Deck 2: The Payments System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/102
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: The Payments System
1
The Reserve Bank of Australia is responsible for minimising payments system risks, promoting the system's efficiency and promoting competition in the market for payment services.
True
2
All payment instructions are settled on a deferred net settlement basis.
False
3
The payment order processing system for inter-ADI payments is the Reserve Bank's Information and Transfer System.
True
4
The clearing of retail payment orders refers to the actual payment of exchange settlement (ES)funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Payments in the retail payment system can be described as relatively low value and low volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Providers of payment services process payment instructions that have been authorised by their customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In value terms, the payments system's major role is settling the payment instructions arising from transactions in the financial markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Verification of a payment instruction's authorisation is always required before the instruction can be settled.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Retail payments can be defined as payments between shops (retailers)and their customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
We are fast becoming a 'cashless society'.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The overnight delay in the settlement of retail payments between ADIs poses settlement risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Barter is a system of exchange in which items (or services)are exchanged for each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A cheque deposited into your ADI account will not earn interest until it is verified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A cheque's BSB number identifies the bank and relevant branch of its depositor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The netting of payments in the clearing process for retail payment orders increases settlement risk in the system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Debit cards allow customers additional time to pay the amount due.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An example of a direct credit to your account is when you are paid by your employer.An example of a direct debit is your monthly payment to your car insurer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Charge cards are issued by banks to allow customers to access their funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Financial institutions such as banks hold funds in exchange settlement accounts with the RBA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A transaction is an agreement between a buyer and seller to exchange an item or service for payment (whether this is cash, a payment order or another item).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Real-time gross settlement operates during the business day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
RTGS clears payments and then places them in a queue for settlement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The RBA's intraday repurchase agreements facilitate the smooth flow of the RTGS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The introduction of explicit fees for the use of another ADI's ATM has improved efficiency within the retail payments system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The Payments System Board's (PSB)reform of credit cards reduced the interchange fees charged by the credit card companies, and eliminated the surcharge imposed by merchants when accepting credit card payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Banks prefer to hold their liquid assets in the money market rather than in their exchange settlement accounts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Banks earn no interest on their exchange settlement account balances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
During the GFC, the banking system reduced their demand for ES funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the 'early morning' RTGS session, ADIs will increase their ESA balances through interbank transfers and by selling eligible securities to the RBA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
On days when the RBA makes payments to ADIs on behalf of the government it will prevent unintentional changes to the cash rate by buying securities from ADIs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The increasing use of direct entries has resulted in a decline in the usage of cheques.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Electronic payment instructions have become the most important (in terms of their value)payment instructions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Payments by the RBA increase aggregate exchange settlement balances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Banks in Australia are subject to a reserve requirement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Contagion risk refers to a domino effect initially caused by the settlement default of a single bank.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Credit and debit cards have become the most frequently used non-cash retail payment instruments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
ADIs earn a margin over the cash rate for funds deposited in the inter-bank overnight market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The problem of intraday illiquidity is overcome by banks being required to hold large ESA balances so they can cover their RTGS payments without relying on receipts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
RTGS can face liquidity problems which result from ADIs holding insufficient ES funds to meet their overall daily RTGS payment obligations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The RBA stabilises the financial system's liquidity by trading with ADIs to sterilise the impact on aggregate ES balances of payments to and by it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is a retail payment order but is not settled using DNS?
A)Cash.
B)Cheques.
C)Debit cards.
D)Charge cards.
E)Direct entries.
A)Cash.
B)Cheques.
C)Debit cards.
D)Charge cards.
E)Direct entries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
As at 2013, real-time gross settlement is used to settle payment instructions from:
A)the clearinghouses in the debt (Austraclear)and foreign exchange (SWIFT)markets
B)the retail payment system
C)the batch feeder facility used for share market trades.
D)None of these.
E)All of these.
A)the clearinghouses in the debt (Austraclear)and foreign exchange (SWIFT)markets
B)the retail payment system
C)the batch feeder facility used for share market trades.
D)None of these.
E)All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Of the following, which is generally settled on a deferred net basis in Australia's payments system?
A)Cash, EFTPOS instructions and cheques.
B)EFTPOS instructions, cheques and direct entries.
C)Cheques, financial markets transactions and direct entries.
D)Financial markets transactions.
E)More than one of these is true.
A)Cash, EFTPOS instructions and cheques.
B)EFTPOS instructions, cheques and direct entries.
C)Cheques, financial markets transactions and direct entries.
D)Financial markets transactions.
E)More than one of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
________________ is the process by which ADIs agree on their payments system obligations whereas_________________ is the actual payment of ES funds.
A)DNS; RTGS
B)Clearing; settlement
C)DNS; settlement
D)Settlement; clearing
E)RTGS; settlement
A)DNS; RTGS
B)Clearing; settlement
C)DNS; settlement
D)Settlement; clearing
E)RTGS; settlement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which statement regarding cheques is INCORRECT?
A)Cheques were once the principal form of payment order.
B)The cheque verification process means that funds are not credited to the depositor's account for several days.
C)Cheques are authorised by the drawer's signature.
D)Cheques are a written instruction.
E)Cheque payments can be dishonoured.
A)Cheques were once the principal form of payment order.
B)The cheque verification process means that funds are not credited to the depositor's account for several days.
C)Cheques are authorised by the drawer's signature.
D)Cheques are a written instruction.
E)Cheque payments can be dishonoured.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The account that a financial institution has with the RBA is known as a(n):
A)fund settlement account
B)money settlement account
C)payment settlement account
D)exchange settlement account.
E)None of these.
A)fund settlement account
B)money settlement account
C)payment settlement account
D)exchange settlement account.
E)None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Identify the correct statement regarding cash:
A)Cash is the most commonly used payment instrument.
B)Cash is frequently used for small-value payments .
C)The proportion of payments made with cash has been declining.
D)Cash is a payment instrument but not a payment order.
E)All of these.
A)Cash is the most commonly used payment instrument.
B)Cash is frequently used for small-value payments .
C)The proportion of payments made with cash has been declining.
D)Cash is a payment instrument but not a payment order.
E)All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Inter-ADI payment orders:
A)transfer funds between accounts held with ADIs
B)must be cleared before they are settled
C)are settled by transfers of exchange settlement funds
D)include payment methods such as cheques and direct entry.
E)All of these.
A)transfer funds between accounts held with ADIs
B)must be cleared before they are settled
C)are settled by transfers of exchange settlement funds
D)include payment methods such as cheques and direct entry.
E)All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The RBA provides two mechanism to help ADIs manage period of intraday illiquidity.These are:
A)intraday repos and payment queue adjustments
B)the inter-bank overnight market
C)open-market operations and the cash rate
D)the overnight market and intraday repos
E)overnight funds from the RBA and payment queue adjustments.
A)intraday repos and payment queue adjustments
B)the inter-bank overnight market
C)open-market operations and the cash rate
D)the overnight market and intraday repos
E)overnight funds from the RBA and payment queue adjustments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which retail payment order displays a very high number of transactions but relatively low total value of transactions?
A)Cash.
B)Cheques.
C)Credit and debit cards.
D)Direct debits.
E)Direct credits.
A)Cash.
B)Cheques.
C)Credit and debit cards.
D)Direct debits.
E)Direct credits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following statements is NOT true about the wholesale payments system?
A)It has very few participants compared to the retail system.
B)The main participants are banks and dealers.
C)Transactions are settled on a deferred net settlement basis.
D)It transfers funds between exchange settlement accounts of the payer and the payee.
E)It mainly settles financial markets transactions.
A)It has very few participants compared to the retail system.
B)The main participants are banks and dealers.
C)Transactions are settled on a deferred net settlement basis.
D)It transfers funds between exchange settlement accounts of the payer and the payee.
E)It mainly settles financial markets transactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
During the early morning RTGS session (7.30am to 8.45am)ADIs will:
A)settle their DNS payment obligations
B)make inter-bank ES transfers and sell eligible securities to the RBA
C)net settle their daily RTGS payment obligations.
D)All of these.
E)None of these.
A)settle their DNS payment obligations
B)make inter-bank ES transfers and sell eligible securities to the RBA
C)net settle their daily RTGS payment obligations.
D)All of these.
E)None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The very large number of retail payment orders:
A)exposes receiving institutions to significant settlement risk
B)includes cash, cheques and EFTPOS
C)are netted, which greatly reduces the settlement amounts
D)are settled on a same-day basis.
E)All of these.
A)exposes receiving institutions to significant settlement risk
B)includes cash, cheques and EFTPOS
C)are netted, which greatly reduces the settlement amounts
D)are settled on a same-day basis.
E)All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The organisation responsible for controlling risks and promoting competition and efficiency in the payment system is:
A)the Australian Payments Clearing Association
B)Austraclear
C)the Payments System Board
D)the RBA's Payment Settlement Review Group
E)SWIFT.
A)the Australian Payments Clearing Association
B)Austraclear
C)the Payments System Board
D)the RBA's Payment Settlement Review Group
E)SWIFT.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which retail payment mechanism has experienced the most dramatic decline in usage?
A)Cash.
B)Cheques.
C)Credit cards.
D)Debit cards.
E)Direct entry.
A)Cash.
B)Cheques.
C)Credit cards.
D)Debit cards.
E)Direct entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A personal identification number (PIN):
A)authorises the transaction
B)verifies the transaction
C)settles the payment
D)authorises and verifies the transaction
E)authorises and verifies the transaction and settles the payment.
A)authorises the transaction
B)verifies the transaction
C)settles the payment
D)authorises and verifies the transaction
E)authorises and verifies the transaction and settles the payment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which retail payment mechanism has experienced the most dramatic increase in usage (when measured in terms of the value of transactions)?
A)Cash.
B)Cheques.
C)Credit cards.
D)Debit cards.
E)Direct entry.
A)Cash.
B)Cheques.
C)Credit cards.
D)Debit cards.
E)Direct entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which payment mechanism allows organisations to make payments to, and receive payments from, large groups?
A)Direct entries.
B)Credit and debit cards.
C)EFTPOS.
D)Cheques.
E)All of these.
A)Direct entries.
B)Credit and debit cards.
C)EFTPOS.
D)Cheques.
E)All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which payment mechanism is pre-authorised and verified?
A)Direct entries.
B)Credit and debit cards.
C)EFTPOS.
D)Cheques.
E)None of these.
A)Direct entries.
B)Credit and debit cards.
C)EFTPOS.
D)Cheques.
E)None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
As at 2013, different payment systems exist for the settlement of retail and wholesale payment instructions in Australia.The wholesale payment system:
A)is, in total, of less daily value than retail payment system
B)settles on a real-time gross settlement basis
C)settles more transactions than the retail payment system
D)is used for all large transactions.
E)All of these.
A)is, in total, of less daily value than retail payment system
B)settles on a real-time gross settlement basis
C)settles more transactions than the retail payment system
D)is used for all large transactions.
E)All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Most Australian shops accept payments via EFTPOS but not by cheque.What advantages does EFTPOS (and other electronic instruments)have over cheques for the shopkeeper? What are the advantages for the customer?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Planned changes to the settlement of retail payments will place additional liquidity pressures on ADIs.The RBA plans to help ADIs cope through:
A)increasing the interest rate on ESA balances
B)increasing the interest rate in the overnight inter-bank market
C)intraday repos
D)open repos
E)requiring a liquidity reserve.
A)increasing the interest rate on ESA balances
B)increasing the interest rate in the overnight inter-bank market
C)intraday repos
D)open repos
E)requiring a liquidity reserve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Briefly describe the two broad categories of payment orders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Explain why institutions have exchange settlement accounts and describe the main features of these accounts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
An ADI that requires additional exchange settlement funds to meet its retail payment obligations at 9am can:
A)borrow from the RBA at the cash rate
B)draw on its reserves held in the overnight inter-bank market
C)purchase additional money-market securities
D)sell a parcel of bonds
E)delay the payment until later that day
A)borrow from the RBA at the cash rate
B)draw on its reserves held in the overnight inter-bank market
C)purchase additional money-market securities
D)sell a parcel of bonds
E)delay the payment until later that day

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Contagion (within the payments system)is NOT:
A)likely
B)serious
C)the collapse of the payments system
D)less likely because of RTGS
E)potentially devastating to the economy.
A)likely
B)serious
C)the collapse of the payments system
D)less likely because of RTGS
E)potentially devastating to the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following would put downward pressure on the cash rate?
A)Payments between ADIs.
B)Sales of securities by the RBA to ADIs.
C)Payments of taxation from ADIs to the RBA.
D)Welfare payments by the RBA (on behalf of the government)to ADIs.
E)All of these.
A)Payments between ADIs.
B)Sales of securities by the RBA to ADIs.
C)Payments of taxation from ADIs to the RBA.
D)Welfare payments by the RBA (on behalf of the government)to ADIs.
E)All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Exchange settlement accounts:
A)must be in credit
B)hold funds that belong to banks and other financial market dealers
C)earn a return of 25 bps less than the cash rate
D)are the means of settling transactions between institutions.
E)All of these.
A)must be in credit
B)hold funds that belong to banks and other financial market dealers
C)earn a return of 25 bps less than the cash rate
D)are the means of settling transactions between institutions.
E)All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The RBA conducts market operations:
A)to offset the impact of its own or government transactions upon the cash rate
B)once a month only
C)to offset the impact of transfers between ADIs on the cash rate
D)secretly, so that the market does not know its position
E)All of these.
A)to offset the impact of its own or government transactions upon the cash rate
B)once a month only
C)to offset the impact of transfers between ADIs on the cash rate
D)secretly, so that the market does not know its position
E)All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Explain the responsibilities of the Payments System Board.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The auto-offset process within RTGS:
A)involves searching the payment system queue for offsetting payments
B)increases efficiency in the payments system
C)reduces the amount of ES funds ADIs require
D)keeps uncleared payments in the queue for later retesting.
E)All of these.
A)involves searching the payment system queue for offsetting payments
B)increases efficiency in the payments system
C)reduces the amount of ES funds ADIs require
D)keeps uncleared payments in the queue for later retesting.
E)All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Briefly explain the settlement process for retail payment orders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Give a brief description of the direct entry system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Define a payment order and explain the two steps required to process them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Explain the difference in the cost of processing cheques and EFTPOS instructions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Assume that there are three banks in Australia: Alpha, Beta and Delta.On a particular day: 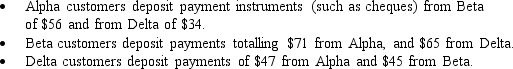 Use the following grid to determine the banks multilateral net obligations to the system on this day.
Use the following grid to determine the banks multilateral net obligations to the system on this day. 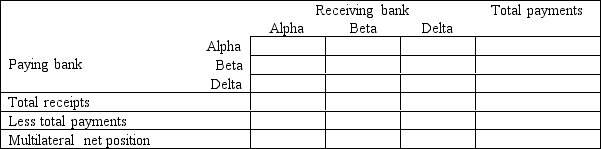
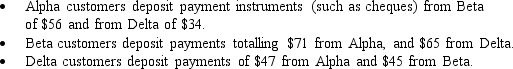 Use the following grid to determine the banks multilateral net obligations to the system on this day.
Use the following grid to determine the banks multilateral net obligations to the system on this day. 

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Why do retail payment orders require authorisation and verification? How is this achieved?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
List and describe the main types of retail payment instruments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Uncertainty during the GFC led some banks in Australia to increase:
A)cash holdings
B)deposits in the inter-bank market
C)ES funds
D)reserves of money and bond market securities
E)their borrowings from the RBA.
A)cash holdings
B)deposits in the inter-bank market
C)ES funds
D)reserves of money and bond market securities
E)their borrowings from the RBA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Identify and briefly explain three differences between the retail and wholesale payment systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



