Deck 26: Capital Investment Decisions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/122
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Capital Investment Decisions
1
The payback period and accounting rate of return (ARR) methods are suitable to investments with a short time span.
True
2
Which of the following describes the word "capital budgeting"?
A) It involves budgeting for yearly operational expenses.
B) It involves preparing the sales budget for the coming year.
C) It involves deciding among various long-term investment decisions.
D) It involves analyzing various alternatives of financing available to a company.
A) It involves budgeting for yearly operational expenses.
B) It involves preparing the sales budget for the coming year.
C) It involves deciding among various long-term investment decisions.
D) It involves analyzing various alternatives of financing available to a company.
C
3
Capital rationing is a process adopted when a company has limited resources, and it must find ways to reduce operating expenses in all of its divisions and units.
False
4
An operational asset used for a long period of time is known as a capital asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following best describes the term "capital rationing"?
A) a method of determining the period within which the cash invested is recouped
B) a process of ranking and choosing among alternative capital investments based on the availability of funds
C) a method which shows the effect of the investment on the company's accrual-based income
D) a process of controlling operating costs when adequate funds are not available
A) a method of determining the period within which the cash invested is recouped
B) a process of ranking and choosing among alternative capital investments based on the availability of funds
C) a method which shows the effect of the investment on the company's accrual-based income
D) a process of controlling operating costs when adequate funds are not available

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following two methods are typically used for initial screening of investments, rather than for detailed, in-depth analysis?
A) payback and accounting rate of return
B) net present value and payback
C) internal rate of return and net present value
D) accounting rate of return and net present value
A) payback and accounting rate of return
B) net present value and payback
C) internal rate of return and net present value
D) accounting rate of return and net present value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Most capital budgeting methods focus on cash flows rather than book income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following best describes a post-audit in capital budgeting?
A) an audit of an operating unit of a company
B) an audit performed after financial statements have been issued
C) an analysis of an investment's cash flows prior to committing to the initial investment
D) a comparison of actual results of capital investments with projected results
A) an audit of an operating unit of a company
B) an audit performed after financial statements have been issued
C) an analysis of an investment's cash flows prior to committing to the initial investment
D) a comparison of actual results of capital investments with projected results

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
To determine the investment's net cash inflows, the inflows are netted against the investment's initial cash outflow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Net present value and internal rate of return consider the time value of money, so they are appropriate for longer-term capital investments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is a capital budgeting method that is used to screen potential investments?
A) return on assets
B) acid test ratio
C) accounting rate of return
D) debt-to-equity ratio
A) return on assets
B) acid test ratio
C) accounting rate of return
D) debt-to-equity ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The last step in the capital budgeting process is control which compares the actual results with the projected results. These comparisons are known as:
A) cash inflows.
B) post-audits.
C) ranks.
D) cash outflows
A) cash inflows.
B) post-audits.
C) ranks.
D) cash outflows

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The accounting rate of return method uses accrual-based accounting income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is true of projecting future cash flows of an investment?
A) Information on cash flow will also include non-cash transactions like depreciation.
B) Cash inflows and cash outflows are treated separately, rather than being netted together.
C) Cash flows are projected by accounting personnel without considering input from other business functions.
D) The initial investment is always treated separately from all other cash flows.
A) Information on cash flow will also include non-cash transactions like depreciation.
B) Cash inflows and cash outflows are treated separately, rather than being netted together.
C) Cash flows are projected by accounting personnel without considering input from other business functions.
D) The initial investment is always treated separately from all other cash flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is a capital budgeting method?
A) return on assets
B) net present value
C) inventory turnover
D) return on equity
A) return on assets
B) net present value
C) inventory turnover
D) return on equity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A post-audit in capital budgeting is a comparison of actual results of capital investments with the projected results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The acquisition or construction of a capital asset is known as a capital investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Two methods of analyzing potential capital investments-payback and accounting rate of return-ignore the time value of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The payback method and the accounting rate of return method are often used to perform an initial screening of investments, rather than a detailed, in-depth analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Payback provides management with valuable information about the time period within which the cash invested will be recouped.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is a capital budgeting method that ignores the time value of money?
A) payback
B) internal rate of return
C) return on assets
D) net present value
A) payback
B) internal rate of return
C) return on assets
D) net present value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The payback considers only those cash flows that occur during the payback period and ignores any cash flows that occur after that period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Newman Automobiles Manufacturing is considering two alternative investment proposals with the following data: Calculate the payback period for Proposal X.
A) 5 years
B) 4 years
C) 8 years
D) 10 years
A) 5 years
B) 4 years
C) 8 years
D) 10 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A major criticism of the payback method is that it focuses only on time to recover the investment, and ignores profitability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The payback method can only be used when the net cash inflows from a capital investment are the same for each period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The accounting rate of return is also known as average rate of return or annual rate of return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The accounting rate of return is calculated by dividing the average annual operating income by the average amount invested.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Cortes Company is considering three investment opportunities with the following payback periods: Use the decision rule for payback to rank the projects from most desirable to least desirable, all else being equal.
A) Y, Z, X
B) X, Y, Z
C) Z, Y, X
D) Y, X, Z
A) Y, Z, X
B) X, Y, Z
C) Z, Y, X
D) Y, X, Z

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The payback method is the most thorough and comprehensive way to choose the best investment among alternatives, than any other capital budgeting methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The payback method ignores cash flows that an asset generates, whereas the accounting rate of return includes them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The payback method uses discounted cash flows to make investment decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Flip Flop company is considering investing in production-management software that costs $600,000, has $60,000 residual value, and should lead to cost savings of $150,000 per year for its five-year life. Calculate the average amount invested in the asset that should be used for calculating the accounting rate of return?
A) $660,000
B) $600,000
C) $330,000
D) $60,000
A) $660,000
B) $600,000
C) $330,000
D) $60,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Net cash inflows from a capital investment arise from an increase in revenues, a decrease in expenses, or both.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
All else being equal, investments with longer payback periods are preferable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The accounting rate of return method of analyzing a potential capital investment considers the time value of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The accounting rate of return method and the payback method are often used as preliminary screening measures, but are insufficient to fully evaluate a capital investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Capital budgeting is:
A) the process of planning the investment in long-term assets.
B) preparing the budget for operating expenses.
C) the process of evaluating the profitability of a business.
D) the process of making pricing decisions for products.
A) the process of planning the investment in long-term assets.
B) preparing the budget for operating expenses.
C) the process of evaluating the profitability of a business.
D) the process of making pricing decisions for products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The accounting rate of return method evaluates the lifetime return of an asset, whereas return on investment evaluates an annual return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which capital budgeting method uses accrual accounting, rather than net cash flows, as a basis for calculations?
A) payback
B) accounting rate of return
C) net present value
D) internal rate of return
A) payback
B) accounting rate of return
C) net present value
D) internal rate of return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The accounting rate of return method focuses on net operating income instead of net cash inflow generated by an asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Compound interest means that interest is calculated only on the principal amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Compound interest assumes that all interest earned will be reinvested at the same rate of interest at which the investment was originally made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Caliber Company is considering the purchase of a new machine costing $800,000. The company's management is estimating that the new machine will generate additional cash flows of $180,000 a year for ten years and have a salvage value of $50,000 at the end of ten years. What is the machine's payback period?
A) 4.44 years
B) 6.77 years
C) 3.33 years
D) 5.33 years
A) 4.44 years
B) 6.77 years
C) 3.33 years
D) 5.33 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The following details are provided by a manufacturing company. Calculate the payback period for the investment.
A) 2.5 years
B) 2.83 year
C) 3.0 years
D) 3.5 years
A) 2.5 years
B) 2.83 year
C) 3.0 years
D) 3.5 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A company is evaluating three possible investments. Following information is provided by the company. What is the payback period for Project A? (Assume that the company uses the straight-line depreciation method.)
A) 3.0 years
B) 2.0 years
C) 4.0 years
D) 5.0 years
A) 3.0 years
B) 2.0 years
C) 4.0 years
D) 5.0 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Logy Inc. is evaluating two possible investments in depreciable plant assets. The company uses the straight-line method of depreciation. The following information is available: Calculate the payback period for Investment B.
A) 3 years
B) 2 years
C) 4 years
D) 5 years
A) 3 years
B) 2 years
C) 4 years
D) 5 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Nylan Company is considering an investment in new equipment costing $850,000. The equipment will be depreciated on a straight-line basis over a five-year life and is expected to have a salvage value of $50,000. The equipment is expected to generate net cash inflows of $1,000,000 in total during the five years life. What is the accounting rate of return associated with the equipment investment?
A) 9.99%
B) 8.89%
C) 7.56%
D) 9.32%
A) 9.99%
B) 8.89%
C) 7.56%
D) 9.32%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A company is evaluating three possible investments. Each uses straight-line method of depreciation. Following information is provided by the company. What is the accounting rate of return for Project B?
A) 15.08%
B) 10.214%
C) 15.45%
D) 14.54%
A) 15.08%
B) 10.214%
C) 15.45%
D) 14.54%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Paramount Company is considering purchasing new equipment costing $700,000. The company's management has estimated that the equipment will generate cash flows as follows: Residual value is zero. What is the payback period?
A) 4.5 years
B) 3.2 years
C) 3.5 years
D) 3.8 years
A) 4.5 years
B) 3.2 years
C) 3.5 years
D) 3.8 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A company is evaluating three possible investments. Each uses straight-line method of depreciation. Following information is provided by the company. What is the accounting rate of return for Project C?
A) 15%
B) 12%
C) 18%
D) 10%
A) 15%
B) 12%
C) 18%
D) 10%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Newman Automobiles Manufacturing is considering two alternative investment proposals with the following data: Calculate accounting rate of return for Proposal Y.
A) 8.95%
B) 10.21%
C) 7.50%
D) 6.57%
A) 8.95%
B) 10.21%
C) 7.50%
D) 6.57%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Software Hub is deciding whether to purchase new accounting software. The cost of the software package is $55,000, and its expected life is 10 years. The payback for this investment is four years. Assuming equal yearly cash flows, what are the expected annual net cash savings from the new software? (Assume the investment has zero salvage value.)
A) $5,500
B) $37,800
C) $13,750
D) $220,000
A) $5,500
B) $37,800
C) $13,750
D) $220,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An annuity refers to a series of equal cash flows received or paid annually.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Dartis Company is considering investing in a specialized equipment costing $600,000. The equipment has a useful life of 5 years and a residual value of $60,000. Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method. The expected net cash inflows from the investment are given below. What is the accounting rate of return on the investment?
A) 7.95%
B) 8.78%
C) 8.48%
D) 9.25%
A) 7.95%
B) 8.78%
C) 8.48%
D) 9.25%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The fact that invested cash earns income over time is called the time value of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
All else being equal, the shorter the investment period, the higher the total amount of interest earned.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Landmark Company is considering an investment in new equipment costing $500,000. The equipment will be depreciated on a straight-line basis over a five-year life and is expected to generate net cash inflows of $120,000 the first year, $140,000 the second year, and $150,000 every year thereafter until the fifth year. What is the payback period for this investment? The residual value is zero.
A) 4.5 years
B) 3.6 years
C) 2.9 years
D) 3.2 years
A) 4.5 years
B) 3.6 years
C) 2.9 years
D) 3.2 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following capital budgeting methods uses accrual accounting information?
A) payback
B) accounting rate of return
C) net present value
D) internal rate of return
A) payback
B) accounting rate of return
C) net present value
D) internal rate of return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Clapton Corporation is considering an investment in new equipment costing $900,000. The equipment will be depreciated on a straight-line basis over a ten-year life and is expected to have a salvage value of $90,000. The equipment is expected to generate net cash flows of $140,000 for each of the first five years and $100,000 for each of the last five years. What is the accounting rate of return associated with the equipment investment?
A) 8.89%
B) 9.23%
C) 8.52%
D) 7.88%
A) 8.89%
B) 9.23%
C) 8.52%
D) 7.88%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Logy Inc. is evaluating two possible investments in depreciable plant assets. The company uses the straight-line method of depreciation. The following information is available: Calculate the payback period for Investment A.
A) 3 years
B) 4 years
C) 1 year
D) 5 years
A) 3 years
B) 4 years
C) 1 year
D) 5 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Net present value is defined as the difference between the present value of the project's net cash inflows and the cost of investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Arriyana has just received an inheritance of $100,000, and she would like to put it into an investment portfolio for 20 years. Which of the following would be useful to calculate the value of the investment at the end of 20 years?
A) Present Value of $1
B) Present Value of an Annuity of $1
C) Future Value of $1
D) Future Value of an Annuity of $1
A) Present Value of $1
B) Present Value of an Annuity of $1
C) Future Value of $1
D) Future Value of an Annuity of $1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following most accurately describes the term annuity?
A) an investment which produces increasing cash flows overtime
B) an installment loan with amortizing principal payments
C) a stream of equal installments of cash flows made at equal time intervals
D) a term life insurance policy
A) an investment which produces increasing cash flows overtime
B) an installment loan with amortizing principal payments
C) a stream of equal installments of cash flows made at equal time intervals
D) a term life insurance policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
James has just won the lottery after purchasing one $10 lottery ticket. The state offers him the following three payout options for after-tax prize money:
1. $50,000 per year at the end of each of the next six years
2. $300,000 (lump sum) now
3. $400,000 (lump sum) six years from now
Calculate the present value of each scenario using an 8% discount rate. Round to nearest whole dollar.
Present value of annuity of $1:
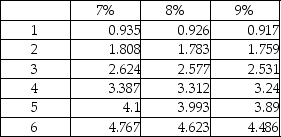 Present value of $1:
Present value of $1:
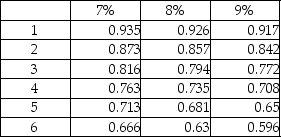
1. $50,000 per year at the end of each of the next six years
2. $300,000 (lump sum) now
3. $400,000 (lump sum) six years from now
Calculate the present value of each scenario using an 8% discount rate. Round to nearest whole dollar.
Present value of annuity of $1:
 Present value of $1:
Present value of $1:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Nylan Manufacturing is considering two alternative investment proposals with the following details: What is the total present value of future cash inflows from Proposal X?
Present value of annuity of $1:
Present value of $1:
A) $742,340
B) $650,070
C) $568,650
D) $599,700
Present value of annuity of $1:
Present value of $1:
A) $742,340
B) $650,070
C) $568,650
D) $599,700

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Paramount Company is considering purchasing new equipment costing $700,000. Company's management has estimated that the equipment will generate cash flows as follows: The company's required rate of return is 10%. Using the factors in the table below, calculate the present value of the cash inflows. Present value of $1:
A) $765,000
B) $768,921
C) $798,650
D) $780,000
A) $765,000
B) $768,921
C) $798,650
D) $780,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The residual value is discounted as a single lump sum because it will be received only once at the end of life of the asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The only difference between present value and future value is the amount of interest that is earned in the intervening time span.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Management's minimum desired rate of return on a capital investment is known as the return on investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Paramount Company is considering purchasing new equipment costing $700,000. The management has estimated that the equipment will generate cash flows as follows: Present value of $1:
The company's required rate of return is 8%. Using the factors in the table, calculate the present value of the cash inflows. (Round all calculations to the nearest whole dollar)
A) $890,000
B) $750,000
C) $850,000
D) $841,000
The company's required rate of return is 8%. Using the factors in the table, calculate the present value of the cash inflows. (Round all calculations to the nearest whole dollar)
A) $890,000
B) $750,000
C) $850,000
D) $841,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
John wins the lottery and has the following three payout options for after-tax prize money:
1) $50,000 per year at the end of each of the next six years
2) $300,000 (lump sum) now
3) $500,000 (lump sum) six years from now
The required rate of return is 9%. What is the present value if he selects the third option? Round to nearest whole dollar.
Present value of $1:
A) $250,000
B) $230,000
C) $238,400
D) $298,000
1) $50,000 per year at the end of each of the next six years
2) $300,000 (lump sum) now
3) $500,000 (lump sum) six years from now
The required rate of return is 9%. What is the present value if he selects the third option? Round to nearest whole dollar.
Present value of $1:
A) $250,000
B) $230,000
C) $238,400
D) $298,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If $10,000 is invested annually in an account with 7% interest compounded yearly, what will the balance of the account be after six years? Refer to the following Future Value table: Future value of annuity of $1:
A) $79,050
B) $71,530
C) $18,020
D) $83,290
A) $79,050
B) $71,530
C) $18,020
D) $83,290

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
John wins the lottery and has the following three payout options for after-tax prize money:
1) $150,000 per year at the end of each of the next six years
2) $300,000 (lump sum) now
3) $500,000 (lump sum) six years from now
The required rate of return is 9%. What is the present value if he selects the second option? Round to nearest whole dollar.
Present value of $1:
A) $650,000
B) $100,000
C) $400,000
D) $300,000
1) $150,000 per year at the end of each of the next six years
2) $300,000 (lump sum) now
3) $500,000 (lump sum) six years from now
The required rate of return is 9%. What is the present value if he selects the second option? Round to nearest whole dollar.
Present value of $1:
A) $650,000
B) $100,000
C) $400,000
D) $300,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Nylan Manufacturing is considering two alternative investment proposals with the following details: What is the total present value of future cash inflows from Proposal Y?
Present value of annuity of $1:
A) $266,750
B) $291,600
C) $290,000
D) $250,000
Present value of annuity of $1:
A) $266,750
B) $291,600
C) $290,000
D) $250,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following describes the term time value of money?
A) Money can be used only at certain times and only for certain purposes.
B) Money loses its purchasing power over time through inflation.
C) Wasted time can result in wasted money.
D) Value of a dollar received today will be higher than that received after some time.
A) Money can be used only at certain times and only for certain purposes.
B) Money loses its purchasing power over time through inflation.
C) Wasted time can result in wasted money.
D) Value of a dollar received today will be higher than that received after some time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Paramount Company is considering purchasing new equipment costing $700,000. Company's management has estimated that the equipment will generate cash flows as follows: Present value of $1:
The company's required rate of return is 9%. Using the factors in the table, calculate the present value of the cash flows.
A) $850,000
B) $819,300
C) $820,500
D) $852,000
The company's required rate of return is 9%. Using the factors in the table, calculate the present value of the cash flows.
A) $850,000
B) $819,300
C) $820,500
D) $852,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Zane has received a prize which entitles him to receive annual payments of $10,000 for the next 10 years. Which of the following is to be referred to in order to calculate the total value of the prize today?
A) Present Value of $1
B) Present Value of an Annuity of $1
C) Future Value of $1
D) Future Value of an Annuity of $1
A) Present Value of $1
B) Present Value of an Annuity of $1
C) Future Value of $1
D) Future Value of an Annuity of $1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Lara is going to receive $10,000 a year at the end of each of the next five years from her insurer to meet her education cost. Using a discount rate of 14%, the present value of the receipts can be stated as:
A) PV = $10,000 (Annuity FV factor, i = 14%, n = 5).
B) PV = $10,000 (PV factor, i = 14%, n = 5).
C) PV = $10,000 (Annuity PV factor, i = 14%, n = 5).
D) PV = $10,000 (FV factor, i = 14%, n = 5).
A) PV = $10,000 (Annuity FV factor, i = 14%, n = 5).
B) PV = $10,000 (PV factor, i = 14%, n = 5).
C) PV = $10,000 (Annuity PV factor, i = 14%, n = 5).
D) PV = $10,000 (FV factor, i = 14%, n = 5).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
John wins the lottery and has the following three payout options for after-tax prize money:
1) $150,000 per year at the end of each of the next six years
2) $300,000 (lump sum) now
3) $500,000 (lump sum) six years from now
The required rate of return is 9%. What is the present value if he selects the first option? Round to nearest whole dollar.
Present value of annuity of $1:
Present value of $1:
A) $750,000
B) $672,900
C) $450,000
D) $450,050
1) $150,000 per year at the end of each of the next six years
2) $300,000 (lump sum) now
3) $500,000 (lump sum) six years from now
The required rate of return is 9%. What is the present value if he selects the first option? Round to nearest whole dollar.
Present value of annuity of $1:
Present value of $1:
A) $750,000
B) $672,900
C) $450,000
D) $450,050

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If $15,000 is invested annually in an account with 9% interest compounding yearly, what will the balance of the account be after five years? Refer to the following Future Value table: Future value of annuity of $1:
A) $26,180
B) $26,211
C) $58,350
D) $25,125
A) $26,180
B) $26,211
C) $58,350
D) $25,125

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



