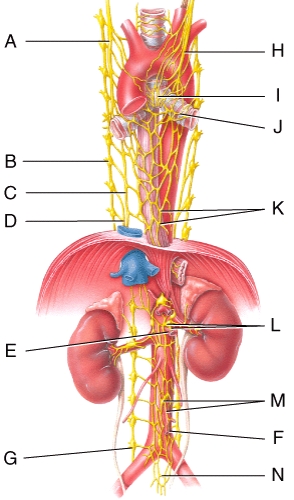
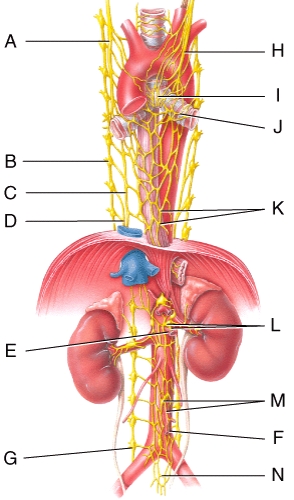
Where is the cardiac plexus in the figure?
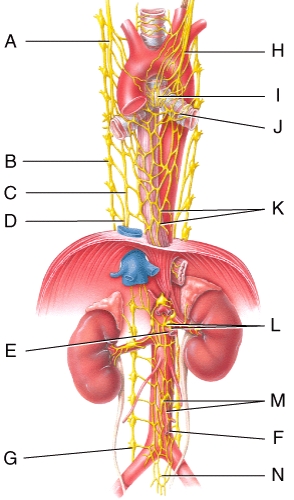
A)A
B)B
C)H
D)I
E)J

A)A
B)B
C)H
D)I
E)J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Postganglionic neurons from the otic ganglion supply the
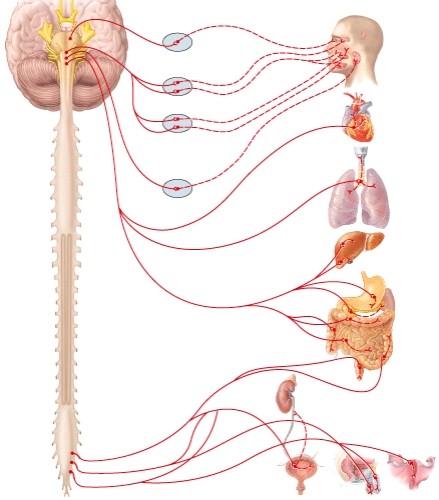
A)parotid gland.
B)heart.
C)lungs.
D)liver.
E)ureter.

A)parotid gland.
B)heart.
C)lungs.
D)liver.
E)ureter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following does NOT contribute to the longer lasting and more widespread effects observed with sympathetic activation versus parasympathetic activation?
A)Norepinephrine is more slowly removed from synapses than ACh.
B)Additional norepinephrine is released from the adrenal gland.
C)Greater divergence occurs in sympathetic neural pathways.
D)Blood flow to the hypothalamus is decreased when sympathetic activation occurs.
A)Norepinephrine is more slowly removed from synapses than ACh.
B)Additional norepinephrine is released from the adrenal gland.
C)Greater divergence occurs in sympathetic neural pathways.
D)Blood flow to the hypothalamus is decreased when sympathetic activation occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Where is the right vagus nerve in the figure?
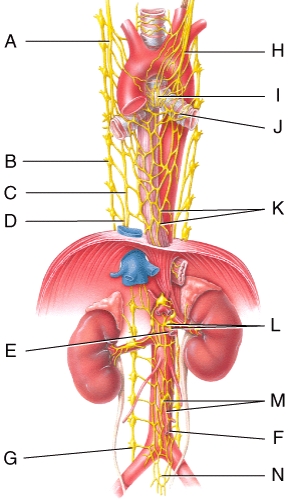
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)H
E)K

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)H
E)K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Where is the greater splanchnic nerve in the diagram?
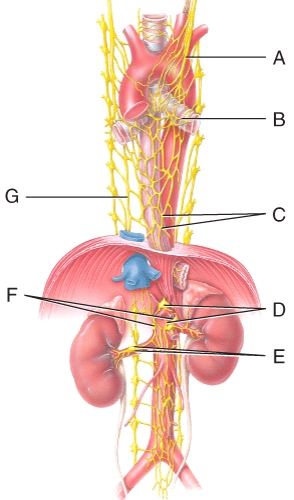
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)E
E)G

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)E
E)G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What type of nervous system pathway is shown in the figure?
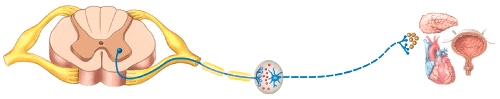
A)Somatic motor pathway
B)Somatic sensory pathway
C)Autonomic motor pathway
D)Autonomic sensory pathway
E)None of these choices

A)Somatic motor pathway
B)Somatic sensory pathway
C)Autonomic motor pathway
D)Autonomic sensory pathway
E)None of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which neurotransmitter is released at the autonomic ganglion by the preganglionic neuron in the diagram?
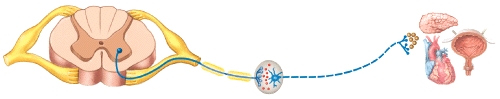
A)Norepinephrine
B)Acetylcholine
C)Epinephrine
D)Dopamine
E)Serotonin

A)Norepinephrine
B)Acetylcholine
C)Epinephrine
D)Dopamine
E)Serotonin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Where is the pulmonary plexus in the diagram?
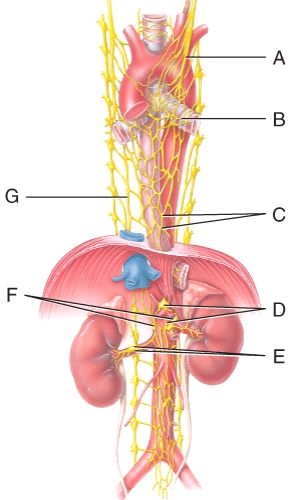
A)A
B)E
C)D
D)B
E)G

A)A
B)E
C)D
D)B
E)G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A patient with chronic skeletal muscle spasms was placed on an anticholinergic medication.After taking the medication,the patient's muscle spasms ceased,but now the patient reports a loss of muscle strength.In addition,the patient's resting heart rate has increased.Explain the effects of the medication the patient received.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which neurotransmitter is released by the preganglionic neuron at the autonomic ganglion in the diagram?

A)Norepinephrine
B)Acetylcholine
C)Epinephrine
D)Dopamine
E)Serotonin

A)Norepinephrine
B)Acetylcholine
C)Epinephrine
D)Dopamine
E)Serotonin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If the pathway shown in the diagram is a parasympathetic division pathway,which neurotransmitter acts at the effector?

A)Norepinephrine
B)Acetylcholine
C)Epinephrine
D)Dopamine
E)Serotonin

A)Norepinephrine
B)Acetylcholine
C)Epinephrine
D)Dopamine
E)Serotonin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Where is the left vagus (X)nerve in the diagram?
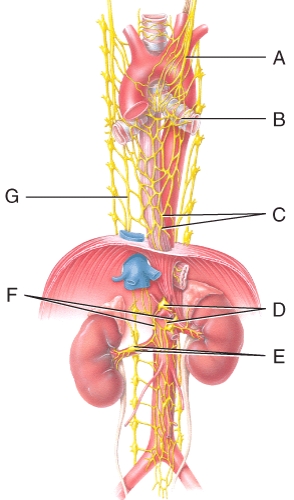
A)A
B)C
C)D
D)F
E)G

A)A
B)C
C)D
D)F
E)G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Where is the esophageal plexus in the diagram?
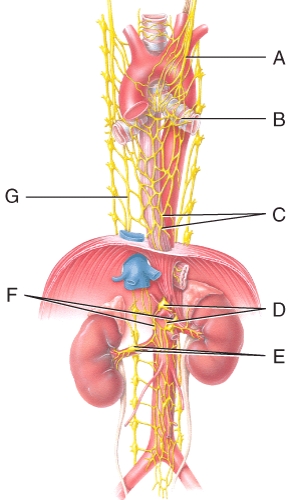
A)A
B)B
C)D
D)C
E)G

A)A
B)B
C)D
D)C
E)G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which plexus or nerve shown in the diagram supplies the bronchial tree?
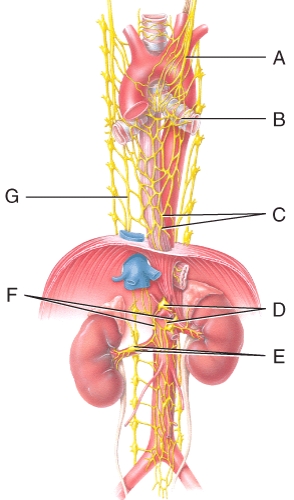
A)A
B)C
C)F
D)B
E)E

A)A
B)C
C)F
D)B
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
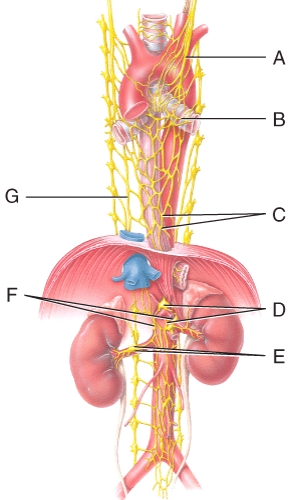
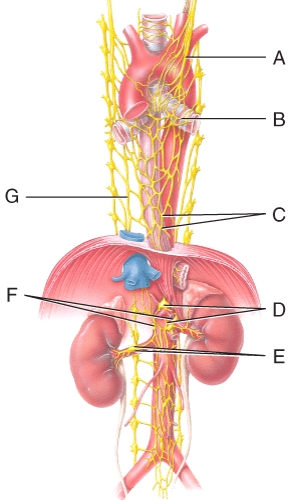
Which plexus or nerve shown in the diagram supplies the renal arteries?
A)B
B)C
C)D
D)E
E)F

A)B
B)C
C)D
D)E
E)F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Where is the aorticorenal ganglion in the diagram?

A)C
B)D
C)E
D)F
E)G

A)C
B)D
C)E
D)F
E)G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Where is the renal ganglion and renal plexus in the diagram?
A)A
B)B
C)D
D)E
E)G

A)A
B)B
C)D
D)E
E)G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If the pathway shown in the diagram is a sympathetic division pathway,which neurotransmitter acts at the effector?
A)Norepinephrine
B)Acetylcholine
C)Epinephrine
D)Dopamine
E)Serotonin

A)Norepinephrine
B)Acetylcholine
C)Epinephrine
D)Dopamine
E)Serotonin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which neurotransmitter is released at the gland by the preganglionic neuron in the diagram?
A)Norepinephrine
B)Acetylcholine
C)Epinephrine
D)Dopamine
E)Serotonin

A)Norepinephrine
B)Acetylcholine
C)Epinephrine
D)Dopamine
E)Serotonin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Where is the celiac ganglion and plexus in the diagram?
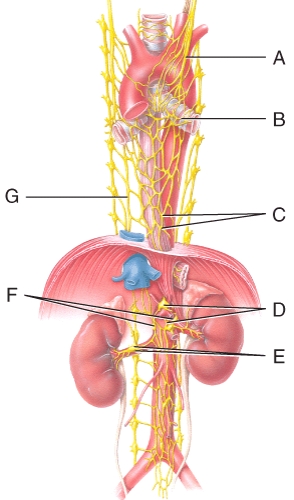
A)A
B)B
C)D
D)C
E)G

A)A
B)B
C)D
D)C
E)G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Compare and contrast the overall responses of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
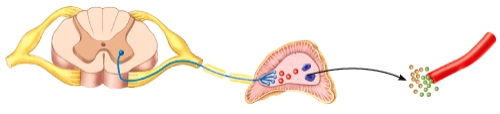
58
The structure labeled 2 in the diagram is a
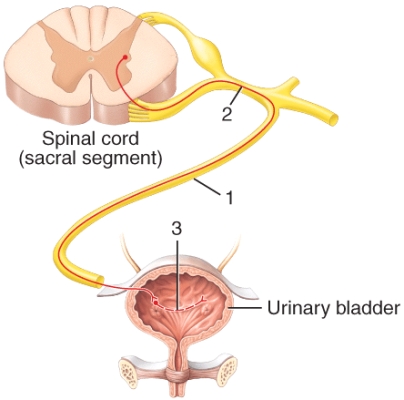
A)somatic motor neuron.
B)parasympathetic preganglionic neuron.
C)parasympathetic postganglionic neuron.
D)sympathetic preganglionic neuron.
E)somatosensory neuron.

A)somatic motor neuron.
B)parasympathetic preganglionic neuron.
C)parasympathetic postganglionic neuron.
D)sympathetic preganglionic neuron.
E)somatosensory neuron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The structure labeled 3 in the diagram is a
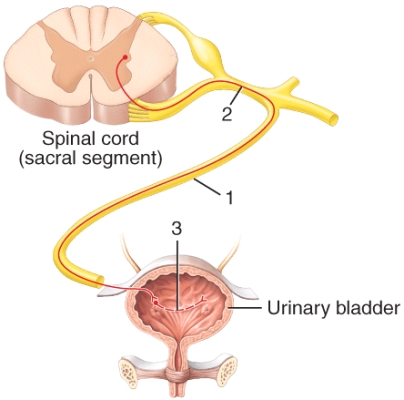
A)somatic motor neuron.
B)parasympathetic preganglionic neuron.
C)parasympathetic postganglionic neuron.
D)sympathetic preganglionic neuron.
E)somatosensory neuron.

A)somatic motor neuron.
B)parasympathetic preganglionic neuron.
C)parasympathetic postganglionic neuron.
D)sympathetic preganglionic neuron.
E)somatosensory neuron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Explain how blood flow to tissues changes during the fight-or-flight response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following types of adrenergic receptors are found on cardiac muscle fibers where their activation stimulates increased force and rate of contraction of the heart?
A)α1-adrenergic
B)α2-adrenergic
C)β1-adrenergic
D)β2-adrenergic
E)β3-adrenergic
A)α1-adrenergic
B)α2-adrenergic
C)β1-adrenergic
D)β2-adrenergic
E)β3-adrenergic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following types of adrenergic receptors are only found in brown adipose tissue where their activation stimulates heat production?
A)α1-adrenergic
B)α2-adrenergic
C)β1-adrenergic
D)β2-adrenergic
E)β3-adrenergic
A)α1-adrenergic
B)α2-adrenergic
C)β1-adrenergic
D)β2-adrenergic
E)β3-adrenergic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The structure labeled 1 in the diagram is the
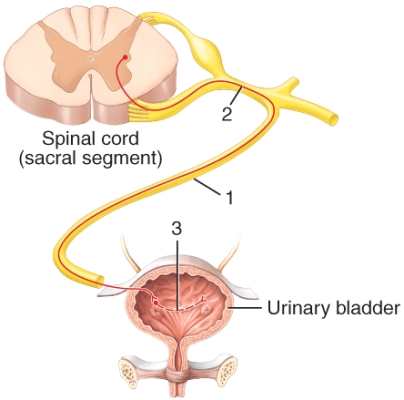
A)femoral nerve.
B)sciatic nerve.
C)pelvic splanchnic nerve.
D)pudendal nerve.
E)genitofemoral nerve.

A)femoral nerve.
B)sciatic nerve.
C)pelvic splanchnic nerve.
D)pudendal nerve.
E)genitofemoral nerve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which division of the ANS innervates the sweat glands and the hair follicles?
A)Parasympathetic
B)Sympathetic
C)Neither division innervates these effectors
D)Both divisions innervate these effectors
A)Parasympathetic
B)Sympathetic
C)Neither division innervates these effectors
D)Both divisions innervate these effectors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which disorder is a type of neuropathy often caused by long term diabetes mellitus?
A)Raynaud's phenomenon
B)Autonomic dysreflexia
C)Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
D)Diabetic neuropathy
E)Horner's Syndrome
A)Raynaud's phenomenon
B)Autonomic dysreflexia
C)Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
D)Diabetic neuropathy
E)Horner's Syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following statements describes a common response of an autonomic effector during the "fight-or-flight" response?
A)Gastric motility and secretory activity increases.
B)Blood vessels serving skeletal muscles constrict.
C)Adipose tissues stores away triglycerides for later use.
D)The pupils of the eyes dilate.
E)Blood vessels serving the kidneys and digestive organs dilate.
A)Gastric motility and secretory activity increases.
B)Blood vessels serving skeletal muscles constrict.
C)Adipose tissues stores away triglycerides for later use.
D)The pupils of the eyes dilate.
E)Blood vessels serving the kidneys and digestive organs dilate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which the following regions of the brain serve as the major control and integration center of the ANS?
A)cerebrum
B)cerebellulum
C)thalamus
D)hypothalamus
E)pituitary
A)cerebrum
B)cerebellulum
C)thalamus
D)hypothalamus
E)pituitary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla possess what type of receptor that makes them responsive to the ACh released by preganglionic sympathetic neurons?
A)muscarinic receptors
B)nicotinic receptors
C)β1-adrenergic
D)β2-adrenergic
E)β3-adrenergic
A)muscarinic receptors
B)nicotinic receptors
C)β1-adrenergic
D)β2-adrenergic
E)β3-adrenergic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which disorder is characterized by an exaggerated response of the sympathetic division of the ANS that occurs in most individuals with spinal cord injury at or above T6?
A)Raynaud's phenomenon
B)Autonomic dysreflexia
C)Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
D)Diabetic neuropathy
E)Horner's Syndrome
A)Raynaud's phenomenon
B)Autonomic dysreflexia
C)Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
D)Diabetic neuropathy
E)Horner's Syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which endocrine gland is directly innervated by sympathetic preganglionic axons?
A)Pituitary gland
B)Hypothalamus
C)Pancreas
D)Adrenal gland
E)Thyroid gland
A)Pituitary gland
B)Hypothalamus
C)Pancreas
D)Adrenal gland
E)Thyroid gland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which disorder involves the loss of sympathetic innervation to one side of the face due to inherited mutation,injury or disease?
A)Raynaud's phenomenon
B)Autonomic dysreflexia
C)Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
D)Diabetic neuropathy
E)Horner's Syndrome
A)Raynaud's phenomenon
B)Autonomic dysreflexia
C)Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
D)Diabetic neuropathy
E)Horner's Syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
One of the main differences between a somatic reflex and autonomic reflex is the type of effectors that are activated.The effectors in somatic reflexes are _____,while the effectors in autonomic reflexes are _____.
A)skeletal muscles;smooth muscle,cardiac muscle,and glands
B)striated muscles;smooth muscle and glands
C)skeletal muscles and glands;smooth muscle and cardiac muscle
D)glands;skeletal muscles,smooth muscle,and cardiac muscle
E)skeletal muscles;smooth muscle only
A)skeletal muscles;smooth muscle,cardiac muscle,and glands
B)striated muscles;smooth muscle and glands
C)skeletal muscles and glands;smooth muscle and cardiac muscle
D)glands;skeletal muscles,smooth muscle,and cardiac muscle
E)skeletal muscles;smooth muscle only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following lists the components of an autonomic reflex arc in the proper sequence of activation?
A)receptor - sensory neuron - integrating center - motor neuron - effector
B)receptor - motor neuron - integrating center - sensory neuron - effector
C)effector - sensory neuron - integrating center - motor neuron - receptor
D)integrating center - receptor - sensory neuron - motor neuron - effector
E)receptor - sensory neuron - motor neuron - effector - integrating center
A)receptor - sensory neuron - integrating center - motor neuron - effector
B)receptor - motor neuron - integrating center - sensory neuron - effector
C)effector - sensory neuron - integrating center - motor neuron - receptor
D)integrating center - receptor - sensory neuron - motor neuron - effector
E)receptor - sensory neuron - motor neuron - effector - integrating center

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Thoracolumbar is another name for which division of ANS?
A)Parasympathetic
B)Sympathetic
C)Somatic nervous system
D)Autonomic ganglia
E)Craniosacral division
A)Parasympathetic
B)Sympathetic
C)Somatic nervous system
D)Autonomic ganglia
E)Craniosacral division

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Based on your knowledge of ANS receptors,explain how beta blockers are able to manage conditions such as hypertension (high blood pressure)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



